Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
IMCI Job-Aid Users' Manual: Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Imci) : Age 0 To 2 Months
Hochgeladen von
COMDIS-HSDOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IMCI Job-Aid Users' Manual: Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Imci) : Age 0 To 2 Months
Hochgeladen von
COMDIS-HSDCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
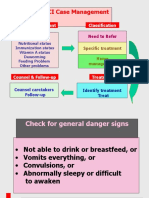
INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD ILLNESS (IMCI): AGE 2 MONTHS UP TO 5 YEARS
USE ALL BOXES THAT MATCH THE CHILDS SYMPTOMS TO CLASSIFY THE ILLNESS
1. Greet, look for danger signs or emergency signs. If any present, manage urgently according to the job aid.
Check: age and whether patient has an acute illness or is a follow-up.
2. Ask: `What is your problem? `How long you had the problem? `Any other problems? Learn also about their
concerns.
3. Look, listen and feel for the signs and symptoms in the first column for each problem.
4. Classify, Start at the top of the classification table according to patients problems. Assess `IF signs present:
start from the top pink (signs for severe), then yellow row, then green row signs. Once you find a
row/classification, do not go down any further in that box.
5. Treat according to the classification in the right hand column. If classified in the pink row, arrange urgent
referral; if yellow treat condition and arrange follow up in 2 days unless stated otherwise. Mild illnesses are
coloured in green. These patients need only symptomatic treatment and preventive advice, but no antibiotic.
For all classifications, explain when to return urgently.
6. Give preventive care and advice related to their problems.
SYMPTOMS FOUND
IF
GENERAL DANGER SIGNS Any danger sign present
NOT ABLE TO DRINK OR
BREASTFEED
VOMITS EVERYTHING
CONVULSIONS (Has or
hashad)
LETHARGIC/UNCONSCIOUS
THEN CLASSIFY
VERY SEVERE
DISEASE
TREATMENT
Advise mother to ensure appropriate
feeding to prevent low blood glucose
level
Advise mother to keep her child warm
Refer URGENTLY to Upazila Health
Complex (UHC)
If a child has any general danger sign, he/she needs urgent care: assess quickly to give prereferral treatment and refer to UHC urgently
COUGH OR DIFFICULT
BREATHING
For how long?
Count the breaths in one
minute (Record in register)
Age
2mo. 12 mo.
Fast breathing
50 breaths per
min or more
40 breaths per
min or more
Check if: (Child must be calm)
CHEST INDRAWING
WHEEZE
STRIDOR
Any general danger sign
OR
Chest in-drawing or
Stridor
Fast breathing
(according to age)
No signs of
pneumonia or very
severe disease
SEVERE
PNEUMONIA
OR VERY
SEVERE
DISEASE
PNEUMONIA
NO PNEUMONIA: COLD,
COUGH
SYMPTOMS FOUND
One of the following
DIARRHOEA
Ask if the child has diarrhoea? signs:
Lethargic or uncon
If yes ask:
scious
For how long?
Sunken eyes
- Record in register, and
Not able to drink or
If > 14 days is persistent
drinks poorly
and see rows below
Skin pinch goes back
Is there blood in stool?
very slowly
Check if:
LETHARGIC OR
UNCONSCIOUS?
RESTLESS AND IRRITABLE?
SUNKEN EYES?
GIVE FLUID TO CHECK:
- NOT ABLE TO DRINK OR
DRINKS POORLY?
- DRINKS EAGERLY
(THIRSTY)/
SKIN PINCH GOES BACK
- VERY SLOWLY (takes
more than 2 seconds)?
- SLOWLY?
