Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Characteristics, Applications and Challenges in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANET) : Overview
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Characteristics, Applications and Challenges in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANET) : Overview
Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Characteristics, Applications and Challenges in
Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANET): Overview
Abdalftah Kaid Said Ali1, Dr. U. V. Kulkarni2
1
Research Scholar, S.G.G.S. Institute of Engg. & Tech, S.R.T.M. University, Nanded, Mahrarashtra, India
2
Professor, Dept. of Computer Sci & Engg, S.G.G.S. Institute of Engg & Tech, Nanded,
S.R.T.M. University, Nanded, Mahrarashtra, India
ABSTRACT
A Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) is a contenting collection of mobile devices, the wireless network can reconfigure by itself
contenting group of mobile devices. This network can work without any fixed infrastructure, the nodes in the networks work as
router as well as host. This paper provides insight a comprehensive overview of Mobile Ad hoc networks. This paper also
reviews the various characteristics, challenges, applications of MANETS. Moreover, routing protocol for MANET have been
presented in this paper.
Keywords: MANET, Proactive, Reactive, Hybrid, Routing Protocols.
1. INTRODUCTION
In the beginning, the mobile packet radio network was used in the military. Then, in the past few years, it has been fast
developed into mobile ad hoc network (MANEN), which allow users to access service and exchange information
electronically without any consideration of the geographical advancement in the domain of personal common people to
use mobile phones to communicate with other people any where anytime irrespective of their being far off [1]. The
wireless network, which is a growing new technology, allows users to access services and information. It can be
expanded anywhere or building without a wired connection between the clients. The wireless network can be classified
into two main types: the infrastructure network (WLAN) and the Infrastructureless (ad-hoc) network. Infrastructure
network is composed of some of nodes and access point (AP), which acts as a central coordinator between all nodes.
The nodes cant work outside the domain of access point. An ad hoc network typically refers to any group of networks
where all devices have equal status on a network and are free to connect with any other ad hoc network devices in link
range. An ad hoc network can be defined as a collection of mobile nodes which form an instant network without fixed
topology. The node functions as a router and host at the same time, and it can move out or join in the network freely
[2]. The ad hoc network that is instantly created does not possess any base infrastructures that are used in the
conventional network. In spite of that, it is compatible with the traditional networks. Wireless network has been
popularized in the domain of computing industry.
The Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) enjoys some of characteristics: distributed operation, dynamic topology, lightweight terminals, multi hop routing, shared physical medium and autonomous terminal, which will be discussed in
some detail later in this paper. Due to the rapid and growing expansion of the mobile ad hoc network, it has many
typical applications such emergency services, education, entertainmentetc. In spite of all this characteristics of the
MANET, it faces some challenges the most significant of which are limited bandwidth, routing overhead, quality of
service and security [3]. There are many routing protocols proposed for MANET, which can be classified into three
main categories: Proactive, Reactive and Hybrid. Proactive routing protocols attempt to maintain consistent, up-to-date
routing information from each node to every other node in the network, whereas Reactive routing protocols create just
routes in case there is a desire to send information by the source node. Once a route has been established, it is
maintained by a route maintenance procedure. Hybrid routing protocols has the advantage of combining both proactive
and reactive routing protocols and overcome their shortcomings [4].
This paper is structured as follows: Section II present the type of Wireless networks, Section III discusses the
characteristics of MANET, Section IV investigates some of the application for MANET, Section V discuss in details
the main challenge of MANET, Section VI present advantages of MANET, Section VII present disadvantages of
MANET and section VIII investigates the routing protocols of MANET.
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 6
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
2. WIRELESS NETWORKS
Wireless networks allow flexible connection between clients who are in various places. furthermore, the network can be
expanded anywhere or building without a wired connection between the clients. Wireless networks are split into two
kinds: Infrastructure networks and Ad Hoc networks (infrastructure less) [5], as can be seen in Figure 1.
Wireless Networks
Infrastructure Networks
Ad-Hoc Networks
Figure 1: Wireless Networks Categories
2.1 Infrastructure Networks
This kind of infrastructure wireless network relies on the third fixed party and in this architecture which allows the
wireless stations to communicate between themselves as seen in Figure 2.An Access Point (AP) acts as a central
coordinator between all nodes. Any node can join the network through AP. Also, AP organizes the connection between
the Basic Set Services (BSSs) in order to make the route ready when it is needed. When a source node wants to make a
communication with a destination node, the source node tells the base station about that. In spite of that, one
shortcoming of using an infrastructure network is the large overhead of maintaining the routing tables [5].
Figure 2: Infrastructure networks
2.2 Infrastructure less Networks or Ad Hoc Networks
This kind of network is understood as Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) which can make correspondence with one
another without the assistance from centralized administrator. That is the wireless ad hoc network which is a
decentralized type of wireless network. In other words, the network is ad hoc since it does not depend on a preexisting
infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed (infrastructure) wireless networks. Ad
Hoc networks do not have a fixed topology or a central coordination point. Therefore, the source node and the
destination node can communicate with each other by sending and receiving packets which is more sophisticated than
infrastructure networks [5], as can be seen in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Mobile Ad Hoc Network
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 7
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
3. CHARACTERISTICS OF MANETS
MANET has some characteristics that make it popularized everywhere everytime. These characteristics that are
desirable in Ad-Hoc Routing protocols [6] [7] [8] [9] are as follows:
3.1Distributed operation
There is no background network for the central control of the network operations. The control of the network is
distributed between the nodes. The nodes that participate in a MANET should cooperate with each other and
communicate among themselves and each node functions as a relay as needed, to fulfill specific functions such as
routing and security.
3.2Multi hop routing
If a node wants to send information to another nodes which is outside of its communication domain, the packet has to
resend through one or more intermediate nodes.
3.3 Autonomous terminal
In MANET, every mobile node is an independent node. It can perform two tasks that are as a host and a router.
3.4Dynamic topology
In MANET, the network topology may randomly change and at unpredictable time. The nodes are free to move
arbitrarily in the network domain with various speeds. Therefore, The nodes in the MANET dynamically establish
routing between themselves as they travel around, forming their own network.
3.5Light-weight terminals
In maximum cases, the nodes at MANET are mobile with less CPU capability, low power storage and small memory
size, so that the people can take it everywhere.
3.6Shared Physical Medium
The wireless communication medium is characterized as accessible to any entity with the proper equipment and
adequate resources. Accordingly, access to the channel cannot be limited.
4. APPLICATIONS OF MANETS
The MANET is nowadays so popularized that it has many applications in several fields in the practical life. The
following are the main applications for MANET [6] [9] [10]:
4.1Tactical Networks
MANET has many uses in the army. Some of these usages are in the military communication and operations among
army units. Moreover, it is used in the automated battlefield.
4.2Emergency services
MANET is used in many operations at emergency time. For example, it is used in search and rescue operations. When
disasters occurs, MANET becomes significant in that casualties discovery and rescue. It is also useful in the case of
environmental disasters, for it replaces the fixed infrastructure. It is also used in policing and fire fighting. It is useful
in medical area, because it supports doctors and nurses in hospitals.
4.3Commercial and civilian Environment
MANET is used in the commercial and civilian environment. It is used in the E-commerce such as electronic payments
anytime and anywhere environments. It is also useful in business for the purpose of dynamic database access by
mobiles and offices . it is very important in the vehicular services, because it is used as road or accident guidance and
it is used in transmission of road and weather conditions, taxi cab network, and inter-vehicle networks. In addition, it
is used in sports stadiums, trade fairs, and shopping malls. It service as networks of visitors at airports.
4.4Home and enterprises Networking
MANET functions as home/office wireless networking. It is used for exchange data in the conferences and meeting
rooms. It is used as personal area networks (PAN) and Personal networks (PN). It is also used as networks at
construction sites.
4.5Educations
MANET is of huge importance in the educational section. It is inevitable in the universities and campus settings. It is
urgently required in virtual classrooms. In addition, it is used in ad hoc communications during meetings or lectures.
4.6Entertainment
MANET is used in many entertainment application such as: Multi-user games. It is used also in Wireless P2P
networking, Outdoor internet access , Robotic pets as well as Theme parks .
4.7Sensor network
MANET is required in home applications such as smart sensors and actuators embedded in consumer electronics. It is
useful in body area networks (BAN). It is also used for the purpose of data tracking of environmental conditions,
animal movements, and chemical/biological detection.
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 8
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
4.8Context aware services
MANET is useful in the follow-on services like call-forwarding and mobile workspace. Moreover, it is used in
information services such as location specific services, time dependent services. It is used in the touristic sector for
exchanging information.
4.9Coverage extension
MANET is used for the purpose of extending cellular network access. It is also used for linking up with the Internet,
intranets, etc.
5. CHALLENGES OF MANETS
Is spite of the characteristics which the MANET has, it is not free from some challenges that have to be overcome.
MANETs have been popular field of study during the last few years. Almost every aspect of the network has been
explored in one way or another at different level of problem. The most important challenges of the MANET are
mentioned bellow: [6] [9] [10]
5.1 Limited bandwidth
One of the challenges of the MANET is that the Wireless link continues to have significantly lower capacity than
infrastructure networks. Moreover, the realized throughput of wireless communication after accounting for the effect of
multiple access such as fading, noise, and interference conditions, etc., is often much less than a radios maximum
transmission rate.
5.2 Dynamic topology
In MANET, dynamic topology membership may shake the trust relationship among nodes. The trust may also be
weakened if some nodes are detected as compromised.
5.3Routing Overhead
In wireless ad hoc networks, nodes often alter their position within network. Thus, some stale routes are produced in
the routing table which results in unnecessary routing overhead.
5.4Hidden terminal problem
In the MANET, the hidden terminal problem refers to the collision of packets at a receiving node because of the
simultaneous transmission of those nodes that are not within the direct transmission range of the sender, but are within
the transmission range of the receiver.
5.5Packet losses due to transmission errors
Ad hoc wireless networks experiences a much higher packet loss owing to some factors such as increased collisions,
the presence of hidden terminals, presence of interference, uni-directional links, frequent path breaks which are caused
by mobility of nodes.
5.6Mobility-induced route changes
The network topology in an ad hoc wireless network is highly dynamic because of the movement of nodes. Therefore,
an continuous session suffers frequent path breaks. This situation often results in frequent route changes.
5.7Battery constraints
MANET suffers from the shortcoming of the battery constraints. Devices which are used in these networks suffer
restrictions on the power source in order to maintain portability, size and weight of the device.
5.8Security threats
MANET suffers from a particular security problems. It also has the reliability problem due to the limited wireless
transmission range. The nature of wireless mobile ad hoc (MANETs) brings about new security challenges to the
network design. As the wireless medium is vulnerable to eavesdropping and ad hoc network functionality is established
through node cooperation, mobile ad hoc networks are intrinsically subjected to numerous security attacks.
5.9Quality of Service (QoS)
The quality of service is considered one of the most significant challenges of MANET because of its mobility
environment. The inherent stochastic feature of communications quality in a MANET makes it difficult to provide
fixed guarantees on the services offered to a device. An adaptive QoS has to be fulfilled over the conventional resource
reservation to support the multimedia services
5.10Inter-networking
In addition to the communication within an ad hoc network, communication between MANET and a fixed network is
considered a challenge. Inter-networking between MANET and fixed networks (mainly IP based) is often expected in
many cases. The coexistence of routing protocols in such a mobile device is taken to be a challenge for the harmonious
mobility management.
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 9
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
5.11Location-aided Routing
The routing is spatially oriented and limited, because location-aided routing uses positioning information to define
associated regions. This is analogous to associatively-oriented and restricted broadcast in ABR.
6. ADVANTAGE OF MANET
MANET [6] [8] [10] enjoys several advantages which are summed up bellow
They provide access to information and services irrespective of geographic position.
Independent from central network administration.
Self-configuring network, nodes are also function as routers.
Less expensive as compared to wired network.
Scalableaccommodates the addition of more nodes.
Advanced Flexibility.
Robust owing to decentralize administration.
The network can be established at any place and time
It can be established easily and fast and without pulling cables through walls and ceiling .
It has increased reliability due to multiple paths.
7. DISADVANTAGE OF MANET
Although MANET has several advantages, it suffers from some of the disadvantages the most important of which are
mentioned bellow [11]:
Some security protocol in the network is not working properly in the ad-hoc
If any malicious nodes with in entire network it is hard to find the malicious
There is some good protocol in the wired network but it is tough to implement in the wireless node
8. ROUTING PROTOCOLS
Routing is the operation of selecting paths in a network for moving a packets of data from source node to destination
node via number of nodes. A routing protocol consist of a routing algorithm with a set of rules that monitors the
operations of the network .The key issue in MANETs is that the routing protocols have to be able to respond quickly to
topological changes of the network [12]. Ad-Hoc network Routing Protocols can be divided to three kinds: Proactive ,
reactive and hybrid routing protocols [13]. as shown in figure 4.
MANET Routing Protocols
Proactive
Ractive
DSDV
AODV,DSR
Hybrid
ZRP
Figure: 4 Classification of MANET routing protocols
8.1Proactive Routing
Proactive or it is called table-driven routing protocols. In proactive routing, each node has to maintain one or many
tables for storage routing information, and any update in network topology need to be reflected by propagating change
throughout the network in order to maintain a proportionate network . Example of such schemes are the conventional
routing schemes: Destination sequenced distance vector (DSDV). They try to maintain consistent, up-to-date routing
information of the whole network. It reduce the delay in communication and allow nodes to quickly define which nodes
are present or reachable in the network [14].
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 10
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
8.2Reactive Protocols
Reactive or it is called on-demand routing protocol, because they do not maintain routing information or routing
activity at the network nodes if there is no communication. If any node wants to transfer a packet to another node then
this protocol searches for the route in an on-demand manner and create the connection in order to transfer and receive
the packet. Examples of reactive routing protocols are the Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector routing (AODV) and
Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) [14].
8.3Hybrid Protocols
These protocols collect the good properties of both the pro-active and reactive protocols. It accumulate the group of
nodes into zones in the network topology. As the network is split into zones, the proactive approach is used within each
zone for maintenance of routing information. Reactive approach is used for routing packets between different zones.
ZRP is one of the types of the hybrid routing protocols [9].
9. CONCLUSIONS
The current paper includes seven sections which deal with the mobile ad hoc network which is includes: the types of
Wireless network, the characteristics, the applications, challenges, advantages, disadvantages, and routing protocol of
MANET. Mobile ad hoc network is decentralized, self-organize, anywhere, anytime network, and provides cheap
communications. It is called infrastructure less nature. This paper conducts a survey of characteristics of MANET,
various application of the mobile ad hoc network and several challenges as there are still many challenges confronting
wireless ad hoc networks. It also presents a brief but sound account of the advantages and disadvantages of the
MANET. This paper also presents the classification of MANET routing protocols: proactive, reactive and hybrid of
routing protocols.
References
[1] Ankur O. Bang and Prabhakar L. Ramteke, MANET: History, Challenges and Applications, International
Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering and Management (IJAIEM), Volume 2, Issue 9, pp. 249-251,
September 2013.
[2] A. Saleh Ali K.AL-Omar and Putra Sumari, An Overview Ad hoc Networks for the Exiting Protocols and
Applications, Journal on Application of Grph theory in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks (JGRAPH-HOC), Volume 2,
no.1, pp. 87-110, March 2010.
[3] Anuj K. Gupta, Harsh Sadawarti, and Anil K. Verma, Review of Various Routing Protocols for MANETs,
International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Volume 1, No. 3, pp. 251-259, November
2011.
[4] Amandeep Makkar, Bharat Bhushan, Shelja, and Sunil Taneja, Behavioral Study of MANET Routing Protocols,
International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Volume 2, No. 3, June 2011, pp. 210-216.
[5] Dr.S.S.Dhenakaran and Dr.S.S.Dhenakaran, An Overview of Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, Volume 3, Issue 2,
pp. 251-259, February 2013.
[6] Aarti and Dr. S. S. Tyagi, Study of MANET: Characteristics, Challenges, Application and Security Attacks,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering (IJARCSSE),
Volume 3, Issue 5, pp. 252-257, May 2013.
[7] Seema Dev Aksatha D and Lalitha T, A Comprehensive Overview on Manet, International Journal of
Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT), Volume 3 Issue 6, pp. 242-244, August 2014.
[8] Jai Shree Mehta, Shilpa Nupur, Swati Gupta, An Overview of MANET: Concepts, Architecture & Issues,
International Journal of Research in Management, Science & Technology, Volume 3, No. 2, pp.98-101, April
2015.
[9] Manjot Kaur, Anand Nayyar, A Comprehensive Review of Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETS), International
Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS), Volume 2, Issue 6, pp. 196-210,
(November December) 2013.
[10] Sukhpreet Kaur, Sukhpreet kaur and Chandan Sharma , An Overview of Mobile Ad hoc Network: Application,
Challenges and Comparison of Routing Protocols, IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) Volume
11, Issue 5, pp. 7-11, (May. - Jun.) 2013.
[11] V. Saravanan Asst and D.Vijayakumar, Performance Of Reactive And Proactive MANET Routing Protocols With
Trajectories, International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology (IJERT), Volume 1, Issue 8, pp. 111, October 2012
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 11
IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)
A Publisher for Research Motivation........
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Web Site: http://www.ipasj.org/IIJEC/IIJEC.htm
Email: editoriijec@ipasj.org
ISSN 2321-5984
[12] E. Edwin Lawrence and Dr.R.Latha, A Comparative Study of Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks,
International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing (IJCSMC), Volume 3, Issue. 1, pp. 46 53,
November 2014.
[13] Sunil Taneja and Ashwani Kush, A Survey of Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks , International
Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Volume 1, No. 3, pp. 279-285, August 2010.
[14] Parvinder and Dr. V.K. Suman, A Review On Routing Protocol In Manet , International Journal of Advanced
Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), Volume 4, Issue 5, pp. 243-250, (July August) 2013.
AUTHOR
Abdalftah Kaid Said Ali has completed M.Tech in Information Engineering from Aleppo UniversitySyria in 2011 and B.Tech degree in Engineering of Computers and controls from Sanaa UniversityYemen in 1997. And know Ph.D researcher at S. G. G.S. Institute of Engineering & Technology.
affiliated to S.R.T.M. University, Nanded, Mahrarashtra, India. His interests area is wireless
Networking, Mobile Ad Hoc Networks.
Uday V. Kulkarni, Ph.D. (SRTMUN), MIET, AMIETE, LMISTE, Professor, Department of
Computer Science and Engineering, S. G. G. S. Institute of Engineering and Technology, Vishnupuri,
Nanded - 431606, Maharashtra, India. Cell: 009325612705; Land line: 02462-269195, Fax: 02462229236
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2015
Page 12
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Line Differential Red670Dokument12 SeitenLine Differential Red670Ashish ChughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two-way car alarm manualDokument11 SeitenTwo-way car alarm manualRichard Bernal50% (2)
- Essentials GPIOZero v1Dokument106 SeitenEssentials GPIOZero v1Trung Nguyễn Vũ100% (1)
- Preliminary Design of a 500kW D.C. Generator ArmatureDokument8 SeitenPreliminary Design of a 500kW D.C. Generator ArmatureRafael DeocuarizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shield-Arc 400AS-50: IMA 554CDokument24 SeitenShield-Arc 400AS-50: IMA 554Cahmedhassankhan100% (1)
- Security Vulnerabilities in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDokument7 SeitenSecurity Vulnerabilities in Mobile Ad Hoc Networksatulverma8800978622Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANETsDokument53 SeitenIntroduction to Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (MANETsManjeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobility Trends Whats Ahead For Automotive SemiconductorsDokument11 SeitenMobility Trends Whats Ahead For Automotive SemiconductorsLarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks: Lu Han October 8, 2004Dokument6 SeitenWireless Ad-Hoc Networks: Lu Han October 8, 2004pinku0077Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Detection of Fruits and Vegetable Spoiled Detetction SystemDokument8 SeitenDesign and Detection of Fruits and Vegetable Spoiled Detetction SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryDokument8 SeitenImpact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uwjcs V3 2020-2Dokument10 SeitenUwjcs V3 2020-2Jannath Beegam. JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Issues, Research Trends and ExperimentsDokument7 SeitenMobile Ad Hoc Networks: Issues, Research Trends and Experimentsmanpreet2k7Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Review Over MANET-Issues and Challenges: April 2013Dokument14 SeitenA Review Over MANET-Issues and Challenges: April 2013Thanh HàNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of MANET: Characteristics, Challenges, Application, Routing Protocol and Security AttacksDokument10 SeitenStudy of MANET: Characteristics, Challenges, Application, Routing Protocol and Security AttacksHayder KadhimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks ReviewDokument14 SeitenRouting Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks ReviewRuhulamin SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Ad Hoc Networking: An Essential Technology For Pervasive ComputingDokument6 SeitenMobile Ad Hoc Networking: An Essential Technology For Pervasive Computingrajumone19Noch keine Bewertungen
- LD Identifying Misbehaving Nodes in MANETDokument5 SeitenLD Identifying Misbehaving Nodes in MANETEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared by Abhinav Srivastava M.Tech (IT) Roll No: 04IT6014 School of Information TechnologyDokument13 SeitenPrepared by Abhinav Srivastava M.Tech (IT) Roll No: 04IT6014 School of Information Technologykranthi1231Noch keine Bewertungen
- MANET - Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDokument15 SeitenMANET - Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksŁeejLa INoch keine Bewertungen
- A Seminar Report On Mobile Ad Hoc Network (Manets) : Department: Computer Engg. & Application Gla University, MathuraDokument10 SeitenA Seminar Report On Mobile Ad Hoc Network (Manets) : Department: Computer Engg. & Application Gla University, MathuraHemant Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Management Schemes in MANET-A Detailed Review: Dr.S.SekarDokument6 SeitenKey Management Schemes in MANET-A Detailed Review: Dr.S.SekarEighthSenseGroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Issues in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network With Implication of Key Management: A ReviewDokument5 SeitenSecurity Issues in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network With Implication of Key Management: A ReviewKumarushes IlrrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijaret: International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (Ijaret)Dokument8 SeitenIjaret: International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (Ijaret)IAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3Dokument17 SeitenUnit-3link7096907539Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Manet Routing Protocols and Its VulnerabilitiesDokument11 SeitenA Review On Manet Routing Protocols and Its VulnerabilitiesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDokument11 SeitenChallenges in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksMamilla BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)Dokument5 SeitenInternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks Its Advantages and Challenges-1736Dokument6 SeitenMobile Ad-Hoc Networks Its Advantages and Challenges-1736Sebasa7x16Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Enhanced Route Discovery Algorithm To Maximize Network Life Time in MANETDokument7 SeitenAn Enhanced Route Discovery Algorithm To Maximize Network Life Time in MANETerpublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Ad-Hoc Network (MANETS) : Security Related IssuesDokument8 SeitenMobile Ad-Hoc Network (MANETS) : Security Related IssuesNeha Shinde HolkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issues in Wireless Sensor Networks: Gowrishankar.S, T.G.Basavaraju, Manjaiah D.H, Subir Kumar SarkarDokument12 SeitenIssues in Wireless Sensor Networks: Gowrishankar.S, T.G.Basavaraju, Manjaiah D.H, Subir Kumar SarkarTaiwoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Research Vol II Iss I 1Dokument14 SeitenGlobal Research Vol II Iss I 1editorglobalresearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issues in Wireless Sensor Networks ResearchDokument12 SeitenIssues in Wireless Sensor Networks ResearchMukil BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link Quality Driven Multipath Routing For Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksDokument9 SeitenLink Quality Driven Multipath Routing For Mobile Ad Hoc NetworksEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Adhoc Network (MANETS) : Proposed Solution To Security Related IssuesDokument9 SeitenMobile Adhoc Network (MANETS) : Proposed Solution To Security Related IssuesrachikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis Performance of Different Routing Protocols For MANETs Using NS2 SimulatorDokument9 SeitenAnalysis Performance of Different Routing Protocols For MANETs Using NS2 SimulatorIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi HopDokument3 SeitenMulti HopSowjanya PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extending Wireless Range Using AODVDokument8 SeitenExtending Wireless Range Using AODVSangita DharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASROP: AD HOC Secure Routing ProtocolDokument20 SeitenASROP: AD HOC Secure Routing ProtocolJohn BergNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Approach For Secure Energy Efficient Routing in ManetDokument10 SeitenAn Approach For Secure Energy Efficient Routing in ManetIJAET JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANET History, Challenges and ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenMANET History, Challenges and ApplicationsАйдауNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neha Report 1Dokument32 SeitenNeha Report 1Neha RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks: Types, Applications, Security GoalsDokument6 SeitenWireless Ad-Hoc Networks: Types, Applications, Security GoalsJagadeesanSrinivasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Final 1Dokument34 SeitenSynopsis Final 1shubhamkr91234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qos in ManetDokument51 SeitenQos in ManetpsabutNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of MANET: Applications, Attacks and ChallengesDokument10 SeitenAn Overview of MANET: Applications, Attacks and Challengespradnya sadigaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANET Seminar Report SummaryDokument28 SeitenMANET Seminar Report SummaryDhairav PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Ad Hoc NetworkDokument3 SeitenWireless Ad Hoc NetworkarulnatrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ReportDokument33 SeitenFinal Reportyousef tamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection of Rushing Attack by Comparing Energy, Throughput and Delay With AODVDokument6 SeitenDetection of Rushing Attack by Comparing Energy, Throughput and Delay With AODVInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks: Types, Applications, Security GoalsDokument6 SeitenWireless Ad-Hoc Networks: Types, Applications, Security Goalsece.kavitha mamcetNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Based On Mobile Ad-Hoc Network (MANET)Dokument10 SeitenA Project Based On Mobile Ad-Hoc Network (MANET)Moses DevaprasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection and Segregation of Misbehavior Node (S) For MANETS OLSR ProtocolDokument7 SeitenDetection and Segregation of Misbehavior Node (S) For MANETS OLSR ProtocolInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On Throughput Analysis of DSR Routing Protocol in ManetsDokument6 SeitenA Survey On Throughput Analysis of DSR Routing Protocol in Manetswarse1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Ad Hoc Network Applications & ChallengesDokument12 SeitenMobile Ad Hoc Network Applications & ChallengesAnonymous gud2poNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icaet 018Dokument4 SeitenIcaet 018Jannath Beegam. JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Multicast Routing Protocols: Puma and Odmrp: S Sumathy, Beegala Yuvaraj, E Sri HarshaDokument9 SeitenAnalysis of Multicast Routing Protocols: Puma and Odmrp: S Sumathy, Beegala Yuvaraj, E Sri HarshaIJMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of Routing in Smart Grids Using Intelligent TechniquesDokument5 SeitenOptimization of Routing in Smart Grids Using Intelligent TechniquesDeepa KalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proactive Vs ReactiveDokument4 SeitenProactive Vs ReactiveAakash SanthanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijecet: International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (Ijecet)Dokument8 SeitenIjecet: International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (Ijecet)IAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Improvement in Congestion Control Using Multipath Routing in MANETDokument10 SeitenAn Improvement in Congestion Control Using Multipath Routing in MANETAshish BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Paper 1Dokument8 SeitenReference Paper 1Rajakumar SriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Relative Study of MANET and VANET: Its Applications, Broadcasting Approaches and Challenging IssuesDokument7 SeitenA Relative Study of MANET and VANET: Its Applications, Broadcasting Approaches and Challenging IssuesIk RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManetDokument7 SeitenManet23Pratyasha Kar100% (1)
- Secure Retrieval of Information For Manets Using Self Manageable ClusteringDokument10 SeitenSecure Retrieval of Information For Manets Using Self Manageable ClusteringInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Networks: Wireless Networking for Personal DevicesVon EverandPersonal Networks: Wireless Networking for Personal DevicesBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Industrial Sensors and Controls in Communication Networks: From Wired Technologies to Cloud Computing and the Internet of ThingsVon EverandIndustrial Sensors and Controls in Communication Networks: From Wired Technologies to Cloud Computing and the Internet of ThingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSDokument7 SeitenTHE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementDokument9 SeitenCustomer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesDokument6 SeitenDetection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyDokument6 SeitenAnalysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewDokument9 SeitenAn Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterDokument7 SeitenExperimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiDokument12 SeitenStudy of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSDokument7 SeitenTHE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewDokument9 SeitenAn Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterDokument7 SeitenExperimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesDokument6 SeitenDetection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mexican Innovation System: A System's Dynamics PerspectiveDokument12 SeitenThe Mexican Innovation System: A System's Dynamics PerspectiveInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiDokument12 SeitenStudy of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementDokument9 SeitenCustomer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyDokument6 SeitenAnalysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staycation As A Marketing Tool For Survival Post Covid-19 in Five Star Hotels in Pune CityDokument10 SeitenStaycation As A Marketing Tool For Survival Post Covid-19 in Five Star Hotels in Pune CityInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Stabilization of Road by Using Spent WashDokument7 SeitenSoil Stabilization of Road by Using Spent WashInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Load Flow Study and Stability Analysis of A Real Time SystemDokument8 SeitenAdvanced Load Flow Study and Stability Analysis of A Real Time SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Digital Record For Privacy and Security in Internet of ThingsDokument10 SeitenA Digital Record For Privacy and Security in Internet of ThingsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Effective Communication To Enhance Management SkillsDokument6 SeitenThe Impact of Effective