Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gastrointestinal System: GI Osmotic: Laxative/Antacid, Anticonvulsant, Electrolyte Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: Duration
Hochgeladen von
syerly0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten4 SeitenThis document provides information on the use of magnesium-containing compounds as antacids, laxatives, and for systemic purposes. It discusses the examples of magnesium compounds used, how they work, dosing, administration, monitoring, contraindications, side effects, and patient education. The key points are that magnesium compounds can be used as antacids to neutralize gastric acid, as laxatives for their osmotic effect in the intestines, and systemically as an electrolyte and for conditions like hypertension and seizures. Proper dosing and monitoring of side effects like hypermagnesemia are important when using these compounds.
Originalbeschreibung:
DFGHJ
Originaltitel
c18 GI Osmotic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document provides information on the use of magnesium-containing compounds as antacids, laxatives, and for systemic purposes. It discusses the examples of magnesium compounds used, how they work, dosing, administration, monitoring, contraindications, side effects, and patient education. The key points are that magnesium compounds can be used as antacids to neutralize gastric acid, as laxatives for their osmotic effect in the intestines, and systemically as an electrolyte and for conditions like hypertension and seizures. Proper dosing and monitoring of side effects like hypermagnesemia are important when using these compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten4 SeitenGastrointestinal System: GI Osmotic: Laxative/Antacid, Anticonvulsant, Electrolyte Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: Duration
Hochgeladen von
syerlyThis document provides information on the use of magnesium-containing compounds as antacids, laxatives, and for systemic purposes. It discusses the examples of magnesium compounds used, how they work, dosing, administration, monitoring, contraindications, side effects, and patient education. The key points are that magnesium compounds can be used as antacids to neutralize gastric acid, as laxatives for their osmotic effect in the intestines, and systemically as an electrolyte and for conditions like hypertension and seizures. Proper dosing and monitoring of side effects like hypermagnesemia are important when using these compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
1
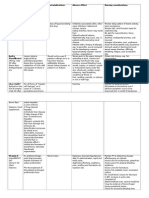
CHAPTER 18 Gastrointestinal System
GI Osmotic: Laxative/Antacid, Anticonvulsant, Electrolyte
Use
Treatment/prevention
of hypomagnesemia.
Treatment of hypertension,
torsade de pointes,
encephalopathy, seizures
associated with acute
nephritis, constipation,
hyperacidity.
Example
How it works
Half-life:
UK
Magnesium chloride
Magnesium citrate
(Citrate of Magnesia)
Magnesium hydroxide
(MOM)
Magnesium oxide
(Mag-ox)
Magnesium protein
complex (Mg-PLUS)
Magnesium sulfate
(Epsom salt, magnesium
sulfate injection)
Onset:
Route
dependent
Route:
PO/IM/IV
Peaks:
Route
dependent
Pregnancy
category: C
Duration:
Route
dependent
Pharmacokinetic:
Antacid, laxative:
minimal absorption
through intestine.
Absorbed dose
primarily excreted
in urine; Systemic:
Widely distributed;
primarily excreted
in urine.
Antacid: Acts in stomach to neutralize gastric acid, increase pH.
Laxative: Osmotic effect primarily in small intestine. Draws
water into intestinal lumen, produces distention, promotes
peristalsis, bowel evacuation.
Systemic (dietary supplement, replacement): Found primarily
in intracellular fluids. Essential for enzyme activity, nerve
conduction, and muscle contraction.
Anticonvulsant: Blocks neuromuscular transmission, amount
of acetylcholine released at motor end plate, producing
seizure control.
CHAPTER 18 Gastrointestinal System
GI Osmotic: Laxative/Antacid, Anticonvulsant, Electrolyte (continued)
Adult dose
Hypomagnesemia (magnesium sulfate):
IM/IV: 1 g q6 h for 4 doses
PO: 3 g q6 h for 4 doses
Hypertention, seizures (magnesium sulfate)
IM/IV: 1 g q6 h for 4 doses as needed
Torsade de pointes (magnesium sulfate)
UVL 2550 mg/kg/dose; maximum 2 g
Laxative
Magnesium citrate: PO: 150300 mL
Magnesium hydroxide: PO: 3060 mL/day
Antacid
Magnesium hydroxide: Note: Up to 4 times/day; PO: (tablet):
6221244 mg/dose; (liquid concentrate: 2.57.5 mL/dose;
(liquid): 515 mL/dose
Before administration
Assess if patient is sensitive to magnesium.
Antacid: Assess GI pain (duration, location, time of occurrence,
relief with food, or caused by food or alcohol, constant or
sporadic, worsened when lying down or bending over).
Laxative: Assess color, amount, consistency of stool. Assess
bowel habits (usual pattern), bowel sound for peristalsis.
Assess patient for any abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea,
vomiting, history of recent abdominal surgery.
Systemic: Assess renal function, magnesium level.
Administration
PO (antacid): Shake suspension well before use; chewable
tablets should be chewed thoroughly before swallowing and
follow with full glass of water.
PO (laxative): Drink full glass of liquid (8 oz) with each dose
(prevents dehydration); Flavor may be improved by following
with fruit juice or citrus carbonate beverage; refrigerate citrate
of magnesia (retains potency, palatability).
IM: Use 250 mg/mL (25%) or 500 mg/mL (50%) magnesium
sulfate concentration.
IV: Store at room temperature; must dilute (do not exceed
20 mg/mL concentration); do not exceed magnesium sulfate
concentration 200 mg/mL (20%); do not exceed IV infusion
rate of 150 mg/min.
CHAPTER 18 Gastrointestinal System
GI Osmotic: Laxative/Antacid, Anticonvulsant, Electrolyte (continued)
After administration
Antacid: Assess for relief of gastric distress; monitor renal
function (especially if dosing is long term or frequent).
Laxative: Monitor stools for diarrhea or constipation; maintain
adequate fluid intake.
Systemic: Monitor renal function, magnesium levels, EKG
for cardiac function; test patellar reflex or knee jerk reflexes
before giving repeat parenteral doses (used as indication of
CNS depression; suppressed reflex may be sign of impending
respiratory arrest). Patellar reflex must be present, respiratory
rate >16/min before each parenteral dose. Provide seizure
precautions.
Contraindications
Antacids: Severe renal impairment; appendicitis or symptoms
of appendicitis, ileostomy, intestinal obstruction.
Laxatives: Appendicitis, undiagnosed rectal bleeding, CHF,
intestinal obstruction, hypersensitivity, colostomy, ileostomy.
Systemic: Heart block, myocardial damage, renal failure.
Cautions: Safety in children <6 years not known; Antacids:
Undiagnosed gastrointestinal or rectal bleeding, ulcerative
colitis, colostomy, diverticulitis, chronic diarrhea. Laxative:
Diabetes mellitus or patients on low-salt diet (some products
contain sugar: sodium). Systemic: Severe renal impairment.
Side effects/
adverse reaction
Frequent: Antacid: Chalky taste, diarrhea, laxative effect.
Occasional: Antacid: Nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps.
Antacid, laxative; prolonged use of large dose with renal
impairment may cause increased magnesium (dizziness,
irregular heartbeat, mental changes, tiredness, weakness);
laxative: cramping, diarrhea, increased thirst, gas. Systemic:
reduced respiratory rate, decreased reflexes, flushing,
hypotension, decreased heart rate.
Adverse/toxic: Antacid, laxative: None significant. Systemic: May
produce prolonged PR interval, widening of QRS intervals; may
cause loss of deep tendon reflexes, heart block, respiratory paralysis, and cardiac arrest. Antidote: 1020 mL 10% calcium gluconate (510 mEq of calcium).
CHAPTER 18 Gastrointestinal System
GI Osmotic: Laxative/Antacid, Anticonvulsant, Electrolyte (continued)
Patient education
Antacid:
Give at least 2 hours apart from other medications.
Do not take >2 weeks unless directed by physician.
For peptic ulcer take 1 and 3 hours after meals and at bedtime
for 46 weeks.
Chew tablets thoroughly followed with glass of water.
Shake suspensions well.
Repeat dosing/large doses may have laxative effect.
Laxative:
Drink full glass (8 oz liquid) to aid stool softening.
Use only for short term.
Do not use if abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea are present.
Systemic:
Inform health care provider of any signs of hypermagnesemia
(confusion, irregular heartbeat, cramping, unusual tiredness or
weakness, lightheadedness, or dizziness).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GI DrugsDokument35 SeitenGI DrugsIconMaicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The G.I.T.Dokument11 SeitenDrugs Affecting The G.I.T.Mona MahfouzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On GitDokument119 SeitenDrugs Acting On GitNathaniel Mbiu Tim100% (1)
- Osmotic LaxativesDokument2 SeitenOsmotic LaxativesACanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printed Material Module 7 Gastrointestinal System Drugs - PDFDokument45 SeitenPrinted Material Module 7 Gastrointestinal System Drugs - PDFShang MacarayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDokument45 SeitenGastrointestinal DrugsCindy MaslagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium ChlorideDokument2 SeitenPotassium ChlorideSetiram Zenitram50% (2)
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyAl-nazer Azer AlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Gastrointestinal Pharmacology (Powerpoint)Dokument30 SeitenLecture 1 Gastrointestinal Pharmacology (Powerpoint)j.doe.hex_87100% (2)
- 14 Antidiarrhead Laxatives UpdDokument52 Seiten14 Antidiarrhead Laxatives Updone_nd_onlyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Tract - Nutrition/EliminationDokument51 SeitenGI Tract - Nutrition/Eliminationnick_nock08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDokument12 SeitenDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Lec (10) Word G I TDokument9 SeitenLec (10) Word G I TAhmed EngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal TractDokument111 SeitenDrugs Used in Gastrointestinal TractIsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium BicarbonateDokument3 SeitenSodium BicarbonateAubrey Unique EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationDokument4 SeitenBrand Name: Generic Name: Stock Dose: Route: Frequency: ClassificationApril Joy MangsatNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI DrugsDokument79 SeitenGI DrugsreecoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patient AssignmentDokument6 SeitenPatient AssignmentRj MagalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapy For GI Disorders PDFDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapy For GI Disorders PDFmeeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Polystyrene SulfonateDokument11 SeitenSodium Polystyrene SulfonatejanellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiulcer Chapter 40Dokument9 SeitenAntiulcer Chapter 40triddle1969Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laxatives AND Antidiarrheals: DR Mohd Suhaimi Jabatan FarmakologiDokument31 SeitenLaxatives AND Antidiarrheals: DR Mohd Suhaimi Jabatan FarmakologiChokJunHoongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti EmeticsDokument112 SeitenAnti Emeticsjoel david knda mjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal SystemDokument5 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal SystemPaul André AzcunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antacids H Antagonists Proton Pump InhibitorsDokument49 SeitenAntacids H Antagonists Proton Pump Inhibitorsmelvingodric_arceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management and Care of Patients With Ascites: Prepared by Nisha Thomas MspuDokument12 SeitenManagement and Care of Patients With Ascites: Prepared by Nisha Thomas MspuShilpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Acting On Gastrointestinal SystemDokument41 SeitenDrugs Acting On Gastrointestinal SystemDivya JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT - Part IIDokument23 SeitenGIT - Part IIDiyar ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2hypomagnesemia & HypermagnesemiaDokument6 Seiten3.2hypomagnesemia & HypermagnesemiaBooz Waief CaluzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal Agents & Antiulcer Drugs: MedanDokument56 SeitenGastrointestinal Agents & Antiulcer Drugs: MedanSartika NapitupuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agents Used To Treat Gastrointestinal DisordersDokument53 SeitenAgents Used To Treat Gastrointestinal DisordersQuolette ConstanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Antacids and Controllers UpdDokument63 Seiten13 Antacids and Controllers Updone_nd_onlyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyJashtine JingcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal TractDokument61 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal TractSameera DahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ancog-KALIUM DURULEDokument3 Seitenancog-KALIUM DURULEtpmellizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSN - 2 Gastrointesinal (GIT) Pharmacology Lecture 2Dokument35 SeitenBSN - 2 Gastrointesinal (GIT) Pharmacology Lecture 2Alana CaballeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDan DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti DiarrheaDokument40 SeitenAnti DiarrheaNofilia Citra CandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument17 SeitenDrug StudyJoan RabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminum HydroxideDokument3 SeitenAluminum HydroxideCay SevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Dokument13 SeitenCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriDokument29 SeitenNursing Implication: OB, Lactation, Pedi: GeriGlyssa CabarrubiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laxatives and Anti-DiarrhealDokument28 SeitenLaxatives and Anti-DiarrhealimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesDokument52 SeitenDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesWidia Isa Aprillia SujanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaxativesDokument27 SeitenLaxativesSK TalkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 GI DrugsDokument45 SeitenChapter 4 GI DrugsKIDUS YAREDNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Gastroesophogeal Reflux DiseaseDokument14 SeitenWhat Is Gastroesophogeal Reflux DiseaseAhmed SadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Gi Tract: Myla M - Guadiz, R.N., M.A.NDokument37 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Gi Tract: Myla M - Guadiz, R.N., M.A.NRachel CabiguenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Act On Hyper AcidityDokument33 SeitenDrugs Act On Hyper AcidityAzifah IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument8 SeitenDrug Name Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesMcDo DonatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyLovely Saad TubañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES MNGTDokument44 SeitenFLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES MNGTremerose100% (1)
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/Ti Ming/route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument3 SeitenName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/Ti Ming/route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskyle100% (1)
- NovaluzidDokument2 SeitenNovaluzidianecunar100% (2)
- Pharmacotherapy of Gastric Acidity, Peptic UlcersDokument19 SeitenPharmacotherapy of Gastric Acidity, Peptic UlcersZaid Al-KadhimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionVon EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Oxalate Cookbook: Low Oxalate Diet Cookbook With Nutritional Guide To Prevent Kidney StonesVon EverandLow Oxalate Cookbook: Low Oxalate Diet Cookbook With Nutritional Guide To Prevent Kidney StonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Recipes for One and TwoVon EverandDiabetic Recipes for One and TwoBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Gastrointestinal System: Anticholinergic Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationDokument2 SeitenGastrointestinal System: Anticholinergic Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationsyerlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System: Antihistamine Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationDokument3 SeitenGastrointestinal System: Antihistamine Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationsyerlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System: Antidiarrheals Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationDokument2 SeitenGastrointestinal System: Antidiarrheals Half-Life: Onset: Peaks: DurationsyerlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- c18 Serotonin AntagonistDokument2 Seitenc18 Serotonin AntagonistsyerlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Ethics Report: Therac-25: Ryan Brown Student No.160181997Dokument5 SeitenComputer Ethics Report: Therac-25: Ryan Brown Student No.160181997Ryan BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product CatalogDokument13 SeitenProduct Catalogkleos70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Silver Hill Hospital Chronic Pain and Recovery CenterDokument8 SeitenSilver Hill Hospital Chronic Pain and Recovery CenterSilver Hill HospitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 Introduction To CounsellingDokument14 SeitenUnit-1 Introduction To CounsellingAaquib Zaved100% (1)
- Nutrition Needs: Daily Pre-Workout During Workout Post-WorkoutDokument1 SeiteNutrition Needs: Daily Pre-Workout During Workout Post-WorkoutS.odysseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI)Dokument36 SeitenCatheter Related Bloodstream Infection (CRBSI)aringkinkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluoxetine Combined With Clorazepate Dipotassium and BehaviourDokument5 SeitenFluoxetine Combined With Clorazepate Dipotassium and BehaviourAngélica Lozano CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 - Stavridakis - Immediate Dentin Sealing of Onlay Preparations - Thickness of Pre-Cured Dentin Bonding Agent and Effect of Surface CleaningDokument11 Seiten2005 - Stavridakis - Immediate Dentin Sealing of Onlay Preparations - Thickness of Pre-Cured Dentin Bonding Agent and Effect of Surface CleaningAndreea BorislavschiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS of Sulphur TrioxideDokument5 SeitenMSDS of Sulphur Trioxidemehfuzansari1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indocollyre PDFDokument6 SeitenIndocollyre PDFUpik MoritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meloxicam 7.5 MG Daily and Naproxen 750Dokument7 SeitenMeloxicam 7.5 MG Daily and Naproxen 750kwadwobrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint On Henna LeavesDokument10 SeitenPowerpoint On Henna LeavesloloayungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keravita Pro Review - Ultimate Solution To Your Fungal Infections!Dokument2 SeitenKeravita Pro Review - Ultimate Solution To Your Fungal Infections!molikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Dog Bites: Thorough History TakingDokument6 SeitenManagement of Dog Bites: Thorough History TakingElvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Side Effects of Systemic GlucocorticoidsDokument47 SeitenMajor Side Effects of Systemic GlucocorticoidsCdcgs PWin100% (1)
- The Dangers of CrammingDokument2 SeitenThe Dangers of CrammingIntan Shafira RachmadhiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasal Surgery For Sleep-Disordered BreathingDokument6 SeitenNasal Surgery For Sleep-Disordered Breathinglaljadeff12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes and Its Permanent Cure With Homeopathic Medicines - DRDokument28 SeitenDiabetes and Its Permanent Cure With Homeopathic Medicines - DRkrishna kumar67% (3)
- Drug Study CADokument8 SeitenDrug Study CAAna Marie Besa Battung-ZalunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eyelid Surgery Los AngelesDokument2 SeitenEyelid Surgery Los AngelesVeronica HinmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Exam NCM 145Dokument17 SeitenComprehensive Exam NCM 145Adrian Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- DaldaDokument4 SeitenDaldaMuhammad UmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Apical PulseDokument5 SeitenAssessing Apical PulseMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- Mindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) LeafletDokument2 SeitenMindfulness Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) Leafletxnlr810Noch keine Bewertungen
- Suven Life Sciences Secures Two (2) Product Patents in Macau and New Zealand (Company Update)Dokument2 SeitenSuven Life Sciences Secures Two (2) Product Patents in Macau and New Zealand (Company Update)Shyam SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inservice Education Plan On GlutenDokument3 SeitenInservice Education Plan On GlutenchandlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Case StudyDokument2 SeitenNCP Case StudyGerome Isaiah RabangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Calculations 10th Brown Test BankDokument20 SeitenDrug Calculations 10th Brown Test BankSaifoqq100% (1)
- Konker AbstractDokument39 SeitenKonker AbstractWigunaNoch keine Bewertungen