If > 14 days is persistent =>
Give rst dose of amoxicillin (if able to
take)
Give paracetamol if temp is 101 oF or
above
Ensure appropriate feeding to prevent
low blood glucose level
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
Treat with amoxicillin for 5 days
If wheezing give salbutamol for 5 days
If coughing >21 days, or recurrent
wheeze, refer to UHC for diagnosis
Advise mother when to return
URGENTLY
Follow up in 2 days
If wheezing give salbutamol for 5 days
If coughing >21 days, or recurrent
wheeze, refer to UHC for diagnosis
Soothe the throat and relieve the cough
with a safe remedy
Advise mother when to return
URGENTLY
Follow-up in 2 days if not improving
IF
SEVERE
DEHYDRATION
One of the following
signs:
Restless and irritable
Drinks eagerly
(thirsty)
Skin pinch goes back
slowly
SOME
DEHYDRATION
Not enough signs to
classify as some or
severe dehydraon
NO
DEHYDRATION
14 days or more
diarrhoea and dehydraon present
14 days or more
diarrhoea and no
dehydraon
If blood in the stool = >
THEN CLASSIFY
Blood in stool
SEVERE
PERSISTENT
DIARRHOEA
PERSISTENT
DIARRHOEA
DYSENTERY
TREATMENT
Refer URGENTLY to UHC. Ask mother to
give frequent sips of ORS on the way (if
the child can drink)
Give ORS in clinic for 4 hours and reassess
(Plan B)
Ask mother to also connue breast feeding
Give ZINC supplements for 10-14 days
Advise the mother when to return urgently
Follow up in 2 days if not improving
Counsel the mother on home treatment
(Plan A):
- Give extra uid
- Give ZINC supplements for 10-14
days
- Connue feeding
- Advise the mother when to return
urgently
- Follow up in 2 days if not improving
Refer URGENTLY to UHC with mother
giving frequent sips of ORS as soon as
the child can drink.
Give uid and food to treat diarrhoea
at home
Advise mother on feeding at home
Give ZINC tablet for 10-14 days
Follow up in 5 days
Give cotrimoxazole for 5 days
and advise mother on home care
Give ZINC tablets for 10-14 days
Follow up in 2 days
SYMPTOMS FOUND
IF
Any general danger sign
FEVER (NON-MALARIA)
(Fever by history, or feels hot, OR:
Child 3 months or less
or temperature more than
Bulging fontanelle
99.5 F)
Neck sness
Ask:
Non blanching rash
How long has the fever been
Capillary rell > 2
present? (Record in register)
seconds
Check If :
Temperature
CHILD 3 MONTHS OR LESS
102 F if age <6months
BULGING FONTANELLE
Fast breathing
NECK STIFFNESS
Signs of dehydraon
NON BLANCHING RASH
Swelling of, and/or
CAPILLARY REFILL > 2
not using, a arm, leg
SECONDS
or joint
TEMPERATURE 102 C OR
HIGHER IF AGE <6 MONTHS
No cause idened for
SIGNS OF DEHYDRATION
fever AND one or more
(see page above)
RAISED RESPIRATORY RATE of:
Age
2mo. 12 mo.
12mo. 5 yrs.
Fast breathing
50 breaths per
min or more
40 breaths per
min or more
VOMITING
POOR FEEDING
DECREASED ACTIVITY
SWELLING, OR NOT USING
ARM, LEG OR JOINT
RASH
RUNNY NOSE
RED EYES
CLOUDING OF CORNEA
PUS DRAINING FROM EYE
MOUTH ULCERS
RED/INFLAMED/DISCHARGI
NG SKIN OR WOUND
ABDOMINAL/ LOIN PAIN
PASSING URINE OFTEN
PAIN ON PASSING URINE
JAUNDICE
THEN CLASSIFY
MENINGITIS/
SEVERE FEBRILE
DISEASE
TREATMENT
Give rst dose of amoxicillin syrup or
cotrimoxazole tablet
Advise mother about proper feeding to
avoid glucose insuciency
Give one dose of paracetamol if
temperature is equal or more than 101 oF
AND
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
SEPTIC
JOINT or BONE
Refer to UHC
POSSIBLE UTI
Refer to UHC for urine test and treatment
FEVER (CAUSE
UNKNOWN)
FEVER (POSSIBLY
MALARIA)
(Fever by history, or feels
hot, or temperature more
than 99.5 F)
RDT posive and:
Any general danger
sign or
Neck sness
If lives in, or has visited a
malarial endemic area:
(Chiagong, Coxes Bazar,
Rangama, Bandarban,
Khagrachari)
EAR PROBLEM
EAR PAIN
EAR DISCHARGE
AND NUMBER OF DAYS
MALNUTRITION
SKIN INFECTION
Refer to UHC
Generalised rash
AND
Runny nose or red eyes
MEASLES
Apply cloramphenicol eye ointment if pus
in the eye
Treat mouth ulcers with 0.25% genan
violet
If clouding of cornea/extensive mouth
ulcers, give rst dose of amoxicillin and
refer URGENTLY to UHC
