Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 2: Controllers
Hochgeladen von
Bhartish AchutaraoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 2: Controllers
Hochgeladen von
Bhartish AchutaraoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
CONTROLLERS
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
Derivative Controllers
We never use derivative controllers alone. It should be used in
combinations with other modes of controllers because of its few
disadvantages which are written below:
1. It never improves the steady state error.
2. It produces saturation effects and also amplifies the noise
signals produced in the system.
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
Now, as the name suggests in a derivative controller the output
(also called the actuating signal) is directly proportional to the
derivative of the error signal. Now let us analyze derivative
controller mathematically. As we know in a derivative controller
output is directly proportional to the derivative of the error signal,
writing this mathematically we have,
Removing the sign of proportionality we have,
Where Kd is proportional constant also known as controller gain.
Derivative controller is also known as rate controller.
Advantages of Derivative Controller
The major advantage of derivative controller is that it improves
the transient response of the system.
Proportional and Integral Controller
As the name suggests it is a combination of proportional and an
integral controller the output (also called the actuating signal) is
equal to the summation of proportional and integral of the error
signal. Now let us analyze proportional and integral controller
mathematically. As we know in a proportional and integral
controller output is directly proportional to the summation of
proportional of error and integration of the error signal, writing
this mathematically we have,
Removing the sign of proportionality we have,
Where Ki and kp proportional constant and integral constant
respectively.
Advantages and disadvantages are the combinations of the
advantages and disadvantages of proportional and integral
controllers.
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
Proportional and Derivative Controller
As the name suggests it is a combination of proportional and a
derivative controller the output (also called the actuating signal)
is equals to the summation of proportional and derivative of the
error signal. Now let us analyze proportional and derivative
controller mathematically. As we know in a proportional and
derivative controller output is directly proportional to summation
of proportional of error and differentiation of the error signal,
writing this mathematically we have,
Removing the sign of proportionality we have,
Where Kd and kp proportional constant and derivative constant
respectively.
Advantages and disadvantages are the combinations of advantages
and disadvantages of proportional and derivative controllers
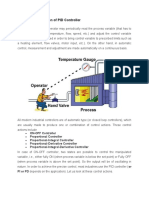
PID Control
Under Control SystemPID control stands for proportional plus
derivative plus integral control. PID control is a feedback
mechanism which is used in control system. This type of control is
also termed as three term control. By controlling the three
parameters - proportional, integral and derivative we can achieve
different control actions for specific work. PID is considered to be
the best controller in the control system family. Nicholas Minorsky
published the theoretical analysis paper on PID controller. For PID
control the actuating signal consists of proportional error signal
added with derivative and integral of the error signal. Therefore,
the actuating signal for PID control is -
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
The Laplace transform of the actuating signal incorporating PID
control is
There are some control actions which can be achieved by using any
of the two parameters of the PID controller. Two parameters can
work while keeping the third one to zero. So PID controller
becomes sometimes PI (Proportion integral), PD (proportional
derivative) or even P or I. The derivative term D is responsible for
noise measurement while integral term is meant for reaching the
targeted value of the system. In early days PID controller was used
as mechanical device. These were pneumatic controllers as they
were compressed by air. Mechanical controllers include spring,
lever or mass. Many complex electronic systems are provided with
PID control loop. In modern days PID controllers are used in PLC
(programmable logic controllers) in the industry. The proportional,
derivative and integral parameters can be expressed as - Kp, Kd
and Ki. All these three parameters have effect on the closed loop
control system. It affects rise time, settling time and overshoot and
also the steady state error.
Control Response
Rise time
Settling time
Overshoot
Steady state error
Kp
Decrease
small change
increase
decrease
Kd
small change
decrease
decrease
no change
Ki
Decrease
increase
increase
Eliminate
PID control combines advantages of proportional, derivative and
integral control actions. Let us discuss these control actions in
brief.
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
Proportional control : here actuating signal for the control action in
a control system is proportional to the error signal. The error signal
being the difference between the reference input signal and the
feedback signal obtained from input.
Derivative control : the actuating signal consists of proportional
error signal added with derivative of the error signal. Therefore,
the actuating signal for derivative control action is given by,
Integral control : for integral control action the actuating signal
consists of proportional error signal added with integral of the error
signal. Therefore, the actuating signal for integral control action is
given by
PID controller have some limitations also apart from being one of
the best controller in control action system. PID control is
applicable to many control actions but it does not perform well in
case of optimal control. Main disadvantage is the feedback path.
PID is not provided with any model of the process. Other drawbacks
are that PID is linear system and derivative part is noise sensitive.
Small amount of noise can cause great change in the output.
The output is as shown in the below figure
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
UNIT 2: CONTROLLERS
Compiled by Prof Bharatish A, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, RVCE
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- P Pi ControllerDokument4 SeitenP Pi ControllerYawar AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week14pidmay242016pe3032 160530081519Dokument57 SeitenWeek14pidmay242016pe3032 160530081519AztvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ControllersDokument4 SeitenTypes of ControllersJamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proportional Integral Derivative (PID)Dokument27 SeitenProportional Integral Derivative (PID)GilagidkidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Over View of PID ControllerDokument2 SeitenOver View of PID ControllerJawad SandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlssDokument21 SeitenPlssKrishi ChhedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Working Principle of A PID Controller For BeginnersDokument15 SeitenThe Working Principle of A PID Controller For BeginnersSaber AbdelaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Dokument13 SeitenTarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Christian MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemDokument30 SeitenControl SystemGarimaAsthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID ControllersDokument6 SeitenPID ControllersNguyễn HảiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID Controller Working Principle Explained For BeginnersDokument6 SeitenPID Controller Working Principle Explained For BeginnersPramillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID ReportDokument38 SeitenPID ReportNishiya Vijayan100% (1)
- PID Controllers: Abhishek Mehta EEE Department UIET, Panjab University September 11,2015Dokument18 SeitenPID Controllers: Abhishek Mehta EEE Department UIET, Panjab University September 11,2015aditee saxenaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID ControllersDokument9 SeitenPID Controllerszs94qjqcx7Noch keine Bewertungen
- EVMS Full Notes PDFDokument78 SeitenEVMS Full Notes PDFNaveen DhanurajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of DA Based PID Controller Using Verilog CodingDokument6 SeitenDesign and Simulation of DA Based PID Controller Using Verilog Codingjamal2877Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modren Control: Prepared by The StudentDokument12 SeitenModren Control: Prepared by The StudenthassanalabasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apc Term PaperDokument9 SeitenApc Term PaperDarshan MalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pidcontrollers 150912140326 Lva1 App6892 PDFDokument18 SeitenPidcontrollers 150912140326 Lva1 App6892 PDFKalyan TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controls YsDokument17 SeitenControls Ysbamboo shackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemsDokument18 SeitenControl Systemsgayatri jaltareNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A PID ControllerDokument11 SeitenWhat Is A PID ControllerANRG Batch 11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cs Project Report: Comparative Analysis of P, I, D, PI, PD, PID On Speed Control of DC Motor Using MATLAB SimulinkDokument25 SeitenCs Project Report: Comparative Analysis of P, I, D, PI, PD, PID On Speed Control of DC Motor Using MATLAB Simulink2K19/EE/259 TUSHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCD ProjectDokument3 SeitenPCD ProjectSasmilah KandsamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Instrumentation Training Report: Kariba South Power StationDokument12 SeitenControl and Instrumentation Training Report: Kariba South Power StationtrynoskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Lab Project ReportDokument28 SeitenControl Lab Project ReportDanyal QamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Flow Control Using PID and Fuzzy Logic ControllerDokument5 SeitenBoiler Flow Control Using PID and Fuzzy Logic Controllerحسين شنيقيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working or Operation of PID ControllerDokument7 SeitenWorking or Operation of PID Controllerjohn glenn magnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pid ThoryDokument24 SeitenPid ThoryPravin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does A PID Controller Work - Structure & Tuning MethodsDokument12 SeitenHow Does A PID Controller Work - Structure & Tuning Methodsmurugan1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- PID Lab HandoutDokument16 SeitenPID Lab HandoutsteedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control AdoresDokument6 SeitenControl AdoresRebeca LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Speed Control of DC Motor With Unknown Transfer Function Through PIDDokument6 SeitenReal Time Speed Control of DC Motor With Unknown Transfer Function Through PIDArbab HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 4 Control Configuration 4.1 Pid ControllerDokument8 SeitenChapter - 4 Control Configuration 4.1 Pid ControllerMoorthy ManikandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Experiment #5 PID Controller. Done By: Abdallah Husain Sulieman Daldoom. 31502020130. Eng. Saleem GhanayemDokument6 SeitenSubject: Experiment #5 PID Controller. Done By: Abdallah Husain Sulieman Daldoom. 31502020130. Eng. Saleem GhanayemAbdallah DaldoomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanji MIMO DissDokument3 SeitenSanji MIMO DissSanjaya SrinathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeDokument11 SeitenName: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeMayukh BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID Control of Mechanical System Using Suitable Simulation SoftwareDokument12 SeitenPID Control of Mechanical System Using Suitable Simulation Softwareanagha joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID ControlDokument5 SeitenPID ControlVignesh RajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universidad Politécnica Salesiana: Sistema de Control en Tiempo ContinuoDokument6 SeitenUniversidad Politécnica Salesiana: Sistema de Control en Tiempo ContinuoAndres LozanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1 Process Under ControlDokument9 SeitenFigure 1 Process Under ControlKajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory SERVO Linear Position ControlDokument7 SeitenTheory SERVO Linear Position ControlEnMaa 96Noch keine Bewertungen
- PID ControllerDokument5 SeitenPID ControllerAbhilash MallikarjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27.ijaest Vol No 8 Issue No 2 DC Motor Control Using Fuzzy Logic Controller 291 296Dokument6 Seiten27.ijaest Vol No 8 Issue No 2 DC Motor Control Using Fuzzy Logic Controller 291 296Vikas PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic TheoryDokument5 SeitenBasic TheoryzakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto1 Kupe6 Co2 Resurreccion DefinitionsDokument4 SeitenAuto1 Kupe6 Co2 Resurreccion DefinitionsaltheiaarabeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- JSME - Volume 12 - Issue 4 - Pages 53-66Dokument14 SeitenJSME - Volume 12 - Issue 4 - Pages 53-66Nguyễn Trung ThôngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 PLC PDFDokument15 SeitenUnit 3 PLC PDFMahesh ShendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control: ObjectivesDokument5 SeitenProportional-Integral-Derivative Control: ObjectivesQuenneBelocuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3a Industrial Control SystemsDokument25 SeitenUnit 3a Industrial Control SystemsT. Rajpradeesh MECH-LECTNoch keine Bewertungen
- CST 04Dokument95 SeitenCST 04Sourav ChoubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Control System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokument21 SeitenUnit 1 - Control System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inAltmash RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contro EngineeringDokument29 SeitenContro EngineeringNor AshimyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Pid Controller - 72S173Dokument15 SeitenDigital Pid Controller - 72S173Pandimadevi GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- InTech-Pid Control TheoryDokument17 SeitenInTech-Pid Control TheoryAbner BezerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar ReportDokument23 SeitenSeminar ReportSwapnil Behera100% (1)
- Ce Mod1Dokument22 SeitenCe Mod1AYUSH CHANDRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Indentation Hardness Measurements at Macro-, Micro-, and Nanoscale: A Critical OverviewDokument18 SeitenIndentation Hardness Measurements at Macro-, Micro-, and Nanoscale: A Critical OverviewBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy Logic Research PaperDokument15 SeitenFuzzy Logic Research PaperBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- COF and Wear Related PaperDokument19 SeitenCOF and Wear Related PaperBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DrawingDokument240 SeitenEngineering DrawingKhelly Shan C. Sta. RitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C5RA21361DDokument15 SeitenC5RA21361DBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Raman Spectra of Disordered and Amorphous CarbonDokument13 SeitenInterpretation of Raman Spectra of Disordered and Amorphous CarbonBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edgehouse2019 PDFDokument10 SeitenEdgehouse2019 PDFBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPONSORING AGENCIES Financial Resources For Research & Development Sponsored AgenciesDokument118 SeitenSPONSORING AGENCIES Financial Resources For Research & Development Sponsored AgenciesAshoka VanjareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Composite Thin Films Prepared by Pulsed Laser DepositionDokument10 SeitenMechanical Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Composite Thin Films Prepared by Pulsed Laser DepositionBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Independent Researcher Grants - 260916Dokument80 SeitenIndependent Researcher Grants - 260916Bhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano-Emulsions: Nicolas Anton and Thierry F. VandammeDokument24 SeitenNano-Emulsions: Nicolas Anton and Thierry F. VandammeBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Books PDFDokument118 SeitenResearch Books PDFAnonymous 9Yv6n5qvSNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEA Mock TestDokument1 SeiteFEA Mock TestBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funding Agencies PDFDokument5 SeitenFunding Agencies PDFpnaik048711Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Reduction GearsDokument9 SeitenUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Reduction GearsBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO1Dokument1 SeiteCO1Bhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pdd-16me6c5 Co1Dokument6 SeitenPdd-16me6c5 Co1Bhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Open Engineering) Laser Surface Texturing of Tool Steel Texturedsurfaces Quality EvaluationDokument8 Seiten(Open Engineering) Laser Surface Texturing of Tool Steel Texturedsurfaces Quality EvaluationBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Pressure DistributionDokument184 SeitenContact Pressure DistributionBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Metrology and Measurement Systems) Problem of Non-Measured Points in Surface Texture MeasurementsDokument12 Seiten(Metrology and Measurement Systems) Problem of Non-Measured Points in Surface Texture MeasurementsBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D SSPP Ergonomics LabDokument120 Seiten3D SSPP Ergonomics LabBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research TechniquesDokument5 SeitenResearch TechniquesBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Surface TexturingDokument15 SeitenLaser Surface TexturingBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Metrology and Measurement Systems) Problem of Non-Measured Points in Surface Texture MeasurementsDokument12 Seiten(Metrology and Measurement Systems) Problem of Non-Measured Points in Surface Texture MeasurementsBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 11 14 Quantitative Research Methods and ToolsDokument83 Seiten2011 11 14 Quantitative Research Methods and ToolsBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Diagram Reduction and Signal Flow GraphsDokument16 SeitenBlock Diagram Reduction and Signal Flow GraphsBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1Dokument7 SeitenPaper 1Bhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-Alumina Coating PDFDokument5 Seiten02-Alumina Coating PDFBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics & Laser TechnologyDokument11 SeitenOptics & Laser TechnologyBhartish AchutaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project ON: Full Wave RectifierDokument11 SeitenPhysics Project ON: Full Wave RectifierkartikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minecraft Franchise Fact Sheet - Updated - 1 19 18 1Dokument3 SeitenMinecraft Franchise Fact Sheet - Updated - 1 19 18 1Johnny ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - FET Biasing: Your Answer: Correct AnswerDokument6 SeitenChapter 6 - FET Biasing: Your Answer: Correct AnswerXiao XiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Control For Home Water Heater Saving PDFDokument111 SeitenSmart Control For Home Water Heater Saving PDFPrashant JagadaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Globe G2 User Guide S-63 1.1Dokument23 SeitenE-Globe G2 User Guide S-63 1.1krupa kumar100% (1)
- Pnwman Feb12Dokument194 SeitenPnwman Feb12batrarobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Td01602002e PDFDokument4 SeitenTd01602002e PDFAllan SeminarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIMA Service ManualDokument52 SeitenTRIMA Service ManualUku KukrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Secador Mdcw50Dokument115 SeitenManual Secador Mdcw50daniel menaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI eDokument66 SeitenSI eGerman Ocampo100% (1)
- Pca 6003Dokument1 SeitePca 6003drmnsyhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 1Jean100% (1)
- Terberg Network Structure-3661600586101635Dokument14 SeitenTerberg Network Structure-3661600586101635yousufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Addressable Remote Transducer ProtocolDokument5 SeitenHighway Addressable Remote Transducer ProtocolKhaled RabeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE357 Course InformationDokument7 SeitenECE357 Course InformationVictor HughesNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC 60079-18 - 2009 - Encapsulated Protection - Ex M PDFDokument35 SeitenIEC 60079-18 - 2009 - Encapsulated Protection - Ex M PDFRadu Babau100% (1)
- E Jac ManualDokument10 SeitenE Jac ManualJhon Elier Arango TrillosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Example Report: TitleDokument63 SeitenDesign Example Report: TitleJose BenavidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blade Service ManualDokument185 SeitenBlade Service ManualDiego Alejandro Gomez80% (5)
- 2141005Dokument2 Seiten2141005Janak TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Acs800 Crane Control Manualn697 PDFDokument340 SeitenAbb Acs800 Crane Control Manualn697 PDFDaniel Tando100% (1)
- High Voltage and Ustable States of MatterDokument21 SeitenHigh Voltage and Ustable States of MatterSyedTamkanatMunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 221 Mutually Coupled CircuitsDokument26 SeitenEE 221 Mutually Coupled Circuitsaswak0% (1)
- Streamline Modular Electronic Sounder: Model SLM700Dokument2 SeitenStreamline Modular Electronic Sounder: Model SLM700GersonDarioOrtizReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 74HC4520Dokument8 Seiten74HC4520pnlinh28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emcomm Ham Radio PDFDokument170 SeitenEmcomm Ham Radio PDFMichael Yurkovich100% (1)
- Digital Scale 340368 - A - D - IE - ENDokument47 SeitenDigital Scale 340368 - A - D - IE - ENDimitar KirovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modular Lead Exit - Info SheetDokument2 SeitenModular Lead Exit - Info SheetSunil GurubaxaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 8: FM DemodulatorDokument20 SeitenExperiment 8: FM Demodulatorslay17Noch keine Bewertungen
- ANSI-IEEE, NEMA and UL Requirements For SwitchgearDokument4 SeitenANSI-IEEE, NEMA and UL Requirements For Switchgearefmartin21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNVon EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsVon EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsVon EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamVon EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Von EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZVon EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsVon EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterVon EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (3)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksVon EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Unlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsVon EverandUnlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsVon EverandFreeCAD | Step by Step: Learn how to easily create 3D objects, assemblies, and technical drawingsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationVon EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachVon EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityVon EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionVon EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamVon EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyVon EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyBewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (2)