Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pain Management
Hochgeladen von
barrihamid0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
43 Ansichten1 SeiteA growing body of evidence suggests that we should re-assess our management of osteoarthritis (OA) in dogs. Pain is not only a consequence of OA, but may also play a part in driving the disease process. This new understanding has profound implications for the way we manage dogs. Intermittent NSAID treatment, to treat flareups, may not provide the best long-term outcome. Continuous NSAID therapy (daily for 28 days or longer) may be more beneficial.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenA growing body of evidence suggests that we should re-assess our management of osteoarthritis (OA) in dogs. Pain is not only a consequence of OA, but may also play a part in driving the disease process. This new understanding has profound implications for the way we manage dogs. Intermittent NSAID treatment, to treat flareups, may not provide the best long-term outcome. Continuous NSAID therapy (daily for 28 days or longer) may be more beneficial.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
43 Ansichten1 SeitePain Management
Hochgeladen von
barrihamidA growing body of evidence suggests that we should re-assess our management of osteoarthritis (OA) in dogs. Pain is not only a consequence of OA, but may also play a part in driving the disease process. This new understanding has profound implications for the way we manage dogs. Intermittent NSAID treatment, to treat flareups, may not provide the best long-term outcome. Continuous NSAID therapy (daily for 28 days or longer) may be more beneficial.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
0954 - Trocoxil Pre Launch Advertorial_FINAL.
pdf 24/7/09 09:28:00
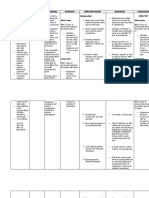
Pain and the progression of canine OA
A growing body of evidence heightens the intensity of pain experienced Reassessing pain management
following noxious stimuli. This is very important
suggests that we should re-assess because the changes are anatomical and
– Clinical evidence supporting
our management of osteoar- long lasting. Once established, central this theory
thritis (OA) if we are to provide sensitization is difficult to control, even with A soon-to-be-published systematic review
potent analgesics – so prevention can be the of all the published studies on long-term
pets with the best possible key to management. continuous NSAID therapy (daily for 28 days
long-term prognosis. or longer) in dogs with OA indicated a benefit
Osteoarthritic pain is harmful in several ways: of long-term continuous treatment with
In recent years our understanding of joint A vicious cycle develops whereby repeated NSAIDs over short-term treatment and no
pain, and in particular the mechanisms that exposure to pain leads to central sensitization evidence of any increase in side-effects.10
drive it, has changed. It is now apparent that which in turn makes the pain more severe and
pain is not only a consequence of osteoarthritis, difficult to control and further perpetuates Will owners play their part?
but may also play a part in driving the disease central sensitization.
process.1 Dogs with painful OA are reluctant to With continuous NSAID therapy owners can
exercise. Reduced activity leads to muscle be reassured that their pet is relieved of the
This new understanding has profound implica- wasting, which is one of the factors that may pain and inflammation of OA, allowing
tions for the way we manage dogs with contribute to OA disease progression.4 improved joint function and mobility, and
osteoarthritis. It increases the importance of Central sensitization can increase the level perhaps slower disease progression.
minimising or preventing pain. Providing of inflammation in joints.5 Inflammatory However this approach requires an increased
intermittent NSAID treatment, to treat flare- mediators such as PGE2 have been shown to commitment from the owner. Daily dosing is
ups, may not provide the best long-term contribute to cartilage degradation.6 undoubtedly inconvenient and at times may
outcome. Instead, continuous NSAID therapy reduce compliance. One answer lies in the
may be more beneficial. use of a new long-acting NSAID.
The role of NSAID therapy
COX-2 enzymes have been shown to play
Sensitization
a role in the development of central
Trocoxil™ – the first and
Research has shown that the components of the sensitization7, and their inhibition by NSAIDs
only once-monthly NSAID
pain pathway can change in response to a can prevent its development.8 Treatment of Trocoxil (mavacoxib) is a new, innovative
pain stimulus. Pain receptors `up-regulate´ in central sensitization has been shown to preferential COX-2 inhibitor with a profile
response to painful stimuli and become more reduce joint inflammation in models of which is ideally suited to continuous
sensitive to subsequent pain. As a result, arthritis.9 treatment of pain and inflammation
previously non-painful events (such as touch) associated with canine OA. After the
can be interpreted as painful stimuli. Pain second dose, Trocoxil is administered
If administration of daily NSAIDs is not once a month in the form of flavoured
sensitization (`wind-up´) can also result in continuous, there is a risk that dogs will suffer chewable tablets.
hyperalgesia where the pain threshold to pain which will stimulate pain pathways
noxious stimuli is lessened, so that mild to A multicentre study involving client owned
resulting in central sensitization. dogs with OA has shown that successive
moderate pain is experienced as a more
monthly dosing with Trocoxil leads to contin-
intense pain. These changes occur in both The message is clear: potentially if pain ued improvement.
11
peripheral and central pain pathways.2,3 can be prevented by continuous
In the central pain pathways, exposure to In clinical field studies, the side-effects
pain management, then the pain seen with Trocoxil have been similar in
repeated painful stimuli changes the way pain is pathways will not be sensitized and type, frequency and duration to those seen
processed. This so-called `central sensitization´ central sensitization will not occur. with daily carprofen.
11
References 1. Fiorentino PM et al. Spinal Interleukin-1β in a mouse model of arthritis
and joint pain. Arthritis Rheum 2008. 58(10): 3100-9 2. Hellyer P et al. AAHA/AAFP
PAIN Load Pain Management Guidelines for Dogs & Cats. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2007; 43(5):
235-48 3. Schaible HG et al. Pathophysiology and treatment of pain in joint
disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2006; 58(2): 323-42 4. Herzog W et al. The role of
muscles in joint degeneration and osteoarthritis. J Biomech 2007; 40(suppl 1):
S54-63 5. Sluka KA et al. Joint inflammation is reduced by dorsal rhizotomy and not
Obesity by sympathectomy or spinal cord transection. Ann Rheum Dis 1994; 53(5): 309-14
6. Hardy MM et al. Cyclooxygenase 2-dependent Prostaglandin E2 modulates
cartilage proteoglycan degradation in human osteoarthritis explants. Arthritis Rheum
INFLAMMATION 2002; 46(7): 1789-803 7. Samad TA et al. Interleukin-1β–mediated induction of
COX-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 2001;
Central 410(6827): 471-5 8. Veiga AP et al. Prevention by celecoxib of secondary
Sensitization Inactivity hyperalgesia induced by formalin in rats. Life Sci 2004; 75(23): 2807-17 9. Sluka
KA et al. Reduction in joint swelling and hyperalgesia following post-treatment with a
`WIND-UP´ non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist. Pain 1994; 59(1): 95-100 10. Innes et
al. Systematic review of the safety and efficacy of long term NSAID use in the
treatment in canine osteoarthritis. Vet Record. (In press) 11. Payne-Johnson et al.
Determination of the efficacy and safety of mavacoxib tablets administered monthly
at 2mg/kg bw in the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with
Rate osteoarthritis in dogs. BSAVA abstract 2009.
of cartilage DISUSE
degradation muscle wasting
Joint
instability
The pain sensitization `wind-up´ cycle
For further information please contact Pfizer Animal Health, Walton Oaks, Tadworth, Surrey KT20 7NS POM-V
Trocoxil contains Mavacoxib.
AH314/09
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TVP-2020 Pain-Management EbookDokument44 SeitenTVP-2020 Pain-Management Ebookizabelle.pereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MacFarlane - Chronic Pain in DogsDokument9 SeitenMacFarlane - Chronic Pain in DogsSara ConnorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greene, S. A. Chronic Pain Pathophysiology and Treatment Implications. Topics in Companion Animal Medicine, v.25, n.1, p.5-9. 2010 PDFDokument5 SeitenGreene, S. A. Chronic Pain Pathophysiology and Treatment Implications. Topics in Companion Animal Medicine, v.25, n.1, p.5-9. 2010 PDFFran WermannNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SM PDFDokument4 Seiten1 SM PDFUtibe Tibz IkpembeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Exposure Physical Therapy (PEPT) in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1: A Systematic ReviewDokument8 SeitenPain Exposure Physical Therapy (PEPT) in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1: A Systematic ReviewSabrina JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Basic Consideration PDFDokument4 SeitenPain Basic Consideration PDFCiprian CorneaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dysfunctional Analgesia During ExerciseDokument10 SeitenDysfunctional Analgesia During ExerciseEric MatsuzakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TL 4Dokument4 SeitenTL 4ĐôngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effectiveness of Myofascial Trigger Point Release Technique To Evaluate Pain in Chronic Tension Type Headache Patients.Dokument40 SeitenEffectiveness of Myofascial Trigger Point Release Technique To Evaluate Pain in Chronic Tension Type Headache Patients.Dr.Gopinath SaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Analgesics Opioids, Tramadol, and Tapentadol (Part 2)Dokument7 SeitenAn Overview of Analgesics Opioids, Tramadol, and Tapentadol (Part 2)幸福KoreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- APJP2023 (PP 01) - 01 GalluccioDokument6 SeitenAPJP2023 (PP 01) - 01 GallucciomalvindersahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidepressand Pain 2006Dokument7 SeitenAntidepressand Pain 2006Paulo MaurícioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Neuropathic PainDokument10 SeitenManaging Neuropathic PainAgusBhakti100% (1)
- Management of Mixed PainDokument19 SeitenManagement of Mixed PainGita FitrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Chronic Pain. The Role of Learning and Brain PlasticityDokument12 Seiten2014 Chronic Pain. The Role of Learning and Brain PlasticityCristian OyarzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articulo 4Dokument12 SeitenArticulo 4Catherinne Quiñonez GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms of PainDokument3 SeitenMechanisms of PainPembaca sejatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acupuncture and Pain: A Review of The Literature: Ladan Eshkevari, CRNA, MS, Dipl. AcDokument10 SeitenAcupuncture and Pain: A Review of The Literature: Ladan Eshkevari, CRNA, MS, Dipl. AcRatrika SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Nasari 2012Dokument8 SeitenFor Nasari 2012basma adianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 The Pain of Tendinopathy - Physiological or PathophysiologicalDokument15 Seiten2014 The Pain of Tendinopathy - Physiological or PathophysiologicalDavid Alejandro Cavieres AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology and Pathophysiology of Chronic Pain (Part II) How Does Pain Become Chronic?Dokument4 SeitenPhysiology and Pathophysiology of Chronic Pain (Part II) How Does Pain Become Chronic?Stra LettNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is This Thing Called Pain (2010)Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is This Thing Called Pain (2010)Hugo FalquetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Analgesics in (Headache) Pain Therapy: Shotgun Approach or Precise Multi-Target Therapeutics?Dokument15 SeitenCombined Analgesics in (Headache) Pain Therapy: Shotgun Approach or Precise Multi-Target Therapeutics?NirmalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute Pain Rhea FinalDokument1 SeiteNCP Acute Pain Rhea FinalSolsona Natl HS MaanantengNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is This Thing Called PainDokument4 SeitenWhat Is This Thing Called PainSetiawan Fritzgetald WicaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myofascial Trigger Point Pain: Understanding Referred Pain PatternsDokument10 SeitenMyofascial Trigger Point Pain: Understanding Referred Pain PatternsJay ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic-Pain-Common Pain-Syndromes-ArticleDokument17 SeitenChronic-Pain-Common Pain-Syndromes-ArticleVinay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal - Relief of PainDokument6 SeitenJurnal - Relief of PainChandra NepaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Specific Arm PainDokument4 SeitenNon-Specific Arm PainSabrina Jones100% (1)
- Palmitoylethanolamide in The Treatment of Chronic Pain Caused by Different EtiopathogenesisDokument10 SeitenPalmitoylethanolamide in The Treatment of Chronic Pain Caused by Different EtiopathogenesisSpore FluxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyeah Astarii Jurnal ReadingDokument25 SeitenDyeah Astarii Jurnal Readingfeby ary annasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesiology 250 Learning ModulesDokument32 SeitenAnesthesiology 250 Learning ModulesNiña AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managment NyeriDokument12 SeitenManagment NyeriKabag KeperawatanMHSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Cord Stimulation, MILD Procedure, and Regenerative Medicine, Novel Interventional Nonopioid Therapies in Chronic PainDokument7 SeitenSpinal Cord Stimulation, MILD Procedure, and Regenerative Medicine, Novel Interventional Nonopioid Therapies in Chronic PainRobert MacedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIDNDokument21 SeitenFIDNBeta WattimenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descending Pain Modulation and Chronification of Pain: ReviewDokument9 SeitenDescending Pain Modulation and Chronification of Pain: ReviewJose PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tapentadol ThiocholchicosideDokument2 SeitenTapentadol ThiocholchicosideMohammad Shahbaz Alam100% (1)
- Cancer Pain ManagementDokument8 SeitenCancer Pain ManagementMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan PainDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Painjanmarc goreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs and Symptoms ofDokument8 SeitenSigns and Symptoms ofNegin HekmatjooNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPDS-Multifactorial Etiology and Varied Pathophysiology: A ReviewDokument7 SeitenMPDS-Multifactorial Etiology and Varied Pathophysiology: A Reviewsnehal jaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mert 2017Dokument8 SeitenMert 2017G PalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-s2.0-S188783692030065X-mainDokument6 Seiten1-s2.0-S188783692030065X-mainmarcello BoninoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Post-Operative PainDokument8 SeitenManaging Post-Operative PainAminn Alhassan ContehNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is This Thing Called Pain?: Review Series IntroductionDokument3 SeitenWhat Is This Thing Called Pain?: Review Series Introductionluis bulnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCT 2Dokument20 SeitenPCT 2Wialda Dwi rodyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery For Chronic Back Pain or Chronic Neck Pain Does It WorkDokument4 SeitenSurgery For Chronic Back Pain or Chronic Neck Pain Does It WorkHerald Scholarly Open AccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Neuropathic Pain ManagementDokument32 SeitenOverview of Neuropathic Pain ManagementBernad NauliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuropathic Pain: Redefinition and A Grading System For Clinical and Research Purposes - TreedeDokument8 SeitenNeuropathic Pain: Redefinition and A Grading System For Clinical and Research Purposes - TreedeNahu SteinmannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem List 1. Acute Pain 2. Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements 3. Impaired Physical Mobility 4. Impaired Skin Integrity 5. Disturbed Body ImageDokument12 SeitenProblem List 1. Acute Pain 2. Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements 3. Impaired Physical Mobility 4. Impaired Skin Integrity 5. Disturbed Body Imagebernadette babaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Needling X Disfunção TemporomandibularDokument1 SeiteDry Needling X Disfunção TemporomandibularRafel FisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Management and Wound Care: Kari Bechert, MPT, Steve E. Abraham, DPMDokument7 SeitenPain Management and Wound Care: Kari Bechert, MPT, Steve E. Abraham, DPMmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TENSDokument2 SeitenTENSmengtingNoch keine Bewertungen
- BurstDr Visceral PainDokument11 SeitenBurstDr Visceral Painnavid.amirabadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referred Muscle Pain Basic and Clinical FindingsDokument9 SeitenReferred Muscle Pain Basic and Clinical FindingsaavalverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Mechanisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis: D.F. Mcwilliams, D.A. WalshDokument8 SeitenPain Mechanisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis: D.F. Mcwilliams, D.A. WalshAmer WasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms and Manifestations in Musculoskeletal.4 PDFDokument17 SeitenMechanisms and Manifestations in Musculoskeletal.4 PDFRodrigo Yarzábal RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EFEK KOMPRES HANGAT DAN DINGIN TERHADAP NYERI SENDI REUMATOIDDokument11 SeitenEFEK KOMPRES HANGAT DAN DINGIN TERHADAP NYERI SENDI REUMATOIDchrisamariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Neuralgia and Related Nerve DisordersVon EverandA Simple Guide to Neuralgia and Related Nerve DisordersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Neuropathic Pain (Neuralgia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandNeuropathic Pain (Neuralgia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Performance AppraisalDokument19 SeitenPerformance AppraisalUsman HaziqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Leadership Theory Application and Skill Development 6th Edition Lussier and AchuaDokument50 SeitenTest Bank For Leadership Theory Application and Skill Development 6th Edition Lussier and AchuaReham AbdelRaheem50% (2)
- PBL Inside Out PlanDokument8 SeitenPBL Inside Out Planapi-299778497Noch keine Bewertungen
- As Man ThinkethDokument18 SeitenAs Man ThinkethKulvir RickNoch keine Bewertungen
- First & Last Talk - U.G.krishnamurtiDokument18 SeitenFirst & Last Talk - U.G.krishnamurtimi777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics and The Invisible PsychologistDokument11 SeitenEthics and The Invisible PsychologistJohn GavazziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Becoming a Transformational Leader (39Dokument21 SeitenBecoming a Transformational Leader (39JohnVanMagnoBalazuela50% (2)
- New ECD Checklist-IndividualDokument4 SeitenNew ECD Checklist-IndividualJash MinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective Cues Subjective Cues: (Kozier & Erb's Fundamentals of Nursing, PG 948)Dokument4 SeitenSubjective Cues Subjective Cues: (Kozier & Erb's Fundamentals of Nursing, PG 948)Diana Anne MarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Howard Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences ExplainedDokument50 SeitenHoward Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences ExplainedIda Marie Vega EscolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trent Testa Cover SheetDokument5 SeitenTrent Testa Cover SheetTrent TestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Comprehension - Sleep CycleDokument2 SeitenReading Comprehension - Sleep CycleMartin HauserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why a Liberal Arts Education Teaches You to Think, Learn, and See the WholeDokument9 SeitenWhy a Liberal Arts Education Teaches You to Think, Learn, and See the WholeSyairah Banu DjufriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link Between Motivational Theory and Reward Business EssayDokument4 SeitenLink Between Motivational Theory and Reward Business EssayRussell MonroeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCPD: Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument4 SeitenOCPD: Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentRana Muhammad Ahmad Khan ManjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Misunderstandings About AA and DVDokument1 SeiteCommon Misunderstandings About AA and DVDawn FarmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zuberbu - 2005 - The Phylogenetic Roots of Language Evidence From Primate Communication and CognitionDokument5 SeitenZuberbu - 2005 - The Phylogenetic Roots of Language Evidence From Primate Communication and CognitionJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cindy Juarez ResumeDokument2 SeitenCindy Juarez ResumeCindy Juárez-ChozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Motivated Functions of ArtDokument3 SeitenNon-Motivated Functions of ArtJamee Bruha100% (2)
- BibliografiDokument778 SeitenBibliografiRizali DjaelangkaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Grade 7Dokument1 SeiteLP Grade 7ayatolla ayatollaTM100% (1)
- Overcoming Negaholism: The Global Epidemic of Negative ThinkingDokument6 SeitenOvercoming Negaholism: The Global Epidemic of Negative ThinkingraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dgbtdjdyrty 76 YfDokument3 SeitenDgbtdjdyrty 76 YfSolaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Applied Psychophysiology - Carlson, J., Seifert, R. & Birbaumer, NDokument284 SeitenClinical Applied Psychophysiology - Carlson, J., Seifert, R. & Birbaumer, NJuan Esteban100% (1)
- De Thi Chinh Thuc Dot 1 Nam 2021 Mon Tieng Anh Ma de 404Dokument4 SeitenDe Thi Chinh Thuc Dot 1 Nam 2021 Mon Tieng Anh Ma de 404nhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misty Isa Recommendation LetterDokument1 SeiteMisty Isa Recommendation Letterapi-252563272Noch keine Bewertungen
- FC Training 101Dokument3 SeitenFC Training 101GS HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emotions Healthy PerspectiveDokument25 SeitenEmotions Healthy PerspectiveMohamed HeshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-4-The Scholarship Jacket WorksheetDokument5 Seiten4-4-The Scholarship Jacket WorksheetOlivia EscocheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leigh McCullough - Treating Affect PhobiaDokument385 SeitenLeigh McCullough - Treating Affect PhobiaIftah Weiss-RoiNoch keine Bewertungen