Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mathematics Form 3
Hochgeladen von
CaliphCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mathematics Form 3
Hochgeladen von
CaliphCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
WEEK
1.
Lines and
Angles II
1
3/1 7/1
1.1
Understand and use
properties of angles
associated with
transversal and
parallel lines
II
III
IV
V
WEEK
2-3
2.
Polygons II
2.1
Understand the
concept of regular
polygons
I
II
10/1 21/1
III
IV
Identify:
a) transversals
b) corresponding
angles
c) alternate angles
d) interior angles
Determine that for parallel lines:
a)
corresponding angles are equal
b)
alternate angles are equal
c)
sum of interior angles is 1800
Find the values of:
a) corresponding angles
b) alternate angles
c) interior angles
associated with parallel lines
Determine if two given lines are parallel
based on the properties of angles
associated with transversals
Solve problems involving properties of
angles associated with transversals
Determine if a given polygon is a regular
polygon.
Find
a) the axes of symmetry
b) the number of axes of symmetry
of a polygon
Sketch regular polygons
Draw regular polygons by dividing
equally the angle at the centre
Communication
Enquiry
discovery
Mastery
learning
Multiple
intelligence
Identifying
patterns
Rational
Sincerity
Identifying
relations
Cooperation
Comparing and
differentiating
Classifying
Finding all possible
solutions
Constructivism
Drawing diagrams
Rational
Contextual
learning
Making
generalizations
Punctuality
Neatness
Multiple
intelligence
ICT
Arranging
sequentially
Systematic
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
V
2.2
Understand and use
the knowledge of
exterior and interior
angles of polygons
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
WEEK
2-3
24/1 11/2
3.
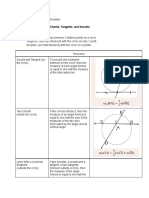
Circles II
3.1
Understand and use
properties of circles
involving symmetry,
chords and arcs
I
II
Construct equilateral triangles, squares
and regular hexagons
Identify the interior angles and exterior
angles of a polygon
Find the size of an exterior angle when
the interior angle of a polygon is given
and vice versa
Determine the sum of the interior angles
of polygons
Determine the sum of the exterior angles
of polygons
Find
a) the size of an interior angles of a
regular polygon given the number
of sides
b) the size of an exterior angle of a
regular polygon given the number
of sides
c) the number of sides of a regular
polygon given the size of the
interior or exterior angle
Solve problems involving angles and
sides of polygons
Identify a diameter of a circle as an axis
of symmetry
Determine that:
a) a radius that is perpendicular to
a chord divides the chord into
two equal parts and vice versa
Communication
Mastering
learning
Identifying
patterns
Honesty
Sharing
Identifying
relations
Cooperation
Constructivism
Cooperative
learning
Contextual
learning
Using algorithm
and relationship
Hardworking
Finding all possible
solutions
ICT
Communication
Drawing diagrams
Neatness
Enquiry
discovery
Using algorithm
and relationship
Systematic
Rational
Mastery
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
III
3.2
Understand and use
properties of angles
in circles
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
b) perpendicular bisectors of two
chords intersect at the centre
c) two chords that are equal in
length are equidistant from the
centre and vice versa
d) chords of the same length cut
arcs of the same length
Solve problems involving symmetry,
chords and arcs of circles
Identify angles subtended by an arc at
the centre and at the circumference of a
circle
Determine that angles subtended at the
circumference by the same arc are
equal
Determine that angles subtended:
a) at the circumference
b) at the centre
by arcs of the same length are equal
Determine the relationship between
angle at the centre and angle at the
circumference subtended by an arc
Determine the size of an angle
subtended at the circumference in a
semicircle
Solve problems involving angles
subtended at the centre and angles at
the circumference of circles
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Diligence
ICT
Finding all possible
solutions
Communication
Drawing diagrams
Neatness
Enquiry
discovery
Using algorithm
and relationship
Systematic
Rational
Mastery
learning
Recognizing and
representing
ICT
Finding all possible
solutions
Diligence
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Communication
Drawing diagrams
Neatness
Enquiry
discovery
Using algorithm
and relationship
Systematic
Students will be able to:
DATE
3.3
Understand and use
the concept of cyclic
quadrilaterals
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
VII
WEEK
7-9
4.
