Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SuperWiFi Overview
Hochgeladen von
Shahzad ShabbirCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SuperWiFi Overview
Hochgeladen von
Shahzad ShabbirCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
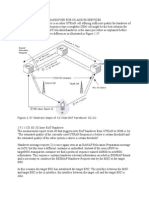
Super Wi-Fi Technologies
The world is increasingly interconnected through mobile, high-speed communications
yet two thirds of the worlds population have yet to gain access to the Internet.
UN Millennium Goals , 2012 Update Report
Introduction
As defined by the UN, access to the Internet is now among
global citizens most basic rights. The European Commissions
Digital Agenda goes one step further by similarly highlighting
broadband access as a basic right. To achieve this near ubiquity
of access, radical changes will need to be made in how citizens
of every country connect to the Internet. Many impediments
exist on the path towards this goal, but one of the most
important challenges is delivering ubiquitous, affordable
access to all consumers.
To achieve this goal, different technologies wired and wireless
will need to be used in different settings. For the vast majority
of the worlds population, wireless technologies are proving the
most economically efficient way of delivering reliable, affordable
broadband access. But, even within wireless, a mix of solutions
will need to be used. For example, technologies and business
models that work well for delivering access to urban or wealthier
populations might not work well for delivering access to rural
or disadvantaged populations. Moreover, to address growing
demand, wireless Internet service providers are increasingly
encouraging consumers to use multiple forms of broadband
access for example, 3G and Wi-Fi with the same devices.
One promising wireless technology is what is known as Dynamic
Spectrum Access, which uses location-aware devices and online
databases to deliver low-cost broadband access and other forms
of connectivity to consumers. This approach is rooted in the idea
that devices with greater knowledge of their surroundings can
opportunistically use available radio spectrum. There are many
TV broadcast channels that are unused in nearly every location
in the world these empty channels (blocks of spectrum) are
what is known as white spaces. Dynamic Spectrum Access
will first be used in TV-band White Spaces to deliver what we
call Super Wi-Fi. Much like todays license-exempt (unlicensed)
technologies most notably Wi-Fi Super Wi-Fi will be provided
over radio spectrum that is shared among different users and
Internet service providers. This under-utilized spectrum is proving to
be a key part of the future of not just universal broadband access but
of the solution for the explosion of devices connecting the Internet.
Benefits of Super Wi-Fi
Super Wi-Fi, or using TV broadcast spectrum for Wi-Fi
like connectivity, has several distinct advantages.
Greater Distances
Super Wi-Fi networks work in much the same way as
conventional Wi-Fi, but the signals travel over longer distances
than the typical Wi-Fi signal. In typical applications, a strong
Wi-Fi signal can cover 100 meters while a Super Wi-Fi signal
at the same power level can easily travel 400 meters and
with higher power can cover many kilometers.
Super Wi-Fi Signals Travel Farther
Wi-Fi: 100 Meters
Super Wi-Fi: 400 Meters (with increased flexibility,
could be up to 8 kms or more)
Four times the distance: 16 times the area
covered. Same power comparing 2.4 GHz to
600 MHz. The result is more bandwidth, lower
network costs, lower power consumption.
Penetrates Common Obstructions
Conventional Wi-Fi is relatively weak when it comes to working
in typical physical settings bumping up against concrete
obstructions and many types of walls. Most population centers
have thousands of likely Wi-Fi impediments and almost any
installation in a building with more than a few rooms will eventually
hit limits. Likewise, many rural areas are difficult to serve using
existing technologies due to heavy foliage or topographical
challenges. Super Wi-Fi can overcome these limits. Just as your
TV signal passes through walls (and many of them), the wireless
signal for your Internet connection will as well.
Super Wi-Fi Signals Penetrate More Walls
In a typical home, a Wi-Fi signal
can penetrate up to two walls.
At the same time, a TV white spaces
signal can penetrate through more
walls and obstacles,enabling whole
home media distribution.
This will simplify and enrich in-home/
in-building networking opportunities.
Greater Efficiencies
Covering a longer and wider range with approximately the same
power and computing requirements results in systems that
will deliver more bandwidth and more consumer benefits at
lower network costs and lower power consumption. In addition,
consumers will be able to satisfy their ever increasing bandwidth
appetites and Internet providers will be able to provide more
throughput in more places to more consumers.
How it Works
The most common implementation of Super Wi-Fi networks
will be accessed using smart, radio-enabled devices that report
their location to an Internet database. The database will tell the
device which TV white spaces channels, and at what power level, it
is permitted to operate on in its current location. The database has
a list of all protected TV stations and frequencies across the country,
so the devices can avoid causing interference to TV broadcasts and
wireless microphone signals. This technology is truly dynamic as
different TV channels become available, Super Wi-Fi devices
that can opportunistically switch from one group of channels
to another. This win-win translates to greater network capacity,
allowing a greater number of users in a given area while, at the
same time, protecting television reception from interference. All of
this engineering will be invisible to the consumer, who will simply
experience more ubiquitous broadband connectivity.
Who Benefits from TV White Spaces Broadband
Using Super Wi-Fi to deliver broadband connectivity will benefit
almost every part of the wireless Internet ecosystem. End
users, network operators, and content providers are all potential
beneficiaries and as the spectrum utilization continues to grow
new enhancements will emerge including Internet of things
and ubiquitous machine to machine communication. These
latter two scenarios have the potential to ignite entirely new
sectors of the global economy much like the first generation
of Wi-Fi did for the Internet.
Super Wi-Fi Access Safeguards Incumbents from Interference
1. Devices only use the TV white spaces
channels specified by the database.
2. Devices are required to re-check
the database for the list of
available channels.
Some of the most immediate beneficiaries will be people
currently living in what areas that cannot be affordably reached
with existing technologies. These people range from rural
inhabitants in mature markets such as the US or Western Europe
as well as sparse populations spread out over large areas in remote
parts of developing markets such as India, Brazil and across Africa.
3. Databases are prohibited from
providing devices access to the
channels occupied by incumbent
operators (e.g. broadcasters).
4. Databases are required to
maintain up-to-date lists
of protected operators.
5. Databases can block newly
occupied channels to prevent
further white spaces access.
Progress to Date
Microsoft has been working with industry consortiums and regulators around the world to demonstrate the viability and potential
of Super Wi-Fi. With over a dozen successful trials and demonstrations, it is clear the approach works and most of the technical
questions have been addressed. Demonstrations have been successfully implemented in Belgium, Kenya, Switzerland, Singapore,
the United Kingdom, the United States, Uruguay, and other countries. The U.S. FCC has already adopted regulations allowing
non-exclusive license-exempt access to the TV White Spaces. A recent full scale deployment trial in Cambridge, UK was completed
with results that exceeded expectations and the UK regulator, Ofcom, is using these results to inform regulatory proceedings.
Other regulators, in addition to the FCC in the US and Ofcom in the UK, have begun to implement the changes necessary to enable
commercialization of this approach and it is only a matter of time before both the heavy bandwidth users in developed markets and
those yet to even be connected in the furthest corners of the world to benefit from the innovative use of Super Wi-Fi.
Super Wi-Fi
Trials & Demos
WA
NV
Ottawa
TX
Isle of Bute
Cambridge
Brussels
Helinski
Munich
Geneva
VA
NC
South Korea
Japan
Philippines
Nairobi
Completed or Ongoing
Planned
Brazil
Uruguay
Singapore
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 90-Day Performance ReviewDokument2 Seiten90-Day Performance ReviewKhan Mohammad Mahmud HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Observation of Defects in Cast Iron Castings by Surface AnalysisDokument19 SeitenObservation of Defects in Cast Iron Castings by Surface Analysisgonzalo gimenez100% (1)
- Company Work Execution Plan For A Long Form ContractDokument4 SeitenCompany Work Execution Plan For A Long Form Contractshojaee1063Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synposis FPGA Synthesis User GuideDokument484 SeitenSynposis FPGA Synthesis User GuideVijendraKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute ValueDokument19 SeitenAbsolute Valueapi-70433300Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Electronics 1968 10 S OCRDokument84 SeitenPractical Electronics 1968 10 S OCRCarlos SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC-2800 - Service Manual V1.1 PDFDokument109 SeitenBC-2800 - Service Manual V1.1 PDFMarcelo Ferreira CorgosinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of All Entrance Exams A Student Can Appear After Passing 12th in IndiaDokument2 SeitenList of All Entrance Exams A Student Can Appear After Passing 12th in IndiaDeepak Gupta100% (1)
- Alignment On Sundyne Compor PumpDokument23 SeitenAlignment On Sundyne Compor PumpBen Sijhi100% (1)
- The Work of Frei Otto By. Ludwig GlaeserDokument137 SeitenThe Work of Frei Otto By. Ludwig GlaeserUntal Aparicio100% (1)
- Caledonian: BS 6346 PVC Insulated, Armored Power and Control CablesDokument28 SeitenCaledonian: BS 6346 PVC Insulated, Armored Power and Control CablessurenediyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Savitha S. Panikar, PH.DDokument4 SeitenSavitha S. Panikar, PH.Diboorose7Noch keine Bewertungen
- File Handling in C PDFDokument86 SeitenFile Handling in C PDFDeepak ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color CCD Imaging With Luminance Layering: by Robert GendlerDokument4 SeitenColor CCD Imaging With Luminance Layering: by Robert GendlerbirbiburbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compact and Reliable Switching - Smaller, More Efficient and Simpler Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS)Dokument6 SeitenCompact and Reliable Switching - Smaller, More Efficient and Simpler Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS)qxzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03-Instruction Set ArchitectureDokument40 Seiten03-Instruction Set ArchitectureccoccoheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standing Seam Installation-23-11-21Dokument35 SeitenStanding Seam Installation-23-11-21Gokulnath TgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lat Soal Kls 6Dokument3 SeitenLat Soal Kls 6evho darmaoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yahclick: Satellite InternetDokument6 SeitenYahclick: Satellite InternetVasco JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy LogicDokument27 SeitenFuzzy LogicvibhutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appexchange Publishing GuideDokument29 SeitenAppexchange Publishing GuideHeatherNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Choose Circuit Breakers For Electric MotorsDokument2 SeitenHow To Choose Circuit Breakers For Electric Motorsحسن التميميNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter Rat Handover GSM UmtsDokument4 SeitenInter Rat Handover GSM UmtsadanakebapNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17118Dokument5 Seiten17118hairilmasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRP NoticeDokument6 SeitenRRP NoticeLucky TraderNoch keine Bewertungen
- DER11001 Reference DrawingsDokument2 SeitenDER11001 Reference DrawingsPrime Energy Warehouse-YemenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHC-S9D AmplificadorDokument28 SeitenMHC-S9D AmplificadorEnyah RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quad Exclusive or Gate: PD CC oDokument7 SeitenQuad Exclusive or Gate: PD CC oHungChiHoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog Profilitec2010Dokument202 SeitenCatalog Profilitec2010nasuemilNoch keine Bewertungen
- のわる式証明写真メーカー|PicrewDokument1 Seiteのわる式証明写真メーカー|PicrewpapafritarancheraNoch keine Bewertungen