Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
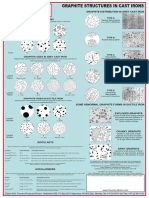
Effects of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast Iron
Hochgeladen von
arnaldorcr8646Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Effects of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast Iron
Hochgeladen von
arnaldorcr8646Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Technical Information 12
Effects of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast Iron
Small quantities of many elements can occur in cast irons and have a marked influence on the
structure and properties of the castings. Some are present as deliberate additions while others
arise from trace impurities in the raw materials. Several of these elements have beneficial effects,
particularly in grey irons, while others are very damaging and must be avoided as far as possible.
The following table lists the common sources of these elements, the levels at which they are likely
to occur and their principle effects. The use of some of these elements (e.g. chromium) as major
alloying elements is not included in the table.
Normal
Element Common Sources Levels (%) Effects in Cast Irons
Promotes hydrogen pinholes in light sections
Al-killed steel scrap,
above about 0.005 %Al. Neutralizes nitrogen.
Aluminium inoculants, ferro-alloys, light
Up to Promotes dross formation. Detrimental to nodular
Al alloy components, additions
0.03 graphite above approx. 0.08%. May be neutralized
of aluminium.
by cerium. Strong graphite stabilizer.
Steel scrap, vitreous
Antimony Up to Strong pearlite and carbide promoter.
enamel scrap, bearing
Sb 0.02 Inhibits nodularity in absence of rare earth’s.
shells, deliberate additions
Arsenic Up to Strong pearlite and carbide promoter.
Pig iron, steel scrap.
As 0.05 Improves nodular graphite shape.
Barium Barium containing Up to Improves graphite nucleation and reduces fading.
Ba inoculants. 0.003 Reduces chilling tendency and promotes graphite
Promotes chill and undesirable graphite forms.
Rarely
Bismuth Deliberate additions, mould Increases nodule number in ductile irons
above
Bi coatings containing Bi. containing rare earth’s (cerium). Excessive nodule
0.01
counts may cause shrinkage problems.
Above 5 ppm promotes ferrite. Above 10 ppm pro-
Boron Vitreous enamel scrap, Up to
motes carbides particularly in ductile irons. 20 ppm
B deliberate additions as FeB. 0.01
improves annealing of malleable irons.
Improves spheroidization of graphite nodules.
Calcium Ferro-alloys, nodularizers, Up to
Improves graphite nucleation.
Ca inoculants. 0.01
Reduces chilling tendency and promotes graphite.
Normally not used in grey irons.
Most magnesium alloys or
Cerium Up to Suppresses deleterious elements in ductile irons.
added as mishmetall or
Ce 0.02 Improves spheroidization of graphite. Carbide
other rare earth sources.
stabilizing due to segregation.
Alloy steel, chromium plate, Promotes chill and pearlite. Increases strength.
Chromium Up to
some pig irons, ferro- Form carbide segregates in ductile irons above
Cr 0.3
chromium. 0.05%.
Cobalt Up to
Tool steel No significant effects in cast irons.
Co 0.02
Copper wire, copper-based Promotes pearlite. Improves strength.
Copper Up to
alloys, steel scrap, Impairs ferritization in ductile irons.
Cu 0.5
deliberate additions of Cu. No harmful effects.
Produces sub-surface pinholes. Has a mild chill-
Damp refractories, mould
Hydrogen promoting action. Promotes "inverse chill" when
materials and humid
H there is insufficient manganese present to
additions.
neutralize sulphur. Promotes coarse graphite.
Elkem ASA, Foundry Products © Copyright Elkem ASA
Postal address Office address Telephone Web Revision
P.O.Box 5211 Majorstuen Hoffsveien 65B +47 22 45 01 00 www.foundry.elkem.com No. 2.1
NO-0302 Oslo Oslo Telefax Org. no. 20.03.2004
Norway Norway +47 22 45 01 52 NO 911 382 008 MVA
Technical Information 12 2
Normal
Element Common Sources Levels (%) Effects in Cast Irons
Causes spiky and undesirable graphite structures
in grey irons and severely reduces strength at
Old paints, some vitreous
levels above 0.004 %. Promotes pearlite and
Lead enamel, free-cutting steel,
Up to carbides.
Pb terne plate, solder, petrol
0.005 Cause degenerated nodular graphite forms.
engine deposits.
Effects on graphite in ductile irons are neutralized
by rare earth’s (cerium).
Promotes nodular graphite in ductile irons.
Magnesium Additions of magnesium
0.03 - 0.08 Carbide stabilizing effect in ductile irons.
Mg alloys (nodularizers).
Not used in grey irons.
Most pig irons, steel scrap, Neutralizes sulphur by forming MnS.
Manganese additions of ferro Promotes pearlite formation. Forms carbide
Mn manganese lump or 0.2 - 1.0 segregates in ductile irons. Promotes gas holes at
briquettes. high levels in conjunction with high sulphur levels.
Refined pig irons, alloy Mild pearlite promoter.
Molybdenium Up to
steels, ferro-molybdenum Increases strength.
Mo 0.1
additions. Can promote shrinkage and carbides.
Nickel Nickel plate, steel scrap, Up to Small amounts have little effects.
Ni refined irons, NiMg alloy. 0.5 Graphitizing effect in larger quantities.
Coke, carburizers, core Compacts flake graphite. Promotes pearlite.
Nitrogen binders, steel scrap, Increases strength. High levels causes fissure
Up to
N additions of nitrided ferro- defects in heavier sections. Can be neutralized by
0.015
manganese. Al, Ti and Zr. Has little effect in ductile irons.
Increases CEV. Increases fluidity. Forms
Phosphorous Phosphoric pig iron and Up to phosphide eutectic. Damaging in ductile irons
P scrap, additions of FeP. 0.1 above 0.05 %. At levels above 0.04%, can cause
metal penetration.
Silicon Ferro-silicon alloys, steel Promotes graphitization, reduces chill, stabilizes
0.8-4.0
Si scrap, pig iron. ferrite, improves castability.
Very damaging to structure and properties unless
Coke, carburizers, pig iron, Up to 0.15 balanced by manganese. Improves grey irons
Sulphur
scrap iron, additions of iron (grey response to most inoculants. Increases Mg
S
sulphide. irons) requirements in ductile irons.
Should be below 0.03 % in ductile irons.
Strontium Strontium containing Up to Improves graphite nucleation in grey and ductile.
Sr inoculants. 0.003 Strongly reduces chilling tendency in grey irons.
Strongly promotes carbides. Causes many
Free-cutting copper, mould
Tellurium undesirable forms of graphite. Effects observed as
coatings, cooling curve Up to
Te low as 0.0003 %. Effects reduced by combination
carbon samples. 0.003
with Mg and Ce in ductile irons.
Solder, tin plated steel Strongly promotes pearlite. Improves strength.
Tin Up to
scrap, bronze components, Embrittles ductile irons above 0.08 %.
Sn 0.15
tin additions. No other harmful effects.
Some pig irons, some
Neutralizes nitrogen in grey irons. Promotes
paints and vitreous
Titanium hydrogen pinholing due to aluminium. Promotes
enamels, CG-iron returns, Up to
Ti undercooled graphite in grey iron. Suppresses
additions of titanium or 0.10
nodular graphite in CG-irons.
ferro-titanium
Tungsten Up to Rarely found in significant amounts.
High speed tool steel
W 0.05 Mild pearlite promoter.
Steel scrap, tool steel,
Vanadium Up to Promotes chill formation. Refines flake graphite.
some pig irons, ferro-
V 0.10 Markedly increases strength.
