Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Application Note On Crane Duty
Hochgeladen von
JAY PARIKH0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten4 SeitenCrane duty motor
Originaltitel
Application Note on Crane Duty
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCrane duty motor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten4 SeitenApplication Note On Crane Duty
Hochgeladen von
JAY PARIKHCrane duty motor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
Application Note on Crane Duty
What is an overhead crane?
An overhead crane is a type of crane where the hook-and-line mechanism runs
along a horizontal beam that runs along two widely separated rails. Often it is in a
factory building and runs along its walls. Overhead cranes are commonly known as
Electrical Overhead travel or EOT cranes.
What are the types of Overhead cranes?
There are three main types of EOT cranes:
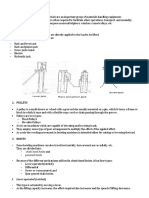
1) Jib Crane: A jib crane has one fixed leg, a cantilevered boom that rotates around
the fixed leg, and a hoist/trolley unit that traverses the boom and lifts loads for
placement somewhere else. A jib crane is helpful in a high-repetition lift process
where an overhead crane would be otherwise tied up. Jib cranes are typically
one to two tons, but sometimes reach five ton capacity.
Fig 1: Jib Crane
2) Overhead Bridge Crane: An overhead bridge crane operates on a raised and
fixed track. Typically the height under and overhead bridge crane is 20 or more.
On an overhead crane, end trucks are equipped with wheels to provide for
moving the entire crane. A bridge girder (single or double) spans the rails, and
provides support for the hoist/trolley unit. Finally, the trolley traverses the bridge
girders and usually has a hoist mounted on it to lift the load with either chain or
wire rope.
.
Fig 2: Overhead Bridge Crane
3) Gantry Crane: A gantry crane is similar to a bridge crane, but typically has legs at
either end of the bridge girders, which are then mounted with end trucks at the
bottom of the legs to move the gantry along ground-level tracks. Gantry cranes
are more frequently found outdoors where no raised runway is present. Also,
small non-powered gantry cranes are used in light duty applications such as
small machine shops or automobile garages. These gantry cranes typically do
not have a fixed path, but rather have rubber tires
Fig 3: Gantry Crane
Basics of Contactor switching duties/Definitions as
per IEC 60947-4-1
Conventional thermal Current: The conventional free air thermal current I th for
motor starters in enclosures is defined as an eight hour current. It is the maximum
current which can be conducted for this period of time during which no switching
operations are carried out, without the need for intervention and without the
temperature limit being exceeded.
AC1 duty: It involves the switching of non inductive or slightly inductive loads eg:
resistive furnaces. While running on AC1 duty, the switching device must be capable
of making and breaking one times the rated operational current.
AC2 duty: It involves the switching of slip ring induction motors. AC-2 utilization
category is of particular importance in the selection of contactors for use with slip
ring motors in cranes. While running on AC 2 duty, the switching device must be
capable of making and breaking 2.5 times the rated operational current. This in not
always a realistic value as in many cases the actual dynamic loading of the
contactor may be substantially lower.
Types of Movements of an Overhead Crane:
There are three main movements in an Overhead crane: Up travel, Cross travel and
Long travel.
