Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SHG 37
Hochgeladen von
Suresh RamakrishnanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SHG 37
Hochgeladen von
Suresh RamakrishnanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 1 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
Management of Change Authorization Guideline
and
Pre-Startup Safety Review Guideline
1.0
PURPOSE
To manage changes, and ensure the safe startup/commissioning of changes in compliance with the
Process Safety Management (PSM) program. (OSHA 29 CFR PART 1910.119)
2.0
SCOPE
The Management of Change Authorization (MOCA) guideline will be used to approve a change, and
to document any change that is not "replacement in kind". This guideline covers Temporary,
Permanent, and Emergency Changes. (See MOCA /PSSR form)
The Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR) guideline will be used to assure that all changes are
completed as per the approved MOCA. (See MOCA/PSSR form)
3.0
4.0
DEFINITIONS
Change is meant to include not in kind changes in or additions of: chemicals, technology or
equipment relating to covered processes. See Attachment I for examples of "in kind" and
"not in kind" changes.
Originator the person requesting the change
Covered Process New or existing Operating Units, Tank Farm, Docks, Loading/Unloading
Racks, Lab, Utilities, Pipelines and connecting piping
Process Hazard Analysis an evaluation which identifies, evaluates and recommends
controls of hazards in the process.
RESPONSIBILITY
Responsible
Group /Individual
Originator
Reviewer(s)
Responsibilities
Determine the need for the change.
Correctly fill out Work Notification, if required.
Complete Section A of the Management of Change Authorization
MOCA form as outlined in 6.1.
Assure that reviews under Section "B" are completed and signed.
Return the MOCA to their Department Manager to be resolved at a higher
level if any individual refuses to sign-off under Section "B" for any reason.
Submit any changes to an approved MOCA as a revision to
Directors/Managers (except vents or bleeder valves which shall be
noted on the P&ID)
Review the documentation attached to the MOCA for operability, design,
environmental, safety and health considerations.
Complete Section B of the Management of Change Authorization
MOCA form as outlined in 6.2.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
Department
Directors/
Managers
Owning Area/Craft
Supervisor
Or designee
Section D and E
Assignees
MOCA/PSSR
Coordinator
PSSR Team
5.0
Upon approval of Section A, assure Section B reviewers are assigned.
Assure that required documentation for the change is attached to the
MOCA
Complete the Risk Level Assessment Form (Attachment 3) as appropriate
to determine if a PHA is required for change.
Complete, Section C of the Management of Change Authorization
MOCA form as outlined in 6.3.
Complete, if required, the MANAGERS REQUIREMENT FOR PRESTARTUP SAFETY REVIEW section as outlined in 6.6.
Approve revisions to MOCA.
Void an approved MOCA when necessary.
Review and approve the need for the change.
Coordinate or initiate the work.
When a PSSR is not required, verify that sections B through D of
MOCA are complete before commissioning.
Complete requirements of Section D and/or Section E of the
Management of Change Authorization MOCA form as outlined in 6.4 and
6.5.
Coordinate the PSSR with input from all other departments as outlined in
Section 6.6 and 6.7.
Assure that the change reviewed during the PSSR has been performed
per the approved MOCA.
Complete the Pre-Startup Safety Review as outlined in Section 6.7.
AVAILABILITY
6.0
SHG #37
Page 2 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
Blank MOCA / PSSR forms are available in the Engineering Library or on the
electronic Right to Know stations. Original MOCA/PSSR forms are to consist of one
pink sheet of paper. The MOCA Form is printed on the front of the sheet with the
PSSR printed on the reverse side.
Completed MOCA/PSSRs and associated documentation will be available for review
in the Engineering Library.
GUIDELINES
The following guidelines contain typical instructions for processing a proposed
modification/addition to the refinery, and performing a pre-startup safety review. For special
circumstances such as Emergency Changes, Temporary Changes or MOCAs After Business
Hours refer to Section 7.0, 8.0 or 9.0 for specific instructions for each case.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
6.1.
SHG #37
Page 3 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
SECTION A GENERAL INFORMATION
The intent of this section is to formally document the origination of the Management of Change. In
completing Section A, the originator should provide a detailed description of the proposed
modification, and supply sufficient documentation to obtain approval from the Area Supervisor and
the Originators Department Director or Manager. Section A should be completed by supplying the
following information:
Fill in DATE, W.O./AFE NUMBER, and ORIGINATOR (S) name.
Obtain AREA SUPERVISOR APPROVAL (signature required).
Obtain ORIGINATORS DEPT DIRECTOR/MANAGER APPROVAL (signature required).
Check box(s) for EMERGENCY JOB, PERMANENT CHANGE or TEMPORARY
CHANGE. Reference Sections 7.0, 8.0, and 9.0 for specific instructions concerning,
Emergency Changes or Temporary Changes.
Check a box(s) for REASON FOR CHANGE. If PHA REC # is checked, fill in the
reference number from the PHA report. If OTHER is checked, state the reason.
Fill in EQUIP./INST. MODIFIED (TAG#). Identify the primary affected
equipment/instruments being modified or added.
Write a full detailed description of the modification in DESCRIPTION FOR PROPOSED
CHANGE (ATTACH JUSTIFICATION AS REQUIRED).
Upon completion of Section A, a change review should be performed by the assigned individuals as
specified in Section B.
6.2.
SECTION B REQUIREMENTS FOR CHANGE REVIEW
The intent of this section is to perform a detailed review and obtain approval to ensure operational
requirements, design specifications, environmental, health and safety standards are met. Section B
is completed by having the following information reviewed and approved:
PROCESS SKETCH/OPERABILITY REVIEW - A review of the package to assure operational
requirements are met by reviewing marked up P&IDs, loop drawings, other sketches and/or
other documentation.
BASIC DESIGN REVIEW - A review of the detailed design information to assure that equipment,
piping and other components complies with recognized and generally accepted good
engineering practices. This review will also assure that all required documentation is attached.
ENVIRONMENTAL REVIEW - A review of the documentation to assure compliance with
applicable environmental regulations
HEALTH AND SAFETY REVIEW - A review of the documentation to assure compliance with
applicable OSHA standards, NFPA Standards, Valero company standards, etc.
FACILITY SECURITY REVIEW A review of the documentation to assure compliance with the
Facility Security Plan.
Approval is documented by obtaining the required signature/initials and date from the individual
specified in the department and person column. If any individual refuses to approve the change, the
originator MUST return the MOCA to their Manager or Director to be resolved at a higher level.
Upon completion of Section B, the MOCA package should be submitted to the Directors/ Managers
for review as specified in Section C.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
6.3.
SHG #37
Page 4 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
SECTION C MANAGEMENT REVIEW/APPROVAL
The intent of this section is to obtain final approval from management to perform the work requested
by the Management of Change. Section C is completed by having the following information
reviewed and approved:
TECH. SERVICE The department Manager or designee will review the detailed design
information to assure that equipment, piping and other components have been reviewed against
recognized and generally accepted good engineering practices.
OPERATIONS The department Director or designee will review the initial package to assure
operational requirements are met by reviewing marked up P&IDs, loop drawings, other sketches
and/or other documentation.
MAINTENANCE - The department Director or designee will review the detailed design
information to assure that equipment, piping and other components have been reviewed against
recognized and generally accepted good engineering practices.
HEALTH, SAFETY AND ENVIRONMENTAL - The department Director or designee will review
the documentation against applicable environmental regulations, OSHA standards, NFPA
Standards, Valero company standards, etc.
CONTROL SYSTEMS The department Manager or designee will review the detailed design
information to assure that control systems and logic have been reviewed against recognized and
generally accepted good engineering practices.
Approval of the original MOCA or any revision is documented by obtaining the required signatures
and date from the department Directors or designee. If any individual refuses to sign-off on the
change, the MOCA package is returned to the originator to resolve any documentation issues for resubmittal.
Upon approval in Section C, the Director or designee is to assign responsibilities in Section D and
E. Also, if a Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR) is necessary, the managers requirement for prestartup safety review form is to be completed.
Additionally, the Department Directors or designee will complete the Risk Level Assessment Form,
as appropriate, to determine if the change required that a PHA be performed.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
6.4.
SHG #37
Page 5 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
SECTION D REQUIREMENTS TO BE COMPLETED BEFORE CHANGE IS
COMMISSIONED
The intent of this section is to assign responsibilities, and document that the specified responsibilities
are performed before commissioning the change. The following are checked yes or no and
assignments are made as required.
PROCESS HAZARD ANALYSIS If the complexity of the change warrants a more in-depth
review than the MOCA and PSSR can supply, a HAZOP, What-If or Checklist type Process
Hazards Analysis (PHA) may be required. The PHA is considered to be complete after the PHA
has been performed, and all recommendations have been addressed, and target completion
dates have been assigned and approved for each recommendation.
Typically, the Department Directors or designees will make this determination during their review
of the MOCA. However, the originator or person performing the basic design review may
indicate that a PHA is necessary prior to the Department Directors review.
DCS UPDATE - Update the DCS as required. Because of the nature of the Distributed Control
System, some software changes are necessary before the hardware is commissioned. Also, see
Attachment 1 for examples of not in kind changes.
UPDATE CARSEAL LIST update the Complex carseal list as required.
NEW/REVISED OPERATING/ISOLATION PROCEDURES Review and update any changes
which affect operating manuals and equipment isolation procedures (equipment numbers,
operating parameters, etc.).
OPERATOR TRAINING/AWARENESS Determine and coordinate the training or awareness
requirements. Depending on the impact of specific safety/health/environmental hazards,
operation complexity, safe work practices, and/or employee job task, operators and contractors
may have to be trained in the change, or made aware of the change.
NEW/REVISED MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES Review and update any changes which
affect maintenance craft procedures
MAINTENANCE TRAINING/AWARENESS - Determine and coordinate the training or
awareness requirements. Depending on the impact of specific safety/health/environmental
hazards, mechanical/maintenance complexity, safe work practices, and employee job task,
maintenance employees and contractors may have to be trained in the change, or made aware
of the change.
NEW MSDS/SAFETY PROCEDURE/TRAINING Review, update and/or add documentation if
there is a new MSDS or new/revised safety procedures. Provide training as needed.
ERT/PLANTWIDE TRAINING/AWARENESS Depending on the impact of the change,
Emergency Response Personnel or all employees may have to be trained on the change, or
made aware of the change.
PRE-STARTUP SAFETY REVIEW If the change is significant enough to require a change to
process safety information, a pre-startup safety review will be required. Reference Section 6.7.
The need for a Pre-Startup Safety Review is determined by agreement of the individuals giving
final approval to the MOCA.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 6 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
Completion of this section is signified by the responsible person initialing and dating the time at
which the assignment is completed. Note that employees who are not present at the time of
commissioning, but are affected by the change, are required to be trained or made aware of the
change before operating or maintaining the equipment related to the change.
6.5.
SECTION E REQUIREMENTS TO BE COMPLETED SHORTLY AFTER
COMMISSIONING
The intent of this section is to ensure that all documentation related to the change is accurate,
complete and updated. Updates are needed when any additions, deletions or modifications are
made to process safety information and other items listed below. The following are checked yes
or no and assignments are made as required.
PROCESS FLOW DIAGRAM UPDATE Update and attach any appropriate Process Flow
Diagram if primary flow, major equipment, and/or major instrumentation is changed.
P&ID UPDATE Update and attach existing and revised copy of P&ID.
DATABOOK UPDATE Update any process safety information related to the change such as
equipment specification sheets, pump curves, PSV calculations, design data, drawings, etc.
INFO PLUS Update the Info Plus data as required.
LOOP/ONE LINE DRAWING UPDATE Update and attach any affected Loop Diagrams and/or
Electrical One Line drawings.
ISOMETRIC DRAWING UPDATE Update isometric drawings as necessary.
SAP UPDATE Update any information related to SAP.
INSPECTION RECORDS UPDATE Update the inspection records affected by any piping or
equipment changes.
ROTATING EQUIPMENT UPDATE Update the rotating equipment records affected by any
changes to a pump, compressor, blower, etc.
SPARE PARTS UPDATE Update and attach the spare parts information as needed for piping,
piping components, rotating equipment, fixed equipment, etc.
ENVIRONMENTAL FUGITIVE TAGGING UPDATE Update environmental fugitive tagging as
required.
SPEC. SHEET UPDATE Update and attach any mechanical specification sheets as noted.
RIGHT TO KNOW UPDATE IS initial after completing the Right To Know Update.
OTHER Update and attach any documentation listed in other.
Completion of this section is signified by the responsible person initialing and dating the time at
which the assignment is completed.
6.6.
MANAGERS REQUIREMENT FOR PRE-STARTUP SAFETY REVIEW
The intent of this section is to assign primary contacts for performance of the Pre-Startup Safety
Review (PSSR). This section is filled out, only if a PSSR is required, as indicated in Section D. The
Director or their designee should initial their decision and specify an individual, when yes is
selected.
OPERATIONS REVIEW A member of Operations is mandatory as a primary contact for all
PSSRs.
MAINTENANCE REVIEW A member of Maintenance is mandatory as a primary contact for all
PSSRs.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 7 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
ENGINEERING REVIEW Depending on the nature of the change, this can be selected yes or
no.
ENVIRONMENTAL REVIEW - Depending on the nature of the change, this can be selected
yes or no.
HEALTH/SAFETY/FACILITY SECURITY REVIEW - Depending on the nature of the change, this
can be selected yes or no.
6.7.
PRE-STARTUP SAFETY REVIEW
(PSSR)
The intent of this section is to ensure that a PSSR is performed and completed as required per the
management of change authorization form and pre-startup safety review form.
After the Directors/Managers approve the change in Section C of the MOCA form, the Owning
Area Lead Tech. or designee will attach "PSSR REQUIRED" tags to the isolation point or valves
of the equipment to be commissioned.
A PSSR is initiated when the pre-startup safety review is checked yes in Section D of the
Management of Change Authorization form. At that time, the primary contacts shall be identified
on the Managers Requirement for Pre-Startup Safety Review.
Once the need for a PSSR has been determined, the MOCA/PSSR Coordinator or his/her
designee will coordinate with Operations, Maintenance, Environmental, Tech Services, and
Safety/Health Departments as needed to complete the PSSR.
Under NO circumstances shall a PSSR be considered complete and the equipment
commissioned, until three (3) employees knowledgeable of the change and trained in the PSSR
procedure, sign off on the PSSR that the change is ready for commissioning.
The PSSR must be completed PRIOR to the project being commissioned. When the Lead Tech.
or designee has ensured that the PSSR has been approved and completed, the PSSR
REQUIRED tags will be removed and the change implemented. All items are self-explanatory and
each item listed must be marked in the applicable box. Those items to which an answer of "NO" is
given must be provided with an explanation and the change will not be commissioned until the
negatives are resolved and the resolution recorded on the PSSR.
After required signatures have been obtained, the Area Supervisor or their designee shall route the
original MOCA which contains the PSSR along with all attachments to Process Safety Management
for document updating and archiving.
7.0
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF CHANGE
If the requested change is an emergency (IMMINENT SAFETY OR ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT),
the Shift Supervisor will write a Work Order and contact the Operations Director or the designee
and other Directors affected by the change for approval.
The Shift Supervisor will initiate the MOCA form prior to end of the shift and give it to the Area
Supervisor or their designee for completion.
Before an emergency change is commissioned it is the responsibility of the Shift Supervisor to
inform affected employees and contractors that are present of the change, ensure their
understanding of the change and obtain their signatures on the Change Notification Form.
The Shift Supervisor will ensure that all affected incoming employees/contractors are informed of
the change and obtain their signatures on the Change Notification Form before working the
process.
The Shift Supervisor will be responsible for completing a Pre-Startup Safety Review before
commissioning change.
The MOCA form will be completed no later than the Area Supervisor's or their designee's next
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 8 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
work day and turned in to Directors/Managers along with a copy of the Work Order for final
approval.
8.0
9.0
TEMPORARY CHANGES
A date will be given stating when the change is to be returned to the original state.
Prior to the expiration date, Operations will follow up to ensure that the temporary change is
reviewed to determine if the change date should be extended, changes made permanent or if it
can be returned to the original state.
If the temporary change date should be extended, the originator and Operations will determine
the new date and resubmit the original MOCA, as a revision, to the Directors/Managers for
approval.
If a temporary change is made permanent, a new MOCA must be prepared and submitted by the
originator.
If the temporary change is returned to original state, a copy of the change and a revised Change
Notification Form will be reissued by the Area or Craft Supervisor.
MOCA AFTER BUSINESS HOURS
If the need for a change requiring an MOCA should occur after business hours and has to be
commissioned before the next scheduled work day, the Shift Supervisor will be responsible for
contacting all Department Directors/Managers or their designees to sign or give verbal approval
before the change can be initiated. This will be documented on Sections A, B, C & D of the
MOCA form.
The Directors/Managers Requirements for Pre-Startup Safety Review will be completed and if a
representative is required, that individual will be called. The Shift Supervisor will be responsible
for completing a Pre-Startup Safety Review before commissioning the change.
Section E will need to be completed shortly after the commissioning of the MOCA.
The MOCA will then be forwarded to the Area Supervisor on the next working day to be reviewed
by the Directors and assigned a MOCA number.
Before the change is commissioned, it is the responsibility of the Shift Supervisor to inform
affected employees and contractors that are present of the change, ensure their understanding
of the change and obtain their signatures on the Change Notification Form.
The Shift Supervisor will ensure that all affected incoming employees/contractors are informed of
the change and obtain their signatures on the Change Notification Form before working the
process.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 9 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
ATTACHMENT I
IN-KIND CHANGES
VALVES:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Must be same style. Example: Gate to Gate, Globe to Globe.
Must be same specification.
Must be same rating. Example: 150# to 150#, 300# to 300#.
Must be same size. Example: 4" to 4", 6" to 6".
PIPING AND FLANGES
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Must be same size. Example: 6" to 6", 8" to 8".
Piping must be same schedule. Example: Sch.40 to Sch.40, Sch.80 to Sch.80.
Must be same specification.
Flanges must have same rating. Example: 150# to 150#, 300# to 300#.
Flanges must have same facing. Example: Raised Face to Raised Face, Ring Joint to Ring
Joint.
Temporary piping when process is not involved. Example: Temporary piping used for the
purpose of cleaning units for shutdowns.
PUMPS AND COMPRESSORS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Must be same material (includes internals).
Must have same flange rating, size, and facing.
Must have same capacity and head. Example: 300 GPM to 300 GPM, 2000 SCFD to 2000
SCFD, 300 psi to 300 psi.
Must have same type, manufacturer and model number of seal.
Must be same manufacturer and model number.
TURBINES, STEAM DRIVERS (Reciprocating), AND MOTORS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Must be same material (includes internals).
Turbines and steam drivers must have same flange rating, size, and facing.
Must have same capacity. Example: 200 HP to 200 HP, 400 HP to 400 HP.
Must have same type, manufacturer and model number of seal. Example: Mechanical to
Mechanical.
Motors must have same electrical rating. Example: 460 volts to 460 volts, 240 volts to 240
volts.
Must have same type of lubrication system. Example: Pure Mist to Pure Mist, Purge Mist to
Purge Mist.
Must be same manufacturer and model number. (Does not apply to electrical motors.)
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 10 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
INSTRUMENTATION
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Must have same range. Example: 0-10, 0-150.
Must have same multiplier. Example: X10, X50, X100.
Must measure same units. Example: GPM, SCFD, Lb/HR.
Must use same sensing element. Example: Orifice Plate, P/D Cell.
Changes to deviation/discretionary alarms.
Must be same manufacturer and model number.
MISCELLANEOUS
1.
2.
Temporary changes that occur during a shift and will not last past that shift do not require
MOCA.
Safety and Fire protection equipment taken out of service for repair will not require a
MOCA if its temporary removal for repairs has no effect on emergency response or normal
operating procedures or if existing procedures provide guidance on how to operate the
affected system during the temporary outage. In any case, prompt notification of affected
personnel will be done via e-mail, postings, orders, etc. in addition to any MOCA required.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 11 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
NOT IN KIND CHANGES
VALVES
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Change in style. Example: Gate to Globe, Globe to Gate.
Change in specification.
Change in rating. Example: 150# to 300#, 300# to 600#.
Change in size. Example: 4" to 6", 6" to 8".
Change in packing material.
PIPING AND FLANGES
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Change in size. Example: 6" to 8", 8" to 6".
Change in piping schedule. Example: Sch.40 to Sch.80, Sch.80 to Sch.40.
Change in specification.
Change in flange rating. Example: 150# to 300#, 300# to 150#.
Change in flange facing. Example: Raised Face to Ring Joint, Ring Joint to Raised Face.
PUMPS AND COMPRESSORS
1.
2.
3.
2.
3.
Change in material (includes internals).
Change in flange rating, size, and facing.
Change in capacity or head. Example: 300 GPM to 500 GPM, 2000 SCFD to 1000 SCFD,
300 psi to 500 psi.
Change in type of seal.
Change in manufacturer or model number.
TURBINES, STEAM DRIVERS (Reciprocating), AND MOTORS
1.
Change in material (includes internals).
2.
Turbines and steam drivers change in flange rating, size, and facing.
3.
Change in capacity. Example: 200 HP to 500 HP, 400 HP to 800 HP.
4.
Change in type of seal.
5. Change in motors electrical rating. Example: 460 volts to 240 volts, 240 volts to 460 volts.
6. Change of lubrication system. Example: Pure Mist to Purge Mist, Purge Mist to Pure Mist.
7. Change in manufacturer or model number. (Does not apply to electrical motors.)
INSTRUMENTATION
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Change in range. Example: 0-10 to 0-150, 0-150 to 0-20.
Change in multiplier. Example: X10 to X50, X100 to X200.
Change in measuring units. Example: GPM to Lb/HR, SCFD to SCFH.
Change in DCS set point clamps.
