Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Methotrexate
Hochgeladen von
e u n i c eCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Methotrexate
Hochgeladen von
e u n i c eCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
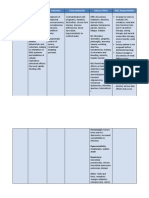
Generic Name
Methotrexate
Trade Name
Folex
Pharmacologic
Class
Folic acid antagonist
Minimum Dose
7.5 mg 1 tab
BID
Therapeutic Class
Antimetabolite.
Antineoplastic,
Antipsoriatic,
Antirheumatic
Maximum
Dose
15 mg 1 tab q6
Pregnancy Risk
Factor
X
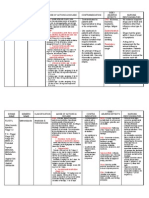
Contents
Methotrexate
Availability
and color
- Tablets- 2.5, 5, 7.5
10, 15mg
- Powder for
injection- 20 mg, 1 g
per vial
- Injection- 25 mg/mL
Routes of
administration
Oral
Intramuscular
Intravenous
Inhibits folic acid reductase,
leading to inhibition of DNA
synthesis and inhibition of
cellular replication; selectively
affects the most rapidly
dividing cells (neoplastic and
psoriatic cells)
Pharmacokinetics
A: Rapidly absorbed from the
GI tract at low doses, higher
doses are less well absorbed.
Rapidly and completely
absorbed after IM doses.
D: Tissues and extracellular
fluids; crosses the blood-brain
barrier and placenta; enters
breast milk. Small amounts in
saliva and breast milk. 50%
bound to plasma proteins.
Bound as polyglutamate
conjugates, bound drug may
remain in the body for several
mth, particularly in the liver.
M: Partly by intestinal flora.
Does not undergo significant
metabolism at low dose
therapy; 7-hydroxy metabolite
is detected at high-doses.
E: Primarily via urine; small
amounts in bile, feces.
Rout
e
Oral
IM
IV
Onse
t
Varie
s
Rapi
d
Rapi
d
Peak
1-2 hr
0.5-1
hr
0.5-1
hr
Drug Half Life
3-15 hr
Duratio
n
Unknow
n
Unknow
n
Unknow
n
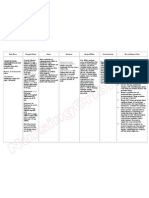
General Indications
- Burkitt's lymphoma
- Acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia
- Choriocarcinoma
- Mycosis fungoides
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Crohn's disease
- Osteosarcoma
- Breast cancer
- Advanced
lymphosarcoma
- Acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia
- Choriocarcinoma
- Acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia
- Mycosis fungoides
- Crohn's disease
- Psoriasis
- Meningeal leukaemia
- Hydatidiform mole
Concentrations
- Pregnancy
- Lactation
- Alcoholism
- Chronic liver
disease
- Immune
deficiencies
- Blood dyscrasias
- Hypersensitivity
Precaution
- Renal disease
- Infection
- Peptic ulcer
- Ulcerative colitis
- Debility
Drug interaction
Drug to drug
- Potentially serious
to fatal reactions
when given with
NSAIDs
- Risk for toxicity
with alcohol
- Increased risk of
toxicity with
salicylates,
probenecid,
sulfonamides
- Decreased serum
levels and
therapeutic effects of
digoxin
- May decrease
theophylline
clearance
Drug to food
- none reported
CNS: Headache,
drowsiness, blurred vision,
aphasia, hemiparesis,
paresis, seizures, fatigue,
malaise, dizziness
Dermatologic:
Erythematous rashes,
pruritus, urticaria,
photosensitivity,
depigmentation, alopecia,
ecchymosis, telangiectasia,
acne, furunculosis
GI: Ulcerative stomatitis,
gingivitis, pharyngitis,
anorexia, nausea, vomiting,
diarrhea, hematemesis,
melena, GI ulceration,
bleeding, enteritis, hepatic
toxicity
GU: Renal failure, effects on
fertility
Hematologic: Severe bone
marrow depression,
increased susceptibility to
infection
Hypersensitivity:
Anaphylaxis, sudden death
Respiratory: Interstitial
pneumonitis, chronic
interstitial obstructive
pulmonary disease
Other: Chills and fever,
metabolic changes, cancer
Before
- Observe 15 rights in drug
administration.
- Assess for contraindications of the
drug.
- Arrange for tests to evaluate CBC
urinalysis, renal and liver function
tests, and chest X-ray before
therapy.
- Ensure that patient is not pregnan
before administering.
- Prepare a calendar of treatment
days.
During
- Arrange for tests to evaluate CBC
urinalysis, renal and liver function
tests, and chest X-ray during
therapy.
- Do not administer any other
medications containing alcohol.
- Arrange for adequate hydration
during therapy to reduce risk of
hyperuricemia.
- Arrange to have leucovrin readily
available as antidote for
methotrexate overdose.
- Instruct to use contraceptives
during therapy.
After
- Arrange for tests to evaluate CBC
urinalysis, renal and liver function
tests, and chest X-ray several
weeks after therapy.
- Instruct to report black tarry
stools, fever, chills, sore throat,
unusual bleeding or bruising, cough
or shortness of breath, darkened or
bloody urine, abdominal, flank or
joint pain, jaundice symptoms,
mouth sores.
- Arrange for an antiemetic if
nausea and vomiting is severe.
- Reduce dosage or discontinue if
renal failure occurs.
- Arrange for frequent, regular
medical check-ups.
Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009
Lippincotts Nursing
Drug Guide, p. 767768
Source:
http://www.keele.ac.uk/
Karch, Amy: 2009
Lippincotts Nursing Drug
Guide, p. 767
Source:
http://mims.com.ph/, Karch, Amy: 2009
Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, p.
768
Source:
http://mims.com.ph/
Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009
Lippincotts Nursing Drug
Guide, p. 769
Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts
Nursing Drug Guide, p. 769
Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincotts Nursing Drug
Guide, p. 769
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cisplatin Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteCisplatin Drug StudykyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Dokument3 SeitenContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Supplements PDFDokument74 SeitenSupplements PDFjoey100% (1)
- Promethazine HCLDokument2 SeitenPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- AmpicillinDokument1 SeiteAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Methotrexate Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteMethotrexate Drug StudyAlexa Lexington Rae Zagado0% (1)
- MetoclopramideDokument1 SeiteMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- HydrocortisoneDokument2 SeitenHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- HydrocortisoneDokument2 SeitenHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyGladys Joy Peña100% (1)
- School Nursing Common DRUG STUDYDokument10 SeitenSchool Nursing Common DRUG STUDYMaria Francheska OsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (2)
- Lumantas MD v. CalapizDokument2 SeitenLumantas MD v. CalapizIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Penicillin G BenzathineDokument1 SeitePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDokument18 SeitenEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium SulfateDokument1 SeiteMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Drug StudyDokument19 SeitenDrug StudyIsagani Socrates Loreto100% (1)
- Sample Case ScenarioDokument10 SeitenSample Case ScenarioKarilee Salcedo AyunayunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study SitagliptinDokument3 SeitenDrug Study SitagliptinEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- MethadoneDokument2 SeitenMethadoneIvanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG CeftazidimeDokument1 SeiteDRUG Ceftazidimerholiboi0% (1)
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - DiazepamDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - DiazepamCerie Anne Olay40% (5)
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDokument64 SeitenDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GentamicinDokument2 SeitenGentamicinMiguel Sanico0% (2)
- Drug Study - CisplatinDokument3 SeitenDrug Study - CisplatinDanielle Aglusolos50% (2)
- Tamoxifen DrugstudyDokument2 SeitenTamoxifen Drugstudyjessica queenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marked Myelosuppression, Previous Treatment With Cumulative Doses ofDokument5 SeitenMarked Myelosuppression, Previous Treatment With Cumulative Doses ofMac Mac100% (2)
- Czarina Drug Study JuneDokument20 SeitenCzarina Drug Study JuneNicoh AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Nifedipine PODokument1 SeiteDrug Study - Nifedipine POJet BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- DiazepamDokument1 SeiteDiazepamIvanne Hisoler71% (7)
- DisulfiramDokument1 SeiteDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Terbutaline SulfateDokument1 SeiteTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- OxytocinDokument1 SeiteOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Methotrexate )Dokument2 SeitenMethotrexate )Angela Tenorio100% (2)
- NaproxenDokument1 SeiteNaproxenAlexis Coronado100% (1)
- DigoxinDokument1 SeiteDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- FurosemideDokument2 SeitenFurosemideIvanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clindamycin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDokument4 SeitenClindamycin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComChristian LlerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co-Trimoxazole Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteCo-Trimoxazole Drug Studyjonelo123100% (1)
- Tobramycin + Dexamethasone Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenTobramycin + Dexamethasone Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDokument1 SeiteRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluorouracilDokument2 SeitenFluorouracilHyacinth Bueser BondadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study MgSO4Dokument1 SeiteDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- HydralazineDokument1 SeiteHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- PhenobarbitalDokument1 SeitePhenobarbitalSherwin LauronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study For Prednisone Case INPDokument2 SeitenDrug Study For Prednisone Case INPChristina Barroga100% (3)
- Dopamine HCLDokument1 SeiteDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDokument1 SeiteVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study IbuprofenDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Ibuprofendawnscribd80% (5)
- CefepimeDokument2 SeitenCefepimeshendae cosmianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug Studymike_steven12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study AmpicillinDokument6 SeitenDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- OmeprazoleDokument1 SeiteOmeprazoleFritz JanobasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUGSTUDY: Dolfenal - Mefenamic AcidDokument2 SeitenDRUGSTUDY: Dolfenal - Mefenamic AcidYum CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study CefuroximeDokument2 SeitenDrug Study CefuroximeDave Michael GeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuinineDokument3 SeitenQuinineDoubleHeartedNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeostigmineDokument4 SeitenNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyOlive Keithy Ascaño ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AeknilDokument2 SeitenAekniljaycey24Noch keine Bewertungen
- BetamethasoneDokument3 SeitenBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azathioprine (Drug Study)Dokument2 SeitenAzathioprine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (4)
- AMINOPHYLLINEDokument2 SeitenAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Bleomycin Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteBleomycin Drug StudykyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Tamiflu, FlagylDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - Tamiflu, Flagylmark_gain100% (1)
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDokument2 SeitenDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineDokument5 SeitenDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteNifedepine Drug StudyMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study MetforminDokument5 SeitenDrug Study MetforminSabita PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinDokument2 SeitenDRUG STUDY - AmoxicillinFlorenz Gatchalian60% (5)
- Mycophenolate MofetilDokument1 SeiteMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDokument1 SeiteTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug Studyapi-3717941100% (6)
- ChlorphenamineDokument1 SeiteChlorphenaminereinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyNicole Blanch BuenavistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDokument13 SeitenDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDokument1 SeiteGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- CefuroximeDokument1 SeiteCefuroximeRox SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DactinomycinDokument1 SeiteDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- Drug Study 1.1Dokument2 SeitenDrug Study 1.1Arianne Nicole PinuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Dokument31 SeitenLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Assignment PlanDokument2 SeitenDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Dokument1 SeiteCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons - Midterms NotesDokument23 SeitenPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DroperidolDokument1 SeiteDroperidolIvanne HisolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DactinomycinDokument1 SeiteDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- ACP Employability WorkshopDokument12 SeitenACP Employability Workshoplalit saraswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyDONITA DALUMPINESNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28 Premarketing Applications of Pharmacoepidemiology: Harry A. GuessDokument19 Seiten28 Premarketing Applications of Pharmacoepidemiology: Harry A. GuessAnisa FitriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of The Neonate With Seizures 2020Dokument7 SeitenEvaluation of The Neonate With Seizures 2020Eduardo Rios DuboisNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of TherapiesDokument3 SeitenList of TherapiesAK KJNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1 1 578 648 PDFDokument6 Seiten10 1 1 578 648 PDFhusni gunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Internasional MenopauseDokument8 SeitenJurnal Internasional MenopauseLembang DamariansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otc GITDokument142 SeitenOtc GITMai MosaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine Sarcoma - Pharmacologic Management - Cancer Therapy AdvisorDokument32 SeitenUterine Sarcoma - Pharmacologic Management - Cancer Therapy AdvisorIrfan FathurrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies For ADDokument24 SeitenPathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies For ADShuaib AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Clinical Assessment of Antibiotic Used in Chronic Kidney Disease PatientsDokument8 SeitenA Study On Clinical Assessment of Antibiotic Used in Chronic Kidney Disease PatientsMITA RESTINIA UINJKTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knoll Price ListDokument16 SeitenKnoll Price ListkadapanehruparkyogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Clinical Pharmacy II - Lab. 1Dokument4 SeitenPractical Clinical Pharmacy II - Lab. 1Ali AbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Management of Epilepsy & SeizuresDokument9 SeitenEmergency Management of Epilepsy & SeizuresDavid MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: METOPROLOL: Metoprolol 200mg Tab PO OD X 30 DaysDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: METOPROLOL: Metoprolol 200mg Tab PO OD X 30 Daysbobo gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACIProduct ListDokument27 SeitenACIProduct ListFerdousNoch keine Bewertungen
- March: Operating Room 1 ItemDokument16 SeitenMarch: Operating Room 1 ItemJoybee ThiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Diseases With Oral Manifestations 19Dokument141 SeitenSystemic Diseases With Oral Manifestations 19Hanin AbukhiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyFirst SnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- mcq ثانيDokument4 Seitenmcq ثانيمحمدأميندماج100% (1)
- Renr Week 7th 2017 Questions SheetDokument21 SeitenRenr Week 7th 2017 Questions SheetSasha UterNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Pharmacy QA Unit: Course ILOS Classification Course Title: Code: 701507-2 Year/Level: 5/9Dokument10 SeitenCollege of Pharmacy QA Unit: Course ILOS Classification Course Title: Code: 701507-2 Year/Level: 5/9hamam salih badriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Liver in Times of COVID-19 What Hepatologists Should KnowDokument6 SeitenThe Liver in Times of COVID-19 What Hepatologists Should KnowFita FitriantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication Safety Book 13-09-2021 Complete PDFDokument42 SeitenMedication Safety Book 13-09-2021 Complete PDFW A B Nishan WickramaarachchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Maps in MedicineDokument159 SeitenMind Maps in MedicineAnonymous jSTkQVC27b100% (44)
- Cell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsDokument27 SeitenCell Wall Synthesis InhibitorsAYO NELSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- VSim Pharm (Mary Richards)Dokument3 SeitenVSim Pharm (Mary Richards)Jay Blastic's arts and FunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric General Anesthesia: Moderator-Dr Tripat Kaur. Presenter - DR Ikjot KaurDokument80 SeitenPediatric General Anesthesia: Moderator-Dr Tripat Kaur. Presenter - DR Ikjot Kaurashwini priyaNoch keine Bewertungen