1) Up travel and the associated interlocks: This includes the Vertical motion of
the hoist inorder to pickup and drop off the load. The motion of the hoist is
controlled by a motor Depending on the direction of motion and whether the
hoist is loaded or not, the motor will have to perform forward/reverse motoring
or Forward/Reverse breaking operation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Report On Gantry Crane and Overhead CraneDokument23 SeitenReport On Gantry Crane and Overhead CraneAbhay UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Principles: Ishikawajima Rio de JaneiroDokument14 SeitenMechanical Principles: Ishikawajima Rio de JaneirokartheepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Materials and Construction: Presentation On CranesDokument10 SeitenBuilding Materials and Construction: Presentation On Cranesamit jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types: Overhead CraneDokument8 SeitenTypes: Overhead CraneVishnu DuraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Eclectric Overhead Traveling Cranes PDFDokument121 SeitenOverview of Eclectric Overhead Traveling Cranes PDFSamik Mukherjee100% (1)
- New Eot Crane TrainingDokument11 SeitenNew Eot Crane Trainingsurnaik100% (5)
- Electric Overhead Traveling Nav GNFCDokument7 SeitenElectric Overhead Traveling Nav GNFCkeyur1109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Shipboard CranesDokument5 SeitenTypes of Shipboard Cranesegyinspectoryahoo100% (1)
- Hoisting EquipmentDokument101 SeitenHoisting EquipmentmichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting Device Used in ConstructionDokument18 SeitenLifting Device Used in ConstructionAr Deyvanai Kannan100% (1)
- Bridge CranesDokument83 SeitenBridge Cranesflasnicug100% (1)
- Application of A.C Motor in Industrial EOT CranesDokument20 SeitenApplication of A.C Motor in Industrial EOT CranesBalaki SrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- EOT CraneDokument84 SeitenEOT CraneSambhav Poddar80% (5)
- Mechanical System ReportDokument9 SeitenMechanical System ReportLea MaligsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Overhead CranesDokument2 SeitenGuide To Overhead CranesReneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Technology-Static CranesDokument14 SeitenConstruction Technology-Static CranesPrarthana roy RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project WorkDokument94 SeitenProject Workroopa_rainbowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevators: Electrical Load Classification According To Load Function Lighting LoadDokument44 SeitenElevators: Electrical Load Classification According To Load Function Lighting LoadHassen Lazhar100% (2)
- Heavy DutyDokument23 SeitenHeavy DutyEmran MuftiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design ProjectDokument13 SeitenDesign Projectumanr18075Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting and Handling EquipmentsDokument54 SeitenLifting and Handling Equipmentsalvin100% (1)
- Building ServicesDokument57 SeitenBuilding Servicessofiya0% (1)
- Design Guide For Overhead CranesDokument3 SeitenDesign Guide For Overhead CranesralluinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ProposalDokument1 SeiteProject ProposalbanjrouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information On Bridge Cranes, Overhead Cranes, Single Girder Cranes, Double Girder Cranes, Top Running Cranes and Under Running Cranes PDFDokument5 SeitenInformation On Bridge Cranes, Overhead Cranes, Single Girder Cranes, Double Girder Cranes, Top Running Cranes and Under Running Cranes PDFvenkatrangan2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Hydraulic Cranes Work: Main Science EngineeringDokument9 SeitenHow Hydraulic Cranes Work: Main Science Engineeringsunil481Noch keine Bewertungen
- MH CH-2Dokument12 SeitenMH CH-2Nebiyou KorraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of CraneDokument7 SeitenTypes of CraneAltayeb YassinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Overhead Crane and Analysis of Components Depending On SpanDokument5 SeitenReview of Overhead Crane and Analysis of Components Depending On SpanBalamanikandan ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting by 03 CraneDokument11 SeitenLifting by 03 CraneViet Linh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Week NotesDokument39 Seiten10 Week Notescharusri74Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Unit 4Dokument99 Seiten4 - Unit 4Saran T SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Crane TerminologyDokument11 SeitenGlossary of Crane TerminologyvizonspiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Requirements of 8 Transportation Systems in A Building.Dokument40 SeitenFunctional Requirements of 8 Transportation Systems in A Building.Umar Faruq AfokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Cranes: Presented by Sayantan Das ROLL NO: 1854003Dokument49 SeitenTypes of Cranes: Presented by Sayantan Das ROLL NO: 1854003SacrosanctSayantan100% (1)
