Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drugs I3-1 (Emmeline) PDF
Hochgeladen von
ivankcurryOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drugs I3-1 (Emmeline) PDF
Hochgeladen von
ivankcurryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
I3 TEST 1 - PHARMACOLOGY
Drug
Aspirin
(acetylsalicylic
acid)
Therapeutic Use
Low dose: protection against
cardiovascular disease
Platelet aggregation
protection (MIs, strokes, etc.)
Mechanism of Action
Non-selective irreversible
inhibitor of COX-1/2.
For COX-1, alters active
binding site to prevent
substrate entry.
Drug/Drug
Interactions
Probenecid blocks
elimination.
Inflammatory bowel disease
See also NSAID uses.
Salicylate
Cogener for aspirin.
See aspirin.
Ibuprofen (Advil)
NSAID
Naproxen (Aleve)
Low dose: analgesia (pain
relief), antipyretic (fever
reducer)
Reversible competitive
inhibitor of COX-1/2.
Inhibition of prostaglandin
synthesis.
Indomethacin
(Idocin)
High dose: antiinflammation, closure of
patent ductus arteriosus for
newborns circulation
Interacts with lithium
and fluconazole drugs.
Compete against the
protective effects of
low-dose aspirin.
Adverse effects with
ACE inhibitor (HT
drug)
Adverse Effects
Phys. Disposition
(ADME)
- Contraindicated in
Aspirin hydrolyzed in
children with fever due
plasma to salicylate.
to virus (may cause
Conjugated by
Reyes syndrome).
glutathione, glucoronic
- GI bleeding/uclers
acid, and sulfate
- Analgesic nephropathy, eliminated renally.
progressive renal failure
- Hepatic injury
- Respiratory and
metabolic acidosis if at
toxic levels.
More adverse effects
Metabolized by CYP
than aspirin.
GI discomfort and stress Acidic so well absorbed.
hemorrhage and
perforation.
Renal excretion,
extensively metabolized,
Analgesic nephropathy
undergo EH circulation.
Postpartum hemorrhage
for pregnant users (also
prolonged gestation and
inhibition of labor)
May reduce risk for colon
cancer.
Found in synovial fluid
(useful for joint pain)
Naproxen has longer
half-life than ibuprofen.
Celecoxib
NSAID
(anti-inflammation)
Inhibits COX-2
Misoprostol
Prevents peptic ulcers that
result from NSAIDs
Heparin
Anti-coagulant
PGE1analog (replaces lost
PGs in GI from
NSAIDs/COX inhibition)
Catalysts for antithrombin
III inhibition of both
thrombin and FXa.
Prevent PE, DVT; acute MI,
Highly protein bound
Cardiovascular disease
(uncontrolled platelet
aggregation).
Black box warning.
Protamine sulfate
antagonist.
- Bleeding
- Hypersensitivity
(sometimes)
Not easily absorbed
because large IV or
subcutaneous injection.
Drug
Therapeutic Use
unstable angina; prevent
thrombosis in extracorporeal
devices
Enoxaparin
(Lovenox)
Anti-coagulant
Prevent DVT,
thromboembolism, Pts with
HIT
Fondaparinux
(Arixtra)
Anti-coagulant
Prevent PE, DVT;
thromboprophylaxis for Pts
undergoing hip/knee surgery,
Pts with HIT
Dabigatran
(PRADAXA)
Anti-coagulant
Rivaroxaban
(Xarelto)
Apixaban
(Eliquis)
Warfarin
(Coumadin)
Anti-coagulant
Anti-coagulant
Anti-coagulant
Mechanism of Action
Drug/Drug
Interactions
- Transient
thrombocytopenia
- Heparin-induced
thrombocytopenia
- Contraindications:
history of
hypersensitivity to
heparins, active
bleeding, threatened
abortion, surgical
procedures in general,
infective endocarditis
- Bleeding
- Hypersensitivity
(sometimes)
- Transient
thrombocytopenia
See above for
contraindications.
- Bleeding
- Hypersensitivity
(sometimes)
- Transient
thrombocytopenia
See above for
contraindications.
Long chains wrap
thrombin and antithrombin together.
Catalysts for antithrombin
III inhibition of FXa (cant
wrap around thrombin).
Catalysts for antithrombin
III inhibition of FXa:
synthesized
pentasaccharide mimics
the binding site on
antithrombin III,
enhancing FXa binding
and inhibition.
Inhibits FII (thrombin) via
blocking active site
Inhibits FXa via blocking
active site
Indirect inhibition of FXa
active site
Vitamin K analog
inhibits VKOR prevents
Adverse Effects
Transported by Pglyocoprotein (drugs
that inhibit PGP will
enhance dabigatran,
drugs that induce will
inhibit)
Phys. Disposition
(ADME)
Does not cross into
placenta.
Must routinely monitor
Pt. because drug is
mixture of
unfractionated peptides.
Subcutaneous injection
Oral dose
Bleeding
Administered as
dabigatran etexilate
(prodrug).
Bleeding
Metabolized by CYP3A4
Bleeding
MANY. See last page.
Bleeding
100% bioavailable;
highly bound to plasma
Drug
Therapeutic Use
Mechanism of Action
Drug/Drug
Interactions
Gla modifications in
clotting factors factors
inactive
Adverse Effects
Pro-cogulative states
(inhibition of protein C
and S)
Can be overcome by
excess Vitamin K.
Phys. Disposition
(ADME)
protein; long half-life.
Extensively metabolized
(CYP-2C9), excreted in
urine.
Crosses placenta can
be teratogen.
Desirudin
Anti-coagulant
Bivalrudin
Anti-coagulant
Agratroban
Anti-coagulant
Clopidogrel
(Plavix)
Anti-coagulant (anti-platelet)
Use with Pt who are allergic
to aspirin or need synergic
effect with aspirin.
Aspirin
Anti-coagulant (anti-platelet)
Abciximab
NSAID
Anti-coagulant (anti-platelet)
Cortisol
Anti-inflammatory steroid;
immuno-suppressant
Direct acting inhibitor of
thrombin
Direct acting inhibitor of
thrombin
Direct acting inhibitor of
thrombin (blocks catalytic
active site)
Irreversibly binds to
P2Y12 receptor no
ADP activation of platelet
aggregation
No TXA2 formation.
No hemostasis (platelet
change initiation).
Ig that inhibits GP2b/3a
receptor on platelets no
fibrinogen binding no
aggregation
- Inhibit phospholipase A2
(AA mobilization) via
increased synthesis of
annexin-1
- Decrease production of
PG and LT
- Inhibit COX-2 upregulation/synthesis
- Decrease TNF-
production by inhibiting
Rash, diarrhea,
abdominal pain,
dyspepsia, bleeding,
thrombotic
thrombocytopenia
Well absorbed;
extensive metabolism by
liver; 8 hr half life; urine
and fecal elimination
See above.
See above.
Needs to get
metabolized to be active.
See above.
May cause
hypertension because
also interacts with
mineralcorticoid
receptor with high
affinity.
(Licorice has
glycyrrhizic acid
which inhibits 11HSD 2 from
Abrupt cessation of
therapy acute adrenal
insufficiency (fever,
myalgia, arthralgia,
malaise).
Fat soluble, go through
membranes. Prepared as
nasal sprays, inhalers,
topical, injectable,
sprays well absorbed.
High doses: HPA
suppression,
hypertension,
hyperglycemia,
Inactivated by liver
conjugation into inactive
metabolites, excreted in
liver
Drug
Therapeutic Use
Mechanism of Action
NFB (TNF-
transcription factor)
Prednisolone
Dexamethasone
Aldosterone
Flurocortisone
Chlorpheniramine
(Chlortrimeton)
Diphenhydramine
(Benadryl)
Dimenhydrinate
(Dramamine)
Anti-inflammatory steroid;
immuno-suppressant
Anti-inflammatory steroid;
immuno-suppressant
Diagnose causes of
hypercorticism
Mineralcorticoid (low blood
pressure)
Replacement therapy of
mineralcorticoid (low blood
pressure, aldosterone
deficiency)
Anti-histamine (1
generation)
st
Allergic rhinitis,
conjunctivitis, itching, atopic
& contact dermatitis,
urticaria, drug reactions,
motion sickness, local
Cortisol analog with
intermediate half life (4x
more potent)
Drug/Drug
Interactions
regulating high
cortisol levels.)
See Cortisol.
Cortisol analog with longer See Cortisol.
half life (25x more potent)
Adverse Effects
increased susceptibility
to infection, peptic ulcer
disease, osteoporosis,
osteonecrosis,
myopathy,
cataracts,behavior
disturbance, growth
suppression, Cushings
syndrome
See Cortisol.
See Cortisol.
Phys. Disposition
(ADME)
Use the lowest dose
possible to achieve
desired result because
not specific/curative.
See Cortisol.
Active ingredient for
prednisone. If Pt has
hepatic failure,
administer prednisolone
straight.
See Cortisol.
Retains Na+
Retains Na+ (125x
potency)
Inverse agonists to H1
receptor on smooth
muscle, endothelial
vessels, and CNS.
Depression drugs
inhibit MAO more
histamine
accumulation
Sodium and water
retention, high blood
pressure, edema, low
potassium, muscle
weakness, fatigue,
increase susceptibility to
infection, peptic ulcer,
cataracts, hyperglycemia
Impairment of alertness,
cognition, learning,
memory, and
performance. Sinus
tachycardia, reflex
tachycardia,
antimuscurinic effects
(pupil dilation, blurred
Moderate glucocorticoid
potency.
Fat soluble, go through
membranes. Well
absorbed.
Hepatic metabolism.
Liposoluble, well
absorbed. Metabolized
by liver. Renal
excretion.
Crosses placenta and
breast milk.
Penetrates BBB anti-
Drug
Therapeutic Use
Mechanism of Action
Drug/Drug
Interactions
anesthetic, insomnia, some
symptom relief for colds
Loratadine
(Claritin)
Cetirizine
(Zyrtec)
Fexofenadine
(Allegra)
Anti-histamine (2nd
generation)
Adverse Effects
vision, dry eyes, dry
mouth, urinary retention,
constipation, ED),
fatality in young
children
Inverse agonists to H1
receptor on smooth muscle
and endothelial vessels
Allergic rhinitis,
conjunctivitis, itching, atopic
& contact dermatitis,
urticaria, drug reactions
Depression drugs
inhibit MAO more
histamine
accumulation
Contraindicated for
people with glaucoma,
prostatic hypertrophy,
impaired renal function,
elderly (impairs their
cognition), pregnant and
lactating women,
neonates, infants and
young children.
Even 30x overdose has
not seen any adverse
effects or fatality!
Contraindicated for
pregnant and lactating
women.
Phys. Disposition
(ADME)
Ach and sedation.
Liposoluble, well
absorbed. Metabolized
by liver. Renal
excretion.
Crosses placenta and
breast milk.
Differences:
Does not penetrate BBB,
longer lasting, some
metabolized by CYP3A4
Cetirizine is metabolite
of hydroxyzine.
Fexofenadine excreted
by bile and abs is
inhibited by some fruit
juices.
Cromolyn sodium
(Nasalcrom)
Mast cell stabilizer
Blocks ion channels on
mast cells directly
inhibits degranulation
no histamine release
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF WARFARIN.
1.
Phenobarital induces microsomal enzymes that increase warfarin metabolism
2.
Sulfinpyrazone inhibition of CYP-450 will cause inhibition of warfarin metabolism
3.
Decrease of binding to plasma protein-sulfonamides increase in free warfarin
4.
Aspirin interference with normal platelet function intensified anticoagulation function
5.
Cholestyramine binds to warfarin and inhibits absorption in GI
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Alliance of Virtue (Or Get Your Bags Together)Dokument9 SeitenAlliance of Virtue (Or Get Your Bags Together)ivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Bitcoin May Change Our World in Ways As Profound As The Internet' - TheStreetDokument11 Seiten'Bitcoin May Change Our World in Ways As Profound As The Internet' - TheStreetivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- I3 002 S RegulationHematopoiesisPart1 Han PDFDokument42 SeitenI3 002 S RegulationHematopoiesisPart1 Han PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- I3 Week 1 Review Guide PDFDokument38 SeitenI3 Week 1 Review Guide PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Reasons Why Many Christian Girls Remain Single - SuperChampInc PDFDokument36 Seiten5 Reasons Why Many Christian Girls Remain Single - SuperChampInc PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- I3 Lectures Exam 1Dokument3 SeitenI3 Lectures Exam 1ivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Huge Mistakes I Made As A Wife (I'm The Ex-Wife Now) - YourTango PDFDokument6 Seiten4 Huge Mistakes I Made As A Wife (I'm The Ex-Wife Now) - YourTango PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Things The History Books Don't Tell Us About Native People - Everyday Feminism PDFDokument7 Seiten8 Things The History Books Don't Tell Us About Native People - Everyday Feminism PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Things You Need To Know About Oregon's Patriot Movement PDFDokument14 Seiten5 Things You Need To Know About Oregon's Patriot Movement PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Bitcoin May Change Our World in Ways As Profound As The Internet' - TheStreetDokument11 Seiten'Bitcoin May Change Our World in Ways As Profound As The Internet' - TheStreetivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- I3 001 R Blood&BoneMarrowHistologyHandout Jurjus PDFDokument23 SeitenI3 001 R Blood&BoneMarrowHistologyHandout Jurjus PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Blood Elements on a Blood SmearDokument12 SeitenIdentify Blood Elements on a Blood SmearivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1 - I3 PathologyDokument7 SeitenExam 1 - I3 PathologyivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematopoiesis, Bone Marrow Exhippy Training, Questions, Amination, and AnemiasDokument15 SeitenHematopoiesis, Bone Marrow Exhippy Training, Questions, Amination, and AnemiasivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Blood ChartDokument1 SeiteComponents of Blood ChartivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Blood Iron Test Results GuideDokument1 SeiteAbnormal Blood Iron Test Results GuideivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Findings I3-1 (Emmeline) Components of Blood ChartDokument5 SeitenClinical Findings I3-1 (Emmeline) Components of Blood ChartivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease Chart I3-1 (Emmeline)Dokument20 SeitenDisease Chart I3-1 (Emmeline)ivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
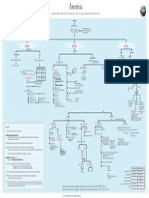
- Components of Blood ChartAnemia FlowchartDokument1 SeiteComponents of Blood ChartAnemia Flowchartivankcurry100% (1)
- AdaptiveComponents of Blood Chart ImmunityDokument8 SeitenAdaptiveComponents of Blood Chart ImmunityivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helminths 2Dokument5 SeitenHelminths 2ivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- HotSpotters GawandeDokument12 SeitenHotSpotters GawandeivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 657.fullhippy Training, Questions, VDokument13 Seiten657.fullhippy Training, Questions, VivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hollywood Uses American Sniper' To Destroy History & Create Myth - RT Op-EdgeDokument7 SeitenHollywood Uses American Sniper' To Destroy History & Create Myth - RT Op-EdgeivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helminths 2Dokument5 SeitenHelminths 2ivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 16 I3 67 Liappis Gram Positive Cocci Infections Therapy 11 2 15 Part3Dokument7 Seiten15 16 I3 67 Liappis Gram Positive Cocci Infections Therapy 11 2 15 Part3ivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematopoiesis, Bone Marrow Exhippy Training, Questions, Amination, and AnemiasDokument15 SeitenHematopoiesis, Bone Marrow Exhippy Training, Questions, Amination, and AnemiasivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 347 Full PDFDokument11 Seiten347 Full PDFivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 079 - FungiFinal - Doccomponents of Blood ChartxDokument5 Seiten079 - FungiFinal - Doccomponents of Blood ChartxivankcurryNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Ball Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsDokument16 SeitenBall Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsABDUL KADHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condition Based Monitoring System Using IoTDokument5 SeitenCondition Based Monitoring System Using IoTKaranMuvvalaRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipotension 6Dokument16 SeitenHipotension 6arturo castilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector 4114NS Sis TDSDokument2 SeitenVector 4114NS Sis TDSCaio OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDokument2 SeitenBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledCesar ValeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolBridge Application 2012Dokument14 SeitenSolBridge Application 2012Corissa WandmacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Box Testing Techniques: Ratna SanyalDokument23 SeitenWhite Box Testing Techniques: Ratna SanyalYogesh MundhraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consensus Building e Progettazione Partecipata - Marianella SclaviDokument7 SeitenConsensus Building e Progettazione Partecipata - Marianella SclaviWilma MassuccoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft SemestralWorK Aircraft2Dokument7 SeitenDraft SemestralWorK Aircraft2Filip SkultetyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LegoDokument30 SeitenLegomzai2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist of Requirements For OIC-EW Licensure ExamDokument2 SeitenChecklist of Requirements For OIC-EW Licensure Examjonesalvarezcastro60% (5)
- Busbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersDokument1 SeiteBusbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersVikram SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab StoryDokument21 SeitenLab StoryAbdul QadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Global Finance Business Management Analyst Program - IIMDokument4 Seiten2020 Global Finance Business Management Analyst Program - IIMrishabhaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masteringphys 14Dokument20 SeitenMasteringphys 14CarlosGomez0% (3)
- Objective Mech II - IES 2009 Question PaperDokument28 SeitenObjective Mech II - IES 2009 Question Paperaditya_kumar_meNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revit 2010 ESPAÑOLDokument380 SeitenRevit 2010 ESPAÑOLEmilio Castañon50% (2)
- Consumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaDokument16 SeitenConsumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaSundaravel ElangovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MQC Lab Manual 2021-2022-AutonomyDokument39 SeitenMQC Lab Manual 2021-2022-AutonomyAniket YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weone ProfileDokument10 SeitenWeone ProfileOmair FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument3 SeitenManagerial EconomicsGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines - MIDA (Haulage)Dokument3 SeitenGuidelines - MIDA (Haulage)Yasushi Charles TeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMDokument41 SeitenCALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMMACARIO QTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ovr IbDokument27 SeitenOvr IbAriel CaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio310 Summary 1-5Dokument22 SeitenBio310 Summary 1-5Syafiqah ArdillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluative Research DesignDokument17 SeitenEvaluative Research DesignMary Grace BroquezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grading System The Inconvenient Use of The Computing Grades in PortalDokument5 SeitenGrading System The Inconvenient Use of The Computing Grades in PortalJm WhoooNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtlasConcorde NashDokument35 SeitenAtlasConcorde NashMadalinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master SEODokument8 SeitenMaster SEOOkane MochiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric 5th GradeDokument2 SeitenRubric 5th GradeAlbert SantosNoch keine Bewertungen