Statistics II
4.1
Represent and
interpret data in pie
charts to solve
problems
Identify cyclic quadrilaterals
Identify the interior opposite angles of
cyclic quadrilaterals
Determine the relationship between
interior opposite angles of cyclic
quadrilaterals
Identify exterior angles and the
corresponding interior opposite angle of
cyclic quadrilaterals
Determine the relationship between
exterior angles and the corresponding
interior opposite angle of cyclic
quadrilaterals
Solve problems involving angles of
cyclic quadrilaterals
Solve problems involving circles
CUTI PERAYAAN TAHUN BARU CINA
7/2 11/2
I
Obtain and interpret information from pie
charts
II
Construct pie charts to represent data
Solve problems involving pie charts
III
Determine suitable representation of data
Rational
Mastery
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Diligence
ICT
Finding all possible
solutions
Contextual
learning
Collecting and
handling data
Tolerance
Sharing
Communicatio
n
Representing and
interpreting data
Kindness
14/2 - 3/3
Mastery
learning
ICT
Cooperation
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
4.2
Understand and use
the concept of mode,
median and mean to
solve problems
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
WEEK
10 - 11
5.
Indices
5.1
Understand the
concept of indices
I
II
III
Determine the mode of
a) sets of data
b) data given in frequency tables
Determine the mode and the respective
frequency from pictographs, bar charts,
line graphs and pie charts
Determine the median for sets of data
Determine the median of data in
frequency tables
Calculate the mean of
a) sets of data
b) data in frequency tables
Solve problems involving mode, median
and mean
UJIAN PENILAIAN KURIKULUM 1
6/3 - 10/3
CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
11/3 19/3
Express repeated multiplication as a n
and vice versa
Find the value of a n
Express numbers in index notation
Contextual
learning
Simulation
Punctuality
Determination
Communicatio
n
Diligence
Mastery
learning
Rational
ICT
Enquiry
discovery
Logical reasoning
Rational
Constructivism
Logical reasoning
Rational
Multiple
intelligent
Making inferences
Systematic
Working out
Sharing
ICT
6/3 17/3
I
5.2
Perform computations II
involving
multiplication of
numbers in index
Verify a m a n a m n
Simplify multiplication of :
a) numbers
b) algebraic terms
expressed in index notation with the
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
notation
III
5.3
Perform computation
involving division of
numbers in index
notation
I
II
5.4
I
Perform computations II
involving raising
numbers and
algebraic terms in
index notation to a
power
III
IV
same base
Simplify multiplication of:
c) numbers
d) algebraic terms
expressed in index notation with the
different bases
Verify a m a n a m n
Simplify division of :
e) numbers
f) algebraic terms
expressed in index notation with the
same base
Derive a a
Simplify
a) numbers
b) algebraic terms
expressed in index notation raised to a
power
Simplify multiplication and division of
a) numbers
b) algebraic terms
expressed in index notation with different
bases raised to a power
Perform combined operations involving
multiplication, division and raised to a
power on
a) numbers
m n
mn
Self access
learning
mentally
Identifying patterns
ICT
Constructivism
Logical reasoning
Rational
Multiple
intelligent
Making inferences
Systematic
Working out
mentally
Sharing
Self access
learning
Constructivism
Identifying patterns
Logical reasoning Rational
Multiple
intelligent
Making inferences
Self access
learning
Working out
mentally
Systematic
Sharing
Identifying patterns
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Constructivism
Logical reasoning
Rational
Multiple
intelligent
Making inferences
Systematic
Working out
mentally
Sharing
Students will be able to:
DATE
b) algebraic terms
5.5
I
Perform computations
involving negative
indices
II
III
5.6
I
Perform computations
involving fractional
indices
II
III
IV
1
and vice versa.
an
Perform combined operations of
multiplication, division and raising to a
power involving negative indices on
a) numbers
b) algebraic terms
n
State a as
Verify a n
State a
1
n
as
State a
m
n
a) a
m
1
n
and vice versa.
a
1
n
Find the value of a
as
1
or a n
Self access
learning
Identifying patterns
Constructivism
Logical reasoning
Rational
Multiple
intelligent
Making inferences
Systematic
Working out
mentally
Sharing
Self access
learning
b) n a or a
Perform combined operations of
multiplication, division and raising to a
power involving fractional indices on
a) numbers
b) algebraic terms
m
1
an
n
Verify a
Identifying patterns
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Communicatio
n
Logical reasoning
Politeness
Comparing and
differentiation
Neatness
Students will be able to:
DATE
m
Find the value of a n
5.7
Perform computation
involving laws of
indices
VI
I
II
WEEK
12 - 13
20/3 -31/3
6.
Algebraic
Expressions III
6.1
Understand and use
the concept of
expanding brackets
6.2
Understand and use
the concept of
factorisation of
algebraic expression
to solve problems
6.3
Perform addition and
subtraction on
algebraic fractions
I
II
I
II
III
IV
I
II
Perform combined operations of
multiplication, division and raised to a
power or combination of these operations
on several numbers expressed in index
notation
Perform combined operations of
multiplication, division and raised to a
power involving positive, negative and
fractional indices
Expand single bracket
Expand two brackets
State factors of an algebraic term
State common factors and the HCF for
several algebraic terms
Factorise algebraic expression:
a) using common factor
b) the difference of two squares
Factorise and simplify algebraic fractions
Add or subtract two algebraic fractions
with the same denominator
Add or subtract two algebraic fractions
with one denominator as a multiple of the
other denominator
Mastery
learning
Hardworking
Future studies
Using algorithm
and relationship
Multiple
intelligence
Identifying patterns
Working out
Sharing
mentally
ICT
Communicatio
n
Recognizing and
representing
Sharing
Determination
Enquiry
discovery
Logical reasoning
ICT
Communicatio
n
Recognizing and
representing
Enquiry
discovery
Logical reasoning
Sharing
Determination
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
III
6.4
Perform multiplication
and division on
algebraic fractions
II
III
WEEK
14
7.
Algebraic
Formulae
7.1
Understand the
concept of variables
and constants
3/4 - 7/4
I
II
III
7.2
Understand the
concept of formulae
to solve problems
I
II
Add or subtract two algebraic fractions
with denominators:
a) without any common factor
b) with a common factor
Multiply two algebraic fractions involving
denominator with:
a) one term
b) two terms
Divide two algebraic fractions involving
denominator with:
a) one term
b) two terms
Perform multiplication and division of two
algebraic fractions using factorisation
involving common factors and the
different of two squares
Determine if a quantity in a given
situation is a variable or a constant
Determine the variable in a given
situation and represent it with a letter
symbol
Determine the possible values of a
variable in a given situation
Write a formula based on a given
a) statement
b) situation
Identify the subject of a given formula
Express a specified variable as the
Identifying patterns
ICT
Communicatio
n
Recognizing and
representing
Sharing
Determination
Enquiry
discovery
Logical reasoning
Identifying patterns
ICT
Communicatio
n
Identifying
relations
Contextual
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Rational
Determination
Contextual
learning
Mastering
learning
Punctuality
Finding all possible
solutions
Identifying
Rational
relations
Determination
Recognizing and
representing
Punctuality
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
Cooperative
learning
Arranging
sequentially
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
III
subject of a formula involving:
a) one of the basic operations +
IV
V
WEEK
15 - 16
10/4 21/4
8.
Solid Geometry
III
8.1
I
Understand and use
the concept of volume
of right prisms and
II
right circular cylinders
to solve problems
III
IV
V
VI
VII
b) powers or roots
c) combination of the basic
operations and powers or roots
Find the value of a variable when it is:
a) the subject of the formula
b) not the subject of the formula
Solve problems involving formulae
Derive the formula for volume of
a) prisms
b) cylinders
Calculate the volume of a right prism in
cubic units given the height and
a) the area of the base
b) dimensions of the base
Calculate the height of a prism given the
volume and the area of the base
Calculate the area of the base of a prism
given the volume and the height
Calculate the volume of a cylinder in
cubic units given:
a) area of the base and the height
b) radius of the base and the height
of the cylinder
Calculate the height of a cylinder given
the volume and the radius of the base
Calculate the radius of the base of a
Finding all possible
solutions
Communicatio
n
Working out
mentally
Diligence
Determination
Constructivism
Mastery
learning
Comparing and
differentiating
Neatness
Using analogies
Multiple
intelligence
Honesty
Finding all possible
solutions
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
VIII
IX
X
8.2
I
Understand and use
the concept of volume
of right pyramids and II
right circular cones to
solve problems
III
IV
V
VI
VII
cylinder given the volume and the height
Convert volume in one metric unit to
another
a)
mm3 , cm3 and m3
b)
cm3 , ml and l
Calculate volume of liquid in a container
Solve problems involving volume of
prisms and cylinders
Derive the formula for the volume of :
a) pyramids
b) cones
Calculate the volume of pyramids in
mm3 , cm3 and m3
given the height and:
a) the area of the base
b) dimensions of the base
Calculate the height of a pyramid given
the volume and the dimension of the
base
Calculate the area of the base of a
pyramid given the volume and the height
Calculate the volume of a cone in mm3 ,
cm3 and m3 given the height and radius
of the base
Calculate the height of a cone given the
volume and the radius of the base
Calculate the radius of the base of a cone
Communicatio
n
Working out
mentally
Diligence
Constructivism
Comparing and
differentiating
Honesty
Mastery
learning
Using analogies
Neatness
Multiple
intelligence
Finding all possible
solutions
Determination
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
VIII
8.3
I
Understand and use
the concept of volume II
of sphere to solve
problems
III
8.4
Apply the concept of
volume to solve
problems involving
composite solids
given the volume and the height
Solve problems involving volume of
pyramids and cones
Calculate the volume of a sphere given
the radius of the sphere
Calculate the radius of a sphere given the
volume of the sphere
Solve problems involving volume of
spheres
Communicatio
n
Comparing and
differentiating
Calculate the volume of composite solids
Communicatio
n
Comparing and
differentiating
II
Solve problems involving volumes of
composite solids
Constructivism
Finding all possible
solutions
Diligence
Determination
Constructivism
Finding all possible
solutions
Mastery
learning
Diligence
Determination
Mastery
learning
WEEK
17 - 18
24/4 5/5
9.
Scale Drawings
9.1
Understand the
concept of scale
drawings
II
Sketch shapes:
a) of the same size as the object
b) smaller than the object
c) larger than the object
using grid papers
Draw geometric shapes according to
scale 1 : n, where n = 1,2,3,4,5,
III
1 1
,
2 10
Draw composite shapes, according to a
Multiple
intelligence
Contextual
learning
Mastering
learning
Drawing diagrams
Freedom
Interpreting
Punctuality
Working out
mentally
Consistent
Neatness
Finding all possible
solutions
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
WEEK
19 - 24
10.
Transformations
II
10.1
Understand and use
the concept of
similarity
IV
V
I
II
given scale using:
a) grid papers
b) blank papers
Redraw shapes on grids of different sizes
Solve problems involving scale drawings
Identify if given shapes are similar
Calculate the lengths of unknown sides of
two similar shapes
Contextual
learning
Identifying
relations
Rational
Communicatio
n
Using analogies
Sharing
Making
generalizations
Politeness
8/5 16/6
10.2
Understand and use
the concept of
enlargement
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
VII
Identify an enlargement
Find the scale factor, given the object and
its image of an enlargement when:
a) scale factor > 0
b) scale factor < 0
Determine the centre of enlargement,
given the object and its image
Determine the image of an object given
the centre of enlargement and the scale
factor
Determine the properties of enlargement
Calculate:
a) the scale factor
b) lengths of the side of the image
c) length of the side of the object
of an enlargement
Determine the relationship between the
Mastery
learning
Multiple
intelligence
Kindness
Using algorithm
and relationship
Finding all possible
solutions
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
WEEK
25
19/6 23/6
11.
Linear
Equations II
11.1
Understand and use
the concept of linear
equations in two
variables
11.2
Understand and use
the concept of two
simultaneous linear
equations in two
variables to solve
problems
area of the image and its object
VIII Calculate the:
a) area of image
b) area of object
c) scale factor
of an enlargement
IX
Solve problems involving enlargement
PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
15/5 26/5
CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN
28/5 11/6
I
Determine if an equation is a linear
equation in two variables
II
Write linear equations in two variables
from given information
III
Determine the value of a variable given
the other variables
IV
Determine the possible solutions for a
linear equation in two variables
I
II
III
Determine if two given equations are
simultaneous linear equations
Solve two simultaneous linear equations
in two variables by
a) substitution
b) elimination
Solve problems involving two
simultaneous linear equations in two
variables
Contextual
learning
Arranging
sequentially
ICT
Logical reasoning
Communication
Recognizing and
representing
Mastery
learning
Arranging
sequentially
Rational
Systematic
Tolerance
Cooperation
Logical reasoning
Finding all possible
solutions
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
WEEK
26 - 28
12.
Linear
Inequalities
12.1
Understand and use
the concept of
inequalities
26/6 14/7
II
III
12.2
Understand and use
the concept of linear
inequalities in one
unknown
I
II
III
Identify the relationship:
a) greater than
b) less than
based on given situations
Write the relationship between two given
numbers using the symbol > or <
Identify the relationship:
a) greater than or equal to
b) less than or equal to
based on given situations
Determine if an given relationship is a
linear inequality
Determine the possible solutions for a
given linear inequality in one unknown:
a) x > h
b) x < h
c) x h
d) x h
Represent a linear inequality:
a) x > h
b) x < h
c) x h
d) x h
on a number line and vice versa
Construct linear inequalities using
symbols:
a)
> or <
b)
or
From given information
Contextual
learning
Estimating
Consistent
Classifying
Honesty
Communication
Method of
learning
Systematic
Mastery
learning
Arranging
sequentially
Constructivism
Making
generalizations
Sincerity
Punctuality
Contextual
learning
Using algorithm
and relationship
Rational
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
12.3
I
Perform computations
involving addition,
subtraction,
multiplication and
division on
II
inequalities
III
State a new inequality for a given
inequality when a number is:
a) added to
b) subtracted from
both sides of the inequalities
State a new inequality for a given
inequality when both sides of the
inequalities are:
a) multiplied by a number
b) divided by a number
Construct inequalities
a) x k m k
b) x k m k
c) kx km
d)
Mastery
learning
Making
generalization
Diligence
Systematic
Constructivism
Identifying
relations
Mastery
learning
Arranging
sequentially
Systematic
Mastery
Using analogies
Determination
x
m
k
k
from given information
12.4
I
Perform computations
to solve inequalities in
one variables
II
III
12.5
Solve a linear inequality by:
a) adding a number
b) subtracting a number
on both sides of the inequality
Solve a linear inequality by:
a) multiplying a number
b) dividing a number
on both sides of the inequality
Solve linear inequalities in one variable
using a combination of operations
Represent the common values of two
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Interpreting /
Translating
Cooperation
Students will be able to:
DATE
Understand the
concept of
simultaneous linear
inequalities in one
variable
WEEK
29
13.
Graphs Of
Functions
13.1
Understand and use
the concept of
functions
II
III
I
II
17/7 21/7
III
13.2
I
II
III
IV
WEEK
30 - 31
24/7 4/8
14.
Ratios, Rates
And Proportions
II
14.1
Understand the
concept of rate and
perform computations
involving rates
I
II
III
simultaneous linear inequalities on a
number line
Determine the equivalent inequalities for
two given linear inequalities
Solve two simultaneous linear
inequalities
State the relationship between two
variables based on the given information
Identify the dependent and independent
variables in a given relationship
involving two variables
Calculate the value of the dependent
variable, given the value of the
independent variable
Construct tables of values for given
functions
Draw graphs of functions using given
scale
Determine from graph the value of y,
given value of x, and vice versa
Solve problems involving graphs of
functions
Determine the rates involved in given
situations and identify the two quantities
involved
Calculate the rate given two different
quantities
Calculate a certain quantity given the
rate and the other quantity
learning
Communication
Politeness
Cooperative
learning
Working out
mentally
Enquiry
discovery
Drawing diagrams
Punctuality
Interpreting
Rational
Mastery
learning
Making inferences
Sharing
Contextual
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Rational
Mastery
learning
Identifying
relations
Diligence
Multiple
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
IV
14.2
Understand and use
the concept of speed
V
I
II
III
IV
V
14.3
Understand and use
the concept of
average speed
I
II
III
14.4
Understand and use
the concept of
acceleration
I
II
Convert rates from one unit of
measurement to another
Solve problems involving rates
Identify the two quantities involved in
speed
Calculate and interpret speed
Calculate:
a) the distance, given the speed
and the time
b) the time, given the speed and
the distance
Convert speed from one unit of
measurement to another
Differentiate between uniform speed and
non uniform speed
Calculate the average speed in various
situations
Calculate:
a) the distance, given the average
speed and the time
b) the time, given the average
speed and the distance
Solve problems involving speed and
average speed
intelligence
Identify the two quantities involved in
acceleration
Calculate and interpret acceleration
Contextual
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Mastery
Identifying
Contextual
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Mastery
learning
Identifying
relations
Rational
Diligence
Multiple
intelligence
Contextual
learning
Recognizing and
representing
Rational
Diligence
Mastery
learning
Identifying
relations
Multiple
intelligence
Rational
Diligence
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
WEEK
32 - 33
7/8 18/8
15.
Trigonometry
15.1
Understand and use
tangent of an acute
angle in a right
angled triangle
II
III
IV
15.2
I
Understand and use
II
sine of an acute angle
in a right angled
III
triangle
15.3
Understand and use
cosine of an acute
angle in a right
angled triangle
15.4
I
II
III
Identify the:
a) hypotenuse
b) the opposite side and the
adjacent side with respect to
one of the acute angles
Determine the tangent of an angle
Calculate the tangent of an angle given
the lengths of sides of the triangle
Calculate the lengths of sides of a
triangle given the value of tangent and
the length of another side
Determine the sine of an angle
Calculate the sine of an angle given the
lengths of sides of the triangle
Calculate the lengths of sides of a
triangle given the value of sine and the
length of another side
Determine the cosine of an angle
Calculate the cosine of an angle given
the lengths of sides of the triangle
Calculate the lengths of sides of a
triangle given the value of cosine and
the length of another side
Calculate the value of other
learning
relations
Multiple
intelligence
Communication
Logical reasoning
Punctuality
Mastery
learning
Representing and
interpreting
Determination
Simulation
Communication
Logical reasoning
Punctuality
Mastery
learning
Representing and
interpreting
Determination
Communication
Simulation
Logical reasoning
Mastery
learning
Representing and
interpreting
Punctuality
Determination
Simulation
Mastery
Comparing and
Cooperative
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Students will be able to:
DATE
Use the values of
tangent, sine and
cosine to solve
problems
II
III
IV
trigonometric ratios given the value of a
trigonometric ratio
Convert the measurement of angles
from:
a) degrees to degrees and minutes
b) degrees and minutes to degrees
Find the value of:
a) tangent
b) sine
c) cosine
of 300, 450 and 600 without using
scientific calculator
Find the value of:
a) tangent
b) sine
c) cosine
using scientific calculators
Find the angles given the values of:
d) tangent
e) sine
f) cosine
using scientific calculators
Solve problems involving trigonometric
ratios
learning
differentiating
Multiple
intelligence
Sharing
Finding all possible
solutions
Diligence
Cooperative
learning
Self access
learning
ICT
PROGRAM PENINGKATAN PRESTASI PT3 (PERCUBAAN)
Estimating
Scheme Of Work Form 3
WEEK
LEARNING
AREA
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES
LEARNING OUTCOMES
GENERICS
Students will be able to:
DATE
4/9 -6/9
CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2
9/9 17/9
PROGRAM INTENSIF PEMBELAJARAN (LATIHAN BERFOKUS)
25/9 6/10
PENTAKSIRAN TINGKATAN 3 - PT3
11 / 10 13/10
CCTS
MORAL
VALUES
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareDokument18 SeitenSolving Quadratic Equations by Completing The SquareLeo EvidorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awesome OrigamiDokument17 SeitenAwesome OrigamiHaritha100% (6)
- Solution:: 2-8 Systems of Equations in Three VariablesDokument28 SeitenSolution:: 2-8 Systems of Equations in Three VariablesHasan EserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan MATHDokument7 SeitenSemi Detailed Lesson Plan MATHEllamarie Salvacion83% (12)
- Melc Math PDFDokument28 SeitenMelc Math PDFAna Carla de CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matematik PT3Dokument16 SeitenMatematik PT3Muhammad Aliff Abdul Rahman40% (5)
- Matematik PT3Dokument16 SeitenMatematik PT3Muhammad Aliff Abdul Rahman40% (5)
- Differential Calculus Das MukherjeeDokument224 SeitenDifferential Calculus Das MukherjeeYousuf AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kbat Kimia SPMDokument9 SeitenKbat Kimia SPMZanariah Binti Lihat67% (6)