- Hydraulic CraneDokument20 SeitenHydraulic CraneRavi Donga55% (11)
- Crane BasicDokument65 SeitenCrane Basiceddy_p_ajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of An Electrical Overhead Traveling Crane: 1. Runway and ConductorsDokument3 SeitenComponents of An Electrical Overhead Traveling Crane: 1. Runway and Conductorstamilselvan416Noch keine Bewertungen
- As Unit 1 PDFDokument89 SeitenAs Unit 1 PDFsaahasitha 14Noch keine Bewertungen
- MRL ElevatorsDokument85 SeitenMRL ElevatorsAkshay PaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fig 1: On Site Picture of CraneDokument10 SeitenFig 1: On Site Picture of Craneansh kushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fig 1: On Site Picture of CraneDokument10 SeitenFig 1: On Site Picture of Craneansh kushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design ELEVDokument30 SeitenDesign ELEVShiella Barroga LorenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevators: Sahar Khan Jadoon FA11-BAR-017Dokument5 SeitenElevators: Sahar Khan Jadoon FA11-BAR-017saharkj67Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guided By:-Presented By: - Prof. P.M. Nemade Amit Maurya (B.E.) CivilDokument30 SeitenGuided By:-Presented By: - Prof. P.M. Nemade Amit Maurya (B.E.) CivilAr Aayush GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of CranesDokument24 SeitenDesign of CranessourabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cargo Winches or Derricks 2. Jib Cranes 3. Gantry Cranes Manual Safety Stops and Cut Outs Maintenance of Cranes Cargo Winches or DerricksDokument36 SeitenCargo Winches or Derricks 2. Jib Cranes 3. Gantry Cranes Manual Safety Stops and Cut Outs Maintenance of Cranes Cargo Winches or DerricksFrednixen Bustamante GapoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting A Pressure Vessel With Two Main Lift Cranes and One Tail CraneDokument12 SeitenLifting A Pressure Vessel With Two Main Lift Cranes and One Tail Cranezeusvares100% (1)
- 1.0 HoistsDokument12 Seiten1.0 HoistsHellena VivianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Truckcrn PDFDokument6 SeitenTruckcrn PDFDusan VeljkovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- EOT CraneDokument3 SeitenEOT CraneHusain BaradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gantry Girders - Sections and Design - Construction - Civil Engineering PDFDokument12 SeitenGantry Girders - Sections and Design - Construction - Civil Engineering PDFDinesh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic CraneDokument20 SeitenHydraulic Cranenavodit1440% (5)
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 312, December 24, 1881Von EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 312, December 24, 1881Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionVon EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideVon EverandHydraulics and Pneumatics: A Technician's and Engineer's GuideBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- CEA Battery ManagementDokument112 SeitenCEA Battery ManagementJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT Testing at ERDA & HALOLDokument3 SeitenCT Testing at ERDA & HALOLJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC CalculationsDokument112 SeitenSC CalculationsJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- SynchroniserDokument21 SeitenSynchroniserJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mx3Eg1A: Automatic SynchronizerDokument38 SeitenMx3Eg1A: Automatic Synchronizersgshekar30Noch keine Bewertungen
- CableDokument2 SeitenCableJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- CableInstallation PDFDokument8 SeitenCableInstallation PDFJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Course For 2 Class Boiler Proficiency Certificate (Gujarat Ibr)Dokument3 SeitenTraining Course For 2 Class Boiler Proficiency Certificate (Gujarat Ibr)JAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement in Primary Air Heater: Why It Is Required ?Dokument4 SeitenImprovement in Primary Air Heater: Why It Is Required ?JAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement Showing Cost & Profitability of Power Generated - Cogeneration PlantDokument19 SeitenStatement Showing Cost & Profitability of Power Generated - Cogeneration PlantJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFBC Boilers & TG Set Auxillaries SpecificationsDokument18 SeitenCFBC Boilers & TG Set Auxillaries SpecificationsJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Water TreatmentDokument7 SeitenBoiler Water TreatmentJAY PARIKH100% (1)
- Procedure For Calculation of Efficiency-1Dokument7 SeitenProcedure For Calculation of Efficiency-1JAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- TG ExcelDokument5 SeitenTG ExcelJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler1 PDFDokument2 SeitenBoiler1 PDFJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.No. Specifications Yokogawa Fisher Rosemount ABB Tata HoneywellDokument1 SeiteS.No. Specifications Yokogawa Fisher Rosemount ABB Tata HoneywellJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Existing Furnace Oil Line Diagram:-B. No:1676: Over Head FO DAY TankDokument2 SeitenExisting Furnace Oil Line Diagram:-B. No:1676: Over Head FO DAY TankJAY PARIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cogeneration: The Benefits of CogenerationDokument23 SeitenCogeneration: The Benefits of CogenerationJAY PARIKH100% (1)
- Ke01 00 000 KD P TD 0015 000 - D03Dokument501 SeitenKe01 00 000 KD P TD 0015 000 - D03Maffone NumerounoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Sizing Example #3Dokument26 Seiten6 Sizing Example #3BryanHarold BrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aci350 3 06Dokument67 SeitenAci350 3 06juantovarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 FORM Personal Daily Report HSEDokument4 Seiten04 FORM Personal Daily Report HSEArga Sakti YusnandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seal Oil System 2Dokument31 SeitenSeal Oil System 2Raga Lasya100% (8)
- High-Workability Concrete High-Workability ConcreteDokument43 SeitenHigh-Workability Concrete High-Workability ConcreteF Azam Khan AyonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolerances Monorail BeamDokument9 SeitenTolerances Monorail BeamLuis MogrovejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tablas de Esfuerzos PDFDokument729 SeitenTablas de Esfuerzos PDFSamuel PohezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FW Terram Roadhighway Brochure 1 PDFDokument32 SeitenFW Terram Roadhighway Brochure 1 PDFCarmen Law NtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space FrameDokument10 SeitenSpace FramePratyush DajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop Manual Citea DAF Euro-5 EnglezaDokument466 SeitenWorkshop Manual Citea DAF Euro-5 EnglezaIgor NistorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koehler Rheology v1Dokument32 SeitenKoehler Rheology v1ShriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forged Steel Globe Valve 800 15NB To 50NBDokument1 SeiteForged Steel Globe Valve 800 15NB To 50NBpriyanka GNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASCE Substation Structure Design GuideDokument6 SeitenASCE Substation Structure Design GuideCarlos FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20191118-Design ReportDokument83 Seiten20191118-Design ReportAJAY SHINDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Type 63EG-98HM Pilot-Operated Relief Valve or Backpressure RegulatorDokument8 SeitenType 63EG-98HM Pilot-Operated Relief Valve or Backpressure RegulatorAlberto CastellanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iare E&c Lecture Notes PDFDokument110 SeitenIare E&c Lecture Notes PDFRichik MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 3rd Edition - Karl Terzaghi, Ralph B. Peck, Gholamreza Mesri - 1996Dokument534 SeitenSoil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 3rd Edition - Karl Terzaghi, Ralph B. Peck, Gholamreza Mesri - 1996Jesus Antonio Hernandez Castro96% (27)
- Method Statement For Road Surfacing in Existing IrrigigationDokument14 SeitenMethod Statement For Road Surfacing in Existing IrrigigationCamille TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- K EjectionDokument21 SeitenK EjectionAmolPagdalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gigant Specification TablesDokument1 SeiteGigant Specification Tablesđức cường trầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Utilities REVIEWERDokument10 SeitenBuilding Utilities REVIEWERtintinchanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOS For Construction of Bridge - 042 Updated at PIC-I-T - 7062Dokument27 SeitenMOS For Construction of Bridge - 042 Updated at PIC-I-T - 7062Najmul QamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohd Faiz Mohammad Zaki Afizah Ayob and Tee Chin FangDokument4 SeitenMohd Faiz Mohammad Zaki Afizah Ayob and Tee Chin FangDenis Dwayne DizzleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chardon Commercial Zoning CodeDokument10 SeitenChardon Commercial Zoning CodeThe News-HeraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Line UndergroundDokument7 SeitenGreen Line UndergroundFrancisco M. RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistivity Testing of SubstationDokument17 SeitenResistivity Testing of SubstationBernard Kipng'enoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C 33Dokument7 SeitenAstm C 33alfonso mendoza0% (1)
- Armada SamplingDokument2 SeitenArmada SamplingDavid RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Training ReportDokument11 SeitenIndustrial Training ReportAashu MahlaNoch keine Bewertungen