Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
IT Phy F5 Topical Test 3 (BI)
Hochgeladen von
rospazitaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IT Phy F5 Topical Test 3 (BI)
Hochgeladen von
rospazitaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SULIT
NAMA: _______________________________________________
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
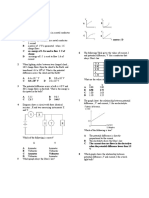
1 Diagram 1 shows a current flowing
in a straight wire passes through a
horizontal
cardboard.
Two
compasses are placed at positions x
and y.
flowing at the end of coil
P
End P
End Q
North
South Clockwise
Anticlockwise
South
North Clockwise
Anticlockwise
North
South
Anticlockwise
Clockwise
South
North
Anticlockwise
Clockwise
6 Which of the following diagrams
shows the correct catapult field?
A
C
Diagram 1
Which of the following pairs of
arrow shows the direction of the
pointer of the compasses correctly?
At x
At y
Questions 2 and 3 are based on Diagram
2.
Diagram 2 shows a current-carrying
solenoid.
4 Which of the following does not
affects the strength of the magnetic
field produced by an electromagnet?
A The current in the solenoid.
B The shape of coil that is used.
C The number of turns on
the solenoid.
D The type of current flows in
the solenoid.
5 Diagram 3 shows two straight wire x
and y pass through a cardboard.
Some iron fillings is sprinkled on the
cardboard.
7 Diagram 4 shows a straight wire
placed vertically in an uniform
magnetic field.
Diagram 3
Diagram 2
2 What is the rule that used to
determine the direction of the
magnetic field produced by a current
flowing through a solenoid?
A Right-hand grip rule
B Maxwells screw rule
C Flemings left-hand rule
D Fleming right-hand rule
Which of the following shows the
magnetic field correctly?
A
B
Diagram 4
3 Which of the following is true about
the poles and direction of current
flowing at each end?
Poles
In which direction will the catapult
force act?
A East
C West
B South
D North
8 Diagram 5 shows a simple motor.
Direction of current
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
21
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
In which direction will the
conducting rod moves when the
switch is closed?
Diagram 5
What will happen to the coil when
the switch is closed?
A The coil does not rotate at all.
B The coil rotates in clockwise
direction.
C The coil rotates in anticlockwise
direction.
D The coil stationary in a vertical
position.
9 Diagram 6 shows an electric circuit
consists
of
two
rectangular
aluminium foils which are placed
close to each other and connected to
a dry cell.
Questions 11 and 12 are based on Diagram
8.
Diagram 8 shows output terminals of an
electric generator is connected to a
cathode-ray oscilloscope(C.R.O.).
Diagram 9
Diagram 8
11 Which of the traces will be
displayed
on the screen when the time-base is
turned on?
A
Diagram 6
Which of the following shows the
acting force correctly when the
switch is closed?
A
C
15 Diagram 10 shows a current-time
graph from a power supply.
10 Diagram 7 shows a conducting rod
placed in a magnetic field.
Diagram 7
13 Which of the following actions will
not produce an induced current flow
through the sensitive galvanometer?
A Moving the magnet towards the
solenoid.
B Moving the solenoid towards the
magnet.
C Both the magnet and solenoid are
moving towards each other.
D Both the magnet and solenoid are
moving with the same velocity.
14 One of the poles of solenoid can be
determined by using a law. What is
the law should be used?
A Lenzs law
B Faradays law
C Maxwells screw rule
D Flemings right-hand rule
Questions 13 and 14 are based on Diagram
9.
Diagram 9 shows an experimental set-up
where a bar magnet placed near a
solenoid which is connected to a
sensitive galvanometer.
12 Which of the following cannot
increase the magnitude of the current
produced by the electric generator
shown?
A Using a stronger magnet
B Rotating the coil at a higher speed
C Increasing the number of turns on
the coil
D Winding the coil on a stainless
steel core
Diagram 10
Based on the graph, calculate the
root mean square (r.m.s.) current for
the power supply.
A 2.0 A
C 5.66 A
B 2.83 A
D 8.0 A
16 Why is the soft iron core is used in a
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
22
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
transformer?
A To reduce resistance produced.
B To produce a uniform magnetic
field.
C To increase the generation of
electrical energy.
D To
be
magnetised
and
demagnetised easily.
efficiency,
what
is
the
output power of a 5 resistor
connectedto the secondary coil, if
the primary coil is connected to a
240 V power supply?
A 1.2 W
C 12 W
B 2.4 W
D 28.8 W
22 What is the advantage of using an
alternating current supply?
A Generation cost is lower.
B The power supply can be changed
easily.
C The voltage of the current can be
changed easily.
D The frequency of the current can
be easily maintained at a constant
value.
23 Why the electrical energy is
normally transmitted at high
voltage?
A To minimise the energy loss.
B To transmit as large as possible of
current.
C Transmitting cables normally
have very low resistance.
D Transmitting system do not
require a step-up transformer.
17 Diagram 11 shows a graph of input
voltage, Vi against the time, t for a
transformer.
Diagram 11
If the transformer has half of the
turns in its secondary coil than its
primary coil, which of the following
graph shows the output voltage, Vo
correctly?
A
18 A transformer is used to change the
main voltage of 240 V to provide a
6 V supply for a bulb. If the number
of turns in primary coil is 1 000,
calculate the number of turns
required in the secondary coil.
A 25
C 80
B 40
D 167
19 What is the function of the laminated
iron core in a transformer?
A To reduce resistance of coil
B To reduce eddy current
C To reduce leakage of magnetic
flux
D To reduce the strength of the
magnetic field produced
20 A step-up transformer is used to
increase the input voltage from
240 V to 360 V. If the efficiency of
the transformer is 75% and the
current flowing through the primary
coil is 1.5 A, what is the current
flowing through the secondary coil?
A 0.75 A
C 1.5 A
B 1.125 A
D 2.25 A
21
PAPER 2
A transformer has 1 000 turns and
50 turns in its primary and
secondary
coil
respectively.
Assume the transformer has 100%
24 Electrical energy is transmitted at a
rate of 250 MW. The current in the
transmitting cable is 820 A.
If the cable has a resistance of
45 , calculate the power loss in the
transmission process.
A 14 MW
C 30 MW
B 21 MW
D 56 MW
25 A power station generates 50 MW of
power at a voltage of 400 kV. If the
resistance of the cable is 25 per
km, calculate the power loss due to
the
500 km length of transmission cable.
A 390 kW
C 8 MW
B 1.5 MW
D 5 MW
SECTION A
1 Diagram 1.1 shows a sections of a moving coil
galvanometer. N and S represent the North pole and the
South pole of a permanent magnet respectively.
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
23
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
Diagram 2.1
(a) In the Diagram 2.2, draw arrows to represent the
directions of pointers when current flows vertically
upwards through the wire.
Diagram 1.1
(a) Diagram 1.2 shows the plan of the galvanometer. On
Diagram 1.2, draw the pattern of the magnetic field
which exists between N and S.
Diagram 2.2
[2 marks]
(b) Diagram 2.3 shows current flows through a solenoid,
RS. The two circles represent compasses.
Diagram 1.2
[2 marks]
(b) A current flows through the galvanometer so that the
pointer deflects and shows a fixed reading of current.
(i) What type of current that flows through the
galvanometer?
_____________________________________
[1 mark]
Diagram 2.3
(i) Draw arrows in the circles on Diagram 2.3 to
represent the direction(s) of the pointers.
[2 marks]
(ii) Explain how the coil of the galvanometer can
rotate?
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
[3 marks]
(ii) The solenoid acts as a magnet. State the poles at R
and S.
Polarity at R :
Polarity at S :
[2 marks]
(iii)What causes the rotation of the coil to stop?
________________________________________
[1 mark]
2 Diagram 2.1 shows four compasses placed on a horizontal
cardboard. A straight wire which is perpendicular to the
cardboard passes through the centre of the cardboard. When
there is no current flows through the wire, the pointers of
the compasses point towards North as shown in Diagram
2.1.
Diagram 2.4
(c) Solenoid RS is now connected to a galvanometer, G as
shown in Diagram 2.4. What happens if a bar magnet is
pushed into the solenoid?
Give reasons for your answer.
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
[3 marks]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
24
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
4 Table 1 shows four different coils that are used to construct
transformers.
3 Diagram 3 shows the structure of a transformer.
Coil
Number of turns
50
200
1 000
2 000
Table 1
(a) Based on Table 1, complete Table 2 with correct pairs of
coils to construct the transformers given.
Type of transformer
Diagram 3
(a)
(i) Name the type of the transformer.
Primary coil
Secondary coil
Step-up
________________________________________
[1 mark]
Step-down
(ii) Draw a symbol for the transformer named in 3(a)
(i).
Table 2
[2
marks]
(b) Determine the pair of coils which step down the voltage
from 240 V to 6 V.
[2 marks]
(c) Diagram 4 shows a simple transformer. When the
switch is on, the bulb lights up with normal brightness.
[1 mark]
(iii) State why the core is made of soft iron.
________________________________________
[1 mark]
(b) The number of turns of the primary coil is 800.
Calculate the number of turns of the secondary coil.
[2 marks]
(c) The transformer is used to switch on a ticker-timer. The
current flows through the primary coil is 0.25 A and the
efficiency is 60%.
(i) Calculate the output power of the transformer.
Diagram 4
(i) Explain how the bulb lights up with normal
brightness.
________________________________________
________________________________________
________________________________________
[3 marks]
[2 marks]
(ii) Suggest a modification to increase the efficiency
of the transformer.
(ii) Calculate the efficiency of the transformer if the
current flows in the primary coil is 0.1 A.
________________________________________
________________________________________
[1 mark]
(d) Give one reason why a radio which is connected to the
output of the transformer does not function when the
radio switched on.
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
[1 mark]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
[3 marks]
[3 marks]
5 Diagram 5.1 shows a wire AB carries a constant current in
the direction from A to B.
25
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
6 Diagram 6 shows the apparatus set-up which is used to
study the effect of magnetic field on copper rod carrying
electric current.
Diagram 5.1
(a) Draw the magnetic field on the horizontal surface in
Diagram 5.1. Mark clearly the direction of the field.
[2 marks]
(b) Diagram 5.2 shows another wire XY which is parallel
and near AB, carries current in the opposite direction to
the current in AB.
Diagram 6
(a) On Diagram 6, mark and label magnetic field with letter
M.
[2 marks]
(b) When the switch is turned on, the copper rod is
observed rolling to one side on copper track.
On Diagram 6,
(i) mark and label the direction of current with letter,
I, on the copper rod.
[1 mark]
(ii) mark and label the direction of force, F, that acts
on the copper rod.
[1 mark]
(c) Explain how the movement of copper rod is produced.
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
[3 marks]
Diagram 5.2
[2 marks]
(i) Draw the resultant magnetic field produced by the
current XY and the current AB.
[2 marks]
(ii) Label the direction of force that acts on wire AB
and wire XY on the diagram in 5(b)(i).
[2 marks]
(iii) Suggest two factors that can increase the
magnitude of the force between the wires AB and
XY.
1._______________________________________
2._______________________________________
[2 marks]
(d) The rheostat in the circuit is adjusted so that the
resistance is reduced. Explain changes made to the
motion of the copper rod.
______________________________________________
______________________________________________
[2 marks]
SECTION B
Diagram 7.1
7 Diagram 7.1 and Diagram 7.2 show solenoid connected to
ammeter, rheostat and d.c. power supply.
Diagram 7.2
When constant current flow in each circuit, pins are
attracted to the iron core.
(a) What is meant by electromagnet ?
[1 mark]
(b) Using Diagram 7.1 and Diagram 7.2, compare the
number of pins attracted and the magnetic strength of
the two electromagnets.
[3 marks]
(c) State the relationship between the magnetic strength
and
(i) the number of turns of wire.
(ii) the number of pins attracted.
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
26
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
[2 marks]
(d) Diagram 7.3 shows the use of electromagnet as a
electromagnetic relay.
Diagram 8.1
(a)
Diagram 7.3
Explain how the electromagnet relay is used to turn on
the air conditioner.
[4 marks]
Diagram 8.2
(i) What is meant by electromagnetic induction?
[1 mark]
(ii) With reference to Diagram 8.1 and Diagram 8.2,
compare the number of magnets used and the
deflection of the galvanometers pointer.
Relate the number of magnets and the deflection
of the galvanometers pointer to make a
deduction between the magnitude of current and
strength of magnetic field.
Name the physics law that explain 8(a)(ii).
[5 marks]
(e) Diagram 7.4 shows a d.c. electric motor which is
supplied with 12 V.
(b) Explain the advantages of the national grid system in
the transmission of electricity.
[4 marks]
(c) Explain the use of transformer in reducing the power
loss in the system of transmission of electric power.
[3 marks]
(d) Diagram 8.3 shows the structure of an a.c. dynamo.
Diagram 7.4
(i) Explain how the motor is able to rotate.
[6 marks]
(ii) Explain the modification that is required to
enable the d.c. motor to become an a.c. motor
that can move faster when connected to 12 V a.c.
supply.
[4 marks]
Diagram 8.3
Explain clearly how it works.
[7
8 Diagram 8.1 and Diagram 8.2 show one magnet and two
magnets are being pushed with uniform speed into the
identical solenoid separately.
marks]
SECTION C
9 (a) Diagram 9.1 shows the structure of a transformer.
Diagram 9.1
Explain the operating principle of a transformer.
[5 marks]
(b) Diagram 9.2 shows a model of an electric transmission
system in a laboratory. The model consists of a power
station which generates 6 V of alternating current, a.c.
transmitting the electrical energy to the users through
transmission wires and transformers J, K and L.
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
27
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
Diagram 10.1
(a)
(i) What is meant by electromagnet induction?
[1 mark]
(ii) State the Lenzs law.
[2 marks]
(iii) Explain what happens to the copper coil when the
bar magnet oscillates and give reasons why the
amplitude of the bar magnet get smaller.
[7 marks]
(b) Diagram 10.2 shows the transmission of electric power
to the consumers.
Diagram 9.2
You are requested to set up the model as in Diagram 9.2
by using the information in Table 3.
Number of
turns of the
coil
Type of metal used for
Type of transformer core
the transmission wire
10
Aluminium
Copper core
48
Copper
Laminated copper core
50
Nichrome
Soft iron core
60
Constantan
Laminated soft iron core
75
Steel
Steel core
360
Iron
Laminated steel core
Table 3
Using the information in Diagram 9.2 and Table 3,
determine:
(i) the number of turns in the primary coil and the
secondary coil of transformers J, K and L.
(ii) the type of metal used for the transmission wire.
Justify your choice.
(iii) the type of core used for the transformers. Justify
your choice.
[10 marks]
(c) Electric power of 990 kW is supplied at 33 kV to a
heavy industry through cable of total resistance 100 .
Calculate
(i) total loss of power from the cable due to heating
effect.
(ii) efficiency of the power transmission.
[5 marks]
Diagram 10.2
Table 4 shows the characteristics of four types of cables.
10 Diagram 10.1 shows a bar magnet that oscillates freely. A
copper coil connecting to a galvanometer is brought close to
the bar magnet.
Cable
Density/
kg m3
Resistance/
km1
Diameter/ cm
Specific heat
capacity/
J kg1 C1
3.0 103
2.5
1.0
450
5.0 103
0.8
2.0
750
2.0 103
0.5
4.0
1 000
6.0 103
1.5
3.0
200
Table 4
Explain the suitability of each characteristics of cables
in Table 4 for use in the transmission of electric power.
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
28
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
Determine the most suitable cable. Give reasons for
your choice.
[10 marks]
PAPER 3
SECTION
A
SECTION B
(iii) calculate the gradient of the graph, m.
Show on the graph how you determine value of m.
[3 marks]
A student carries out an experiment to investigate the
relationship between the number of turns in secondary
coils, Ns and output voltage, Vs of a transformer.
The results of the experiment are shown in the graph Vs
against Ns in Diagram 1.
(b) Given the primary voltage is 240 V a.c., using the
formula Ns / Np = Vs / Vp and the gradient, m in 1(a)(iii),
calculate the number of turns in primary coil.
[2 marks]
(c) Suggest two ways that can be used to improve the
efficiency of the transformer.
[2 marks]
(d) State one precaution that should be taken to improve the
result of this experiment.
[1 mark]
2 Diagram 2.1 and Diagram 2.2 shows a table fan.
In Diagram 2.1, the speed control is set at button 1 and the
fan blade is rotating.
In Diagram 2.2, the speed control is set at button 3 and the
fan blade is rotating faster.
Diagram 1
(a) Based on the graph in Diagram 1,
(i) state the relationship between Vs and Ns.
[1 mark]
(ii) determine the value of Vs when Ns = 40.
Show on the graph how you determine the value
of Vs.
[3 marks]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
29
SULIT
SULIT
Lekat logo
sekolah
di sini
NAMA: _______________________________________________
TINGKATAN: ______________
TOPICAL TEST 3: ELECTROMAGNETISM
PAPER 1
(b) State one hypothesis that could be investigated.
Diagram 2.1
[1 mark]
(c) With the use of apparatus such as magnets, C-shaped
iron yoke, bare copper wire, connecting wires, d.c.
power supply, ammeter and other apparatus, describe an
experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in 2(b).
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i) The aim of the experiment.
(ii) The variables in the experiment.
(iii) The list of apparatus and materials.
(iv) The arrangement of the apparatus.
(v) The procedure of the experiment which should
include the method of controlling the manipulated
variable and the method of measuring the
responding variable.
(vi) The way you tabulate the data.
(vii) The way you analyse the data.
[10 marks]
Diagram 2.2
Based on the observation on Diagram 2.1 and Diagram 2.2
and applying your knowledge of the magnetic effect of
current:
(a) State one suitable inference.
[1 mark]
Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P)
30
SULIT
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IT Phy F5 Topical Test 2 (BL)Dokument12 SeitenIT Phy F5 Topical Test 2 (BL)Jeemion JealiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Current ExerciseDokument12 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Current Exercisemaatla monkgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Soalan SPM p1Dokument6 SeitenChapter 2 Soalan SPM p1ahsohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsVon EverandA Collection of Problems on Mathematical Physics: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied MathematicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDokument4 SeitenMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentXxxxxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9701 w01 Ms 2Dokument4 Seiten9701 w01 Ms 2Hubbak Khan100% (1)
- 9701 w01 Ms 3Dokument4 Seiten9701 w01 Ms 3Hubbak KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Diploma Physics HL P1 2017-22-SampleDokument7 SeitenIB Diploma Physics HL P1 2017-22-SampleNOTINFINITYNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSDokument6 Seiten12 SACE Start of Year Revision SOLUTIONSLydia LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Form 5 Chapter 3 PDFDokument18 SeitenRevision Form 5 Chapter 3 PDFYz PohNoch keine Bewertungen
- TU PTPTN Booklet Guidelines and Procedures 2019 PDFDokument18 SeitenTU PTPTN Booklet Guidelines and Procedures 2019 PDFSachin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convex LensDokument2 SeitenConvex Lensadithya4rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 9 - The Periodic Table - TutorialDokument33 SeitenTopic 9 - The Periodic Table - TutorialMOHAMED SHAMIR BIN TAJUDEENNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2 AnswerDokument7 Seiten7.2 AnswerNurul Afiqah Mohmmad NajibNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Chemistry Paper 2Dokument19 SeitenSPM Chemistry Paper 2AnneLeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics Form 5Dokument46 SeitenSPM Physics Form 5Woody CysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014 PDFDokument56 SeitenModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014 PDFhidayahnurul100% (1)
- Biology SPM Forecast PapersDokument21 SeitenBiology SPM Forecast PaperswhywhyqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio NotesDokument19 SeitenBio NotesMyramel KlarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa International Gcse Physics 9203 Generating and Distributing Electricity and Household UseDokument12 SeitenTopic Test Oxfordaqa International Gcse Physics 9203 Generating and Distributing Electricity and Household Useandhi soesilo100% (2)
- EJSK SK025 Physical PropertiesDokument30 SeitenEJSK SK025 Physical PropertieschiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 Book 13Dokument1 Seite2009 Book 13nayagam74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFDokument70 SeitenKimia Module 1 5 Diagnostik f4 PDFJuan DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulangkaji Berfokus 1 Understanding SkillDokument7 SeitenUlangkaji Berfokus 1 Understanding SkillCart KartikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit QuestionsDokument36 SeitenCircuit QuestionsMuhammad TauseefNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9701 w13 QP 2Dokument36 Seiten9701 w13 QP 2hui1430% (1)
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 2 - StudentDokument16 SeitenForm 5 Physics Chapter 2 - StudentPavithiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio ACE Form 4Dokument3 SeitenBio ACE Form 4Myramel KlarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics IGCSE Past PaperDokument16 SeitenPhysics IGCSE Past Paperjenny1004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Students Should: GuidanceDokument19 SeitenPhysics: Students Should: GuidanceArun MosesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaDokument16 SeitenTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Physics DC CircuitsDokument24 SeitenPhysics DC CircuitsJenessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics Independent Study Booklet Part DDokument13 SeitenMechanics Independent Study Booklet Part DnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main File523 851655521Dokument347 SeitenMain File523 851655521alwafa.q6rNoch keine Bewertungen
- F.3 Chemistry Exercise 3 (Atoms) (Q&A)Dokument4 SeitenF.3 Chemistry Exercise 3 (Atoms) (Q&A)Simon100% (1)
- Electricity Year 9Dokument55 SeitenElectricity Year 9Menaga IlangkovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology A Level OCR 2022Dokument6 SeitenBiology A Level OCR 2022shNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momentum QPDokument6 SeitenMomentum QPXandws -IOS tips and trick and gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics Summative Test 3 - Form 4 Chapter 3 4 5Dokument7 SeitenSPM Physics Summative Test 3 - Form 4 Chapter 3 4 5Winnie Lim Li SzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Dokument27 SeitenStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1Dokument3 SeitenCommon Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1RidwanAbrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDokument12 SeitenH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - Electricity & Chemical Effects of Current (THEORY X ClassDokument6 Seiten01 - Electricity & Chemical Effects of Current (THEORY X ClassArmaan PruthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAL - Physics - Unit - 4Dokument23 SeitenIAL - Physics - Unit - 4sgmdhussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity (Unit: Ii) : One Mark QuestionsDokument13 SeitenCurrent Electricity (Unit: Ii) : One Mark Questionsmechanical_lecturer100% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Dokument59 SeitenModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014NALLATHAMBYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07Dokument21 SeitenChemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07hudazzakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula List New STPM - 2nd TermDokument6 SeitenFormula List New STPM - 2nd TermOne_sofian2715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kDokument22 SeitenChemistry Paper 2 Questions PDF August 24 2011-12-50 PM 472kJamaludin Abu KassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5Dokument13 SeitenForm 5Vanusha AzzrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icse X Magnetism Question BankDokument7 SeitenIcse X Magnetism Question BankanimeshtechnosNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRK10Q42 Diagram 23 Shows A Bar Copper Wire PQ in A Magnetic FieldDokument25 SeitenPRK10Q42 Diagram 23 Shows A Bar Copper Wire PQ in A Magnetic FieldChewLee TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM 2003Dokument18 SeitenSPM 2003faisalsmkpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 11 Electromagnetism RevisionDokument27 SeitenYear 11 Electromagnetism RevisionLawrenceOnthugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Test 02-02-12 Final 12Dokument13 SeitenPhysics Test 02-02-12 Final 12Dewan Olin ChotepadaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1Dokument12 SeitenTrial STPM Physics Term 2 - Module 1annahiaz0% (1)
- Final End 2-Mathayom 3 ScienceDokument10 SeitenFinal End 2-Mathayom 3 ScienceAbdullohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Untuk SPM PDFDokument14 SeitenLatihan Untuk SPM PDFrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Blade For WindmillDokument4 SeitenDesign of Blade For Windmillrospazita100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuideDokument32 SeitenChapter 4 Heat Teacher's GuiderospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InertiaDokument37 SeitenInertiarospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: The Study of and Properties of andDokument17 SeitenPhysics: The Study of and Properties of androspazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawDokument5 SeitenHooke's LawrospazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MESSKO® MTO Technical Data 5784996 04 enDokument44 SeitenMESSKO® MTO Technical Data 5784996 04 ensetiyawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue - Freewater CoffretDokument13 SeitenCatalogue - Freewater Coffretaltax734Noch keine Bewertungen
- GATE 2016 Question Paper Answer EE S2 - 0Dokument17 SeitenGATE 2016 Question Paper Answer EE S2 - 0Akshay SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Simulink Aircraft Electrical Power System Simulation IntroductionDokument75 SeitenMATLAB Simulink Aircraft Electrical Power System Simulation IntroductionqingtaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Data Sheet: Tesys LRD Thermal Overload Relays - 4... 6 A - Class 10ADokument3 SeitenProduct Data Sheet: Tesys LRD Thermal Overload Relays - 4... 6 A - Class 10AtalibanindonesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Ripple Current Reduction On A Single-Phase PWM Voltage-Source RectifierDokument11 SeitenDC Ripple Current Reduction On A Single-Phase PWM Voltage-Source RectifierRajni YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horizontal and Vertical Wind TurbineDokument10 SeitenHorizontal and Vertical Wind TurbinejhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRTS 64Dokument8 SeitenDRTS 64RAJESH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 132KV 2 Line Metering PanelDokument11 Seiten132KV 2 Line Metering PanelUsman RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity: Lightning Is One of The Most Dramatic Effects of ElectricityDokument18 SeitenElectricity: Lightning Is One of The Most Dramatic Effects of ElectricityvaishnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 MCB S200 - AbbDokument32 Seiten04 MCB S200 - AbbVũ Hữu PhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amplifier Anatomy - Part 1: By: Patrick Quilter, Chief Technical Officer QSC Audio Products, IncDokument13 SeitenAmplifier Anatomy - Part 1: By: Patrick Quilter, Chief Technical Officer QSC Audio Products, Inckashif1234567890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Omron MM - Ds - e - 5 - 4 - csm57Dokument17 SeitenOmron MM - Ds - e - 5 - 4 - csm57TaQuangDucNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 DMR 9300 BaseStationsDokument18 Seiten14 DMR 9300 BaseStationsjcolmosmora5212Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9010-9020 Instruction Manual - enDokument42 Seiten9010-9020 Instruction Manual - enRahul DevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QCVN 082009BXD Vietnam Building Code For Urban Underground StructuresDokument66 SeitenQCVN 082009BXD Vietnam Building Code For Urban Underground StructuresNgo Tien VinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Schedule For Board Examination (REE) 2018 PDFDokument1 SeiteReview Schedule For Board Examination (REE) 2018 PDFron villanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhaul DC Motor 1000HP: PT. ABB Sakti IndustriDokument16 SeitenOverhaul DC Motor 1000HP: PT. ABB Sakti IndustriIvan KawempyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenge Folder Medalist 870Dokument2 SeitenChallenge Folder Medalist 870KBR Graphics CanadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huong Dan Lap Dat DCL 220kVDokument16 SeitenHuong Dan Lap Dat DCL 220kVkenlavie1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capstan CabrestanteDokument67 SeitenCapstan CabrestanteFernando CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botai Lighting Jan6 - Price List BT2024Dokument36 SeitenBotai Lighting Jan6 - Price List BT2024ewertoncientistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMMPS-Generator Operations SODokument36 SeitenAMMPS-Generator Operations SOGreenMountainGenerators100% (1)
- Passive Trap Filter For Harmonic ReductionDokument9 SeitenPassive Trap Filter For Harmonic ReductionShiva KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Activity 2Dokument13 SeitenLab Activity 2Kyle GuarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PQSI Coil Lock Model 1003Dokument2 SeitenPQSI Coil Lock Model 1003prabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Sheet 2 PDFDokument13 SeitenLab Sheet 2 PDFmalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSI Device NumbersDokument3 SeitenANSI Device NumbersSalman Ahmed MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 AC To AC ConverterDokument53 SeitenTopic 5 AC To AC ConverterNorain ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutler-Hammer Type Gi 125A Molded Case Circuit Breakers: Current in Multiple of inDokument8 SeitenCutler-Hammer Type Gi 125A Molded Case Circuit Breakers: Current in Multiple of initamarpereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldVon EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (58)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaVon EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellVon EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonVon EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (103)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarVon EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureVon EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (125)
- Highest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersVon EverandHighest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceVon EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (588)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansVon EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyVon EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidVon EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1396)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyVon EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootVon EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterVon EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestVon EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (28)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastVon EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldVon EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsVon EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (242)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterVon EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceVon EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerVon EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (122)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerVon EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (54)
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesVon EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- The Assassination Complex: Inside the Government's Secret Drone Warfare ProgramVon EverandThe Assassination Complex: Inside the Government's Secret Drone Warfare ProgramBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (55)
- Restoration Agriculture: Real-World Permaculture for FarmersVon EverandRestoration Agriculture: Real-World Permaculture for FarmersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (86)
- The Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchVon EverandThe Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (133)