Communication To Enhance Management SkillsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Deep Learning Based Assistant For The Visually ImpairedDokument11 SeitenA Deep Learning Based Assistant For The Visually ImpairedInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparative Analysis of Two Biggest Upi Paymentapps: Bhim and Google Pay (Tez)Dokument10 SeitenA Comparative Analysis of Two Biggest Upi Paymentapps: Bhim and Google Pay (Tez)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance of Short Transmission Line Using Mathematical MethodDokument8 SeitenPerformance of Short Transmission Line Using Mathematical MethodInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges Faced by Speciality Restaurants in Pune City To Retain Employees During and Post COVID-19Dokument10 SeitenChallenges Faced by Speciality Restaurants in Pune City To Retain Employees During and Post COVID-19International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Datasets For Myocardial Infarction Based On Actual DatasetsDokument9 SeitenSynthetic Datasets For Myocardial Infarction Based On Actual DatasetsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchoring of Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy Transparency in IndiaDokument9 SeitenAnchoring of Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy Transparency in IndiaInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secured Contactless Atm Transaction During Pandemics With Feasible Time Constraint and Pattern For OtpDokument12 SeitenSecured Contactless Atm Transaction During Pandemics With Feasible Time Constraint and Pattern For OtpInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting The Effect of Fineparticulate Matter (PM2.5) On Anecosystemincludingclimate, Plants and Human Health Using MachinelearningmethodsDokument10 SeitenPredicting The Effect of Fineparticulate Matter (PM2.5) On Anecosystemincludingclimate, Plants and Human Health Using MachinelearningmethodsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Estimating MethodsDokument10 SeitenElectrical Estimating MethodsJefferson Ayubo BroncanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 36 Lattice Gal18v10Dokument14 Seiten36 Lattice Gal18v10HelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Electronics - 1 (Allied)Dokument155 SeitenApplied Electronics - 1 (Allied)nanobala15100% (1)
- Computer Packages Training Manual PDFDokument164 SeitenComputer Packages Training Manual PDFAnnah GachanjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIT Communications Systems Part IIDokument5 SeitenFIT Communications Systems Part IIDemal BecirovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSN Lte ParameterDokument44 SeitenNSN Lte Parameterzola19Noch keine Bewertungen
- GH 120 GH 200 GH 202 GH 252 GH 300 Instruction - TocDokument4 SeitenGH 120 GH 200 GH 202 GH 252 GH 300 Instruction - TocPilar CaleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- From 2340 To 7200 kVA: Medium Voltage Inverter Station, Customized Up To 7.2 MvaDokument2 SeitenFrom 2340 To 7200 kVA: Medium Voltage Inverter Station, Customized Up To 7.2 Mvaanon_b186Noch keine Bewertungen
- Milenium Carlyle PDFDokument21 SeitenMilenium Carlyle PDFvickers100% (1)
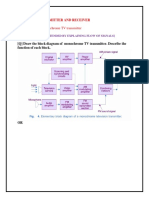
- Topic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterDokument10 SeitenTopic: TV Transmitter and Receiver Block Diagram of Monochrome TV TransmitterNarayan Krishan VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual: USB/MP3/CD/Micro Systems MC-5210SUDokument32 SeitenService Manual: USB/MP3/CD/Micro Systems MC-5210SUhumberto100% (1)
- HS Kalsi 1Dokument65 SeitenHS Kalsi 1paancute8982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiplexing: Techniques in Optical Networks: WDMDokument28 SeitenMultiplexing: Techniques in Optical Networks: WDMSahil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Encoding and DecodingDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Encoding and DecodingSusmitha Cherukuri0% (1)
- MVR - Analog LinksDokument62 SeitenMVR - Analog LinksSonalSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omegas Prezentacija 01Dokument20 SeitenOmegas Prezentacija 01Predrag Djordjevic100% (1)
- Single 2011 MI 2094 CE Multitester AngDokument2 SeitenSingle 2011 MI 2094 CE Multitester AngHector Diaz SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTPC TrainingDokument32 SeitenNTPC TrainingparvejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starline S9v2 InstallationDokument2 SeitenStarline S9v2 InstallationHeyder HeyderovNoch keine Bewertungen
- GL PMG 3500 Vertical Specification SheetDokument1 SeiteGL PMG 3500 Vertical Specification SheetAamir Sohail100% (1)
- Embedded Controlled Drip Irrigation SystemDokument5 SeitenEmbedded Controlled Drip Irrigation SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of DC MachineDokument7 SeitenConstruction of DC MachineAnonymous MAit3mlYm0% (1)
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes ArticlesDokument5 SeitenCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting 50 51 Electrical Notes ArticlesTom100% (1)
- Eaton Online UPS User ManualDokument40 SeitenEaton Online UPS User ManualMatias Loza ZapataNoch keine Bewertungen