Change in scan phase/period.
Changes to DCS historian.
Change in manufacturer or model number.
CHEMICALS AND CATALYST
1. Change in composition or manufacturer.
2. Change in function/reaction.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 12 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
MAINTENANCE CHANGES
1.
A maintenance procedure change that affects the way a piece of equipment is repaired, handled
or replaced in-field or in-shop. Example: Changing a weld procedure.
OPERATIONAL CHANGES
1.
An operating procedure change that affects plant operation or the process.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
2.
3.
A change in the start-up or shutdown procedures.
A change in the emergency procedures.
A change in the normal operating procedures.
Resetting alarm limits except for deviation/discretionary alarms.
Resetting control parameters out of the normal high or low limits.
Changing to a feedstock that a plant is not designed
for.
Bypassing equipment in-service (new bypasses).
A change in operational software that could affect plant operations.
A change in computer control schemes that could affect plant operations.
MISCELLANEOUS CHANGES
1.
2.
3.
4.
Relocation of equipment. Example: Moving a pump from one tank to another tank.
Installing new bleeders in existing lines.
Installing new vents in existing lines.
New piping tie-ins.
a.
New lines to flare/blowoff systems.
b.
New lines to tank fill/suction lines.
c.
New lines to pump suction/discharge lines.
d.
New lines to utility lines (water, steam, air).
5.
Temporary piping when process is involved.
a.
Temporary tank fill line tie-in to remove another tank from service.
b.
Temporary pump suction/discharge line tie-in to remove another pump from service.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Pipe clamps/temporary leak repairs.
Hot taps/stopples.
Lighting changes.
Relief valve changes. Example: Changing settings (Pop at 25# instead of 30#).
Changing a sampling procedure.
A change in technical procedures. Example: Changing piping specifications.
A change in a safety and health guide.
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 13 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
ATTACHMENT II
PROCESS SAFETY INFORMATION
I.
PROCESS CHEMICALS INFORMATION
Following is the minimum required information pertaining to the hazardous chemicals used in the
process units.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
NOTE:
II.
Toxicity Information
Permissible Exposure Limits
Physical Data
Reactivity Data
Corrosive Data
Thermal and Chemical Stability Data
Hazardous Effects of Inadvertently Mixing of Different Materials that Could Foreseeable
Occur
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEETS MEETING THE REQUIREMENTS OF
29CFR1910.1200 (g) MAY BE USED TO COMPLY WITH THIS REQUIREMENT TO THE
EXTENT THEY CONTAIN THE INFORMATION REQUIRED.
PROCESS DESIGN INFORMATION
Following is the minimum process design information required by Process Safety Management.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
NOTE:
III.
Block Flow/Simplified Process Flow Diagrams
Process Chemistry
Maximum Intended Inventory
Safe Upper/Lower Limits (Temperature, Flow, Pressure, etc.)
Evaluation of the Consequences of Deviation
WHERE THE ORIGINAL TECHNICAL INFORMATION NO LONGER EXISTS, SUCH
INFORMATION MAY BE DEVELOPED IN CONJUNCTION WITH THE PROCESS
HAZARDS ANALYSIS IN SUFFICIENT DETAIL TO SUPPORT THE ANALYSIS.
PROCESS MECHANICAL DESIGN
Following is the minimum process mechanical design information required by Process Safety
Management.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Material of Construction
Piping and Instrument Diagrams
Electrical Classification
Relief System Design and Design Basis
Ventilation System Design
Design Codes and Standards Employed
Material and Energy Balances for Processes Built After Effective Date of Standard
Safety System (Such as Interlocks, Detection and Suppression Systems)
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 14 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
ATTACHMENT III
RISK LEVEL ASSESSMENT
MOCA Number:
WO / AFE #
Date:
Risk Assessment Performed by:
MOCA Description of proposed change: ________________________________________________________
Note: Completion of this form may not be required for: 1. Changes in documentation; 2. Changes in equipment
where the functionality of the equipment remains the same; 3. HAZOP Action Items
Section I Degree of Hazard
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Does the change introduce or substantially affect a significant source of chemical, mechanical,
thermal, or electrical energy? (1 point for yes, 0 points for no)
Examples: Installation/modification of a motor; Increasing steam supply pressure to a vessel
Does the change result in any increase in inventory of toxic, flammable, or reactive (equivalent
to a "4" rating in the NFPA or HMIS systems) materials? If so, is this a new threshold for PSM or
RMP covered chemicals? (1 point for yes, 0 points for no)
Are established PSM or RMP boundaries extended to new piping or equipment? (3 points for
yes, 0 points for no)
Will the changed process system contain any materials known or suspected to be thermally,
chemically, or physically unstable in quantities or concentrations high enough to cause a hazard?
(3 points for yes, 0 points for no)
Does the change significantly increase the potential for personnel exposure to a hazardous
material? (2 points for yes, 0 points for no)
Does the change introduce or substantially affect any special or unique hazards that could cause
significant negative community impact? (2 points for yes, 0 points for no)
HAZARD RULE: "Higher" if answers 1-6 total more than 2 points, otherwise "Lower"
Section II Significance of Proposed Change
1.
Could the change take the process or system outside previous limits of normal operation (that is,
outside the well understood and documented "safe operating envelope") during steady state or
transient conditions? (2 points for yes, 0 points for no)
2.
Does the change introduce substances not already present in the process? (1 point for yes, 0
points for no)
3.
Are PSVs or rupture disks affected, changed or bypassed? (1 point for yes, 0 points for no)
4.
Does the change re-order or alter the processing sequence and consequently by this alteration
introduce a hazard? (2 points for yes, 0 points for no)
5.
Does the change significantly impact the energy balance or mass balance? (1 point for yes, 0
points for no)
6.
Does the change affect a safety device? (1 point for yes, 0 points for no)
7.
Does the change alter or bypass a critical control system (2 point for yes, 0 points for no)
8.
Does the change necessitate significant or unique training for operators or technical personnel?
(1 point for yes, 0 points for no)
9.
Does the existing system handle reactively incompatible materials in the same equipment during
different sequences or campaigns? (2 points for yes, 0 points for no)
__
10.
Does the proposed change require the development of a new Maintenance
Procedure/Guideline? (1 point for yes, 0 points for no)
SIGNIFICANCE RULE: "Higher" if answers 1-10 total more than 2 points, otherwise "Lower"
VALERO KROTZ SPRINGS
SHG #37
Page 15 of 15
Revised 06/08/04
Section III Risk Level
Using the Degree of Hazard and Significance of Change results from Sections I and II, determine and circle the
Risk Level of the proposed change:
SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGE
DEGREE OF HAZARD
LOWER
HIGHER
LOWER
HIGHER
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Risk Assessment Requirements
Level 1:Complete MOCA form only
Level 2:Complete MOCA form and perform informal PHA at the Review Teams Discretion
(Note reasons for not performing PHA in comments section)
Level 3:Complete MOCA form and perform an informal PHA
Level 4:Complete MOCA form and perform a HAZOP or informal PHA
COMMENTS:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- H2 Postion Laro S - DDokument1 SeiteH2 Postion Laro S - DSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMP HP SD in Nov 16Dokument2 SeitenRMP HP SD in Nov 16Suresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PaymentDokument1 SeitePaymentSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tef - 2016 Sports & GamesDokument4 SeitenTef - 2016 Sports & GamesSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3247tef-2016 Sports Registration SureshDokument4 Seiten3247tef-2016 Sports Registration SureshSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEFDokument12 SeitenTEFSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIP Accepted IdeasDokument9 SeitenPIP Accepted IdeasSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitynet InvoiceDokument1 SeiteQualitynet InvoiceSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Engineering Drawings, Codes and Standards: Piping & Instrumentation Diagram - Designer ChecklistDokument3 SeitenDetailed Engineering Drawings, Codes and Standards: Piping & Instrumentation Diagram - Designer ChecklistSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reformer Convection SectionDokument7 SeitenReformer Convection SectionSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
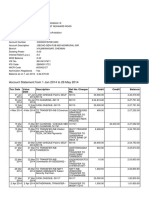
- Account Statement From 1 Jan 2014 To 26 May 2014: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDokument2 SeitenAccount Statement From 1 Jan 2014 To 26 May 2014: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection Section CleaningDokument10 SeitenConvection Section CleaningSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam To Carbon Ratio Calculations: InstructionsDokument8 SeitenSteam To Carbon Ratio Calculations: InstructionsSuresh Ramakrishnan100% (1)
- TEF Sports Day Suresh RegiterDokument1 SeiteTEF Sports Day Suresh RegiterSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMP and Fup H Balance Report: H Production H ConsumptionDokument1 SeiteRMP and Fup H Balance Report: H Production H ConsumptionSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format Loop Description-BlankDokument1 SeiteFormat Loop Description-BlankSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Start Up PlanDokument5 SeitenStart Up PlanSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Stage Programs (Will Be Conducted On 8 May) : Event CodeDokument4 SeitenOn Stage Programs (Will Be Conducted On 8 May) : Event CodeSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Chart: Truth Faith Peace HarmonyDokument1 SeiteHouse Chart: Truth Faith Peace HarmonySuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis Gas - Co - H - MethanolDokument18 SeitenSynthesis Gas - Co - H - MethanolSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convert Ammonia To MethanolDokument16 SeitenConvert Ammonia To MethanolSuresh RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air PreheaterDokument11 SeitenAir PreheaterSuresh Ramakrishnan100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Business Ethics Case StudiesDokument25 SeitenBusiness Ethics Case Studiesswaggerbox100% (2)
- ContemporaryDokument2 SeitenContemporaryAlbert PaggaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ext Abstract BERCYANDYADokument8 SeitenExt Abstract BERCYANDYAvirtualqueen02Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10D Unit-Coral Reefs PDFDokument14 Seiten10D Unit-Coral Reefs PDFIWAN KUNCORONoch keine Bewertungen
- SPPU Report FormatDokument50 SeitenSPPU Report FormatAmit Devidas AherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karma: "Dove La Legge Della Grazia È Attiva, Finisce La Legge Del Karma"Dokument37 SeitenKarma: "Dove La Legge Della Grazia È Attiva, Finisce La Legge Del Karma"Lars JensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Com 1Dokument16 SeitenTech Com 1HawaiiChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIP Report-PRATYUSH (1950-113) - 1Dokument49 SeitenSIP Report-PRATYUSH (1950-113) - 1LOKESH KUMAR SINHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Citaion Style GuideDokument2 SeitenCitaion Style Guideedustar330Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parrot: by Alan BrownjohnDokument2 SeitenParrot: by Alan BrownjohnPADUMI SASIKALA50% (2)
- TI 20220909 SG320HX and SG350HX Short-Circuit Current V1 enDokument5 SeitenTI 20220909 SG320HX and SG350HX Short-Circuit Current V1 en2D EngenhariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-V 191eec303t LicDokument80 SeitenUnit-V 191eec303t LicPonkarthika BNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Updating Health Benefits Plans On Health Technologies Usage and Expenditures The Case of ColombiaDokument24 SeitenThe Impact of Updating Health Benefits Plans On Health Technologies Usage and Expenditures The Case of ColombiaTeana Zapata JaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide Topic 2 - PR TheoriesDokument26 SeitenSlide Topic 2 - PR TheoriesJeneesh RajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toplotna Pumpa Hidria Clint - Eu - Cha K - 182 P 604 P - cls61.7 EngDokument2 SeitenToplotna Pumpa Hidria Clint - Eu - Cha K - 182 P 604 P - cls61.7 EngMuhidin KozicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNC RoboticsDokument17 SeitenCNC RoboticsKunal DuttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.Sc. Mathematics - Ii YearDokument98 SeitenManonmaniam Sundaranar University: B.Sc. Mathematics - Ii YearSadia ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omb ValvesDokument52 SeitenOmb ValvesCesar SotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Samss 009Dokument13 Seiten02 Samss 009barouniamineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coneplot (20170407)Dokument30 SeitenConeplot (20170407)LinggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radical Pedagogies in Architectural Education - Architectural ReviewDokument11 SeitenRadical Pedagogies in Architectural Education - Architectural ReviewGabriella VillaçaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNC Programming Intro & Code PDFDokument127 SeitenCNC Programming Intro & Code PDFAswath SridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAA NotesDokument97 SeitenDAA Notesanish.t.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-Boundary and Initial ConditionsDokument8 Seiten6-Boundary and Initial ConditionsqazwsxNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB High Speed Directional Relays PDFDokument28 SeitenABB High Speed Directional Relays PDFking_electricalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Concepts and Applications 4Th Edition Nevid Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument49 SeitenPsychology Concepts and Applications 4Th Edition Nevid Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFfidelmanhangmhr100% (9)
- Audit Sampling (Chapter 9)Dokument25 SeitenAudit Sampling (Chapter 9)cris100% (2)
- Mid 221Dokument28 SeitenMid 221danecuprijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics of A Novel Nine Degree of Freedom Configurable Gough-Stewart PlatformDokument19 SeitenKinematics of A Novel Nine Degree of Freedom Configurable Gough-Stewart PlatformNeider NadidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Programming NotesDokument0 SeitenVisual Programming NotesSamuel VictorNoch keine Bewertungen