vanadium additions.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Effect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronDokument2 SeitenEffect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronsachinguptachdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronDokument2 SeitenEffect of Minor and Trace Elements in Cast IronsachinguptachdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Grey Iron: Hydrogen Blowhole Nitrogen Fissure Compaction of Graphite Flakes ShrinkageDokument1 SeiteCommon Metallurgical Defects in Grey Iron: Hydrogen Blowhole Nitrogen Fissure Compaction of Graphite Flakes ShrinkageJoao LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Grey Cast Irons 2Dokument1 SeiteCommon Metallurgical Defects in Grey Cast Irons 2Rasool MohammadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection of NodularizersDokument2 SeitenSelection of Nodularizersarnaldorcr8646100% (2)
- Selection of Inoculants For Ductile Cast IronDokument1 SeiteSelection of Inoculants For Ductile Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Inoculation of Heavy Section CastingsDokument2 SeitenInoculation of Heavy Section Castingsarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Poor Nodularity in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenPoor Nodularity in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr864675% (4)
- Slag Defects in Grey IronDokument1 SeiteSlag Defects in Grey Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Magnesium Slag Defects in Ductile IronDokument1 SeiteMagnesium Slag Defects in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Magnesium Contents in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenMagnesium Contents in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrogen in Cast IronDokument4 SeitenNitrogen in Cast IronFaizan TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- SG Iron ProductionDokument20 SeitenSG Iron ProductionShreyashri Nayak100% (1)
- Recommended Target Analysis For Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenRecommended Target Analysis For Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (2)
- Nitrogen FissuresDokument1 SeiteNitrogen Fissuresarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Effect of Bismuth in Ductile IronDokument4 SeitenEffect of Bismuth in Ductile Ironmarcotulio123100% (2)
- Composition of Grey Cast IronDokument2 SeitenComposition of Grey Cast IronPranil GhatageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fading of Nodularity in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenFading of Nodularity in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (4)
- Shrinkage in Ductile IronDokument5 SeitenShrinkage in Ductile Ironkarthikkanda100% (1)
- Carbon Monoxide Blowholes in Grey IronDokument1 SeiteCarbon Monoxide Blowholes in Grey Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elkem 07 Magnesiun Contents in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenElkem 07 Magnesiun Contents in Ductile Ironmarcotulio123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fading of InoculationDokument2 SeitenFading of Inoculationarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- ELMAGDokument2 SeitenELMAGthomazfabricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile IronDokument1 SeiteCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile IronMehdi Koneshlou100% (1)
- Selection of Inoculants For Grey Cast IronDokument2 SeitenSelection of Inoculants For Grey Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Inoculant Alloy CompositionDokument2 Seiten3 Inoculant Alloy CompositionAdams GodoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical InformationDokument78 SeitenTechnical InformationCarlos Barrachina Martínez100% (2)
- S.G IronDokument6 SeitenS.G IronQasim BarkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery of Magnesium in A Ductile Iron Process.: AbstractDokument8 SeitenRecovery of Magnesium in A Ductile Iron Process.: AbstractJorge Prado DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa MetalograficoDokument1 SeiteMapa MetalograficoBreno DellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Alloying Elements On The Micro Structures and Mechanical On Ductile Cast IronsDokument5 SeitenEffects of Alloying Elements On The Micro Structures and Mechanical On Ductile Cast IronsCharlie Chong100% (6)
- Ductile Dross Formation MonitoringDokument27 SeitenDuctile Dross Formation MonitoringsachinguptachdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling of Liquid Cast IronDokument2 SeitenSampling of Liquid Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Equipment for Foundries: Proceedings of the Seminar on Engineering Equipment for Foundries and Advanced Methods of Producing Such Equipment, Organized by the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeVon EverandEngineering Equipment for Foundries: Proceedings of the Seminar on Engineering Equipment for Foundries and Advanced Methods of Producing Such Equipment, Organized by the United Nations Economic Commission for EuropeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Lines For Producing Quality S.G. Iron PDFDokument28 SeitenGuide Lines For Producing Quality S.G. Iron PDFsachinguptachd100% (1)
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Iron EnglishDokument1 SeiteCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Iron EnglishedgarestevessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partition of Slag Phases in The Treatment and Pouring of Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenPartition of Slag Phases in The Treatment and Pouring of Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Back to BASICS: Nitrogen fissures defects in iron castingsDokument2 SeitenBack to BASICS: Nitrogen fissures defects in iron castingsJustin DixonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elkem 19 Aluminum in Cast IronDokument2 SeitenElkem 19 Aluminum in Cast Ironmarcotulio123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elkem 13 Compacted Graphite IronDokument2 SeitenElkem 13 Compacted Graphite Ironmarcotulio123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cerium in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenCerium in Ductile Ironvivek1312100% (2)
- Seminar S.G IronDokument32 SeitenSeminar S.G Ironravikataria02Noch keine Bewertungen
- SG Iron CompositionDokument5 SeitenSG Iron CompositionamirgukharNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnesiumDokument3 SeitenMagnesiumIsidoro LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Late Metal Stream InoculationDokument2 SeitenLate Metal Stream Inoculationarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chunky GraphiteDokument16 SeitenChunky GraphitesachinguptachdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Grey Iron English (1Dokument1 SeiteCommon Metallurgical Defects in Grey Iron English (1sateeshkori100% (2)
- Manganese, Sulfur and Manganese-Sulfur Ratio Effects in Gray Cast IronDokument30 SeitenManganese, Sulfur and Manganese-Sulfur Ratio Effects in Gray Cast IronNetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of MagnesiumDokument4 SeitenFactors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of Magnesiumarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16 ScabbingDokument4 Seiten16 Scabbingvivek13120% (1)
- S.G.Iron GuidelinesDokument28 SeitenS.G.Iron GuidelinesTarun Chakraborty100% (3)
- Surface Graphite Degeneration in Ductile Iron CastDokument8 SeitenSurface Graphite Degeneration in Ductile Iron CastKhairul MuzafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Quality and Cost of FeSiMg Treatment Master Alloy vs. Cored Wire in Production of Ductile Cast IronDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Quality and Cost of FeSiMg Treatment Master Alloy vs. Cored Wire in Production of Ductile Cast IronAdams GodoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials and Construction - Iii: Lecture No. Iv Dated: 08/10/2018Dokument14 SeitenMaterials and Construction - Iii: Lecture No. Iv Dated: 08/10/2018arooj anjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 - 11 - Chemical Composition of Ductile Iron PDFDokument24 Seiten2014 - 11 - Chemical Composition of Ductile Iron PDFfelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Properties of Different Types of Cast IronDokument1 SeiteClassification and Properties of Different Types of Cast IronSanket SavlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elkem - Alloying Elements and Their EffectsDokument8 SeitenElkem - Alloying Elements and Their EffectsDeep Shikha Gupta100% (8)
- Lecture # 7 Steel and Cast IronDokument29 SeitenLecture # 7 Steel and Cast IronTalha SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLUTIONS: Cast IronDokument26 SeitenSOLUTIONS: Cast IronHanif SamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DESIGN 1 NotesDokument7 SeitenDESIGN 1 NoteslordyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast IronDokument10 SeitenCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast IronsateeshkoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen PinholesDokument1 SeiteHydrogen Pinholesarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast IronDokument10 SeitenCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast IronsateeshkoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inoculation of Grey and Ductile Iron A Comparison of Nucleation Sites and Some Practical AdvisesDokument12 SeitenInoculation of Grey and Ductile Iron A Comparison of Nucleation Sites and Some Practical AdvisesZody YtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Monoxide Blowholes in Grey IronDokument1 SeiteCarbon Monoxide Blowholes in Grey Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium Versus Sulphur in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenMagnesium Versus Sulphur in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (2)
- Determining The Optimum Level of Inoculant Addition by Thermal Analysis - A Case Study, Ductile Iron News, Dec 2004Dokument8 SeitenDetermining The Optimum Level of Inoculant Addition by Thermal Analysis - A Case Study, Ductile Iron News, Dec 2004arnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Conservation in Liquid Iron, 2005-07-10Dokument5 SeitenHeat Conservation in Liquid Iron, 2005-07-10arnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Compacted Iron ElkemDokument20 SeitenCompacted Iron ElkemAmol ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium Slag Defects in Ductile IronDokument1 SeiteMagnesium Slag Defects in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Slag Defects in Grey IronDokument1 SeiteSlag Defects in Grey Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Poor Nodularity in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenPoor Nodularity in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr864675% (4)
- Common Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast IronDokument10 SeitenCommon Metallurgical Defects in Ductile Cast IronsateeshkoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrogen FissuresDokument1 SeiteNitrogen Fissuresarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- In The Mould Nodular Is IngDokument2 SeitenIn The Mould Nodular Is Ingarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Shrinkage PorosityDokument1 SeiteInternal Shrinkage Porosityarnaldorcr8646100% (2)
