Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1AM Competency-Based Syllabus PDF
Hochgeladen von
Emir KhanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1AM Competency-Based Syllabus PDF
Hochgeladen von
Emir KhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
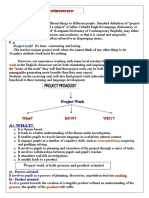
Competency-Based Syllabus
Introduction
In the light of the reform initiated by the Ministry of Education. We are all concerned by
the fact that our learners should be given the best quality of education.
Consequently, we have, in terms of newness, to reconsider the purpose and role of
Education. It is to organize, direct and accelerate the process of learning which will shape
the individual(s) who will contribute:
- To reach their full potential.
- To the fitness of their society which is concerned with the short / long term
competency if it is to survive in competition within globalization.
What is a competency-based- approach?
It is an approach aiming at establishing a link between the learning acquired at school and
the context of use outside the classroom.
This approach enables the learner to learn how: to learn, to share, to exchange and to
cooperate with others.
What is a competency?
It is a know how which integrates and mobilizes a number of abilities and knowledge to
be efficiently used in problem solving situations that have never been met before.
Why a Competency-based approach?
-It stems from economic urgencies and a political decision aiming at facing the effect of
globalization (economic, cultural or other.)
-To ensure interdisciplinary coherence between school syllabuses.
-To make the Algerian learner re-invest his knowledge while performing at school as well
as at social and professional levels.
The Competency-oriented syllabus in 1ere AM
For the first year of English, developing the three competencies is targeted:
-1 Interact orally in English (e.g. listen and speak)
-2 Interpret authentic oral or written documents (e.g. Read and Say, T or F)
-3 Produce simple oral and written messages (e.g. Project)
1)-
The competency based programme
1-1 End-purpose and profiles targeted
1.1.1. End-purpose
The programme of the first complementary year of the middle school i.e.1er AM (or
former 7th AF, formerly 7th fundamental year of Algerian education) is a programme for
teaching the first level of English as a second foreign language (EFL2) and therefore
aims for the acquisition of basic linguistic, methodological and cultural
competencies that will enable pupils to use English as a simple tool for
communication and documentation.
Competency-Based Syllabus
1.1.2. Profiles targeted
First year middle school (1 AM) pupils are parting with an educational environment
in which they spent six full years (i.e. the primary school) .They will have to fit
gradually into a new school
The introduction of a second foreign language at this stage is based on their previous
acquisitions (the language in which they are taught at this stage is based on their
previous acquisition (the language in which they are taught at school-Arabic, and the
first foreign language).This second foreign language will have to be learnt according
to the receptive and productive capacities of pupils of their age.
At the end of the first year of middle school, pupil's should be able to:
1- distinguish between the di fferent sound of the language (simple sound, diphthongs
, etc
2- be sensitive to stress and intonation in English
3- listen to and understand a simple message
2)-
The main features of the programme
The programme recommended and set by the Ministry of national Education is
presented for implementation at the level of first middle school year. It is formulated
in terms of competencies and defines all the elements of knowledge that pupils must
master at the end of the year, thanks to their acquisition of capacities and skill.
3)-
Structure of the programme
3.1. General presentation of the subject.
The programme offers a general presentation through:
- The linguistic, methodological and cultural objectives concerning the first year of
English learning.
- The aims.
- The approach.
- The method.
- The teacher's role.
- The assessment.
- Specific learning features of the discipline:
3.2. Learning procedures inherent in the subject
This part deals with the selected competencies.
3.2.1. Competency statement.
The statement of the competency should reflect a know how which encompasses a
set of integrated skills to be put into practice in a given situation.
3.2.2. Links between competencies.
This stage of the programme consists in highlighting the links existing between the
selected competencies.
3.2.3. Relative importance of competencies.
To complete the previous point, this part specifies the importance and the priorities of
each competency.
3.2.4. Competency scope.
This point describes the progress made by pupils throughout the year.
3.2.5 Context of acquisition
Its specifies the conditions in which the competency is to be practised and the
conditions of assessment, the means to which the pupils can resort, as well as the
constraints imposed by learning and assessment situations.
3.2.6 Assessment criteria
Those are observable and measurable point of reference which allow for the
monitoring of the pupils' learning process.
3.2.7 Learning objectives.
These are known how put to use during the practice of a competency which
integrates skills (intellectual, mental, strategic, socio-affective and psychomotor) and
knowledge.
3.2.8 Success criteria
Those are observable and measurable elements used in a learning situation.
3.2.9 Subject content
This is about the various aspects of knowledge (data, notions, facts, concepts,
strategies, etc).
4)-
The approach
The competency based approach relies on learning and teaching conception that is
both cognitivist and socio- constructivist.
This approach allows the lea
rner to acquire learning
.
strategies and also to learn how to share and exchange knowledge and to
cooperate with others.
5)-
Specific learning features of the discipline
The three competencies to be achieved are:
Competency I:
To interact orally in English
1) Meaning of the competency
The pupil is brought to interact in everyday school situations by using verbal and/ or non
verbal language.
2) Components of the competency
The pupil establishes contact with the interlocutor.
The pupil sends a message.
The pupil maintains an oral interaction
The pupil collaborates
Competency II:
To interpret authentic oral or written documents
1) Meaning of the competency
The pupil is brought to demonstrate his comprehension by oral/or written reformulation
of various types of texts through various didactic supports (songs, tales, comics,
games)
2)Components of the competency
The pupil finds out the global meaning of a written text.
The pupil evaluates his learning
CompetencyIII:
Produce simple messages orally and in writing
1) Meaning of the competency
To express himself orally or in writing the pupil is led to gradually produce simple and
coherent message. The pupil's production will be less and less guided without reaching
total perfection and without being completely mistake free; as far as spelling syntax and
punctuation are concerned
2) Components of the competency
The pupil uses appropriate strategies.
The pupil structures his text
The pupil revises his text.
The pupil evaluates his process
Links between the competencies:
Developed in synergy, the three competencies are complementary and interdependent
at the same time. They are articulated around competence I, "To intract orally", which
is the key competency of the training system. This competency, being of primary
importance in the teaching of English, will be used as background for competency II
and competency III. The three competencies working in synergy will take their full
dimension through activities allowing oral and written interactions.
Relative importance of competencies:
Taking into account the integration of three competencies, their relative importance is
equal. This doesn't prevent us from giving priority to certain competencies, according
to the cycle .Thus in 1st.AM; a great importance is devoted to oral communication.
The move from oral to writing is progressively made through meaningful school
situations.
Learning strategies:
Learning strategies are a set of stages which help pupils acquire, store and use
information.
a) The teacher's role and the learning strategies.
b) The pupil's role and the learning strategies.
The teacher's role and the learning strategies.
Teacher's rle
In the approach currently
used
- holds knowledge.
- provides knowledge.
- Is ever-present in the
classroom.
- takes all decisions in class.
- is authoritarian.
authoritarian.
In the new approach
-gives guidance and help.
- advises pupils.
- facilitates learning.
- is a co-learner.
- engages the pupils in tasks
-provides individual teaching (if
necessary).
-develops learner autonomy
What changes
-A less authoritarian attitude.
-Openness to discussion and
negotiation.
-Sensitiveness to pupils concerns.
concerns.
The pupil's role and the learning strategies.
Pupil's rle
In the approach
currently used
-receives knowledge
- depends on the
teacher.
- applies a model.
- He learns only
because he gets
marks, because of
examination pressure
or under parental
pressure.
In the new approach
- wants to know what he
learns.
- is responsible for his own
learning.
Learn better because he acts
upon what he learns.
- builds his own strategies.
strategies.
- knows the procedures to be
used for work .He acquires
problem-solving skills.
What changes
- learns through what he does
and because he does things.
- increases his... Intellectual
potential.
- improves his memory.
- has positive attitude.
Towards his/her studies.
- gives meaning to his work.
- participates in his own
learning.
- solves problems.
Works for himself and not
only for the teacher.
- learns to co-operate,
exchange and share
information.
- works autonomously.
- Increases his self- concept.
concept.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Competency Based Language TeachingDokument4 SeitenCompetency Based Language TeachingobvgirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Didactic of Teaching English LanguageDokument24 SeitenDidactic of Teaching English LanguageTarik Messaaf86% (14)
- Topic 2. EFLDokument8 SeitenTopic 2. EFLAntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter III: Teaching English As A Foreign Language in The Algerian Secondary SchoolsDokument11 SeitenChapter III: Teaching English As A Foreign Language in The Algerian Secondary SchoolsBoubaker GMNoch keine Bewertungen
- English As Foreign Lge in AlgeriaDokument11 SeitenEnglish As Foreign Lge in Algeriaamel soumatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supòsit Pràctic EOI AnglesDokument5 SeitenSupòsit Pràctic EOI AnglesSandra SánchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Didactics of English - PDF Version 1Dokument24 SeitenDidactics of English - PDF Version 1Raf KhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching English in Algerian Middle School Coordinators Meeting Sept 29 2015Dokument4 SeitenTeaching English in Algerian Middle School Coordinators Meeting Sept 29 2015Samir Bounab92% (25)
- Adopted ELT MethodsDokument6 SeitenAdopted ELT MethodsHasnah HalipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidlines For TeachersDokument71 SeitenGuidlines For Teachersجوهرة جوهرةNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 14. EFLDokument16 SeitenTopic 14. EFLAntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRITISH CURRICULUM English LanguageDokument73 SeitenBRITISH CURRICULUM English LanguageEmma Jones100% (1)
- English ReviewerDokument11 SeitenEnglish ReviewerlimóNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemporary Teacher Leadership 2020 Assignment 1: Executive SummaryDokument3 SeitenContemporary Teacher Leadership 2020 Assignment 1: Executive Summaryapi-517802730Noch keine Bewertungen
- English For Specific PurposesDokument8 SeitenEnglish For Specific PurposesjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gifted. Role-PlayDokument11 SeitenGifted. Role-PlayOposiciones InglésNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Assessment InstrumentsDokument13 SeitenDesign of Assessment InstrumentsArturo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fitriani He PaperDokument11 SeitenFitriani He PaperFitrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Plans-Middle School English Grade 4Dokument24 SeitenAnnual Plans-Middle School English Grade 4Hadjer BelkadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Teacher's General Data.: 2. 1. The Evidences of Students'progress During The Last YearsDokument9 SeitenI. Teacher's General Data.: 2. 1. The Evidences of Students'progress During The Last YearsMaia FurduiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Out+&+About+1 TeachingProgreeamme LOMCE 2015 EngDokument158 SeitenOut+&+About+1 TeachingProgreeamme LOMCE 2015 EngEme RegalizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah Teaching SpeakingDokument15 SeitenMakalah Teaching Speakingika dewi100% (13)
- Out+&+About+1 TeachingProgramme LOMCE 2015 EngDokument160 SeitenOut+&+About+1 TeachingProgramme LOMCE 2015 EngPaula BleiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concise review of Theories, approaches and methods of Teaching English as a second languageDokument7 SeitenConcise review of Theories, approaches and methods of Teaching English as a second languageAna Soria CirilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Presentation English B1+Dokument4 SeitenCourse Presentation English B1+Angelitha SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBE Characteristics and Learning OutcomesDokument4 SeitenOBE Characteristics and Learning OutcomesCheska Garcia CuerdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Syllabus English G12 (02 10 2021)Dokument71 Seiten06 Syllabus English G12 (02 10 2021)abdimoh7522Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Teachers Guide Book Year 4 130908114340 PDFDokument294 SeitenEnglish Teachers Guide Book Year 4 130908114340 PDFCahaya Hidupku NurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample ProposalDokument67 SeitenSample ProposalGiancarla Maria Lorenzo Dingle100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Components of The K-12 CurriculumDokument2 SeitenLesson 4 Components of The K-12 CurriculumBeberly Kim AmaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Teachers Guide Book Year 4 KSSRDokument294 SeitenEnglish Teachers Guide Book Year 4 KSSRPizza4088% (17)
- Project-Based Learning: English Carnival in Universiti Kuala Lumpur-Malaysia France InstituteDokument15 SeitenProject-Based Learning: English Carnival in Universiti Kuala Lumpur-Malaysia France InstituteMazlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- REPORT IWCP2 (Alex) New-1Dokument12 SeitenREPORT IWCP2 (Alex) New-1Sayid Sayid SayidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal PTK Berbahasa Inggris - Demostrative Method at Procedure TextDokument11 SeitenProposal PTK Berbahasa Inggris - Demostrative Method at Procedure TextYUNI HARTONO KHITDHYS100% (6)
- Role of teachin-WPS OfficeDokument10 SeitenRole of teachin-WPS OfficeDomingos Ernesto da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Language Learning 3Dokument2 SeitenTheory of Language Learning 3Prop PepsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tefl Research ModuleDokument12 SeitenTefl Research Modulensaxena03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edu 334 Syllabus Fall 2013Dokument9 SeitenEdu 334 Syllabus Fall 2013api-240817141Noch keine Bewertungen
- ESA model for effective language learningDokument27 SeitenESA model for effective language learningEl Yazid KananeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook For TeachersDokument62 SeitenHandbook For TeachersзульфираNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 ProgramacionDokument34 SeitenA2 ProgramacionninguenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELT Guidelines for CPGE ClassesDokument17 SeitenELT Guidelines for CPGE ClassesYoussef MzabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lomce in EnglishDokument5 SeitenLomce in EnglishTeresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 AM AnglDokument14 Seiten3 AM Anglkaouthar bakoucheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Based Language TeachingDokument6 SeitenCompetency Based Language TeachingSolin SkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2AM Teacher's GuideDokument69 Seiten2AM Teacher's GuideEmir Khan83% (6)
- Smart+Planet+3 TeachingProgramme LOMCE 2015 EngDokument154 SeitenSmart+Planet+3 TeachingProgramme LOMCE 2015 EngElisaZhang100% (1)
- Tefl 1Dokument159 SeitenTefl 1Breeze BoukhrissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foreign Language Project for Year 3 StudentsDokument58 SeitenForeign Language Project for Year 3 StudentsRosa Pancorbo0% (2)
- Communicative Language Teaching - 2022 - PART IIDokument33 SeitenCommunicative Language Teaching - 2022 - PART IIChristina AgnadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gascho, Angela Final Project EDU 579Dokument30 SeitenGascho, Angela Final Project EDU 579Angie GaschoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Speaking Skills and Communicative EfficiencyDokument9 SeitenTeaching Speaking Skills and Communicative EfficiencyArif FlouncxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ludic Strategies For The Promotion of Communicative Competence in 9Th Grade Efl Class at Liceo CristianoDokument11 SeitenLudic Strategies For The Promotion of Communicative Competence in 9Th Grade Efl Class at Liceo CristianoJC TCNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Summary of Communicative Language Teaching TodayDokument14 SeitenA Summary of Communicative Language Teaching TodayAisyah PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multilingualism and Translanguaging in Chinese Language ClassroomsVon EverandMultilingualism and Translanguaging in Chinese Language ClassroomsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching with Tech 2015: Language Educators Talking TechVon EverandTeaching with Tech 2015: Language Educators Talking TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- The language dimension in all subjects: A handbook for curriculum development and teacher trainingVon EverandThe language dimension in all subjects: A handbook for curriculum development and teacher trainingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3AM Making and Responding To A RequestDokument1 Seite3AM Making and Responding To A RequestEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects 2 A.MDokument6 SeitenProjects 2 A.MNardjes LinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3AM Asking For ClarificationDokument3 Seiten3AM Asking For ClarificationEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Framework For Groupwork in Middle School Revised Version - Pour Fusion PDFDokument8 SeitenFramework For Groupwork in Middle School Revised Version - Pour Fusion PDFSamir BounabNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1AM Country NationalityDokument1 Seite1AM Country NationalityEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1AM Useful Pedagogical Recommendation PDFDokument2 Seiten1AM Useful Pedagogical Recommendation PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2AM Teacher's GuideDokument69 Seiten2AM Teacher's GuideEmir Khan83% (6)
- 1AM The Textbook of English PDFDokument4 Seiten1AM The Textbook of English PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slimming Aout 2009 PDFDokument144 SeitenSlimming Aout 2009 PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1AM File Contents PDFDokument2 Seiten1AM File Contents PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1AM Projects PDFDokument7 Seiten1AM Projects PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1AM Project Pedagogy PDFDokument4 Seiten1AM Project Pedagogy PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1AM Assessment PDFDokument3 Seiten1AM Assessment PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1am File Analysis PDFDokument1 Seite1am File Analysis PDFEmir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Thomas Johansen The SeparationDokument17 Seiten2017 Thomas Johansen The SeparationLeonardo TavaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Teknik MenjawabDokument33 SeitenBio Teknik MenjawabSharifah NurainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning Sense ConceptDokument6 SeitenMeaning Sense ConceptinnaspatzNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUP Taguig Language and Literature AssessmentDokument4 SeitenPUP Taguig Language and Literature AssessmentRoxane Rivera75% (4)
- The Construction of Social RealityDokument17 SeitenThe Construction of Social RealityTonyShaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions of Assessment TasksDokument6 SeitenDefinitions of Assessment TasksRosmalia KasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edwards Introduction To DP in McHoul 2001 PDFDokument30 SeitenEdwards Introduction To DP in McHoul 2001 PDFhanan manaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Intelligence: IQ, EI, and MIDokument33 SeitenUnderstanding Intelligence: IQ, EI, and MIMiles WackyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site dance exposes social divisionsDokument5 SeitenSite dance exposes social divisionslimnisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freeston 96Dokument14 SeitenFreeston 96Francisco TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rethinking Culture - Embodied Cognition and The Origin of Culture in OrganizationsDokument332 SeitenRethinking Culture - Embodied Cognition and The Origin of Culture in OrganizationsjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Kinds of Graphic OrganizerDokument2 Seiten5 Kinds of Graphic OrganizerTSN InternetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal PlatonDokument242 SeitenJournal PlatonEdgar PouNoch keine Bewertungen
- US Bias in The Study of Asian Security: Using Europe To Study AsiaDokument9 SeitenUS Bias in The Study of Asian Security: Using Europe To Study AsiaMrWaratahsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories on Origin of Life ExplainedDokument2 SeitenTheories on Origin of Life ExplainedprincessindistressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rogers (Auth.), G. A. J. Rogers, J. M. Vienne, Y. C. Zarka (Eds.) - The Cambridge Platonists in Philosophical ContextDokument258 SeitenRogers (Auth.), G. A. J. Rogers, J. M. Vienne, Y. C. Zarka (Eds.) - The Cambridge Platonists in Philosophical ContextArcanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument25 SeitenReportJunneth Pearl HomocNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Why Students Failed in Examinations''Dokument1 Seite"Why Students Failed in Examinations''louell syNoch keine Bewertungen
- JaggarAllison FeministPoliticsAndEpistemologyJustifyingFeministTheoryDokument42 SeitenJaggarAllison FeministPoliticsAndEpistemologyJustifyingFeministTheoryAnahí RetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learner Motivation - Applied LinguisticsDokument15 SeitenLearner Motivation - Applied LinguisticsErgaleio100% (1)
- Blooms Taxonomy May 2009Dokument1 SeiteBlooms Taxonomy May 2009Alden PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Intuitive ExtratimDokument3 SeitenLogical Intuitive ExtratimcringeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine PPR Copy 18th July 2016Dokument221 SeitenMarine PPR Copy 18th July 2016api-322846171Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Criminal Behavior Through PsychologyDokument76 SeitenUnderstanding Criminal Behavior Through PsychologyGabrielnadala26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proceedings of The Kent State University May 4th Philosophy Graduate Student ConferenceDokument18 SeitenProceedings of The Kent State University May 4th Philosophy Graduate Student ConferenceLahcen BelchkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Technical Terms in Research - Quarter 4Dokument48 SeitenModule 1 - Technical Terms in Research - Quarter 4XY PLAYZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenLesson Planapi-304063472Noch keine Bewertungen
- (English) Opinion, Doubt, Knowledge, and Belief (Aquinas 101) (DownSub - Com)Dokument3 Seiten(English) Opinion, Doubt, Knowledge, and Belief (Aquinas 101) (DownSub - Com)checkm94Noch keine Bewertungen
- First Article The Deductive Approach - Rule Driven LearningDokument4 SeitenFirst Article The Deductive Approach - Rule Driven LearningAmy NovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studi KasusDokument8 SeitenStudi KasusRasbiantoNoch keine Bewertungen