Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Conversion of Geodetic Coordinates To "Earth-Centred" Cartesian Coordinates
Hochgeladen von
Vesna StepanoviOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Conversion of Geodetic Coordinates To "Earth-Centred" Cartesian Coordinates
Hochgeladen von
Vesna StepanoviCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
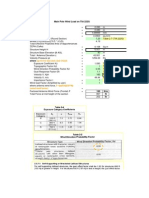
Geodetic (Lat, Long, Ellip Ht.
) to Cartesian (XYZ)
Conversion of Geodetic Coordinates to "Earth-centred" Cartesian Coordinates
Latitude
Longitude
Ellipsoidal height
Ellipsoid
Bessel
Semi major axis (a)
Inverse flattening (1/f)
deg
46
14
462.110
min
41'
29'
secs
34.44000"
09.49000"
X
Y
Z
4,243,058.119
1,096,220.980
4,618,283.821
6377397.16
299.1528
Instructions:
1. Enter the name of the ellipsoid associated with the geodetic coordinates in C12
2. Enter the semi major axis (metres) and inverse flattening of the associated ellipsoid in D13:D14
3. Enter the latitude in D7:F7 (south latitudes are negative)
4. Enter the longitude in D8:D7
5. Enter the ellipsoidal height (metres) in D9 (note that it must be the ELLIPSOIDAL height)
6. Note the Earth-centred Cartesian coordinates (metres) from L7:L9
Input
Output
To see the intermediate calculations, use Excel's outlining tool to show the hidden rows.
http://www.anzlic.org.au/icsm/gdatm.htm
12/10/2015
Similarity Transformation
3 Dimensional Similarity Transformation
INPUT
Bessel
X
4243058.119
1096220.980
4618283.821
Parameters (from -> to)
DX
586.0000 (metres)
DY
89.0000 (metres)
DZ
468.0000 (metres)
RX
-5.1000 (seconds)
RY
-1.4000 (seconds)
RZ
-5.4000 (seconds)
1.1000 (ppm)
Sc
Instructions:
1. Enter the name of the starting coordinate system in C5 (documentation only)
2. Enter the starting coordinates in D6:D8 (by default they will be taken from the output of
the Geodetic to Cartesian sheet.
3. Enter the name of the resulting coordinate system in C5 (documentation only)
4. Enter the 7 transformation parameters in G6:G12
5. Note the transformed position from K6:K8
OUTPUT
WGS 84
Xs
4243651.431
Ys
1096308.079
Zs
4618755.208
Input
Output
Warning: be careful of the sign convention for rotations. See the attached notes.
http://www.anzlic.org.au/icsm/gdatm.htm
12/10/2015
Cartesian (XYZ) to geodetic (lat, long, ellip. ht.)
Conversion of "Earth-centred" Cartesian Coordinates to Geodetic Coordinates
X
Y
Z
Ellipsoid
WGS 84
Semi major axis (a)
Inverse flattening (1/f)
4,243,651.431
1,096,308.079
4,618,755.208
Latitude
Longitude
Ellipsoidal height
deg
46
14
min
41'
29'
sec
33.01011"
06.47425"
509.409
6378137.00
298.2572
Instructions:
1. Enter the name of the reference ellipsoid in C11 (documentation only)
2. Enter the semi major axis (metres) and inverse flattening of the reference ellipsoid in D12 & D13
3. Enter the XYZ coordinates in D6:D8 (by default they are taklen from the transformation sheet)
4. Read the resulting latitude, longitude and ellipsoidal height from G6:I8
(note that it is the ELLIPSOIDAL height)
Input
Output
To see the intermediate calculations, use Excel's outlining tool to show the hidden rows.
http://www.anzlic.org.au/icsm/gdatm.htm
12/10/2015
Test Data
From
deg
Latitude
Longitude
Ellipsoidal height
min
-37
143
Latitude
Longitude
Ellipsoidal height
15.5647"
30.5501"
749.671
DX
-117.763 (metres)
DY
-51.510 (metres)
DZ
139.061 (metres)
RX
-0.292 (seconds)
RY
-0.443 (seconds)
RZ
-0.277 (seconds)
-0.191 (ppm)
Sc
To
secs
39'
55'
deg
min
-37
143
X
Y
Z
-4086966.080
2977519.575
-3875610.134
Ellipsoid
ANS (AGD84)
Semi major axis (a)
Inverse flattening (1/f)
6378160
298.25
-4087095.384
2977467.494
-3875457.340
Ellipsoid
GRS80 (GDA94)
Semi major axis (a)
Inverse flattening (1/f)
6378137
298.257222101
sec
-39
55
-10.1598"
35.3730"
737.574
X
Y
Z
http://www.anzlic.org.au/icsm/gdatm.htm
12/10/2015
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Earth and Life Sciences (Week 1)Dokument18 SeitenEarth and Life Sciences (Week 1)Gerica P. Balicudcud100% (1)
- Eis enDokument941 SeitenEis enAlyssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation WGS84 To PRS92 and Vice VersaDokument5 SeitenTransformation WGS84 To PRS92 and Vice VersaTen Dela Cruz100% (2)
- Higher SurveyingDokument60 SeitenHigher SurveyingJ HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Shallow SETTLEMENT PDFDokument7 SeitenSolution Shallow SETTLEMENT PDFRaja SyarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latitude and Longitude:: Finding Locations On Planet EarthDokument21 SeitenLatitude and Longitude:: Finding Locations On Planet EarthAmazing Top HDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Lateral LoadsDokument11 SeitenDetermination of Lateral LoadschamilcjNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP35s Surveying ProgramsDokument49 SeitenHP35s Surveying ProgramsJose Espejo Vasquez100% (1)
- H.O. No. 211 (Ageton)Dokument45 SeitenH.O. No. 211 (Ageton)terrace306100% (1)
- Main Pole Wind Load On TIA 222G: QZ 0.613 (KZ) (KZT) (KD) (V2) (I)Dokument29 SeitenMain Pole Wind Load On TIA 222G: QZ 0.613 (KZ) (KZT) (KD) (V2) (I)boypardede3552Noch keine Bewertungen
- Social Studies Unit 3 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenSocial Studies Unit 3 Study Guideapi-236678278Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compass Rule and Transit RuleDokument14 SeitenCompass Rule and Transit RuleRommel Dave TejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casio Programs v4Dokument47 SeitenCasio Programs v4a_tacora395350% (2)
- Traverse Computations and Adjustments PDFDokument37 SeitenTraverse Computations and Adjustments PDFFrimeSarmientoAlfanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBC Calculations - BridgeDokument41 SeitenSBC Calculations - BridgeRajendra Prasad Gubbala100% (1)
- Tia 222g LoadDokument29 SeitenTia 222g Loadabeyivan100% (3)
- Water Cycle Quiz PDFDokument2 SeitenWater Cycle Quiz PDFAle FunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waffle SlabsDokument9 SeitenWaffle Slabsahsana2878% (9)
- Conversion of Geodetic Coordinates To "Earth-Centred" Cartesian CoordinatesDokument4 SeitenConversion of Geodetic Coordinates To "Earth-Centred" Cartesian Coordinatesioana_muresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation ConversionDokument3 SeitenTransformation Conversionhamid yousifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datum Transformations of GPS PositionsDokument12 SeitenDatum Transformations of GPS Positionsgordon_greeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4 - AnswersDokument2 SeitenHomework 4 - AnswersZamantha DatinguinooNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDNGI Coordinate Conversion Utility v1 Sep 2009Dokument8 SeitenCDNGI Coordinate Conversion Utility v1 Sep 2009Mfanelo MbanjwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabSheet2 (Traversing) PDFDokument9 SeitenLabSheet2 (Traversing) PDFElilragiGanasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vincenty ACTDokument4 SeitenVincenty ACTLuis Alberto Roman AtilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEC021Dokument2 SeitenEEC021OmShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close RangeDokument5 SeitenClose RangenuruljannatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Symbol Value Units Tashiding HEP Raft Design Given Data: Req Prov 2 2Dokument12 SeitenI Symbol Value Units Tashiding HEP Raft Design Given Data: Req Prov 2 2satyakam0601050Noch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication Fall 2011 Answer KeyDokument7 SeitenSatellite Communication Fall 2011 Answer KeyplutopopNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 312 Lecture 9Dokument26 SeitenEE 312 Lecture 9دكتور كونوهاNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gear Modifications WindDokument11 SeitenGear Modifications Windcosta59dac9242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Partition of Land 05272022Dokument10 SeitenModule 3 Partition of Land 05272022RommelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spatial ReferencingDokument61 SeitenSpatial ReferencingRendy AditamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 25Dokument5 SeitenPaper 25Khang LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Perpetual Help Dalta - CalambaDokument70 SeitenUniversity of Perpetual Help Dalta - CalambaJ HNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Perpetual Help Dalta - CalambaDokument70 SeitenUniversity of Perpetual Help Dalta - CalambaJ HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Workbook - Unit 8 - Transformations InvestigationDokument11 SeitenStudent Workbook - Unit 8 - Transformations Investigationapi-232099327100% (2)
- Lab Report 4Dokument16 SeitenLab Report 4anon_68203647100% (1)
- Area Computation of A Closed TraverseDokument9 SeitenArea Computation of A Closed TraverseNoel Paolo C. Abejo IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Take-Off Angle Calculations For Fault-Plane Solutions and Reconstruction of Nodal Planes From The Parameters of Fault-Plane SolutionsDokument6 SeitenTopic Take-Off Angle Calculations For Fault-Plane Solutions and Reconstruction of Nodal Planes From The Parameters of Fault-Plane SolutionsFrancisco JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying With Construction Applications 8th Edition Kavanagh Solutions ManualDokument20 SeitenSurveying With Construction Applications 8th Edition Kavanagh Solutions Manualdeannarogersjfqznksiyc100% (14)
- Final F1Dokument12 SeitenFinal F1Michael Eriko BernabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SatOrb ReportV1Dokument13 SeitenSatOrb ReportV1João JúniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009-410 Converting Latlon To UtmDokument4 Seiten2009-410 Converting Latlon To UtmAnonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 014 - Simulation 1Dokument15 SeitenCE 014 - Simulation 1SIM CONDRAD CamiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prog For Llh2enuDokument24 SeitenProg For Llh2enuYamini ThilakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Manual Elementary Surveying An Introduction To Geomatics - CompressDokument5 SeitenSolutions Manual Elementary Surveying An Introduction To Geomatics - CompressHannah CiprianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Calculation 2 - Simple Homogeneous Wet SlopeDokument10 SeitenHand Calculation 2 - Simple Homogeneous Wet SlopeWashington BobadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 305047967Dokument11 Seiten305047967coerick40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elev FactDokument10 SeitenElev FactJason AgbotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - G-CodeDokument50 Seiten5 - G-CodeHandriToarPangkeregoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Exam 5Dokument8 SeitenUnit Exam 5Rose AstoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Exam 5FINALDokument8 SeitenUnit Exam 5FINALRose AstoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurveyingDokument8 SeitenSurveyingAira Giann EstañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS01F Thomas Gicira 8671Dokument18 SeitenTS01F Thomas Gicira 8671Ajani HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Seismic Loads Seismic Factors: Seismic Deadloads at Each FloorDokument4 SeitenDetermination of Seismic Loads Seismic Factors: Seismic Deadloads at Each FloorJohn Paul Hilary EspejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGI 3703 Surveying and Geomatics: Example TraverseDokument10 SeitenENGI 3703 Surveying and Geomatics: Example TraverseAbba MuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOM2015 Traverse Tutorial 2016 PDFDokument2 SeitenGEOM2015 Traverse Tutorial 2016 PDFKofi DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prismatic Open Channel SolutionsDokument27 SeitenPrismatic Open Channel SolutionsresearchditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geodesy HomeworkDokument2 SeitenGeodesy HomeworkrandallNoch keine Bewertungen
- TraverseMercator-RedFearns (GeoToGrid)Dokument5 SeitenTraverseMercator-RedFearns (GeoToGrid)ihwan n hNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offsets at Irregular IntervalsDokument16 SeitenOffsets at Irregular IntervalsRenjith S AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument42 SeitenChapter 10Teddy Matthew AudleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulcanicity in AfricaDokument3 SeitenVulcanicity in AfricaMukuka KowaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2 Berkomunikasi Menggunakan PetaDokument38 SeitenM2 Berkomunikasi Menggunakan PetaSani KhyruelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspects of The Geology and Groundwater Conditions of Asaba NigeriaDokument14 SeitenAspects of The Geology and Groundwater Conditions of Asaba NigeriaIgwe, Emmanuel A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument4 SeitenINTRODUCTIONkaitlyn bannisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaster Risk ReductionDokument16 SeitenDisaster Risk ReductionBeatriz Helaena RasonableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash Floods in Uttarakhand (S8-A) 2Dokument39 SeitenFlash Floods in Uttarakhand (S8-A) 2Rebecca MariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Status of Coral Reefs in Malaysia, 2019Dokument87 SeitenStatus of Coral Reefs in Malaysia, 2019arifa hazimah mauludNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monsoon in India Upsc Notes 58Dokument3 SeitenMonsoon in India Upsc Notes 58nikitasharma1431234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Triassic PeriodDokument10 SeitenTriassic Periodlinda santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Período de Complementación y Acreditación de Saberes 3er Año Segunda ParteDokument6 SeitenPeríodo de Complementación y Acreditación de Saberes 3er Año Segunda ParteSebastián OliveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Distance Between The Arctic Circle and The Tropic of Cancer in MilesDokument1 SeiteWhat Is The Distance Between The Arctic Circle and The Tropic of Cancer in MilesbouncingboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jet Contrails Recent ResearchDokument1 SeiteJet Contrails Recent ResearchTysonC1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bevae 181Dokument15 SeitenBevae 181Harsh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typhoon M9Dokument4 SeitenTyphoon M9joefrey BalumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Change Environmental Degradation PDFDokument57 SeitenClimate Change Environmental Degradation PDFAnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORSDM Chapter 2 HydrologyDokument54 SeitenORSDM Chapter 2 HydrologyblNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Change in NepalDokument12 SeitenClimate Change in NepalSameer NepalNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Bihar: Chota Nagpur, Plateau in EasternDokument1 SeiteIndia Bihar: Chota Nagpur, Plateau in EasternSiddharth AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 C25-Q64.1-Pap-152-4252Dokument9 Seiten1 C25-Q64.1-Pap-152-4252Srinivas GokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metar & Speci CodeDokument8 SeitenMetar & Speci CodeFahmi PrayogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Drainage SystemDokument419 SeitenSustainable Drainage SystemMary Grace BorinagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS311: Sustainable Tourism DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenTS311: Sustainable Tourism DevelopmentkartikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendices I-V - Glossary, Contributors, Reviewers, Acronyms, Per MissionsDokument70 SeitenAppendices I-V - Glossary, Contributors, Reviewers, Acronyms, Per MissionsIntergovernmental Panel on Climate ChangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.2 Carbon Dioxide & Methane As Greenhouse Gases QPDokument18 Seiten9.2 Carbon Dioxide & Methane As Greenhouse Gases QPRNoch keine Bewertungen