- Heat Conservation in Liquid IronDokument2 SeitenHeat Conservation in Liquid Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inoculation of Heavy Section CastingsDokument2 SeitenInoculation of Heavy Section Castingsarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- Fading of Nodularity in Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenFading of Nodularity in Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (4)
- Factors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of MagnesiumDokument4 SeitenFactors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of Magnesiumarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Partition of Slag Phases in The Treatment and Pouring of Ductile IronDokument2 SeitenPartition of Slag Phases in The Treatment and Pouring of Ductile Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Late Metal Stream InoculationDokument2 SeitenLate Metal Stream Inoculationarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of MagnesiumDokument4 SeitenFactors Influencing The Recovery and Addition of Magnesiumarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative Tundish Ladle DesignDokument2 SeitenAlternative Tundish Ladle Designarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elkem 19 Aluminum in Cast IronDokument2 SeitenElkem 19 Aluminum in Cast Ironmarcotulio123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Selection of Inoculants For Grey Cast IronDokument2 SeitenSelection of Inoculants For Grey Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Selection of Inoculants For Ductile Cast IronDokument1 SeiteSelection of Inoculants For Ductile Cast Ironarnaldorcr8646100% (1)
- The "Sandwich Pocket Process"Dokument2 SeitenThe "Sandwich Pocket Process"arnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recommended Target Analysis For Grey IronDokument2 SeitenRecommended Target Analysis For Grey Ironarnaldorcr8646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel SAE J405Dokument14 SeitenStainless Steel SAE J405Radu BurloiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equivalent Materials ChartDokument3 SeitenEquivalent Materials Chartarianaseri100% (1)
- Material (Young's Modulus, Modulus of Elasticity) - E - - σ - σDokument14 SeitenMaterial (Young's Modulus, Modulus of Elasticity) - E - - σ - σyoshefus caffaso hautamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Elements in SteelDokument3 SeitenEffect of Elements in SteelJayakrishnan Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- RDSO Vendor ListDokument7 SeitenRDSO Vendor Listernarendersaini62% (13)
- Aluminio BRONMETAL enDokument12 SeitenAluminio BRONMETAL enPerica RakićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloy Analysis Class 12Dokument18 SeitenAlloy Analysis Class 12TusharSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal WorksDokument4 SeitenMetal WorksKhristine Lerie PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD687705Dokument31 SeitenAD687705wmkaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Equations Worksheet (With Periodic Table)Dokument2 SeitenNuclear Equations Worksheet (With Periodic Table)phydotsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A890 4A, A995 4A, CD3MN - Alloy Casting FoundryDokument3 SeitenA890 4A, A995 4A, CD3MN - Alloy Casting FoundrySwapnil ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galvanic ChartDokument2 SeitenGalvanic ChartJason WilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standardi (BBM Italija)Dokument129 SeitenStandardi (BBM Italija)anon_684421324100% (1)
- Periodic Table of Elements W Oxidation States PubChemDokument1 SeitePeriodic Table of Elements W Oxidation States PubChemSHENIVEL BANTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Grades DatasheetsDokument7 SeitenStainless Steel Grades DatasheetsYeda ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Configuration of ElementsDokument3 SeitenElectronic Configuration of ElementsVeeresh Ananda Butti86% (7)
- Cast Iron: Cast Irons Are A Class of Ferrous Alloys WithDokument12 SeitenCast Iron: Cast Irons Are A Class of Ferrous Alloys WithChandima K PriyamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipetro Synergy Engineering SDN BHD: Visual Inspection ReportDokument2 SeitenDipetro Synergy Engineering SDN BHD: Visual Inspection Reportsaffririzal4237Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1917, Rehm Hardware Company, Chicaco USDokument120 Seiten1917, Rehm Hardware Company, Chicaco USHouse HistoriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frichy WebDokument10 SeitenFrichy Webrayssa11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Grades OutokumpuDokument12 SeitenStainless Steel Grades Outokumpuramundt100% (1)
- Valve - Material EquivalentDokument3 SeitenValve - Material Equivalentrenji_dannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 2738-2000Dokument29 SeitenAs 2738-2000Sherry PorlayaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aws D1.3-D1.3M 2018Dokument6 SeitenAws D1.3-D1.3M 2018Lee Chong EeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture On Transition ElementsDokument25 SeitenLecture On Transition Elementssadia SultanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turning TOTIME Grooving Inserts and Holders PDFDokument17 SeitenTurning TOTIME Grooving Inserts and Holders PDFvedrenne92Noch keine Bewertungen
- 中德材料对照表 (1)Dokument7 Seiten中德材料对照表 (1)pkfpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel, Types of SteelDokument50 SeitenSteel, Types of SteelEzhil ThalapathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- D11 Caterpillar Ripper TipDokument2 SeitenD11 Caterpillar Ripper TipMax SashikhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screwed Fiting BSP - 1 PDFDokument12 SeitenScrewed Fiting BSP - 1 PDFNguyen Thanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen