Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Derma Emergency
Hochgeladen von
Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Derma Emergency
Hochgeladen von
Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SJS/TEN
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Bullous Pemhigoid
Erythroderma
Etiology:
TEN: mostly due to drug
SJS: due to drugs or infections
(commonly mycoplasma)
Serious bullous autoimmune disease.
Involves skin and mucous membranes.
Can start in mouth then skin or generalized
acute eruption of both
Painful mouth erosions
Age: 60 to 80 yrs
Redness and scaling of almost
all of the entire surface of the
skin
Drugs:
Sulfanomide
Allopurinol
Antiepileptics
NSAIDs
Skin Lesions : Flaccid bullae easily ruptured
>erosions, bleeding & crustation
- Nikolyskys sign : Positive
Often starts as urticarial lesions
bullae or directly as bullous
eruption
Skin findings:Large tense intact
bullae
Causes:
Drug eruption
eczema
psoriasis
Involvement:
Skin
Mucous membrane (less than
pemphigus)
Nikolsky sign: Negative
SJS < 10% epidermal detachment
SJS / TEN overlap 10 30 %
TEN > 30% epidermal detachment
TEN: + Nikolsky sign
SJS:
-More mucosal involvement but less
skin involvement than TEN
-Better prognosis than TEN .
Skin Pain , burning & tenderness.
Mucous membrane : mouth lesions
are painful and tender.
VARIANT:
-Pemphigus Vegetan
-Pemphigus Foliaceus
-Pemphigus erythematosus
-Drug induced pemphigus (captopril)
-Paraneoplastic pemhigus
Complications of Erythroderma
-Secondary Infections
-Loss of Thermoregulation
-Renal Failure
-Hypoalbuminemia
Complications;
Skin Biopsy:
Skin Biopsy:
-Fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Intraepidermal blister with acantholysis
(separation of keratinocyte from each
other)
Subepidermal blisters with
eosinophils
-Infection (due to loss of skin barrier)
-Skin: Scarring and dyspigmentation
-Eye: Adhesions blindness
-Acute renal failure
Immunoflourscence :
(Patient skin ) Direct: IgG & C3 positive at
intercellular space in epidermis
Immunofluroscence:
-Direct : Linear deposition of IgG &
C3(along the basement
membrane)
(Patient serum) Indirect: autoantibody IgG
+Ve
against desmoglein III
-Indirect : autoantibodies against
BPAg1 & BPAg2
Management:
Management:
Management :
MANAGEMENT
- Stop the causative agent
-Admit to burn unit or ICU
-IVF and electrolyte replacement like
-burn patient
- IV Abx for infection
-Skin dressing daily
-Eye care by opthalmologist daily
- High calori intake
- Folys catheter/ NG tube
-Correction Of Fluid & electrolyte loss
-superpotent topical steroids (for
mild cases)
Wet dressings
Diagnosis confirmation : skin biopsy
-treatment of infection by antibiotics
-systemic steriods (high dose)
-Immunosuprresive therapy
- Systemic steroids
Manage fluid balance and
temperature
(-+) Immunosuppressive agents
Antibiotics
Antihistamines
Aggressively Treat Underlying
Condition
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Safe Food Handlers Course NotesDokument13 SeitenSafe Food Handlers Course NotesJinky PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Examination of The SkinDokument4 SeitenPhysical Examination of The SkinJessica Febrina WuisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatologic Exam GuideDokument3 SeitenDermatologic Exam GuideJessica Febrina WuisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infection of Skin Muscles, Bone FinalDokument90 SeitenInfection of Skin Muscles, Bone FinalNoelani-Mei Ascio100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide To Anxiety DisordersDokument66 SeitenThe Ultimate Guide To Anxiety Disordersnajaxx100% (2)
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDokument174 SeitenSexually Transmitted DiseasesfroizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers 19521Dokument845 SeitenAnswers 19521docerick87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic and Localized Scleroderm11!05!08Dokument99 SeitenSystemic and Localized Scleroderm11!05!08Linux LinuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric OSCE/Short Cases Spot Diagnosis SessionDokument170 SeitenPaediatric OSCE/Short Cases Spot Diagnosis SessionMohd KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-1-2021 Response To LandlordDokument2 Seiten2-1-2021 Response To LandlordJessica SwarnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment Theory and FathersDokument16 SeitenAttachment Theory and FathersGraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatitis Numularis and NeurodermatitisDokument22 SeitenDermatitis Numularis and NeurodermatitisNura ReefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nogales v. Capitol Medical Center DigestDokument4 SeitenNogales v. Capitol Medical Center DigestWilliam AzucenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eczema Types, Causes, and Management in 40 CharactersDokument56 SeitenEczema Types, Causes, and Management in 40 CharactersAdam AriwibawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postnatal Assessment FormatDokument16 SeitenPostnatal Assessment FormatValarmathi92% (13)
- Erythema MultiformeDokument29 SeitenErythema MultiformeSurabhi Sharma100% (1)
- DermaDokument30 SeitenDermalydia_chandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJCTs Pilot Examination Information & InstructionsDokument6 SeitenSJCTs Pilot Examination Information & InstructionsSkep100% (1)
- Gene TherapyDokument15 SeitenGene TherapyRose Mary GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staph Scalded Skin ManagementDokument17 SeitenStaph Scalded Skin ManagementEmily EresumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDX Chart Part 1Dokument5 SeitenDDX Chart Part 1M.DalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erythema Multiforme and HomoeopathyDokument7 SeitenErythema Multiforme and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rashes in Children by Dr. Muhammad - RashidDokument43 SeitenRashes in Children by Dr. Muhammad - RashidAli DkaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erythema MultiformeDokument16 SeitenErythema MultiformeGuen ColisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactive Disorders of The SkinDokument46 SeitenReactive Disorders of The SkinhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatologic Emergencies2Dokument48 SeitenDermatologic Emergencies2Syed AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Emergency Skin Disease - Lecture - 2014Dokument38 Seiten12 Emergency Skin Disease - Lecture - 2014hafizarifin91Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A RashDokument8 SeitenWhat Is A RashJudi Ann MagsacayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Eruption Causes and TypesDokument34 SeitenDrug Eruption Causes and TypesoktarinadyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Common Childhood Rashes in General PracticeDokument5 Seiten#Common Childhood Rashes in General PracticeameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Dermatology NotesDokument6 SeitenGeneral Dermatology NotesPenny_Teoh_3451Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cellulitis: Dr. Vijay DihoraDokument16 SeitenCellulitis: Dr. Vijay DihoraLouije MombzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah SMTR VDokument117 SeitenKuliah SMTR VHorakhty PrideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erythema MultiformeDokument3 SeitenErythema MultiformeSlim SaaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellulitis: Dr. Vijay DihoraDokument16 SeitenCellulitis: Dr. Vijay DihoraLouije MombzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Ulcers & Vesiculobullous Lesions GuideDokument54 SeitenOral Ulcers & Vesiculobullous Lesions GuideAbbas Qahtan JameelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manipal College of Medical Sciences Pokhara, Nepal: Erythema MultiformeDokument56 SeitenManipal College of Medical Sciences Pokhara, Nepal: Erythema MultiformeVaibhav KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shingles Rash Caused by Varicella-Zoster VirusDokument16 SeitenShingles Rash Caused by Varicella-Zoster VirusColleen De la RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument1 SeiteScienceni putu.comsurya dianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJS&TENDokument33 SeitenSJS&TENdr.ronak1996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Herpes ZosterDokument26 SeitenTeaching Herpes ZosterDian UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Ulceration and Vesiculobullous Diseases and 2Dokument107 SeitenOral Ulceration and Vesiculobullous Diseases and 2JustDen09100% (1)
- Fever and Rash: Djatnika SetiabudiDokument50 SeitenFever and Rash: Djatnika SetiabudiNur OctavianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PsoriasisDokument29 SeitenPsoriasisProtantagonist100% (1)
- Dermatitis & Urticaria: Department of Dermato Venereology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityDokument34 SeitenDermatitis & Urticaria: Department of Dermato Venereology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada UniversityadystiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System: DR. Zunaira MazharDokument60 SeitenIntegumentary System: DR. Zunaira MazharSundus Rida KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4integumentary SystemDokument139 Seiten4integumentary SystemMargreth MontejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROMEDokument4 SeitenSTEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROMEValerrie NgenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatitisslide 200715172028Dokument45 SeitenDermatitisslide 200715172028enam professorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kegawat Daruratan KulitDokument175 SeitenKegawat Daruratan KulitDzulkifli SukriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Skin Lesions GuideDokument39 SeitenPrimary Skin Lesions GuideJorelle MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- UKK Non Infectious Dermatosis PDFDokument46 SeitenUKK Non Infectious Dermatosis PDFafdina_melya01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Joshua Radke, MD UC Davis Emergency MedicineDokument47 SeitenJoshua Radke, MD UC Davis Emergency MedicineNguyễn Hoàng DungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of SkinDokument12 SeitenDiseases of SkinpayalpachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYPHILISDokument3 SeitenSYPHILISMalueth AnguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gangguan Kulit Pada LansiaDokument28 SeitenGangguan Kulit Pada LansianoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbio Skin and Eyes LectureDokument30 SeitenMicrobio Skin and Eyes LecturesweetiepotamusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin DisordersDokument8 SeitenSkin Disordersmarie leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDokument4 SeitenBacterial Skin InfectionsFiras HamidehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salivary GlandDokument38 SeitenSalivary GlandWasfe BarzaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atopic Dermatitis: Unit 3: Diseases of The Integumentary & Musculoskeletal SystemsDokument21 SeitenAtopic Dermatitis: Unit 3: Diseases of The Integumentary & Musculoskeletal Systemsunclet12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Psoriasis PDFDokument76 Seiten5 Psoriasis PDFWorku KifleNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSV Lesions and Recurrence RisksDokument24 SeitenHSV Lesions and Recurrence RisksMichael Jansen SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penyakit Kulit Gawat DaruratDokument15 SeitenPenyakit Kulit Gawat DaruratVicky Ilda ViantiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shs.317.lec-03 Skin Infections PDFDokument48 SeitenShs.317.lec-03 Skin Infections PDFHashir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recurrent Aphthous StomatitisDokument50 SeitenRecurrent Aphthous StomatitisRajkumari Sriraman100% (1)
- Psoriasis 1Dokument32 SeitenPsoriasis 1SabaniaresmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisVon EverandComplete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisNoch keine Bewertungen
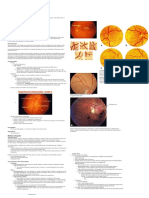
- Retinopathies: Hypertensive RetinopathyDokument3 SeitenRetinopathies: Hypertensive RetinopathyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- At The Time of PublicationDokument2 SeitenAt The Time of PublicationAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- M: Mallampati Classification: Preoperative MedicationDokument1 SeiteM: Mallampati Classification: Preoperative MedicationAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 ContentDokument1 Seite7 ContentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- References: Author: DR Declan HylandDokument1 SeiteReferences: Author: DR Declan HylandAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- William Herring MD, FACR: Book ChapterDokument1 SeiteWilliam Herring MD, FACR: Book ChapterAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase 3B General Anaesthesia Preparing For Intubation: HistoryDokument1 SeitePhase 3B General Anaesthesia Preparing For Intubation: HistoryAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 2Dokument1 SeiteA 2Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe The Steps of Intubation?Dokument1 SeiteDescribe The Steps of Intubation?Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opthal MEQDokument1 SeiteOpthal MEQAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Biopsy for Osteomyelitis TreatmentDokument1 SeiteBone Biopsy for Osteomyelitis TreatmentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Need PDFDokument1 SeiteNeed PDFAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branchial Cyst Definition, Types, Presentation and TreatmentDokument3 SeitenBranchial Cyst Definition, Types, Presentation and TreatmentAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neoplasm Presentation NotesDokument7 SeitenNeoplasm Presentation NotesAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wrong Order Items Replacement RequestDokument1 SeiteWrong Order Items Replacement RequestAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Explanation of The Truth of MonotheismDokument16 SeitenAn Explanation of The Truth of MonotheismAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- AsdfsadfDokument12 SeitenAsdfsadf1qQ1qQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (Notes)Dokument4 SeitenObstructive Sleep Apnoea (Notes)Amirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARMDDokument3 SeitenARMDAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal ChildDokument3 SeitenNormal ChildAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understand DementiaDokument2 SeitenUnderstand DementiaAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual Cycle IrregularitiesDokument2 SeitenMenstrual Cycle IrregularitiesAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain DefectDokument2 SeitenBrain DefectAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Falls in The ElderlyDokument2 SeitenFalls in The ElderlyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain AgingDokument2 SeitenBrain AgingAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychodynamicpsychotherapy PDFDokument2 SeitenPsychodynamicpsychotherapy PDFAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro OphthalmologyDokument2 SeitenNeuro OphthalmologyAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmenorheaDokument7 SeitenAmenorheaAmirul Ashraf Bin ShukeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Reference MDDDokument8 SeitenQuick Reference MDDyus97Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Retardant Research PaperDokument2 SeitenFire Retardant Research Paperapi-318759920Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mary Law PEO Model PDFDokument15 SeitenMary Law PEO Model PDFalepati29Noch keine Bewertungen
- D A Up To 2 YearDokument7 SeitenD A Up To 2 YearNischitha G CNoch keine Bewertungen
- MedEx FAQDokument2 SeitenMedEx FAQJee CHIUN CHENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista Cartilor Elsevier AchizitionateDokument57 SeitenLista Cartilor Elsevier AchizitionateLucica PleșcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemDokument12 Seiten"Classic" Technique Guide: Niti Rotary Instrumentation SystemdrnikhilbobadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snodgrass (1980) A Standardized Set of 260 Pictures. Norms For Name Agreement, Image Agreement, Familiarity, and Visual ComplexityDokument42 SeitenSnodgrass (1980) A Standardized Set of 260 Pictures. Norms For Name Agreement, Image Agreement, Familiarity, and Visual ComplexityΜακίν Ξηροί ΚαρποίNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORA.007 Pharmaceutical Microbiology ManualDokument92 SeitenORA.007 Pharmaceutical Microbiology ManualNindyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument3 SeitenDaftar PustakaErliTa TyarLieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulvovaginal Atrophy in The CRETA Study The Healthcare Professionals PerceptionDokument7 SeitenVulvovaginal Atrophy in The CRETA Study The Healthcare Professionals PerceptionHugo GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection PaperDokument2 SeitenReflection Paperapi-355203086Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Learning Plan 2-Lesson 2Dokument27 SeitenDynamic Learning Plan 2-Lesson 2Cyrah OntiverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- By hkdsegayau: 通識科 IES 滿分 Sample (樣本)Dokument10 SeitenBy hkdsegayau: 通識科 IES 滿分 Sample (樣本)Chi Shing HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Sulphide Safety Around RigDokument14 SeitenHydrogen Sulphide Safety Around RigmohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted SuicideDokument30 SeitenAssisted SuicideAlex Mini AndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q&A2Dokument3 SeitenQ&A2Marv MarvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, Karnataka. Annexure IiDokument7 SeitenRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, Karnataka. Annexure IiGirish SubashNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Consensus On Non Cirrhotic Portal FibrosisDokument41 SeitenNew Consensus On Non Cirrhotic Portal Fibrosisramesh5889Noch keine Bewertungen
- K CC1 102 Hse MSDS 005 - R0 EaDokument8 SeitenK CC1 102 Hse MSDS 005 - R0 EaWalter Gerardo BelluzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Quarter CAPSTONEDokument30 Seiten4th Quarter CAPSTONEWallace RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) - Citric AcidDokument5 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) - Citric AcidMannar1Noch keine Bewertungen