Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Efficiency of That Relay Coordion Analysis Engineering Essay 8
Hochgeladen von
Gary Goh0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten1 Seiterelay
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenrelay
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten1 SeiteEfficiency of That Relay Coordion Analysis Engineering Essay 8
Hochgeladen von
Gary Gohrelay
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
2.5.
2Ground overcurrent relay
This relay is advantage of utilizing a current source that supplies little or no normal current to the relays [12].
2.5.3 Time overcurrent relay function (51)
A time overcurrent relay is a relay that has an inverse time characteristic meaning that when the higher the fault current the
faster the relay operates. This relay operate when input current of the relay exceeds a pre-set pickup current value for a predetermine amount of time as described by a time-current curve (TCC) [30].
2.5.4 Instantaneous Overcurrent relay (50)
Instantaneous overcurrent relay is a relay that has no intentional time delay when it operates with its input current exceeds a
pre-set pickup current value [30]. In order for this relay to operate, the pickup current needs to be specified and CT ratio also
needs to be determined. Instantaneous overcurrent relays will complete its function every time pickup current exceeds the predetermined pickup value to open instantaneously [30] [31].
2.5.5 Overvoltage relay (59)
This relay is a relay that operates when input voltage exceeds pre-determine pickup value. This overvoltage relays will operate
either as instantaneous or time-delay devices. In order to set a time overvoltage relay, its pickup voltage and time dial need to
be assigned and voltage transformer (V.T.) ratio also needs to be determined [30]. Overvoltage relay will operate and close the
output contact when the time of the overvoltage exceeds the time delay described by the time voltage curve [30].
2.5.6 Directional overcurrent relay (67)
This type of relay compares the phase angle relationship of phase currents to phase voltage to locate the direction to the fault.
In high voltage transmission lines and medium voltage distribution lines, a fault location can be in two different directions from a
relay. So, the relay needs to respond quickly and differently for fault in forward or reverse direction [32] [33].
2.5.7 Differential Relay
This relay is well known in the field of protection. Differential relay operates by measuring and direct comparing of the phase
and magnitude of the current entering and leaving the protected zone [22]. So, Current transformer having a suitable ratio of
transformation intervened in the circuit between both the end of the protected equipment [22]. By the way, the zone of
differential relay is limited by a part of the electric circuit between the current transformers and where the relay is connected [5].
In addition, differential relay protection is also used to protect power network from current overloading by localizing the
insulation damages in high-voltage equipment [5].
2.5.8 Distance relay
A distance relay measures the apparent impedance derived from the current and voltage that have been measured. The
impedance of a transmission line is usually distributed constantly all over its length. Therefore, a distance relay can distinguish
with relatively good accuracy between a fault that is internal to the line and one that is external by measuring the apparent
impedance during a fault by providing the protection [34].
2.6 Important terminologies
In relay coordination there are important terms that must be known.
The following terms are:
Time/ Plug setting multiplier (PSM)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Cable Sizing & Voltage Drop Calc Rev 1Dokument58 SeitenCable Sizing & Voltage Drop Calc Rev 1MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
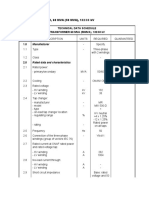
- Technical Data Schedule TRANSFORMER 60 MVA (50MVA), 132/33 KVDokument10 SeitenTechnical Data Schedule TRANSFORMER 60 MVA (50MVA), 132/33 KVGboyega AwelewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- State Space Averaging Model of Boost ConvDokument60 SeitenState Space Averaging Model of Boost ConvBharti Thakur100% (1)
- Mcag14 & Mfac r6136b High Imp Rlys, 0Dokument12 SeitenMcag14 & Mfac r6136b High Imp Rlys, 0smcraftNoch keine Bewertungen
- STATCOM - Working Principle, Design and Application - Electrical ConceptsDokument7 SeitenSTATCOM - Working Principle, Design and Application - Electrical ConceptsJunaid BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Motor ProtectionDokument33 SeitenAC Motor ProtectionLoretta KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gary Eye 2 CN103784573ADokument6 SeitenGary Eye 2 CN103784573AGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Dokument1 SeiteOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gary Eye 1 CN1123631ADokument4 SeitenGary Eye 1 CN1123631AGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Case A in kVARDokument1 SeiteTest Case A in kVARGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Dokument1 SeiteOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Dokument1 SeiteOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Dokument1 SeiteOne-Line Diagram - Olv1 (Short-Circuit Analysis) : U1 228.631 Mvasc 228.631 Mvasc U1Gary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Case A With Panel - !Dokument1 SeiteTest Case A With Panel - !Gary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panel ScheduleDokument2 SeitenPanel ScheduleGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- OLV1 One-Line Diagram Star SequenceDokument1 SeiteOLV1 One-Line Diagram Star SequenceGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Case A in KWDokument1 SeiteTest Case A in KWGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
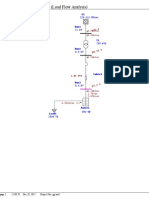
- Givdan Load FlowDokument1 SeiteGivdan Load FlowGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ggivadan Shot CircuitDokument1 SeiteGgivadan Shot CircuitGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 0.4 KV 0.4 KVDokument1 SeiteOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 0.4 KV 0.4 KVGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 496.3 KW 11.8 KvarDokument1 SeiteOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis) : 496.3 KW 11.8 KvarGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drag DropDokument1 SeiteDrag DropGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spore Solar StatisticsDokument1 SeiteSpore Solar StatisticsGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen SpecDokument1 SeiteGen SpecGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Phase Transformer PDFDokument115 Seiten3 Phase Transformer PDFGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental ElectricDokument1 SeiteFundamental ElectricGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteDokument1 SeitePower Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolator GGDokument1 SeiteIsolator GGGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Phase TransformerDokument1 Seite3 Phase TransformerGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Math RotateDokument1 SeiteSpeed Math RotateGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Acting LimiterDokument1 SeiteFast Acting LimiterGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteDokument1 SeitePower Transformer Winding Arrangements: Electrical Circuit Breakers, Fuses, ProteGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- TX Impedance Reader9382Dokument1 SeiteTX Impedance Reader9382Gary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- GG Technical Report 028 Short-CircuitDokument1 SeiteGG Technical Report 028 Short-CircuitGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switchgear Operation and Maintenance Fo : LibraryDokument1 SeiteSwitchgear Operation and Maintenance Fo : LibraryGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Generator RoomDokument1 Seite3D Generator RoomGary GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Columna de Burbujeos PDFDokument6 SeitenColumna de Burbujeos PDFKarin ParraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Electrical System DesignDokument5 Seiten6 Electrical System DesignaoemapNoch keine Bewertungen
- IM12-IS: Ice Maker/Maquina de Hacer Hielo Instruction Manual/Manual de InstruccionesDokument20 SeitenIM12-IS: Ice Maker/Maquina de Hacer Hielo Instruction Manual/Manual de Instruccionesoscar salvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Variac Circuit Diagram and AnalysisDokument6 SeitenAC Variac Circuit Diagram and AnalysisVíctor RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- VFD Cable Selection Guide: NEC Allowable Conductor Ampacity Regulatory CodesDokument1 SeiteVFD Cable Selection Guide: NEC Allowable Conductor Ampacity Regulatory Codescarlos ortizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cigma CP 2 4 8 Zones SITDokument2 SeitenCigma CP 2 4 8 Zones SITABELWALIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Editor: Computer Aided Electrical Drawing (Caed)Dokument29 SeitenPDF Editor: Computer Aided Electrical Drawing (Caed)tare tamiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Services 2019: Power ConsultingDokument15 SeitenTraining Services 2019: Power ConsultingGnanavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Standard For Industrial Machinery PDFDokument354 SeitenElectrical Standard For Industrial Machinery PDFMinh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edoc 025319Dokument28 SeitenEdoc 025319Khairi JahaparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Traning Report by Adefiranye Temitayo AdekunleDokument77 SeitenIndustrial Traning Report by Adefiranye Temitayo AdekunleAdefiranye TemitayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8DAGM Trojan Data SheetsDokument2 Seiten8DAGM Trojan Data SheetsDika Aryana PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yalla UpgradeDokument10 SeitenYalla UpgradeBrett HendricksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simtec P450 Data SheetDokument2 SeitenSimtec P450 Data Sheetacajevtic94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fcma FaqDokument2 SeitenFcma FaqSusovan ParuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Power Quality: TopicDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Power Quality: TopicArpit SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6SQ7GT, Tube 6SQ7GT Röhre 6SQ7GT ID2988, Double Diode-TriodDokument2 Seiten6SQ7GT, Tube 6SQ7GT Röhre 6SQ7GT ID2988, Double Diode-TriodRodrigo GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Needed To Secure An Offtake Agreement S/N Items Required To Secure An Offtake AgreementDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Needed To Secure An Offtake Agreement S/N Items Required To Secure An Offtake AgreementsterlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copper Conductors of Cables, Wires and Flexible CordsDokument1 SeiteCopper Conductors of Cables, Wires and Flexible CordsJayagurunathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System Cabinet AccDokument295 SeitenControl System Cabinet Accan doNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEH851 DDokument59 SeitenFEH851 DJordan MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
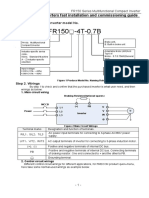
- FR150 - 4T-0.7B: FR150series Inverters Fast Installation and Commissioning GuideDokument129 SeitenFR150 - 4T-0.7B: FR150series Inverters Fast Installation and Commissioning Guidead adNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data Schedule 60mva, 132/33 KV Mobile Substation: Power TransformerDokument7 SeitenTechnical Data Schedule 60mva, 132/33 KV Mobile Substation: Power TransformermahnoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5KE6V8 (C) A - 1.5KE400 (C) A: 1500W Transient Voltage SuppressorDokument4 Seiten1.5KE6V8 (C) A - 1.5KE400 (C) A: 1500W Transient Voltage SuppressorHerberth BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen