Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DVT PE Wallchart A2 1
Hochgeladen von
hussein_faourCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DVT PE Wallchart A2 1
Hochgeladen von
hussein_faourCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TM
The Essential Element
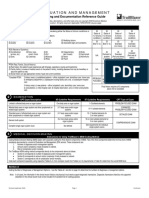
DVT and PE Rule-Out Protocols
Procedure
1. Refer to the DVT Pre-Test Probability Score Table. Add up the score and determine the patients pre-test probability for DVT.
2. Refer to the DVT Diagnostic Algorithm. According to the pre-test probability follow the relevant diagnostic algorithm.
DVT Decision Rule
DVT Diagnostic Algorithm
Wells1 DVT Pre-Test Probability (PTP) Score
Clinical Characteristic
Active cancer (treatment ongoing or within
previous 6 months or palliative)
Paralysis, paresis, or recent plaster immobilisation
of the lower extremities
Recently bedridden for 3 days or more or major
surgery within the previous 12 weeks requiring
general or regional anaesthesia
Localised tenderness along the distribution of
the deep venous system
Entire leg swollen
Calf swelling 3cm > asymptomatic side
(measured 10cm below tibial tuberosity)
Pitting edema confined to the symptomatic leg
Collateral superficial veins (non-varicose)
Previously documented deep-vein thrombosis
Alternative diagnosis as likely or greater than that of DVT
Score
Clinical Probability Assessment
1
1
DVT unlikely (Score <2)
1
1
1
1
1
1
-2
PTP Score
<2
2
D-dimer (Use LMWH if after hours)
D-dimer (Use LMWH if after hours)
Discharge - no DVT
US
US
US
Discharge - no DVT
TREAT
1. Wells PS, Anderson D et al. Evaluation of D-dimer in the Diagnosis of Suspected Deep Vein
Thrombosis N Engl J Med. Sept 25, 2003 349(13): 1227-35
DVT unlikely
DVT likely
DVT likely (Score 2)
No DVT - Follow up
Serial US
TREAT
No DVT - Follow up
Legend: US - Bi-lateral leg vein ultrasonography, LMWH - Low molecular weight heparin
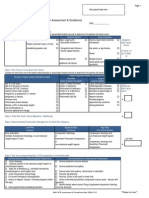
PE Decision Rule
Procedure
1. Refer to the PE Pre-Test Probability Score Table. Add up the score and determine the patients pre-test probability for PE.
2. Refer to the PE Diagnostic Algorithm. According to the pre-test probability follow the relevant diagnostic algorithm.
Wells2 PE Pre-Test Probability (PTP) Score
Clinical Characteristic
PTP Score
Low Probability
<2.0
Moderate Probability 2.0 - 6.0
High Probability
>6.0
Score
Clinical signs and symptoms of DVT (minimum of leg swelling and pain with palpation of the deep veins)
3.0
An alternative diagnosis is less likely than PE
3.0
Heart rate greater than 100 beats/min
1.5
Immobilisation or surgery in the previous 4 weeks
1.5
Previous DVT/PE
1.5
Hemoptysis
1.0
Malignancy (at treatment, treated in the last 6 months or palliative)
1.0
2. Wells P.S., Anderson D. et al. Derivation of a simple Clinical Model to Categorize Patients Probability of Pulmonary Embolism: Increasing the Models Utility with
SimpliRED D-dimer. Thromb Haemost 2000;83:416-20
PE Diagnostic Algorithm
Clinical Probability Assessment
LOW
MODERATE
HIGH
D-dimer
D-dimer
D-dimer
VQ/CT Scan
VQ/CT Scan
PE Excluded
VQ/CT Scan
Normal
High
Non-high
PE Excluded
+
TREAT
PA or
other
tests
High
Non-high
PE Excluded
TREAT
US
US
US
PE Excluded
Normal
TREAT
Manage according to
initial D-dimer result
PE Excluded
+
US
Normal
Non-high
High
US
TREAT
PE Excluded
Manage according to
initial D-dimer result
PE Excluded
in 1 week
TREAT
PA or US
in 1 week
+
TREAT
+
TREAT
Legend: US - Bi-lateral leg vein ultrasonography, PA - Pulmonary Angiography, VQ - Ventilation/Perfusion Scan, CT Computed Tomography
Low PTP single most important step in a safe rule-out protocol 3
3. Kline JA, Wells PS. Methodology for a rapid protocol to rule out pulmonary embolism in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med 2003; 42: 266-76.
This educational tool provided by Wampole Laboratories and Unipath Ltd, distributors of
For more information visit www.wampolelabs.com or www.unipath.com
CMH225-B
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IIIa VTE AlgorithmDokument1 SeiteIIIa VTE AlgorithmJuliana FeronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For UNSW Mock Biomed VivaDokument67 SeitenQuestions For UNSW Mock Biomed VivaReuben TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case-Based Device Therapy for Heart FailureVon EverandCase-Based Device Therapy for Heart FailureUlrika Birgersdotter-GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- D V T: D: Arget Udience BjectiveDokument5 SeitenD V T: D: Arget Udience BjectivedavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas of 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography in Structural Heart Disease Interventions: Cases and VideosVon EverandAtlas of 3D Transesophageal Echocardiography in Structural Heart Disease Interventions: Cases and VideosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final DVTDokument23 SeitenFinal DVTSara MohyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 9: Deep Vein ThrombosisDokument5 SeitenCase 9: Deep Vein Thrombosisintrovoyz041Noch keine Bewertungen
- DVT and Pulmonary Thromboembolism 43Dokument53 SeitenDVT and Pulmonary Thromboembolism 43HussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah Thrombosis 2015 NNDokument39 SeitenKuliah Thrombosis 2015 NNBeladiena Citra SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosisfor PEDokument28 SeitenDiagnosisfor PEMohd Syaiful Mohd ArisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Manual Scores Algorithms Haemostasis ThrombosisDokument64 SeitenPractical Manual Scores Algorithms Haemostasis ThrombosisQuimico Inmunologia GeneticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Article Presentation (Chlorthalidone)Dokument26 Seiten2 Article Presentation (Chlorthalidone)Palak GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Embolism & Deep Vein Thrombosis Definitions: Virchow's TriadDokument7 SeitenPulmonary Embolism & Deep Vein Thrombosis Definitions: Virchow's TriadCitra Eva MeilyndhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdfgDokument9 SeitenAdfgicha shafiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells Score Deep Vein ThrombosisDokument1 SeiteWells Score Deep Vein ThrombosisWiratmono RahmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary EmbolosmDokument15 SeitenPulmonary EmbolosmAETCM Emergency medicineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venous ThromboembolismDokument24 SeitenVenous ThromboembolismubaidrahamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug-Eluting Balloon in Peripheral Intervention For Below TheDokument23 SeitenDrug-Eluting Balloon in Peripheral Intervention For Below TheMuhammad Azhar RosyidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 4 - Presentasi VTE, Kuliah SM Okt 2012Dokument35 SeitenDay 4 - Presentasi VTE, Kuliah SM Okt 2012Maha Satya Dwi PalgunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDokument22 SeitenDeep Vein ThrombosisEznal MahidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocol SummaryDokument4 SeitenProtocol Summaryapi-631272802Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simplified Criteria For PEDokument2 SeitenSimplified Criteria For PESomic8m1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Critical and Unexpected Findings Reporting Policy 1Dokument8 SeitenCritical and Unexpected Findings Reporting Policy 1Firma Nurdinia DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDokument3 SeitenDeep Vein ThrombosisAnonymous cwRgUKv2MQ100% (1)
- SAS Clinical Trails Phase-IDokument70 SeitenSAS Clinical Trails Phase-IAnand KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E&M SheetDokument4 SeitenE&M SheettimvrghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells Criteria / Scoring For PE Present ScoreDokument5 SeitenWells Criteria / Scoring For PE Present ScoreRednose55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance in Hemat LabsDokument38 SeitenQuality Assurance in Hemat LabsSmriti Dwivedi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CG144 Guideline (Updated) 20151125Dokument25 SeitenCG144 Guideline (Updated) 20151125MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) : DisclaimerDokument9 SeitenDeep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) : DisclaimerKaka FebriantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01. 麻醉前評估 - 陳坤堡Dokument58 Seiten01. 麻醉前評估 - 陳坤堡kenny631653Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia Pre Operative EvaluationDokument27 SeitenAnesthesia Pre Operative EvaluationHassan.shehri100% (2)
- Evidence Based Medicine: Kiki Lukman, Bagian Bedah Fakultas Kedokteran UNPAD/ RS DR Hasan Sadikin BandungDokument70 SeitenEvidence Based Medicine: Kiki Lukman, Bagian Bedah Fakultas Kedokteran UNPAD/ RS DR Hasan Sadikin BandungOby BedahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preoperative Patient Assessment and Management: Roxanne Jeen L. FornollesDokument61 SeitenPreoperative Patient Assessment and Management: Roxanne Jeen L. FornollesRyan FornollesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Embolism As Seen in The ED EditedDokument40 SeitenPulmonary Embolism As Seen in The ED EditedSurgicalgownNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTE Assessment & GuidelinesDokument2 SeitenVTE Assessment & GuidelinesAgustreginaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pancreatitis-AGA Institute Medical Position Statement.Dokument7 SeitenAcute Pancreatitis-AGA Institute Medical Position Statement.Nicole BiduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venous Thromboembolic Diseases: Deep Vein Thrombosis: Support For Education and Learning Clinical Case ScenariosDokument64 SeitenVenous Thromboembolic Diseases: Deep Vein Thrombosis: Support For Education and Learning Clinical Case ScenariosNabila TyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Based E/M CodingDokument5 SeitenRisk Based E/M CodingSandra WeeksNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Coding GuidelinesDokument2 SeitenEM Coding Guidelineskar883100% (2)
- PR Wells Khorana PaduaDokument4 SeitenPR Wells Khorana PaduadrIndah NoviantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines DVT PrimaryDokument2 SeitenGuidelines DVT PrimaryRAMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec 9 HospitalDokument36 SeitenSec 9 HospitalAya Eid 7asanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engelberger 2011Dokument5 SeitenEngelberger 2011Kevin TandartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antivenom Reactions IntroductionDokument14 SeitenAntivenom Reactions IntroductionppgpcsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A3 ReportDokument4 SeitenA3 ReportmfernandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking SummaryDokument6 SeitenCritical Thinking Summaryapi-231899545Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical ManagementDokument13 SeitenMedical Surgical ManagementNikki BrodethNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeurosurgeryDokument52 SeitenNeurosurgeryBryan AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence-Based Practice of Anesthesiology Chapter 2: Update On Preprocedure TestingDokument2 SeitenEvidence-Based Practice of Anesthesiology Chapter 2: Update On Preprocedure Testingrtaneja92Noch keine Bewertungen
- M33 - Stase IPD - Hassan Assagaf Guidance For The Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary EmbolismDokument16 SeitenM33 - Stase IPD - Hassan Assagaf Guidance For The Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary EmbolismHasan AssegafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Guideline For Management of Acute Pancreatitis in AdultsDokument13 SeitenClinical Guideline For Management of Acute Pancreatitis in AdultsrivaldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issue 3 Dennis Slater Attract Trial ArticleDokument2 SeitenIssue 3 Dennis Slater Attract Trial Articleapi-400507461Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Updated Analysis of The Survival Endpoints of Ascende-Rt: Clinical InvestigationDokument10 SeitenAn Updated Analysis of The Survival Endpoints of Ascende-Rt: Clinical InvestigationfumadelabuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nrg-Gi002 Protocol PresentationDokument16 SeitenNrg-Gi002 Protocol Presentationapi-508897697Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic and Laboratory Procedures 1. Complete Blood Count (CBC) With APCDokument5 SeitenDiagnostic and Laboratory Procedures 1. Complete Blood Count (CBC) With APCCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.1016/j.thromres.2016.11.009: Thrombosis ResearchDokument35 Seiten10.1016/j.thromres.2016.11.009: Thrombosis ResearchresiNoch keine Bewertungen
- n378.008 Iris Website Staging of CKD PDFDokument8 Seitenn378.008 Iris Website Staging of CKD PDFrutebeufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Hepatic Sclerosing HemangiomaDokument4 SeitenMultiple Hepatic Sclerosing Hemangiomahussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument4 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Female Incontinence and Pelvic Reconstructive SurgeryDokument333 SeitenComplications of Female Incontinence and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeryhussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outpatient Algorithm For The Management of DVT/PE: Optional: HCO LogoDokument1 SeiteOutpatient Algorithm For The Management of DVT/PE: Optional: HCO Logohussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument4 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument3 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument4 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pi Is 2210261215001479Dokument3 SeitenPi Is 2210261215001479hussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table Accessories BrochureJuly2015Web1Dokument36 SeitenTable Accessories BrochureJuly2015Web1hussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting A New Level For Operating Table PerformanceDokument20 SeitenSetting A New Level For Operating Table Performancehussein_faour0% (1)
- Operating: Quality Performance Trust CompletelyDokument12 SeitenOperating: Quality Performance Trust Completelyhussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics & Gynaecology Operating TableDokument6 SeitenObstetrics & Gynaecology Operating Tablehussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pi Is 2210261215001376Dokument6 SeitenPi Is 2210261215001376hussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument4 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument5 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument4 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument3 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument7 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument5 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Case ReportsDokument3 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Case Reportshussein_faourNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 - Chapter 7 PDFDokument41 Seiten11 - Chapter 7 PDFRakesh RakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1-3Dokument55 SeitenChapter 1-3Mark Ryan Nagales0% (1)
- Association Between Subjective Sleep Quality, Hypertension, Depression and Body Mass Index in A Nigerian Family Practice SettingDokument7 SeitenAssociation Between Subjective Sleep Quality, Hypertension, Depression and Body Mass Index in A Nigerian Family Practice SettingFerdy LainsamputtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolygraDokument15 SeitenPolygraAbdul Aziz Akil RiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Revision Test - Basics 1Dokument16 SeitenComprehensive Revision Test - Basics 1drpnnreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 2013 Exam QuestionsDokument13 SeitenSeptember 2013 Exam QuestionsooiziungieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 2Dokument2 SeitenNCP 2hsiria100% (1)
- Literature Review On IbuprofenDokument8 SeitenLiterature Review On Ibuprofenbujuj1tunag2100% (1)
- Ob &gyDokument6 SeitenOb &gyThumz ThuminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frog Dissection LabDokument6 SeitenFrog Dissection Labapi-279500653Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neuroshield ReportDokument2 SeitenNeuroshield Reportrahim pathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Regulation and Syllabus 2013-14Dokument135 SeitenAcademic Regulation and Syllabus 2013-14Sagar MudgalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin A Natural SourcesDokument3 SeitenVitamin A Natural Sourceszoezoe87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Use of Drugs 10 BDokument39 SeitenRational Use of Drugs 10 BAnonymous DgPsK0oQ100% (1)
- KARDEX Case 3Dokument3 SeitenKARDEX Case 3Juviely PremacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer and Rationale Community Health NursingDokument25 SeitenAnswer and Rationale Community Health NursingDENNIS N. MUÑOZ100% (1)
- Drug Study (Tramadol)Dokument2 SeitenDrug Study (Tramadol)esdale83% (6)
- Drug Therapy For PicuDokument32 SeitenDrug Therapy For PicuNeethu Mariya MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Una Coales-Get Through Medical School - 1000 Sbas Bofs and Emqs (Get Through Series) (2003) PDFDokument151 SeitenUna Coales-Get Through Medical School - 1000 Sbas Bofs and Emqs (Get Through Series) (2003) PDFCathy QianNoch keine Bewertungen
- FilariasisDokument5 SeitenFilariasisSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: Report of Two CasesDokument3 SeitenDirect Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: Report of Two Casesemie sitorusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methanol Poisoning OverviewDokument5 SeitenMethanol Poisoning OverviewDya AndryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abductive Inference Computation Philosophy TechnologyDokument314 SeitenAbductive Inference Computation Philosophy Technologyusernameabout100% (1)
- PlacentaDokument21 SeitenPlacentaAttiqaQureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HospPharm 1.1 - DevHistoryDokument18 SeitenHospPharm 1.1 - DevHistoryHeidi Jade Ong BalinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- OET Test 14Dokument10 SeitenOET Test 14shiela8329gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disclosure and Attestation Form - SPEAKERDokument1 SeiteDisclosure and Attestation Form - SPEAKERwethreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sickle Cell Disease, Epidemiology, Genetic History, Complication and ManagementDokument52 SeitenSickle Cell Disease, Epidemiology, Genetic History, Complication and ManagementAnastasiafynnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Meningitis Case StudyDokument5 SeitenPediatric Meningitis Case StudyCheska PalomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchial AsthmaDokument40 SeitenBronchial Asthmasamson bd mokuntil100% (1)