- Irp Set 1Dokument23 SeitenIrp Set 1CaliphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imogen SlidesCarnivalDokument29 SeitenImogen SlidesCarnivalZarith Emily Burgoa AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Form 3Dokument21 SeitenMathematics Form 3CaliphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muka Hadapan PPGBDokument6 SeitenMuka Hadapan PPGBnoorshafiqahahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Plan-CthDokument4 SeitenDaily Lesson Plan-CthCaliphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hari LahirDokument1 SeiteHari LahirnoorshafiqahahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muka Depan KimiaDokument1 SeiteMuka Depan KimiaCaliphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Soalan Saintis MudaDokument18 SeitenContoh Soalan Saintis MudaEllie EllaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Dokument15 SeitenSPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Jia Hui JoanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Scientific Investigation.Dokument32 SeitenChapter 1 Scientific Investigation.CaliphNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABM TampalDokument3 SeitenABM TampalCaliphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Design (CE 207, CE 213) Chapter No. 1 - Part No. 2Dokument5 SeitenLogic Design (CE 207, CE 213) Chapter No. 1 - Part No. 2Freyja SigurgisladottirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Trigo-I Exercise 2cDokument20 SeitenAdv Trigo-I Exercise 2cScientistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics Number Systems GuideDokument22 SeitenDigital Electronics Number Systems GuideBrayaño SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disha Mathematics Revision (LDokument9 SeitenDisha Mathematics Revision (LDakshay AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomials (Lecture Notes)Dokument43 SeitenPolynomials (Lecture Notes)Muhammad AmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pentaksiran Year 1 March 2020Dokument12 SeitenPentaksiran Year 1 March 2020Nor FarehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT175 SamplefinalexamDokument2 SeitenMAT175 SamplefinalexamKkko FhfutNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGINEERING GRAPHICS TITLEDokument39 SeitenENGINEERING GRAPHICS TITLEsugunay123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 MergedDokument84 Seiten1 MergedSadaf NaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 SolutionsDokument38 SeitenChapter 17 SolutionsIvánVillanuevaGavidiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT 1320 DGD WorkbookDokument120 SeitenMAT 1320 DGD WorkbookAurora BedggoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Algebraaic ExpressionsDokument33 SeitenChapter 7 Algebraaic Expressionsnaza9775100% (2)
- AnswersDokument324 SeitenAnswersmajd ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 SpheresDokument2 Seiten10 SpheresSaiteja RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Problems for IIT JEE Rank Boosting CourseDokument2 SeitenArea Problems for IIT JEE Rank Boosting Coursemanoj sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEG11MathPTPaper 12 06 10Dokument12 SeitenNEG11MathPTPaper 12 06 10Rosemarie Velasco DalupangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions of AnglesDokument54 SeitenChapter 5: Trigonometric Functions of AnglesJames LangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic Design: Binary Codes and OperationsDokument33 SeitenDigital Logic Design: Binary Codes and Operations20R25A0420 KONDAMUDI VAMSI ANURAG100% (1)
- Tobago Condary Entrance Assessment: AprilDokument23 SeitenTobago Condary Entrance Assessment: AprilAnna Del Rey ValtersenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Playing With Numbers Class 6 Maths Formulas - Formulae List of Class 6 Playing With NumbersDokument4 SeitenPlaying With Numbers Class 6 Maths Formulas - Formulae List of Class 6 Playing With NumbersdeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1 Marks For Class 12Dokument6 SeitenMath 1 Marks For Class 12Gokul krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerDokument5 SeitenMath GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerGab AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Science Model Paper 2024Dokument90 Seiten12th Science Model Paper 2024ps2616921Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 1 80Dokument80 SeitenEngineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 1 80Epimaque NkurunzizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB - Number Systems and ConversionsDokument30 SeitenIB - Number Systems and ConversionsMd Sifat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen