Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ion Channels
Hochgeladen von
Mizrab NadeemCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ion Channels
Hochgeladen von
Mizrab NadeemCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ASSIGNMENT 1
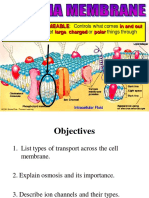
1. Transmembrane proteins that span across the lipid bilayer of a cell
membrane permitting movement of ions such as sodium, potassium into and
out of the cell. This action of the ion channels leads to an establishment of
an action potential across the cell membrane.
2. Answer 2
Voltage-gated channels: potassium and sodium channels. Found in
nerves.
Extracellular ligand-gated channels: GABA, Glycine receptor channels;
these channels are regulated by hormones or neurotransmitters. Present in
nerve and muscle cells.
Intracellular ligand-gated channels: CFTR, ATP, cAMP, cGMP.
3. Answer 3
Ion channels are selective; not all ions can pass through. This property
depends on the size of the ion and the charge it carries.
Can be open or closed; only selectively permeable ions can flow through
when an ion channel is open.
Quick transport of selectively permeable ions.
4. Answer 4
Voltage clamp: controlling of membrane potential.
Patch clamp: Cell attached patch clamp (cell intact) , Inside out patch
(patch pulled loosely from the cell) and Whole cell recording (patch sucked
out using micropipette which is attached to the rest of the cell membrane).
X-ray crystallization: tracing atoms in a protein.
Electron microscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR): determination of short
transmembrane peptides placed in organic solvents.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction): finding the mutation in a codon of Na+
channel by using primers.
Mutagenesis: Changing the sequence of specific amino acids in proteins.
5. Answer 5
A)
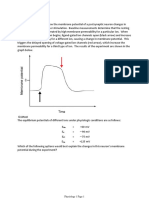
Concentration differences of ions on either side of a membranes - diffusion
potentials - gives rise to a RMP, specially of ions with high permeability which
have a greater effect on the RMP.
B)
Action potential generation causes structural changes in the ion channels
causing them to open to let passage of ions.
Depolarization cause the membrane potential to become more negative
when the sodium channel opens.
Repolarization causes the membrane to return to its resting state. This
occurs when voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are closed.
Depolarization results in a prolongation of a nerve impulse.
6. Answer 6
Neurotransmitters are chemical messenger that bring about a change in the
structural change in the ligand-gated ion channels allowing the ions to pass
through.
The ions pass from the region of their high concentration to low
concentration when the channel is open.
Depolarization occurs as the positively charged ion pass to the inside and
repolarization occurs if there is influx of negatively charged ions.
7. Answer 7
Ligand-gated ion channels: The type of ligand that attaches to the receptor
determines the opening and the closing of these channels.
Volume-regulated ion channels: Increase in volume of cell causes release of
ions that influence cell activity.
Eosinophil cells of the human immune system regulate cell activity and
protection against foreign invaders.
Regulation mainly by protein phosphorylation and dephosphorylating of
serine, tyrosine residues.
8. Answer 8
Calcium channel blockers: inhibition of calcium input in neurons no
excitatory response. E.g. Valproate, Etosuximid. Used as anti-epileptics.
Sodium channel blockers: inhibition of sodium influx.
GABA receptor agonist: Benzodiazepines - enhance GABA receptor
activity.
NMDA receptor antagonist: ketamine injectable anesthetic.
Insulin secretagogues: inhibit potassium channels (depolarization) and
promote insulin release.
Cardiac glycosides: Digoxin - inhibit Na+ K+ ATPase. Decrease in active
transport of sodium and potassium causing a influx of calcium into cell
leading to cardiac muscle contraction.
Proton pump inhibitors: Omeprazole.
Anti-depressants: Serotonin.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Surgical PhsyiologyDokument170 SeitenSurgical PhsyiologySteve FerisNoch keine Bewertungen
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Dokument18 SeitenP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)hendra2darmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 17 PDFDokument71 Seiten12 17 PDFVikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical PhsyiologyDokument170 SeitenSurgical PhsyiologyTamjid Khan100% (2)
- Key Points RevisionDokument124 SeitenKey Points RevisionSumeyyah KemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenMolecular PathophysiologyElisa RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To NeurophysiologyDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Neurophysiologyvenkata ramakrishnaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOC 315 - Lecture - 4Dokument29 SeitenBIOC 315 - Lecture - 4Kevin KipropNoch keine Bewertungen
- A - Cellular PhysiologyDokument12 SeitenA - Cellular PhysiologyMohamad Zekry ZuhairyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankyrin:: Complex of Five Subunits, Having A Binding Site For AcetylcholineDokument3 SeitenAnkyrin:: Complex of Five Subunits, Having A Binding Site For AcetylcholineDrbee10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To RMP ND APDokument78 SeitenIntroduction To RMP ND APHariharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diversity of Ion Channal: Prepared by Maryam Khattak Roll No 14 2 SemsterDokument9 SeitenDiversity of Ion Channal: Prepared by Maryam Khattak Roll No 14 2 Semsteryaqoob008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 The Peripheral Nervous SystemDokument77 SeitenUnit 2 The Peripheral Nervous SystemKemoy FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurochem FinalDokument20 SeitenNeurochem Finalelifulku.a1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Channels and PumpsDokument10 SeitenChannels and Pumpsazazel666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protein ChannelsDokument34 SeitenProtein ChannelsAjay Singh ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurobiophysics2009 PreprintDokument52 SeitenNeurobiophysics2009 PreprintsmiglemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankyrin:: Complex of Five Subunits, Having A Binding Site For AcetylcholineDokument3 SeitenAnkyrin:: Complex of Five Subunits, Having A Binding Site For AcetylcholineDrbee10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cell BiologyDokument14 SeitenAdvanced Cell BiologyUmair AneesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Channelopathies: Ion Channel Defects Linked To Heritable Clinical DisordersDokument12 SeitenChannelopathies: Ion Channel Defects Linked To Heritable Clinical Disorderscote_cote6951Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument6 SeitenNervous SystemarellanokristelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nerve and Muscle PhysiologyDokument82 SeitenNerve and Muscle PhysiologychandsriNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Resting Membrane Potential?: Mechanism of An Action PotentialDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Resting Membrane Potential?: Mechanism of An Action PotentialAli InamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio PsycheDokument16 SeitenBio PsycheShruti DharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology L2Dokument13 SeitenPhysiology L2dfffggg2je443qfdfvhkhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resting Membrane PotentialDokument22 SeitenResting Membrane PotentialSanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 8-Grey Matter - ProcessesDokument6 SeitenTopic 8-Grey Matter - ProcessesYasmin KhundakjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Potential in NeuronsDokument109 SeitenAction Potential in NeuronsAdmin0% (1)
- Tutorial 4.3Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 4.3Rosa FinizioNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 3 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanDokument10 SeitenA2 Level Biology: Coordination-Lecture 3 by Muhammad Ishaq KhanAwais BodlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 111 Week 2 WorksheetDokument4 Seiten111 Week 2 WorksheetjabyleynesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Potential: Nams, Bir Hospital B.SC - MIT 1 Year Suraj Sah Roll No. 9Dokument42 SeitenAction Potential: Nams, Bir Hospital B.SC - MIT 1 Year Suraj Sah Roll No. 9Maxamed Cali AtomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural PhysiologyDokument45 SeitenNeural PhysiologyHakim Asif Haider100% (1)
- 1 Ion Channel - Pertemuan 8-MhsDokument35 Seiten1 Ion Channel - Pertemuan 8-MhsDwi Amalia husnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion Channels Are Pore-FormingDokument11 SeitenIon Channels Are Pore-FormingshanmukhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of The Cell DR - Ayana Wasee: Woreta Health Science and Business CollegeDokument47 SeitenPhysiology of The Cell DR - Ayana Wasee: Woreta Health Science and Business CollegeEyachew TewabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEURONDokument4 SeitenNEURONsummerbombabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System 2Dokument4 SeitenNervous System 2P KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Physiology Assignment 01Dokument9 SeitenHuman Physiology Assignment 01Evaristo MK VincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Neuron Transmission and Communication SystemDokument5 SeitenTypes of Neuron Transmission and Communication SystemRbbani AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ligand Gated Ion ChannelDokument12 SeitenLigand Gated Ion ChannelShoaib PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion ChannelsDokument6 SeitenIon ChannelsNicolas IsformermynameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Topic 2 Lecture 4 5Dokument22 SeitenNervous System Topic 2 Lecture 4 5amjad.46987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cytolog Membrtransport2 (Stud)Dokument4 SeitenCytolog Membrtransport2 (Stud)OnSolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action PotentialDokument21 SeitenAction PotentialjolilarmatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Features: On Channels Are Pore-FormingDokument6 SeitenBasic Features: On Channels Are Pore-Formingmarian lupuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guyton Notes Chapter 05Dokument4 SeitenGuyton Notes Chapter 05aima_uy50% (2)
- 8 - NervousDokument8 Seiten8 - NervousMa. Therese CampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Year Pharm-D (Evening) : Submitted byDokument21 Seiten1 Year Pharm-D (Evening) : Submitted byJawad NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions ExplanationDokument17 SeitenQuestions ExplanationnomintmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 The Origin of Biopotentials (New)Dokument62 Seiten1.0 The Origin of Biopotentials (New)Hanif HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology OralDokument96 SeitenPhysiology OralLucem MiracleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2222 TransportDokument42 Seiten2222 TransportaddwrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nagaba Ritah Acktone 2020Dokument2 SeitenNagaba Ritah Acktone 2020Ritah ACKTONE NAGABANoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion Channel: 2 Biological RoleDokument8 SeitenIon Channel: 2 Biological RoleMartin MayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Targets 2Dokument6 SeitenDrug Targets 2laaraybmehmood1503Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cheng HM Key Concepts Priciples Na GradDokument1 SeiteCheng HM Key Concepts Priciples Na GradAlya LawrentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Signaling PathwaysDokument18 SeitenCell Signaling PathwaysJean Marcel Sousa LiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action PotentialDokument24 SeitenAction PotentialJohn MarcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PancreatitisDokument51 SeitenPancreatitisMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imaging of The Cardiovascular SystemDokument77 SeitenImaging of The Cardiovascular SystemMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imaging of The Respiratory SystemDokument105 SeitenImaging of The Respiratory SystemMizrab Nadeem100% (1)
- Imaging of The Cardiovascular SystemDokument77 SeitenImaging of The Cardiovascular SystemMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin LesionsDokument40 SeitenSkin LesionsMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Lecture NotesDokument190 SeitenENT Lecture NotesMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding and Thrombotic DisordersDokument47 SeitenBleeding and Thrombotic DisordersMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Age Related Changes in Endocrine SystemDokument2 SeitenAge Related Changes in Endocrine SystemMizrab Nadeem0% (1)
- Anatomy of ProstateDokument5 SeitenAnatomy of ProstateMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Taking in DermatologyDokument2 SeitenHistory Taking in DermatologyMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of ProstateDokument5 SeitenAnatomy of ProstateMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapy in Disorders of Male Reproductive SystemDokument4 SeitenDrug Therapy in Disorders of Male Reproductive SystemMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0620 s11 QP 11Dokument16 Seiten0620 s11 QP 11Mizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0620 s11 QP 11Dokument16 Seiten0620 s11 QP 11Mizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- English LanguageDokument2 SeitenEnglish LanguageMizrab NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cusack Protocol .. Supplement Dosages Information Chart. Word PDFDokument2 SeitenCusack Protocol .. Supplement Dosages Information Chart. Word PDFNaomy DC100% (6)
- Animal Experimentation ViewpointsDokument80 SeitenAnimal Experimentation ViewpointschristianbarrigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breeds of DogsDokument257 SeitenBreeds of DogsshayanbzjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Adding Different Levels of Olive Leaf Powder To The Diet On The Production Performance and Some Physiological Characteristics of BroilersDokument9 SeitenEffect of Adding Different Levels of Olive Leaf Powder To The Diet On The Production Performance and Some Physiological Characteristics of BroilersreviewjreNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Vodka Diet Edit 12.20Dokument114 SeitenThe Vodka Diet Edit 12.20Late Knight GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDokument23 SeitenChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocw Humanos y Otros AnimalesDokument4 SeitenOcw Humanos y Otros Animalesmiguel6789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short Stories For KidsDokument14 SeitenShort Stories For KidsSherine Lois QuiambaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction SystemDokument38 SeitenReproduction SystemNurfatin AdilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholesterol Mortality Chart PDFDokument1 SeiteCholesterol Mortality Chart PDFTms Arn100% (1)
- Hypotonic Hypertonic Isotonic Solutions UsesDokument9 SeitenHypotonic Hypertonic Isotonic Solutions UsesImtiaz AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cestode Parasites: Medical Parasitology, 2009 University of Palangkaraya Agus HaryonoDokument45 SeitenCestode Parasites: Medical Parasitology, 2009 University of Palangkaraya Agus HaryonoMeylisa Gerson BayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 7 English - Comprehension PassageDokument7 SeitenCBSE Class 7 English - Comprehension PassagemotherhoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice Natural RemediesDokument12 SeitenJaundice Natural RemediesprkshshrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 16Dokument128 Seiten11 16WoodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Balance and Oxygenation: Blood GasesDokument5 SeitenAcid-Base Balance and Oxygenation: Blood GasesMarcus, RN100% (6)
- Nose Fracture and Deviated SeptumDokument17 SeitenNose Fracture and Deviated Septummimi2188Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Autonomic Nervous System: J J M Medical College, Davangere. Dept of AnesthesiaDokument117 SeitenPhysiology of Autonomic Nervous System: J J M Medical College, Davangere. Dept of AnesthesiaKithminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reams-RBTI Alphabetical Reference Manual by Stanley & Gertrude Gardner Reams Seminars 1975-1977Dokument144 SeitenReams-RBTI Alphabetical Reference Manual by Stanley & Gertrude Gardner Reams Seminars 1975-1977Steve DiverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friesen C4ST Amended Input HC Safety Code 6 - 140 Omitted Studies 224pDokument224 SeitenFriesen C4ST Amended Input HC Safety Code 6 - 140 Omitted Studies 224pSeth BarrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platelet CountsDokument35 SeitenPlatelet Countsshikhar623Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Physiological Changes of PregnancyDokument16 SeitenThe Physiological Changes of PregnancycchaitukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystalloids or ColloidsDokument23 SeitenCrystalloids or ColloidsmuthiashabrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionDokument2 SeitenPathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionMauliza Resky NisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Pressure RegulationDokument11 SeitenBlood Pressure RegulationPaulShaneHerreraZorrillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Cranial Nerves and AssessmentDokument9 Seiten12 Cranial Nerves and AssessmentRella QuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeurosyphilisDokument8 SeitenNeurosyphilisl1o2stNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refinements in The Care and Use of Animals in Toxicology Studies - Regulation, Validation and ProgressDokument8 SeitenRefinements in The Care and Use of Animals in Toxicology Studies - Regulation, Validation and Progressgabriela_mariangela5929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Development of The Fetal Membranes and PlacentaDokument4 SeitenDevelopment of The Fetal Membranes and PlacentaBandula KusumsiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- College Prep Main Ideas WorksheetDokument10 SeitenCollege Prep Main Ideas Worksheetlorrainecarrillo18Noch keine Bewertungen