Review in 2 days
Also look for:
Clouding of cornea
Pus draining from eye
Mouth ulcers
MILD VIRAL
ILLNESS
Give paracetamol if temperature is more
than 101 F
Advise when to return immediately
Return in 2 days if fever persists
Refer to UHC if fever persists 7 days
RDT posive
THEN CLASSIFY
Assess malnutrion:
Use MUAC( Mid Upper
Arm Circumference)
tape to detect red,
yellow or green colour
Check if:
Oedema of both feet
TREATMENT
MALARIA OR
SEVERE FEBRILE
DISEASE
Give an-malarial medicine according to
naonal guideline
Give rst dose of amoxicillin
Advise mother to ensure appropriate
food or drink to prevent low blood
glucose
Give paracetamol if temperature is more
than 101 F
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
MALARIA
Give an-malarial medicine according to
naonal guideline
Give paracetamol if temperature is more
than 101 F
Advise when to return immediately
Follow up in 2 days
For non malarial area if an malarial
drugs are not available refer to UHC
PERFORM A RDT
Refer to UHC for further invesgaons
and treatment
Red/ inamed/
discharging skin or
wound
Runny nose, or red
throat or cough, AND
Alert or easily woken,
acve child
Drinking normally
IF
PUS DRAINING FROM EAR
TENDER SWELLING BEHIND
THE EAR
Voming
Poor feeding
Decreased acvity
Abdominal/loin pain
Passing urine more oen
Pain on passing urine
No cause idened for
fever
AND
If jaundice present
OR
If fever present 7
days or more
SYMPTOMS FOUND
Tender swelling
behind the ear and
pain
MASTOIDITIS
Pus draining from the
ear and discharge is
reported for less
than 14 days OR
Ear pain
ACUTE EAR
INFECTION
Pus draining from
the ear and
discharge is
reported for 14 days
or more
CHRONIC EAR
INFECTION
No ear pain and no
pus draining from
the ear
NO EAR
INFECTION
No treatment
MUAC measure
ment indicang red
colour(less than11.5
cm)
SEVERE
MALNUTRITION
Give vitamin A
Ask mother to ensure appropriate feeding
to avoid low blood glucose level
Keep the child warm
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
Oedema of both feet
Give 1st dose of oral amoxicillin
Give one dose of paracetamol for pain
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
Give amoxicillin for 5 days
Give paracetamol for pain
Ask to dry the ear by wicking
Follow up in 5 days
Dry the ear by wicking
Refer to UHC
MUAC measurement
indicang yellow
colour
(11.5-12.5 cm)
MALNUTRITION
MUAC measurement
indicang green
colour (more than
12.5 cm)
NO
MALNUTRITION
If child is less than 2 years old, assess the
childs feeding and counsel the mother on
feeding according to the advice chart
If feeding problem follow up in 5 days
ANAEMIA
Severe palmar pallor
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
Check if:
Some palmar pallor
SEVERE
ANAEMIA
ANAEMIA
SEVERE PALMAR PALLOR
SOME PALMAR PALLOR
NO PALMAR PALLOR
No palmar pallor
NO ANAEMIA
Assess the childs feeding and counsel the
mother on feeding according to the
advice chart
Follow up in 14 days
If feeding problem follow up in 5 days
Give iron syrup and folic acid for 14 days
Give albendazole if child is 2 year or older
and has not had a dose in previous 6
months
Assess the childs feeding and counsel the
mother on feeding according to the advice
chart
If malaria risk area, perform RDT
Advise mother when to return immediately
Follow up in 14 days
if child is 6 months or older give iron syrup
and folic acid to avoid anaemia
Assess childs immunizaon:
BCG, Pentavalent-1, Pentavalent-2, Pentavalent-3, Polio-1, Polio-2, Polio-3, Measles and Vitamin A. If a child has any
general danger sign then do rest of the assessment quickly and refer the child URGENTLY to Upazila Health Complex.
INTEGRATED MANAGEMENT OF CHILDHOOD ILLNESS (IMCI): AGE 0 TO 2 MONTHS
SYMPTOMS FOUND:
ASK:
Has the infant had convulsions?
Is the infant feeding well?
LOOK,LISTEN,FEEL:
Is the young infant lethargic
or unconscious
Look at the young infants
movements. If the
infant is sleeping ask the
caregiver to wake him/her.
- Does the child move on
his/her own?
-Does the child move only
when smulated?
- Does the infant not move
at all?
