Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Program Outcomes and Performance Indicators
Hochgeladen von
Siegfred LaborteCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Program Outcomes and Performance Indicators
Hochgeladen von
Siegfred LaborteCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Student Outcomes and Performance Indicators
Performance indicators are a means to focus on specific expectations of a program.
They facilitate the curriculum delivery strategies, and assessment procedures. There is
an important first step that must come before the development of performance
indicators, and that is deciding on student outcomes. These are usually communicated
to students in the program description, and are stated in terms that inform the students
about the general purpose of the program and expectations of the faculty. The primary
difference between student outcomes and performance indicators is that student
outcomes are intended to provide general information about the focus of student
learning and are broadly stated of the outcome, not measurable, while performance
indicators are concrete measurable performances students must meet as indicators of
achievement. Performance indicators are developed from program outcomes.
Sample student outcomes:
o Students will work effectively as a member of a team.
o Students can apply the principles of math and science to a technical problem.
o Students will have an appreciation for the need to be lifelong learners.
o Students will have effective communication skills.
Performance indicators indicate what concrete actions the student should be able to
perform as a result of participation in the program. Once program outcomes have been
identified, the knowledge and skills necessary for the mastery of these outcomes should
be listed. This will allow the desired behavior of the students to be described, and will
eliminate ambiguity concerning demonstration of expected competencies. Performance
indicators are made up of at least two main elements; action verb and content
(referent). The expected behavior must be specified by name, using an observable
action verb such as demonstrate, interpret, discriminate, or define.
Sample performance indicators:
o Students will know a professional code of ethics. (knowledge)
o Students will be able to describe the problem solving process.
(comprehension)
o Students will solve research problems through the application of scientific
methods. (application)
Cunningham, G. K. (1986). Educational and psychological measurement. New York:
MacMillan Publishing.
McBeath, R. J., Ed. (1992). Instructing and evaluating in higher education: A
guidebook for planning learning outcomes. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational
Technology Publications.
Revised 04/21/10 G. Rogers
arrange, define, describe, duplicate, identify, label, list,
match, memorize, name, order, outline, recognize, relate,
recall, repeat, reproduce, select, state
classify, convert, defend, describe, discuss, distinguish,
estimate, explain, express, extend, generalize, give
examples, identify, indicate, infer, locate, paraphrase,
predict, recognize, rewrite, report, restate, review, select,
summarize, translate
apply, change, choose, compute, demonstrate, discover,
dramatize, employ, illustrate, interpret, manipulate, modify,
operate, practice, predict, prepare, produce, relate,
schedule, show, sketch, solve, use, write
analyze, appraise, break down, calculate, categorize,
compare, contrast, criticize, diagram, differentiate,
discriminate, distinguish, examine, experiment, identify,
illustrate, infer, model, outline, point out, question, relate,
select, separate, subdivide, test
arrange, assemble, categorize, collect, combine, comply,
compose, construct, create, design, develop, devise,
design, explain, formulate, generate, integrate, manage,
modify, organize, plan, prepare, propose, rearrange,
reconstruct, relate, reorganize, revise, rewrite, set up,
summarize, synthesize, tell, write
appraise, argue, assess, attach, choose, compare,
conclude, contrast, defend, describe, discriminate,
estimate, evaluate, explain, judge, justify, interpret, relate,
predict, rate, select, summarize, support, value
Knowledge
Comprehension
Application
Analysis
Synthesis
Evaluation
Example
memory of specific facts,
terminology, rules, sequences,
procedures, classifications,
categories, criteria, methodology,
principles, theories, and structure
stating problem in own words,
translating a chemical formula,
understanding a flow chart,
translating words and phrases from a
foreign language
taking principles learned in math and
applying them to figuring the volume
of a cylinder in an internal
combustion engine
discussing how fluids and liquids
differ, detecting logical fallacies in a
student's explanation of Newton's 1st
law of motion
writing a comprehensive report on a
problem-solving exercise, planning a
program or panel discussion, writing
a comprehensive term paper
evaluating alternative solutions to a
problem, detecting inconsistencies
in the speech of a student
government representative
Definition
remembering previously
learned information
grasping the meaning of
information
applying knowledge to
actual situations
breaking down objects
or ideas into simpler
parts and seeing how
the parts relate and are
organized
rearranging component
ideas into a new whole
making judgments
based on internal
evidence or external
criteria
Revised 04/21/10 G. Rogers
Gronlund, N. E. (1981). Measurement and evaluation in teaching, 4th ed. New York, Macmillan Publishing.
McBeath, R. J., (Ed.). (1992). Instructing and evaluating in higher education: A guidebook for planning learning outcomes. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology
Illustrative Verbs
Level
analyzing and synthesizing data, applying knowledge, choosing among alternatives in problem-solving, and evaluating ideas or actions.
COGNITIVE learning is demonstrated by knowledge recall and the intellectual skills: comprehending information, organizing ideas,
asks, chooses, describes, follows,
gives, holds, identifies, locates, names,
points to, selects, sits erect, replies,
uses
answers, assists, complies, conforms,
discusses, greets, helps, labels,
performs, practices, presents, reads,
recites, reports, selects, tells, writes
completes, describes, differentiates,
explains, follows, forms, initiates,
invites, joins, justifies, proposes, reads,
reports, selects, shares, studies, works
adheres, alters, arranges, combines,
compares, completes, defends,
explains, generalizes, identifies,
integrates, modifies, orders, organizes,
prepares, relates, synthesizes
acts, discriminates, displays,
influences, listens, modifies, performs,
practices, proposes, qualifies,
questions, revises, serves, solves,
uses, verifies
Receiving
Responding
Valuing
Organization
Characterization by a
value or value complex
the value system becomes a
way of life
organizing various values into
an internalized system
expressing a belief or attitude
about the value or worth of
something
active participation indicating
positive response or
acceptance of an idea or policy
willingness to receive or attend
Definition
a person's lifestyle influences
reactions to many different
kinds of situations
recognizing own abilities,
limitations, and values and
developing realistic aspirations
accepting the idea that
integrated curricula is a good
way to learn, participating in a
campus blood drive
completing homework
assignments, participating in
team problem-solving activities
listening to discussions of
controversial issues with an
open mind, respecting the
rights of others
Example
Revised 04/21/10 G. Rogers
Gronlund, N. E. (1981). Measurement and evaluation in teaching, 4th ed. New York, Macmillan Publishing.
McBeath, R. J., (Ed.). (1992). Instructing and evaluating in higher education: A guidebook for planning learning outcomes. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology
Publications.
Illustrative Verbs
Level
ability to listen and respond in interactions with others, and ability to demonstrate those attitudinal characteristics or values which are
appropriate to the test situation and the field of study.
AFFECTIVE learning is demonstrated by behaviors indicating attitudes of awareness, interest, attention, concern, and responsibility,
listening to the sounds made by guitar strings
before tuning them, recognizing sounds that
indicate malfunctioning equipment
knowing how to use a computer mouse, having
instrument ready to play and watching conductor
at start of a musical performance, showing
eagerness to assemble electronic components to
complete a task
using a torque wrench just after observing an
expert demonstrate a its use, experimenting with
various ways to measure a given volume of a
volatile chemical
dismantling and re-assembling various
components of an automobile quickly with no
errors
using skills developed learning how to operate
an electric typewriter to operate a word
processor
designing a more efficient way to perform an
assembly line task
using sense organs to obtain cues
needed to guide motor activity
being ready to perform a
particular action: mental, physical
or emotional
performing under guidance of a
model: imitation or trial and error
being able to perform a task
habitually with some degree of
confidence and proficiency
performing a task with a high
degree of proficiency and skill
using previously learned skills to
perform new but related tasks
creating new performances after
having developed skills
chooses, describes, detects,
differentiates, distinguishes,
identifies, isolates, relates, selects,
separates
begins, displays, explains, moves,
proceeds, reacts, responds,
snows, starts, volunteers
assembles, builds, calibrates,
constructs, dismantles, displays,
dissects, fastens, fixes, grinds,
heats, manipulates, measures,
mends, mixes, organizes, sketches
(same list as for guided response)
(same list as for guided response)
adapts, alters, changes,
rearranges, reorganizes, revises,
varies
arranges, combines, composes,
constructs, creates, designs,
originates
Perception
Set
Guided response
Mechanism
Complex or overt
response
Adaptation
Origination
Revised 04/21/10 G. Rogers
Gronlund, N. E. (1981). Measurement and evaluation in teaching, 4th ed. New York, Macmillan Publishing.
McBeath, R. J., (Ed.). (1992). Instructing and evaluating in higher education: A guidebook for planning learning outcomes. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology
Publications.
demonstrating the ability to correctly execute a
60 degree banked turn in an aircraft 70 percent
of the time
Example
Definition
Illustrative Verbs
Level
which demonstrate the fine motor skills such as use of precision instruments or tools, or actions which evidence gross motor skills such
as the use of the body in dance or athletic performance.
PSYCHOMOTOR learning is demonstrated by physical skills: coordination, dexterity, manipulation, grace, strength, speed; actions
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Peer-Graded AssignmentDokument2 SeitenPeer-Graded AssignmentNam PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 9001 PresentationDokument28 SeitenISO 9001 PresentationvinothkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hay Guide Chart-Profile Method of Job Evaluation General Use of The Hay SchemeDokument5 SeitenThe Hay Guide Chart-Profile Method of Job Evaluation General Use of The Hay SchemeChayanika MisraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Mix ProblemsDokument11 SeitenProduct Mix ProblemsSiegfred Laborte100% (1)
- Hardware and Network Servicing Level 3Dokument64 SeitenHardware and Network Servicing Level 3ብርሃነ ኣፅብሃ85% (41)
- Grammar Proficiency of Colegio de San Juan de Letran Calamba College Students PDFDokument27 SeitenGrammar Proficiency of Colegio de San Juan de Letran Calamba College Students PDFBea DeLuis de TomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Business For Examination From 2023Dokument22 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: Business For Examination From 2023khalid malikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gcse D&T TextileDokument29 SeitenGcse D&T TextileOlusaye OluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of Procurement Committee, Bid EvaluationDokument6 SeitenFunctions of Procurement Committee, Bid EvaluationIL AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Operations ResearchDokument37 SeitenIntroduction To Operations ResearchSiegfred Laborte100% (1)
- Self-Assessment: Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning (MEAL)Dokument6 SeitenSelf-Assessment: Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning (MEAL)Viviana CalmasiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP 10-20 26 August 2008Dokument41 SeitenGP 10-20 26 August 2008alizareiforoushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dan Shen Unreliability The Living Handbook of NarratologyDokument10 SeitenDan Shen Unreliability The Living Handbook of NarratologyAnonymous uD8YEGVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems Proposal On Inventory ManagementDokument16 SeitenSystems Proposal On Inventory ManagementSiegfred Laborte0% (2)
- ISO 13528 ReviewDokument56 SeitenISO 13528 ReviewFabio Yomayusa100% (7)
- How Encryption Enables Crucial Data Control: Focuses Role of Information Systems Department On Managing and PlanningDokument4 SeitenHow Encryption Enables Crucial Data Control: Focuses Role of Information Systems Department On Managing and PlanningSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- The PIIE-NSC Core Team Primer 1617Dokument10 SeitenThe PIIE-NSC Core Team Primer 1617Siegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPACITY Planner - RotopackDokument3 SeitenCAPACITY Planner - RotopackSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- On - The Statistical Principles Underlying The Control Chart For Fraction Nonconforming Are Based On The Binomial DistributionDokument6 SeitenOn - The Statistical Principles Underlying The Control Chart For Fraction Nonconforming Are Based On The Binomial DistributionSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduling: Project Management (IE 408) - IE42FA3 Ruth Bango Siegfred LaborteDokument20 SeitenScheduling: Project Management (IE 408) - IE42FA3 Ruth Bango Siegfred LaborteSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under CopyrightDokument45 SeitenUnder CopyrightSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hhofma3ech17inst 140930121849 Phpapp01Dokument65 SeitenHhofma3ech17inst 140930121849 Phpapp01Siegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide Um ThermoDokument1 SeiteGuide Um ThermoSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo HistoryDokument15 SeitenThermo HistorySiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawDokument9 SeitenHooke's LawSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
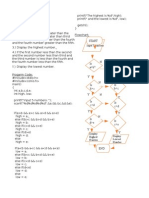
- Start: K H1/10 K1 H1 Is K 1 Display"X'Dokument2 SeitenStart: K H1/10 K1 H1 Is K 1 Display"X'Siegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp2 2appDokument1 SeiteExp2 2appSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Start: Input 5 NumbersDokument1 SeiteStart: Input 5 NumbersSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mata Kuliah QC Iwan PratamDokument75 SeitenMata Kuliah QC Iwan PratamIwan PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ojt Manual 2019Dokument27 SeitenOjt Manual 2019thnrhrghrh5r5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oleh: Trigina Nova Yolanda NIM.1902011022Dokument2 SeitenOleh: Trigina Nova Yolanda NIM.1902011022Trigina NovayolandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Beginnings of American Freedom 1 2Dokument22 SeitenThe Beginnings of American Freedom 1 2api-273985023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of AssessmentDokument2 SeitenDefinition of AssessmentGhriebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 Support Department Cost AllocationDokument27 SeitenTopic 2 Support Department Cost Allocationluckystar251095Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Task 2 of 2 Portfolio and Written Questions: Submission InformationDokument28 SeitenAssessment Task 2 of 2 Portfolio and Written Questions: Submission InformationDiego Grecco100% (1)
- Flex-0bedized ModuleDokument5 SeitenFlex-0bedized ModuleJam CentenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptability of The Basic Electro-Pneumatic Control TrainerDokument3 SeitenAcceptability of The Basic Electro-Pneumatic Control TrainerJeff PereyrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESS 4104 AssignmentDokument9 SeitenESS 4104 AssignmentSamlall RabindranauthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deposition of J. Kevin Lacy - NCDOTDokument126 SeitenDeposition of J. Kevin Lacy - NCDOTSteven LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- All LOs Establish Quality Standard PDFDokument20 SeitenAll LOs Establish Quality Standard PDFHabteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1-1. University of Phoenix Online, School of Advanced Studies, Scholarship, PracticeDokument8 SeitenFigure 1-1. University of Phoenix Online, School of Advanced Studies, Scholarship, Practicedominique babisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management PlanDokument7 SeitenQuality Management PlanAdhesha FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Performance Appraisal System Using Fuzzy LogicDokument7 SeitenEmployee Performance Appraisal System Using Fuzzy LogicDian AbiyogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers & Education: Gi-Zen Liu, Zih-Hui Liu, Gwo-Jen HwangDokument15 SeitenComputers & Education: Gi-Zen Liu, Zih-Hui Liu, Gwo-Jen HwangNoerwanty Yustitiana RidwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation Tool Division ProjectDokument7 SeitenEvaluation Tool Division ProjectJessa DongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi State Legal Services AuthorityDokument17 SeitenDelhi State Legal Services Authorityshivam pandeyNoch keine Bewertungen