Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Set 157e1445f
Hochgeladen von
Kasem AhmedOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Set 157e1445f
Hochgeladen von
Kasem AhmedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
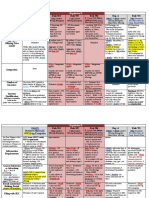
Structure and Function Chapter 8 Nervous System for Final
Study online at quizlet.com/_1uspct
1.
2 Functions of the
Autonomic Nervous System
are..
Regulate the bodys
involuntary functions, Helps
restore Homeostasis
17.
Axons that release
acetylcholineaer classified as
what?
Cholinergic Fibers
2.
3 Thinsg in the brain stem..
Medulla Oblongata, Pons,
Midbrain
18.
Andrenegic Fibers
3.
5 Parasympathetic
Controls...
Constricts pupils, increases
secreation of digestive juices,
slows heartbeat, increases
peristalis, stimulates lens for
near vision
Axons that release
noreppinephrine are classified as
what?
19.
The Branching projection of
neuron
Dendrite
20.
Bundles of Axons located in the
CNS are called
Tracts
21.
Carries messages to and from the
brain to the rest of the body and
mediates reflexes
Spinal Cord
22.
Cells that act as microbe-eating
scavengers in theCNS
Microglia
23.
Cells that make myelin for axons
inside the CNS
Oligodendrocyte
24.
Cells that make myelin for axons
outside the CNS
Schwann Cells
25.
A cerebrovascular accident is
commonly referred to as what?
A Stroke
26.
Cholinergic Fibers result in the
release of what?
Acetylcholine
27.
These Conduct impulse AWAY
from the cell body..
Axons
28.
Conduct impulses between the
spinal cord and ganglion
Preganglionic Neurons
29.
These conduct impulses from
sensory neurons to motor
neurons
Interneurons
30.
These conduct impulses TOWARD
the cell body..
Dendrites
31.
Contraction of a muscle that
causes it to pull away from an
irritating stimulus is know as the
what?
Withdrawl Reflex
32.
Corpus Callosum=
Cerebrum
33.
Cranial Nerves are associated
with what?
12 pairs, Vagus, Optic
34.
Decending tracts conduct
impluses where?
Down the cord from the
brain
35.
Dendrites and cell pbodies of
sympathetic preganglionic
neurons are located in the
Gray matter of the
thoracic and upper
lumbar segments of the
spinal cord
36.
Divison of ANS
Sympathetic System
4.
5.
5 Parts of the Neuroglia..
5 Sympathetic Controls..
Special type of supporting cell,
Astrocytes, Forms the myelin
sheath around central nerve
fibers, Phagocytosis, Multiple
Sclerosis
Produces goose pimples,
increases sweat secreation,
constricts blood vessels,
relaxes bladder, increases
epinephrine secretion
6.
5 Things to do with
Neurons..
Axon, Sensory, Conduct
Impulses, Efferent,
Neurilemma
7.
Abducens=
Cranial nerves
8.
ADH is produced by the?
Hypothalamus
9.
Adrenergic Fibers result in
the release of what?
Norephinephire
All interneurons lie entirely
within the what of the
Central Nevous System?
Gray Matter
11.
Also know as EFFERENT
Motor Neuron
12.
Another Name for the
Parasympathetic Nervous
sytem is..
Craniosacral
The ANS consists of neurons
that conduct impulses
from the spinal cord or
brain stem to the :
Cardiac Muscle Tissue, Smooth
Muscle Tissue, Glandular
Epithelial Tissue
14.
Ascending tracts conduct
impulses where?
Up the cord to the brain
15.
Autonomic Nervous System
Subdivison of the Peripheral
Nervous System
16.
The autonomic nervous
system consistes of neurons
that conduct impulsess
from the brain or spinal
cord to the:
cardiac muscle, smooth
muscle,and the glandular
epithelial
10.
13.
37.
Each synaptic know
besicle contains a very
small quantity of a
chemical compound
called
neurtransmitters
50.
Highly
branched part
of the neuron
that carries
impulses
toward the cell
body
Dendrite
38.
An example of a
Neurotransmitter is
Acetylcholine
39.
Facts of the Cerebrum
lobes corrospond to the bones
that lie over them, most of gray
matter lies on the surface of the
cerebrum, outer region is called
the cerebral cortex
51.
How is your
Heart Rate
Determined?
Combined forces of teh sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous System
52.
How long is the
spinal cord?
17-18 inches long
53.
How many pairs
of cranial nerves
are attached to
the undersuface
of the brain?
12 pairs
54.
How many pairs
of cranial nerves
are there?
12
55.
How many pairs
of nervse come
from the spinal
cord
31
56.
The
hypothalamus
functions by=
acts as major center for controlling the
ANS, helps control most internal organs,
controls hormone secretions of most
endrocrine glands, contains center for
controlling body temp, appetite,
wakefulness and pleasure
57.
Indentionations
between
adjacent
Schwann cells
Nodes of Ranvier
58.
An inward
movement of
positive ions
leaves a Excess
of what on the
outside
Negative Ions
59.
The largest
section of the
brain is what?
Cerebrum
60.
Motor Neurons
that make up
the ANS
Autonomic Neurons
61.
Myelin
Disorder=
Multiple sclerosis
40.
Fight or flight=
sympathetic nervous system
41.
A function of the
Hypothalamus
regulates body temperature
42.
Functions as the center
for all spinal cord reflexes
sensory tracts conduct
impulses to the brain,
motor tracts conduct
impulses from the brain
in the...
Spinal cord
Functions of the Brain
Stem..
Conduct sensory implulse from
the spinal chord to higher
centers of tehe brain, conduct
morot impluses from the
cerebrum to spinal cord, control
heartbeat, respiration and blood
vessel diameter
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
Functions of the
Cerebellum
maintains equilbrium, helps
produce smooth coordinated
movements, maints normal
postures
Functions of the
Cerebrum
Willed Movement,
Consciousness, Memory,
Conscious awareness of
sensations
Functions of the
Hypothalmus
Control the rate of heartbeat,
control the constriction and
dialation of blood vessels, control
contraction of the stomach and
intestines
A ganglion is a group of
nerve cell bodies located
in the?
PNS
Glia cells that help form
teh bood-brain barrier
Astrocytes
Group of changes
induced by the
sympathetic control is
called what?
Fight or Flight Response
62.
The myelin sheath in the brain
and spinal cord is produced
by?
Oligodendrocytes
63.
The name of the outer cell
membrane of a schwann cell is
called?
Neurilemma
64.
Name two Autonomic
Neurotransmitters
Cholinergic Fibers &
Adrenergic Fibers
65.
A nerve impulse is marked by
what?
inward movement of
postitive sodium ions that
leave excess of negative
ions outside the stimulated
point
81.
The PNS connects the brain with the
neck structures where
in the thorax
and abdomen
82.
Regulates body's involuntary functions
Autonomic
Nervous System
83.
Regulates body temperature, water
balance, sleep-wake cycles, appetite
and sexual arousal
Hypothalamus
84.
Regulates Muscle coordination,
maintenance of equilibrium, and
posture
Cerebellum
85.
Sense Organ
Ear, Nose, Eyes
86.
Sensory perception, willed
movements, consciousness and
memory are mediated where?
Cerebrum
87.
Sensory relay station from various
body areas to the cerebal cortex, also
involved with emotions and alterting
and arousal mechanisms
Thalamus
88.
The simplest Kind of Reflex arc is?
Two Neuron Arc
89.
A single projection that carries nerve
impulses away from the cell body is
Axon
90.
Slows heartbeat=
Parasympathetic
nervous system
91.
Spinal nerves are associated with what?
Dermatome,
Shingles,
66.
Nerve Impulses Do Not..
continually race along
every nerve cell's surface
67.
A Nerve Tract Consists of what?
Bundles of Central Axons
68.
Neurons that conduct
impulses from a ganglion..
postganglionic
69.
Neurotransmitters are
chimicals that allow neruons
to do what with each other?
Communicate
70.
Parasympathetic stimulation
frequently results in..
Response by only ONE
organ
71.
Parkinsons disease=
Dopamine
72.
Parkinson's disease is a disease
of what?
The Cerebral Nuclei
92.
Stroke=
CVA
73.
Par of the brainstem that
contains cardiac, respiratory,
and vas motor centers
Medulla Oblongata
93.
Sympathetic Stimulation usually
results in ..
Response by
numerous
organs
74.
Par of the brainstem that
contains relays for visual and
auditory impules
midbrain
94.
Thirty one pairs=
spinal nerves
95.
Schwann Cell
Part of the brainstem that is a
conduction pathway between
areas of the brain and body
and influences respiration
Pons
This forms myelin outside the central
nervous system
96.
Thre are synapsess within what?
sympathetic
ganglia
97.
76.
Parts of the Central Nervous
System
The Brain and Spinal Cord
The three membranes that make up hte
meninges are..
77.
Parts of the Peripheral
Nervous System
All the Nerves
Dura Mater,
Arachnoid, Pia
Mater dura is the
tough outer
lining
the Peripheral beginning of a
sensory neuron's dendrite
receptors
98.
78.
Three neuron arcs consist of what 3
neurons
Sensory,
Interneurons,
Motor Neurons
79.
Peripheral Nercous system is...
the nerves that extend to
the outlaying parts of the
body
99.
Three parts of the brainstem=
Medulla
oblongata, pons,
midbrain
80.
The Peripheral Nervous System
consists of what two kinds of
nerves?
Cranial and Spinal
100.
Tissues to which autonomic neurons
conduct impulses..
Visveral effectors
75.
101.
Two names of neurotransmitters=
acetylcholine,
catecholamines
(norepinephrine,
dopamine,
serotonin)
121.
What consistes mainly of the
posterior pituitary gland, pituitary
stalk and gray matter?
hypothalamus
122.
What consists of sensory neurons
synapsing in teh spinal cord with
interneurons that synapse with
motor neurons?
Three neuron Arcs
102.
Two Parts of the Diencephalon
Thalamus &
Hypothalamus
103.
Two types of cells found in the
Nervous System are?
Neurons and Glia
123.
What forms the H shaped inner core
of the spianl chord
Gray Matter
104.
Ventricles=
Cerebrospinal fluid
124.
Synapic Knob
105.
Visceral effectors=
autonomic neurons
What is a tiny bulge at the end of the
presynapic neurons axon?
106.
Voluntary Actions
Somatic Nervous
System
125.
What is the fatty substance found
around some nerve fibers?
Myelin
107.
Waht are the Islands of grey matter
within the interior of the Cerebrum
called?
Basal Ganglia
126.
What is the largest part of the human
brain?
Cerebrum
127.
Synapse
108.
What are a bundle of peripheral
axons called?
Nerves
109.
What are a cluser of nerve cell
bodies that are located outside the
nervous system?
ganglion
What is the microscopic space that
seperates the axon of one neuron
from the dendrites of another
neuron?
128.
What is the myelin sheath in the brain
and spinal cord produced by?
Oligodendrocytes
What are a group of nerve cell
bodies located in teh peripheral
nervous system?
Ganglion
129.
What is the outer cell membrane of
teh Schwann cell called
neurilemma
130.
Medulla
What area of the Cerebrum is
responsible fore the perception of
sound?
Temporal Lobe
What is the portion of the brain stem
taht joins the spinal cord to the
brain?
131.
Reflex
What are distributed specifically
into groups o fneurons?
Neurotransmitters
What is the response to impulse
conduction over reflex arcs?
132.
Cerebellum
What are groups of warpped axons
called
Fascicles
What is the second largest part of the
human brain?
133.
Two Neuron Arc
What are self propagating waves of
electrical disturbance that travels
along the surface of a neuron
membrane?
Nerve Impulses
What is the simpiest kind of reflex
arc?
134.
What is white matter?
What are the three main types of
Glial Cells?
Astrocytes, microglia,
oligodendrocytes
Tissue composed
primarily of
myelinated axons
(nerves or tracts)
135.
Acetylcholine
116.
What are three parts of a Neuron:
Dendrites, cell body
and axons
What neurotransmitter dose the
sympathetic preganglionic axon
release
117.
What are tough sheaths that cover
the whole nerve?
Epineurium
136.
What neurotransmitters inhibit
conduction of pain impules?
Endorphins and
enkephalins
118.
What can meditaion do to the
Symmpathetic Activity
Decrease it
137.
Thalamus
119.
What conduct impulses away from
teh brain and spinal cord to muscle
and glands:
Motor (Efferent)
Neurons
What part of the brain helps in the
association of sensations with
emotions and aids in the arousal or
altering mechanism?
138.
What conducts impulses toward
teh cell body
Dendrites
What part of the plasma membrane
makes up a portion of the synapse?
the Postsynapic
Neuron
139.
What plays a role in sleep ?
Catecholamines
110.
111.
112.
113.
114.
115.
120.
140.
What serves as the emergency or stress system controlling visceral effectors
during strenuous exercise and strong emotions?
The sympathetic nervous system
141.
What surrounds a grouop of nerve fibers?
Perineurium
142.
What surrounds individual fibers within a nerve?
Endoneurium
143.
What surrounds the entire nerve?
Epineurium
144.
When a sstimulus acts on a neuron it..
increases the permeability of the stimulated point
of its membrane to sodium iions
145.
Where does the spinal cord end?
the bottom of teh first lumbar vertebra
146.
Where implulse conduction in a reflex arc starts
Receptors
147.
Where impulses are transmitted from one neuron to another ..
synapse
148.
Where is Visual Perception Loacated?
Occipital Lobe
149.
The white fatty substance that surrounds and insulates the axon
Myelin
150.
The White Outer Columns of the Spinal Tracts are made up of what?
Bundles of myelinated nerve fibers (Dendrites)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Chart OutlineDokument29 SeitenChart OutlineKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Great Old Property Outline DetailedDokument203 SeitenGreat Old Property Outline DetailedKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Stambovsky V AckleyDokument4 SeitenStambovsky V AckleyKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Mergers and Acquisition OutlineDokument53 SeitenMergers and Acquisition OutlineKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Best Criminal Law OutlineDokument46 SeitenBest Criminal Law OutlineKasem Ahmed75% (4)
- Pfaff Criminallaw Spring 2018 OutlineDokument39 SeitenPfaff Criminallaw Spring 2018 OutlineKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance Outline, Spring 2013Dokument60 SeitenCorporate Finance Outline, Spring 2013Kasem Ahmed100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Torts Outline1Dokument32 SeitenTorts Outline1Kasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Schwarzenegger AobDokument59 SeitenSchwarzenegger AobKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Corporations DBR Fall 2018-OutlinedepotDokument185 SeitenCorporations DBR Fall 2018-OutlinedepotKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Anti ManipulationDokument1 SeiteAnti ManipulationKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutional Law West Falcon 2015Dokument39 SeitenConstitutional Law West Falcon 2015Kasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Lecture Notes GLSDokument5 SeitenLecture Notes GLSKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canadian Geography 1202 2015 Final Exam Study GuideDokument8 SeitenCanadian Geography 1202 2015 Final Exam Study GuideKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Personal. Jurisdiction Attack OutlineDokument11 SeitenPersonal. Jurisdiction Attack OutlineKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Burger King Corp. v. RudzewiczDokument1 SeiteBurger King Corp. v. RudzewiczKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Law B262F Business Law I: Lecturers: Lana Tang (OUHK)Dokument20 SeitenLaw B262F Business Law I: Lecturers: Lana Tang (OUHK)Kasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- DeWeerth v. Baldinger 1994Dokument24 SeitenDeWeerth v. Baldinger 1994Kasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Iraq PMC AffDokument53 SeitenIraq PMC AffKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- WW2 Cornell NotesDokument12 SeitenWW2 Cornell NotesKasem Ahmed100% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Class Lecture Notes 28Dokument16 SeitenClass Lecture Notes 28Kasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- WDI 2004 Lecture NotesDokument7 SeitenWDI 2004 Lecture NotesKasem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Cord Disease by GadisaDokument128 SeitenSpinal Cord Disease by GadisaGadisa DejeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of EarDokument27 SeitenAnatomy of EarKhush BakhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis FormatDokument2 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis FormatRalph Francis Flores Palma100% (1)
- 1437 - Ichd III Beta Cephalalgia Issue 9 2013Dokument187 Seiten1437 - Ichd III Beta Cephalalgia Issue 9 2013kiki melindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The Brainangel16_88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wilson - Cranial NervesDokument243 SeitenWilson - Cranial NervesBiblioteca CSNT100% (13)
- I. Course Plan Unit TIM E (HR S) Objectives Content Teaching Learning Activities A.V. Aids Assessme NT MethodsDokument14 SeitenI. Course Plan Unit TIM E (HR S) Objectives Content Teaching Learning Activities A.V. Aids Assessme NT MethodssimonjosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Pub - Principles and Practice of NeuropathologyDokument608 SeitenPub - Principles and Practice of NeuropathologyArkham AsylumNoch keine Bewertungen
- b1 3 OriginalDokument1 Seiteb1 3 OriginalfabianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Vertigo and Dizziness PDFDokument9 SeitenDiagnosis and Treatment of Vertigo and Dizziness PDFPedro Daniel Alcívar MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parkinson DiseaseDokument49 SeitenParkinson Diseaseiqra100% (1)
- Neuroradiology Sah and StrokeDokument81 SeitenNeuroradiology Sah and StrokeJujhar BoparaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurotransmission Notes 3Dokument4 SeitenNeurotransmission Notes 3api-188978784Noch keine Bewertungen
- To Study The Effect of Taping Technique With Conventional Therapy in Patients With Facial Palsy: A Cross Sectional StudyDokument3 SeitenTo Study The Effect of Taping Technique With Conventional Therapy in Patients With Facial Palsy: A Cross Sectional StudyBaiq LenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone Directory 2020 - Final - 11-05-2020Dokument78 SeitenTelephone Directory 2020 - Final - 11-05-2020Dr. Nivas SaminathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Risk For InjuryDokument3 SeitenNCP - Risk For InjuryMatty JolbitadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrotherapy Stroke ChinaDokument7 SeitenHydrotherapy Stroke China黃姵儒Noch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- PathophysiologyDokument9 SeitenPathophysiologySuzette PipoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral Palsy and BotoxDokument3 SeitenCerebral Palsy and Botoxachaldoshi8217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome: A Comprehensive ReviewDokument12 SeitenLennox-Gastaut Syndrome: A Comprehensive ReviewLuís Felipe AmorimNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Yield Neuroanatomy - James D. FixDokument145 SeitenHigh-Yield Neuroanatomy - James D. FixBahram Dideban100% (2)
- Assessment 2 Melanie IEP ProjectDokument1 SeiteAssessment 2 Melanie IEP ProjectAnna Joy CalilungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurological DisordersDokument117 SeitenNeurological DisordersMohammed JawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Management of Tremor.11Dokument16 SeitenDiagnosis and Management of Tremor.11Stephanie Queiroz Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective Examination (WRT Omt)Dokument19 SeitenSubjective Examination (WRT Omt)Valhala ZerozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Limbic System by DR ShahabDokument23 SeitenPhysiology of Limbic System by DR ShahabShahabuddin Shaikh100% (2)
- Question-Bank: Round-1 Non-Passing Round Instructions For RoundDokument17 SeitenQuestion-Bank: Round-1 Non-Passing Round Instructions For RoundBhawna PandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertigo: Ika Marlia Bagian Neurologi RSUDZA/FK UNSYIAH Banda AcehDokument33 SeitenVertigo: Ika Marlia Bagian Neurologi RSUDZA/FK UNSYIAH Banda AcehChesy oety otawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International League Against Epilepsy Classification and Definition of Epilepsy Syndromes With Onset in Childhood Position Paper by The ILAE Task Force On Nosology and DefinitionsDokument45 SeitenInternational League Against Epilepsy Classification and Definition of Epilepsy Syndromes With Onset in Childhood Position Paper by The ILAE Task Force On Nosology and DefinitionsEduardo Rios DuboisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section of Physical and Rehabilitation MedicineDokument219 SeitenSection of Physical and Rehabilitation MedicineNatalia Loredana100% (4)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (30)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)