Count the breaths in one
minute. Repeat the count if
elevated (60 breaths per
minute or more)
Check whether severe chest
indrawing
Observe and feel for bulging
fontanelle
Measure temperature
Look for jaundice (yellow
eyes or skin)
Check for dehydraon:
- Is the child restless and
irritable?
- Look for sunken eyes
- Pinch the skin on the
- abdomen; does it go back
slowly?
Draining pus from the ear?
Look at the umbilicus. Is it
red and does the redness
extend to the skin?Is it
draining pus?
Look for skin pustules
IF
Lethargic or uncon
scious or
Movement only
when smulated or
no movement
Unable to suck
breast milk or
Convulsions or
Fast breathing (60
breaths per
minute or more) or
Severe chest
indrawing or
Grunng or
Bulging fontanelle or
Fever (above 99.5 F)
or low body
temperature (below
95.9 F) or
Jaundice and:
- Less than 24 hours
old
- More than 3 weeks
old
- Yellow palms and
soles any age or
THEN CLASSIFY
VERY
SEVERE
DISEASE
TREATMENT
Treat to prevent low blood sugar level
If child can breast feed:
Advise mother to connue breast feeding
If child cant breast feed:
Ensure drinking extracted breast milk or
water with sugar (Add 20 gm sugar into
200 ml of water)
Refer URGENTLY to UHC
Advise mother how to keep the infant
warm on the way to the UHC
If dehydrated, advise mother to give
frequent sips of ORS on the way to UHC
Give 1st dose of amoxicillin if child can
take
Establish eecve communicaon with the paent by following steps of WELL (Welcome, Encourage, Look and Listen) as described in
your communicaon guide.
Keep the job-aid in front of you (beside the register book) while talking to the paent. You will be able to look at the job-aid for what
to ask and observe while talking to the paent without any hurdle. The job-aid will guide you to nd the symptoms and diagnose the
paent and will also help you remember proper management of the paent. This will avoid unnecessary delay in diagnosing fatal
illness and emergency referral to Upazila Health Complex.
Dehydraon or
Pus draining from the
ear or
Umbilical redness
extending to the skin
or draining pus
Ask about common danger signs in every child and observe the signs, e.g. drinking dicules, less movement, etc. Ask whether child
is suering from cough, fever or diarrhea. If problem is idened, please see the relevant part of the job-aid. For an example, go to
cough/breathing diculty part if the paent complains cough/breathing diculty. Ask how long the paent suering from cough and
look for symptoms, e.g. breath per minute.
To examine symptoms of serious illness, look at the pink column rst. If any danger sign observed, it would be fatal illness and it is
necessary to urgently refer to Upazila Health Complex.
LOCAL
BACTERIAL
INFECTION
Assess for jaundice (yellow
eyes or skin)
Jaundice appearing
aer 24 hours of age
and less than 3 weeks
of age AND
Palms and soles not
yellow
JAUNDICE
Advise the mother to give home care for
the young infant
Advise the mother to return immediately
if palms and soles appear yellow
Follow up in 1 day
Does the young infant have
diarrhoea*?
*A young infant has diarrhoea if
the stool have changed from the
usual paern and are very
frequent and watery (more
water than faecal maer).
The normally frequent and
semi-solid stools of a breased
baby are not diarrhoea.
No signs of dehydra
on
DIARRHOE
A WITH NO
DEHYDRATION
Give ORS at home for diarrhoea and
connue breaseeding (Plan A)
Advise mother when to return immediately
Follow up in 2 days if not improving
Is pus draining from the eye?
Sign of mouth ulcers or thrush?
Look at the umbilicus for
redness, not extending to the
skin
Is there any skin pustules?
Diagnosis and management instrucons for six common childhood illnesses (cough/breathing diculty, diarrhea, fever, ear problem,
malnutrion and anemia) are given in this job-aid.
Please use page 1 to 4 if age of child is between 2 month and 5 years. Use page 5 for children from 0 to 2 month.
Pus draining from the
eye
Mouth ulcers or
thrush
Umbilical redness not
extending to the skin
and no pus
Skin pustules but not
extensive or severe
Assess for limited local infecons
IMCI Job-Aid Users Manual
If there is pus draining from the eye, treat
with chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops
If there are mouth ulcers treat with 0.25%
genan violet soluon
Treat skin pustules or umbilical redness
with 0.25% genan violet soluon
Review in 2 days and if not improving,
refer to UHC
If no symptoms exist as given in the pink row, look the yellow row for symptoms. If any sign/symptom is observed, provide treatment
and ask for a follow-up in 2 days. A symptom in yellow row indicates that it is possible to treat the paent at the community clinic. But
if medicine or test facilies are not available at the community clinic, advice the paent to go to Upazila Health Complex.
If no sign exists to classify the disease in the pink and yellow row, please look at the green row. These are non-severe diseases; it will
be enough to advice and provide medicaon like Paracetamol. Green row indicates less severe diseases. Paents should not be
prescribed anbiocs, only advice depending on symptoms and observing deterioraon will be required.
If you are not sure about the disease, ask him/her to wait outside. Take your me and use your training manual, job-aid, etc. to decide
on symptoms, disease classicaon and treatment. Otherwise ask the paent to visit again next day for proper treatment.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IMCIDokument42 SeitenIMCIMichael Anthony ErmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessesDokument12 SeitenIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessesRaul Suzara100% (1)
- Integrated Prevention and Management of Selected Acute and Chronic Illness (IPMSACI) - Job AidDokument9 SeitenIntegrated Prevention and Management of Selected Acute and Chronic Illness (IPMSACI) - Job AidCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 4: Main SymptomsDokument86 SeitenSession 4: Main SymptomszerpthederpNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI NewDokument81 SeitenIMCI NewBianca de GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness Flip ChartDokument78 SeitenIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness Flip ChartkjtomananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe The Four Main Symptoms of ImciDokument2 SeitenDescribe The Four Main Symptoms of ImciMartha JulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCIDokument2 SeitenIMCIxtinemarie_d4977Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI Guideline-2023 HeshamElsayedDokument57 SeitenIMCI Guideline-2023 HeshamElsayedMalak Rageh100% (2)
- IMCI-sverreview 2011versionPDFDokument45 SeitenIMCI-sverreview 2011versionPDFNicole PageNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI NewDokument151 SeitenIMCI NewDiana Lane CunananNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI Case Management: Classification Focused AssessmentDokument42 SeitenIMCI Case Management: Classification Focused AssessmentSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCIDokument112 SeitenIMCIJohann Dexter Malimban GloriosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI UpdatedDokument5 SeitenIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ask The Mother What The Child's Problems Are. - Determine If This Is An Initial or Follow-Up Visit For This ProblemDokument43 SeitenAsk The Mother What The Child's Problems Are. - Determine If This Is An Initial or Follow-Up Visit For This ProblemJoereyConelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Management of Ari at PHC LevelDokument29 SeitenCase Management of Ari at PHC Levelapi-3823785Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDokument195 SeitenIntegrated Management of Childhood Illnesskarendelarosa06277100% (1)
- IMCI 2011 Chart BookletDokument14 SeitenIMCI 2011 Chart BookletYam Theresa Remo100% (1)
- Common Childhood Illness Week 12Dokument76 SeitenCommon Childhood Illness Week 12Hydra Olivar - PantilganNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI Revised For CHN 1 NEW 1st Sem 2022Dokument82 SeitenIMCI Revised For CHN 1 NEW 1st Sem 2022Aech Euie100% (1)
- IMCI ChartDokument33 SeitenIMCI Chartrazorblades0012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDokument43 SeitenIntegrated Management of Childhood IllnessMark LugtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSM 5 ImnciDokument52 SeitenPSM 5 ImnciAnagha M NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rash Ihuman Case Study 2022 2023Dokument6 SeitenRash Ihuman Case Study 2022 2023muthiimorris68Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI Nov 2009Dokument141 SeitenIMCI Nov 2009togononkaye100% (1)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses: By: Richelle Anne C. Paliuanan, MSNDokument65 SeitenIntegrated Management of Childhood Illnesses: By: Richelle Anne C. Paliuanan, MSNcheng_leo21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management of Chilhood IllnessesDokument12 SeitenIntegrated Management of Chilhood Illnessescorpuzdarryl3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine CompleteDokument93 SeitenMedicine CompletefdjslajfNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI ReviewDokument39 SeitenIMCI Reviewsue_cideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imci NotesDokument76 SeitenImci Notesjekeri bekeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Management On Childhood Illnesses 0101Dokument132 SeitenIntegrated Management On Childhood Illnesses 0101James Felix Gallano Gales100% (1)
- The Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDokument83 SeitenThe Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesssay04yaocincoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCIDokument87 SeitenIMCIbibs_caigas3744100% (1)
- Management of The Sick Child Aged 2 Months Up To 5 YearsDokument4 SeitenManagement of The Sick Child Aged 2 Months Up To 5 YearsJade TyshurnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cough, Pediatric: What Are The Causes?Dokument2 SeitenCough, Pediatric: What Are The Causes?astarimediantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paeds Complete PDFDokument176 SeitenPaeds Complete PDFjljoioiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 - IMCI - 2mos To 5 YearsDokument62 Seiten9 - IMCI - 2mos To 5 YearsCARMENCITA PACISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health PoliciesDokument3 SeitenHealth Policiesdongpc1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5Dokument66 SeitenGroup 5Cms CSUNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCIDokument35 SeitenIMCIharutoshippuden0Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI Technical UpdatesDokument3 SeitenIMCI Technical Updatesmikaela_pascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EtatDokument121 SeitenEtatBhoja Raj GAUTAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI - ContentDokument13 SeitenIMCI - ContentMarianne Daphne GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care For The Child in Hospital: How To Identify and Treat Children Who Need Urgent CareDokument22 SeitenCare For The Child in Hospital: How To Identify and Treat Children Who Need Urgent CareDahrren Grace JalonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Soap NotesDokument8 SeitenPediatric Soap Noteskenata100% (1)
- IMCIDokument87 SeitenIMCImark100% (3)
- Assess DiarrheaDokument21 SeitenAssess DiarrheaMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 002 Assesment For Cough and Difficult BreathingDokument36 Seiten002 Assesment For Cough and Difficult BreathingSuhazeli AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI - Chart BookletDokument39 SeitenIMCI - Chart BookletJason MirasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCIDokument116 SeitenIMCIPAUL MICHAEL G. BAGUHIN0% (1)
- Sick Young Infants (Referral, Treatment, Oral Drugs) : ImnciDokument46 SeitenSick Young Infants (Referral, Treatment, Oral Drugs) : ImnciTanviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imci Diarrhoea Homework#2Dokument9 SeitenImci Diarrhoea Homework#2Cherub ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Danger Signs and Main Symptoms of Cough Difficult BreathingDokument32 SeitenGeneral Danger Signs and Main Symptoms of Cough Difficult Breathingnasibdin50% (2)
- Care of The Child Applying Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (Imci)Dokument22 SeitenCare of The Child Applying Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (Imci)Jesena SalveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases, Acute Diarrhoeal DiseasesDokument60 SeitenControl of Diarrhoeal Diseases, Acute Diarrhoeal DiseasesSamarjeet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Fever and AntibioticsDokument13 SeitenApproach To Fever and Antibioticsasraf amirullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunizationDokument6 SeitenImmunizationshwetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emesis, (Vomiting) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandEmesis, (Vomiting) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Using Behaviour Change Interventions To Decrease Tobacco Use in NepalDokument4 SeitenUsing Behaviour Change Interventions To Decrease Tobacco Use in NepalCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decentralising Non-Communicable Disease Care in The Kingdom of Eswatini: Successes, Challenges and Recommendations From A Pilot Study in Lubombo RegionDokument8 SeitenDecentralising Non-Communicable Disease Care in The Kingdom of Eswatini: Successes, Challenges and Recommendations From A Pilot Study in Lubombo RegionCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expanding Mental Health Care in The Kingdom of Eswatini: Successes, Challenges and Recommendations From Initial Experiences in Lubombo RegionDokument8 SeitenExpanding Mental Health Care in The Kingdom of Eswatini: Successes, Challenges and Recommendations From Initial Experiences in Lubombo RegionCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supporting Roll-Out of Revised Dengue Prevention and Control Guidelines in MyanmarDokument8 SeitenSupporting Roll-Out of Revised Dengue Prevention and Control Guidelines in MyanmarCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Gender Mainstreaming Is Important When Planning and Implementing Health Interventions: Examples From COMDIS-HSDDokument6 SeitenWhy Gender Mainstreaming Is Important When Planning and Implementing Health Interventions: Examples From COMDIS-HSDCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Use of Antibiotics by Community Health Workers (CHWS) and Caregivers in ZambiaDokument1 SeiteRational Use of Antibiotics by Community Health Workers (CHWS) and Caregivers in ZambiaCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influencing TB Policy and Practice in Bangladesh Using A Public-Private Mix ApproachDokument2 SeitenInfluencing TB Policy and Practice in Bangladesh Using A Public-Private Mix ApproachCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Rational Use of Antibiotics in Childhood Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Rural ChinaDokument2 SeitenImproving Rational Use of Antibiotics in Childhood Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Rural ChinaCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Male Circumcision: Do Women in Swaziland Welcome It For Their Sons and at What Age?Dokument4 SeitenMedical Male Circumcision: Do Women in Swaziland Welcome It For Their Sons and at What Age?COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Can Public-Private Partnerships Enhance The Use of Long Acting Contraceptive Methods in Bangladesh?Dokument4 SeitenHow Can Public-Private Partnerships Enhance The Use of Long Acting Contraceptive Methods in Bangladesh?COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving The Quality of Care at Community Clinics in Rural Bangladesh Through New ApproachesDokument4 SeitenImproving The Quality of Care at Community Clinics in Rural Bangladesh Through New ApproachesCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Treatment For Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis Patients - Lessons From Shandong Province, ChinaDokument2 SeitenImproving Treatment For Multi-Drug Resistant Tuberculosis Patients - Lessons From Shandong Province, ChinaCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Country Public-Private Partnerships Hold The Key To Promoting Inclusiveness in Dutch Trade and International Cooperation AgendaDokument2 SeitenIn-Country Public-Private Partnerships Hold The Key To Promoting Inclusiveness in Dutch Trade and International Cooperation AgendaCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Disease Risk Reduction in Rural China - Policy RecommendationsDokument1 SeiteCardiovascular Disease Risk Reduction in Rural China - Policy RecommendationsCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Reporting in The Kathmandu Post, Nepal. September 2013-August 2014Dokument22 SeitenHealth Reporting in The Kathmandu Post, Nepal. September 2013-August 2014COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decentralising Services For Diabetes and Hypertension in Low - and Middle-Income Countries: 6 Key Policy Areas For Service PlannersDokument4 SeitenDecentralising Services For Diabetes and Hypertension in Low - and Middle-Income Countries: 6 Key Policy Areas For Service PlannersCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing Health Systems Challenges For Diabetes Care in PakistanDokument2 SeitenAddressing Health Systems Challenges For Diabetes Care in PakistanCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Behaviour Change Interventions To Decrease Tobacco Use in NepalDokument1 SeiteUsing Behaviour Change Interventions To Decrease Tobacco Use in NepalCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Should National TB Programmes Prioritise Co-Morbid Mental Health Disorders in MDR-TB Patients?Dokument4 SeitenWhy Should National TB Programmes Prioritise Co-Morbid Mental Health Disorders in MDR-TB Patients?COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schistosomiasis: Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices in Nampula Province, MozambiqueDokument2 SeitenSchistosomiasis: Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices in Nampula Province, MozambiqueCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structured pre-ART' Care: A Pathway To Better Health For People With HIVDokument4 SeitenStructured pre-ART' Care: A Pathway To Better Health For People With HIVCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decentralising Non-Communicable Disease Care in The Kingdom of Eswatini: Successes, Challenges and Recommendations From A Pilot Study in Lubombo RegionDokument8 SeitenDecentralising Non-Communicable Disease Care in The Kingdom of Eswatini: Successes, Challenges and Recommendations From A Pilot Study in Lubombo RegionCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schistosomiasis: Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices in Nampula Province, Mozambique (Portuguese Version)Dokument2 SeitenSchistosomiasis: Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices in Nampula Province, Mozambique (Portuguese Version)COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Reporting in The Kathmandu Post: 2013 - 2014Dokument1 SeiteHealth Reporting in The Kathmandu Post: 2013 - 2014COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing Barriers To IPT2 Uptake in UgandaDokument4 SeitenAddressing Barriers To IPT2 Uptake in UgandaCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extended Seasonal Malaria Chemoprevention: Is It Effective and Acceptable in Areas With Longer Rainy Seasons in Ghana?Dokument4 SeitenExtended Seasonal Malaria Chemoprevention: Is It Effective and Acceptable in Areas With Longer Rainy Seasons in Ghana?COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Care For Garment Factory Workers Using PPP in Bangladesh May2013Dokument4 SeitenTB Care For Garment Factory Workers Using PPP in Bangladesh May2013COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women