Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 5 Theodolite
Hochgeladen von
Youssif SedeakOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 5 Theodolite
Hochgeladen von
Youssif SedeakCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Theodolite
Faculty of Engineering and Technology
Structural Department - Year 1
(Planimetric Surveying 1)
SCM 221
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Theodolite
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Basic Definition
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Theodolite
Types of Theodolite
According to reading method
Vernier
Optical
Digital
Very old and
obsolete
Hz are VL circles
are made from
glass and the
reading are taken
by circle reading
eyepiece
Angular readings
are displayed
digitally on screen
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Theodolite
Theodolite Components
ALIDADE
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Theodolite
Theodolite Components
Telescope
Reticule
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Concept of measuring Horizontal Angle
Theodolite
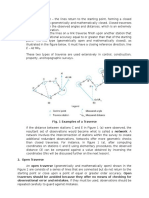
Spatial Directions are projected on the horizontal circle of
the theodolite, and so Horizontal Circle Readings (HCR) are obtained
A
C
HCRA
0
B
<ABC
HCRC
Hz circle fixed and pointer
moves with alidade
o
If ve, then add 360
Horizontal Circle
Hz angle: It is the angle between the projection of two lines on the
horizontal plane passing by the theodolite clockwise direction
Horizontal angle <ABC = = HCRC HCRA
What is important is the difference between readings not the reading itself
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Theodolite
Concept of measuring Vertical Angle
Face Left (FL): VL circle left of observer
Face Right (FR): VL circle right of observer
VL
Vertical angle (V)
Hz Plane
hi
V = 90 Z
+ve Elevation Angle
-ve Depression Angle
It is the angle measured in the vertical plane between the line joining the
theodolite-target (line of sight) and the horizontal plane passing by the theodolite
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Concept of measuring Vertical Angle
Theodolite
180
FL
Turn alidade 180 and telescope 180
FR
Index
90
270
90
270
180
VCRL
VL = 90 VCRL
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
VCRR
Pointer or
index fixed
and VL circle
moves with
telescope
VR = VCRR 270
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Index Error
Theodolite
180
FL
FR
270
90
270
90
180
VCRL
VCRR
VR = VCRR 270 +
VL = 90 VCRL
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Theodolite
How to determine Index Error?
Since VL = VR (for the same point)
90 VCRL = VCRR 270 +
2 = 270 + 90 VCRL VCRR
Index error ()= (360 [VCRL+VCRR])
2
If = ve, then index inclined in opposite
direction, substitute normally with
If (VCRL+VCRR)360, then index error exists
Dr Ahmed Ragheb
Lecture 5
SCM 221 Planimetric Surveying 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TheodoliteDokument29 SeitenTheodolitetalatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To TheodoliteDokument23 SeitenIntroduction To TheodoliteJitendra Kumar SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Horizontal Geodetic Network Precision and Accuracy Determination Using Least Squares TechniqueDokument7 SeitenUnderstanding Horizontal Geodetic Network Precision and Accuracy Determination Using Least Squares TechniqueETEJE SYLVESTSTER OKIEMUTE (Ph.D)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 1254 Surveying IIDokument19 SeitenCe 1254 Surveying IIsaamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Levelling PDFDokument21 SeitenLevelling PDFRahul Sinha100% (3)
- Geodesy Flashcards - QuizletDokument11 SeitenGeodesy Flashcards - QuizletTJ CabatinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Errors and Treatment of Analytical Data by K.n.s.swami..pdf474Dokument26 SeitenErrors and Treatment of Analytical Data by K.n.s.swami..pdf474Ravi ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Architecture, Building and Design Bachelor of Quantity Surveying (Honours)Dokument38 SeitenSchool of Architecture, Building and Design Bachelor of Quantity Surveying (Honours)Akmal AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey Using CompassDokument52 SeitenSurvey Using CompassPranav VaishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying Assignment - Traverse - Chapter1Dokument2 SeitenSurveying Assignment - Traverse - Chapter1Nishchal SigdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResectionDokument3 SeitenResectiontrilokbist04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heron's Formula ExplainedDokument14 SeitenHeron's Formula ExplainedyugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Surveying 1Dokument220 SeitenControl Surveying 1Madaraka DecheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate System and TraversDokument25 SeitenCoordinate System and TraversAhmad Khaled100% (1)
- Introduction to Surveying Instruments and ConceptsDokument69 SeitenIntroduction to Surveying Instruments and ConceptsAnonymous PeFQLw19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Geodesy Concepts for BeginnersDokument44 SeitenBasic Geodesy Concepts for Beginnerselectrical_hackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math and geometry problems with multiple choice answersDokument2 SeitenMath and geometry problems with multiple choice answerscarryon66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geodesytriangulation 151125092103 Lva1 App6892 PDFDokument121 SeitenGeodesytriangulation 151125092103 Lva1 App6892 PDFMrunmayee ManjariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume CalculationsDokument11 SeitenVolume CalculationsAhmad KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of GPSDokument15 SeitenHistory of GPSMiguel FairmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rail Engineering Tutorial - Melbourne Metro Fleet SizingDokument3 SeitenRail Engineering Tutorial - Melbourne Metro Fleet SizingharinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Levelling and SurveyingDokument7 SeitenLevelling and Surveyinghazmee100% (5)
- Civil Engineering Lab Manual for Surveying ExperimentsDokument84 SeitenCivil Engineering Lab Manual for Surveying ExperimentsGSKReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lectures of Weighted Least SquaresDokument19 SeitenLectures of Weighted Least Squares박종훈Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Adjust Comp PDFDokument7 SeitenAssignment Adjust Comp PDFakemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Closed Traverse GuideDokument8 SeitenClosed Traverse GuideMarc Dared CagaoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2005 Traverse SurveyDokument11 SeitenC2005 Traverse SurveyhjwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizontal Control Traverse Types Azimuths Departure LatitudeDokument6 SeitenHorizontal Control Traverse Types Azimuths Departure Latitudewaleed shahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- C !" !! !#$"%&'!$ (#) ( (C !" !!!#$"%+&+'!$ +!%PMDokument8 SeitenC !" !! !#$"%&'!$ (#) ( (C !" !!!#$"%+&+'!$ +!%PMing_nistorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photogrammetry BasicsDokument72 SeitenPhotogrammetry BasicsMadielyn CloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual (CIV 210) Engineering Surveying (2018-19) (For Private Circulation Only)Dokument76 SeitenLaboratory Manual (CIV 210) Engineering Surveying (2018-19) (For Private Circulation Only)gyanendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Surveying InstrumentsDokument26 SeitenFundamentals of Surveying InstrumentsJohn Andrei PorrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review With Calculator Techniques: Use Casio 991 ES Plus CalculatorDokument18 SeitenReview With Calculator Techniques: Use Casio 991 ES Plus CalculatorErnesto GalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dcc3093-Lecture Note Series - t5Dokument23 SeitenDcc3093-Lecture Note Series - t5Alif KarimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurveyingDokument63 SeitenSurveyingShazrin Yusof100% (1)
- Crandall Text-Book On Geodesy and Least Squares (1907 (c1906) )Dokument380 SeitenCrandall Text-Book On Geodesy and Least Squares (1907 (c1906) )Marcelo Silvano de CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leveling-Theory and Methods - 2Dokument22 SeitenLeveling-Theory and Methods - 2Ahmad KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey AssignmentDokument6 SeitenSurvey AssignmentEng20eng 20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying With GPS, TS, TlsDokument55 SeitenSurveying With GPS, TS, TlsYurio WindiatmokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveying I Note, 2015Dokument72 SeitenSurveying I Note, 2015feyselNoch keine Bewertungen
- TraversingDokument27 SeitenTraversingUsha AucharazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths NotesDokument71 SeitenMaths NotesSekar DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Horizontal Control Survey Techniques: J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.ADokument43 SeitenAn Introduction To Horizontal Control Survey Techniques: J. Paul Guyer, P.E., R.AemmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Mine Surveying TermsDokument2 SeitenGlossary of Mine Surveying Termsiamcerbzjr100% (1)
- Adjust Level Nets with Least Squares MethodDokument105 SeitenAdjust Level Nets with Least Squares MethodKhiel YumulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astronomy by HosmerDokument302 SeitenAstronomy by HosmerSumit MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUG533 - Adjustment Computation - LOPOV For Latitude and Departure ComputationDokument2 SeitenSUG533 - Adjustment Computation - LOPOV For Latitude and Departure Computationmruzainimf100% (1)
- Adjustment Theory PDFDokument100 SeitenAdjustment Theory PDFMelih TosunNoch keine Bewertungen
- TVET Certificate V in Land Surveying: Perform Surveying Measurement AdjustmentDokument46 SeitenTVET Certificate V in Land Surveying: Perform Surveying Measurement AdjustmentJEAN DE DIEU MUVARANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Analysis and Adjustment of ObservationsDokument67 SeitenChapter 3 Analysis and Adjustment of ObservationsAbdul AzimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6 Tape Corrections PDFDokument27 SeitenLesson 6 Tape Corrections PDFMikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOMATIC Leveling - Two Peg TestDokument4 SeitenGEOMATIC Leveling - Two Peg TestAK47Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Semster - Lec03 - Introduction To Theodolite PDFDokument24 Seiten2nd Semster - Lec03 - Introduction To Theodolite PDFDakheel malekoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TheodoliteDokument32 SeitenTheodoliteMihaela Roibu100% (1)
- Angular KinematicsDokument42 SeitenAngular KinematicsMarin Calin100% (1)
- Surveying - Chapter 4 (Theodolite)Dokument123 SeitenSurveying - Chapter 4 (Theodolite)Syahirah ZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 10, Theodolite SurveyingDokument20 SeitenPart 10, Theodolite SurveyingMariwan Mirhaj MohamedSalihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Physics A2 Level Course: Second EditionVon EverandCambridge Physics A2 Level Course: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 15. Mechanics of Fluids: Vocabulary of Mechanics in Five Languages: English/German/French/Polish/Russian, Vol. 2Von EverandGroup 15. Mechanics of Fluids: Vocabulary of Mechanics in Five Languages: English/German/French/Polish/Russian, Vol. 2Bewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (3)
- Coordinate Computation: Calculating Length, Bearing, Angles and CoordinatesDokument13 SeitenCoordinate Computation: Calculating Length, Bearing, Angles and CoordinatesYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 3 - Mapping and Scales PDFDokument17 SeitenLecture - 3 - Mapping and Scales PDFYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction PDFDokument10 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction PDFYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- SURVEYING SCALES & MAP DISTANCESDokument1 SeiteSURVEYING SCALES & MAP DISTANCESYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate Computation: Calculating Length, Bearing, Angles and CoordinatesDokument13 SeitenCoordinate Computation: Calculating Length, Bearing, Angles and CoordinatesYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction PDFDokument10 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction PDFYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 3 - Mapping and Scales PDFDokument17 SeitenLecture - 3 - Mapping and Scales PDFYoussif SedeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ged Earth Science Test 1bDokument12 SeitenGed Earth Science Test 1bapi-301605346Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skoda Apprenticeship ProgramDokument4 SeitenSkoda Apprenticeship Programnauval.archNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Reactive System Screening Tool (RSST) : An Inexpensive and Practical Approach To Sizing Emergency Relief SystemsDokument6 SeitenThe Reactive System Screening Tool (RSST) : An Inexpensive and Practical Approach To Sizing Emergency Relief SystemsKam KamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Phase Change Material in Heat Sinks To Cool Electronics Devices With Intermittent UsageDokument19 SeitenUsing Phase Change Material in Heat Sinks To Cool Electronics Devices With Intermittent UsagekaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Coal Geology: John Coggan, Fuqiang Gao, Doug Stead, Davide ElmoDokument10 SeitenInternational Journal of Coal Geology: John Coggan, Fuqiang Gao, Doug Stead, Davide Elmopradhith kattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Air-Conditioning Processes Question OnlyDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Air-Conditioning Processes Question OnlyQHalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- MG Chemicals Sn63Pb37 No Clean Leaded Solder Paste 4860P Technical Data SheetDokument7 SeitenMG Chemicals Sn63Pb37 No Clean Leaded Solder Paste 4860P Technical Data SheetAbdulrahman AlabdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Year 10 Assessment TestDokument16 SeitenPhysics Year 10 Assessment TestJoyceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate ServicesDokument23 SeitenClimate ServicesPeEjay EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume MedisDokument6 SeitenResume MedisRina ekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Discharge Over Rectangular and V-Notch WeirsDokument10 SeitenCalculation of Discharge Over Rectangular and V-Notch WeirszickmoderatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Fillet Weld Strength Parameters: For ShipbuildingDokument64 SeitenReview of Fillet Weld Strength Parameters: For Shipbuildingcarlos ivan carvajal ortizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verification of steam ejector refrigeration model performanceDokument8 SeitenVerification of steam ejector refrigeration model performance고현Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Datasheet: Engineering SteelDokument1 SeiteTechnical Datasheet: Engineering SteelDhanu goswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D3350 - 06 PDFDokument7 SeitenAstm D3350 - 06 PDFRaul Humberto Mora VillamizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCML Qahsed Part Developed by Reverse Engineering Evaluation SopDokument4 SeitenMCML Qahsed Part Developed by Reverse Engineering Evaluation Sopabbas razaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.welding TermDokument10 Seiten3.welding TermAl Amin ZubirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloque de CalibracionDokument5 SeitenBloque de CalibracionRuben Dario Mamani ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Plate Moment Connection (Bolt)Dokument72 SeitenEnd Plate Moment Connection (Bolt)mengxiao74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook t357 Block1 Part3-4 E2i1 n9780749252670 l1Dokument96 SeitenEbook t357 Block1 Part3-4 E2i1 n9780749252670 l1Bobby extramoneyguyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Internship ReportDokument54 SeitenFinal Internship ReportRaju Subedi71% (7)
- Chap 6 SteelDokument18 SeitenChap 6 SteelDaniel VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Productflyer - 978 0 387 74364 6Dokument1 SeiteProductflyer - 978 0 387 74364 6Dhruv PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterDokument13 SeitenF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Murray Centennial P.S. - Revised Carrier Shop Drawings (KP)Dokument68 SeitenMurray Centennial P.S. - Revised Carrier Shop Drawings (KP)Gonzalo OviedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Express: Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy at Different Strain AmplitudesDokument6 SeitenMaterials Express: Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of 7075-T6 Aluminum Alloy at Different Strain Amplitudesadarshravindran1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Mid Term 2022-RevisedDokument4 SeitenThermo Mid Term 2022-RevisedJeet VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCS120 Midterm Additional Review QuestionsDokument12 SeitenPCS120 Midterm Additional Review QuestionsBetty WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- S275 S355 Data Sheet 2021Dokument1 SeiteS275 S355 Data Sheet 2021CarloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme Sec Viii Div-2Dokument31 SeitenAsme Sec Viii Div-2Yash Rami100% (3)