and Their Mental and Social Wellbeing During Multi-Drug Resistant TB Treatment in NepalDokument4 SeitenWomen and Their Mental and Social Wellbeing During Multi-Drug Resistant TB Treatment in NepalCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Health Issues Can Nepali Journalists Write About?Dokument1 SeiteWhat Health Issues Can Nepali Journalists Write About?COMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strengthening Service Delivery For Malaria in Pregnancy - An MHealth Pilot InterventionDokument8 SeitenStrengthening Service Delivery For Malaria in Pregnancy - An MHealth Pilot InterventionCOMDIS-HSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer Case StudyDokument15 SeitenCancer Case StudyRobin HaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tilmicosin Phosphate (Cas 137330-13-3) MSDSDokument7 SeitenTilmicosin Phosphate (Cas 137330-13-3) MSDSMiMi JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand HygieneDokument6 SeitenHand HygieneCarolWestinghouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 5114@wo 2013 39995Dokument6 Seiten10 5114@wo 2013 39995jenny12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bentonite Material Safety Data Sheet PDFDokument6 SeitenBentonite Material Safety Data Sheet PDFWaquar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opioid-Induced Androgen Deficiency in Males (OPIAD Syndrome) : Medicinski Casopis January 2015Dokument7 SeitenOpioid-Induced Androgen Deficiency in Males (OPIAD Syndrome) : Medicinski Casopis January 2015Lilamala LilavelikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteomyelitis Case StudyDokument41 SeitenOsteomyelitis Case StudyJohn Bernard Ting Tizon100% (2)
- Section 1: Organizing Data: Line List Line ListingDokument45 SeitenSection 1: Organizing Data: Line List Line ListingFareeha KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Functional Food Properties of Figs PDFDokument6 SeitenThe Functional Food Properties of Figs PDFChyntia WinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo EquipmentDokument8 SeitenThermo EquipmentlualineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Vestibular Syndrome: David E. Newman-Toker, MD, PHDDokument0 SeitenAcute Vestibular Syndrome: David E. Newman-Toker, MD, PHDArturo CeraciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 5 1st QuarterDokument8 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 5 1st QuarterAndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillar Crypts and Bacterial Invasion of Tonsils: A Pilot StudyDokument4 SeitenTonsillar Crypts and Bacterial Invasion of Tonsils: A Pilot Study'ranu HerjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worry More Live Longer American English Student Ver2 BWDokument5 SeitenWorry More Live Longer American English Student Ver2 BWLanting LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Vitamin You Need To Prevent Prostate CancerDokument3 SeitenThe Vitamin You Need To Prevent Prostate Cancercafjnk100% (1)
- The Phoenix Educator: A LIGHT IN EVERY MIND!: ContactDokument16 SeitenThe Phoenix Educator: A LIGHT IN EVERY MIND!: ContactvitaminveysiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HZVDokument15 SeitenHZVMarviane ThenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyrosine MiaDokument4 SeitenTyrosine MiaHadeer HawasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Sector EHSMS - 9!12!2015Dokument35 SeitenHealth Sector EHSMS - 9!12!2015YL LYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Reproductive HealthDokument10 SeitenPhilippine Reproductive HealthFrankie MacabadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrotherapy in The Treatment of Cancer and VirusesDokument178 SeitenElectrotherapy in The Treatment of Cancer and VirusespitumestresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijms 23 03754Dokument14 SeitenIjms 23 03754Benyam ZenebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Single-Arm Study of Sublobar Resection For Ground-Glass Opacity Dominant Peripheral Lung CancerDokument15 SeitenA Single-Arm Study of Sublobar Resection For Ground-Glass Opacity Dominant Peripheral Lung CancerYTM LoongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bladder 4.1.0.0.rel CapcpDokument19 SeitenBladder 4.1.0.0.rel CapcpkarimahihdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amphotericin B Nephrotoxicity - UpToDateDokument11 SeitenAmphotericin B Nephrotoxicity - UpToDateJuan Diego Fernández MurielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gigantismo PDFDokument4 SeitenGigantismo PDFtonyxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Review ArticleDokument13 SeitenTreatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Review ArticlehoshihopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GuidelinesDokument4 SeitenGuidelinesChidambaram SeevakanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Yttrium OxideDokument6 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Yttrium OxidefructoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Medical ReportDokument6 SeitenAnnual Medical ReportMarvin Joseph AndalNoch keine Bewertungen