Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fia D1319 Sop PDF
Hochgeladen von
aurelianhanganuOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fia D1319 Sop PDF
Hochgeladen von
aurelianhanganuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
US
PET
LAB
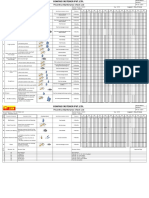
ASTM D1319 SOP for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum
Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
6.2.2
WARNING:
Apparatus is under pressure. Glass could break
and spill contents, which are flammable.
When analyzed correctly, this test method should be
completed in approximately 2 hours. However, higher
boiling constituents could require additional time for
analysis.
This analysis requires
the sample and
apparatus to be
analyzed under
ultraviolet light.
Record Sample
Details in Lab
Logbook
Fill the charge section
to the top of the
spherical joint of a
properly cleaned charge
tube with isopropyl
alcohol or isoamyl
alcohol (See Note 2)
Rev. February 2009
Prepare capillary tube
as instructed in the
capillary preparation
SOP
Chill the sample and the
hypodermic syringe and
needle to less than 4oC
MSV
ENG
Page 1 of 3
Extract 0.75 0.03 mL of
sample into the syringe and
inject the sample
approximately 30 mm
below the surface of silica
gel (See Note 1).
Note:
The analyst should take care in preparation of glassware for each analysis, as contaminants from previous sample can
contribute to inaccurate results. Operator should also be aware that toluene used for cleaning increase the recovery of
aromatic compounds if column is not dried properly.
Connect the charge
tube to the gas manifold
and observe the
connection for any
leaks
Apply 14 2 kPa (2psi)
of gas pressure for 2.5
0.5 minutes
Note 1:
The ease in which the sample syringe needle
can be inserted will give the analyst an ideal
of how tightly packed the silica gel
Gasoline
Is sample a
gasoline or
jet fuel?
Jet Fuel/Diesel
28-69 kPa or
4-10psi is typical
for gasoline
Increase pressure to 34
2 kPa (5psi) for 2.5
0.5 minutes
Adjust pressure to give
a transit time of about 1
hour, Samples with high
molecular weight may
take longer
Note:
Ensure that all glassware, measuring devices, instruments,
and all other items are verified and calibrated if necessary
within their required time period before beginning procedure.
69-103 kPa or
10-15psi is typical
for jet fuels
Note 2:
Isoamyl alcohol may be substituted in place
of isopropyl alcohol when analyzing samples
with a boiling point above 204C (399F)
Note:
Improper packing of the silica gel
can cause gel separation when
pressure is introduced yielding
erroneous results.
Mark the tube when red
boundary is at least
350mm into analyzer
section
Warning:
The analyst should take care in
handling acetone, isopropyl alcohol,
and isoamyl alcohol because all
components are flammable, as well as
health hazards.
Mark as
follows:
A = solvent
front
B = beginning of
most intense
yellow brand
C = first intense
blue
D = upper end
of red boundary
Repeat markings in
reverse order after red
band has moved at
least another 50mm
Continued on page 2
ALWAYS consult MSDS for both samples and reagents to familiarize yourself with chemical hazards before beginning a procedure.
US
PET
LAB
6.2.2
ASTM D1319 SOP for Hydrocarbons Types in Liquid Petroleum
Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
Rev. February 2009
MSV
ENG
Page 2 of 3
Continued From Page 1
Note:
Calculate for
both sets of
markings
(See Page 3).
La, (A-B) = length of the
aromatics zone, mm
Lo, (B-C) = length of the olefins
zone, mm
(La / L) x 100
(Lo / L) x 100
(Ls / L) x 100
Record as volume
% uncorrected aromatics
Record as volume
% uncorrected olefins
Record as volume
% uncorrected saturates
Are both marking results
repeatable according to
Table 3 or Fig. 4?
No
Ls, (C-D) = length of the
saturates zone, mm
L, (A-D) = sum of La + Lo + Ls,
mm
Rerun the
analysis
Yes
Average both sets of results
Calculations:
C = C X 100 - B
100
C = concentration of hydrocarbon type, Vol. %,
on total sample basis
Report results to 0.1% as "total sample
basis " or "uncorrected"
C = concentration of hydrocarbon type, Vol.%,
on an oxygenate-free basis
B = concentration of total blending components
(oxygenates), Vol.%, in sample as determined by
ASTM D4815 or D5599 or equivalent.
Note:
The method determination ranges for the
hydrocarbon types using ASTM D1319 is as
follows:
Aromatics - 5 to 99 Vol.%
Olefins - 0.3 to 55 Vol.%
Saturates - 1 to 95 Vol.%
Correct results for volume of
oxygenates using the total oxygenates
result from ASTM D4815 or D5599
where applicable
Report Adjusted Results as
"Oxygenate-free Basis" or "Corrected"
A result less than the hydrocarbon type range shall
be reported (<) lower limit. i.e. < 5 Vol.% A result
greater than the hydrocarbon type range shall be
reported (>) upper limit. i.e. > 99 Vol.%
Continued on Page 3
ALWAYS consult MSDS for both samples and reagents to familiarize yourself with chemical hazards before beginning a procedure.
US
PET
LAB
6.2.2
ASTM D1319 SOP for Hydrocarbons Types in Liquid Petroleum
Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
Rev. February 2009
MSV
ENG
Page 3 of 3
Continued from Page 2
Note:
The analyst should make certain that
the compound is oxygenate free, as
sometimes samples that contain
oxygenate compounds can be
overlooked. Samples that do contain
oxygenates will typically be reported
as corrected as well as uncorrected.
Make certain the oxygenate values
are reported in volume percent and
not mass, as the values in mass %
are significantly different from values
reported in volume %.
FIG. 3 Pictorial Aid for Identification of Chromatographic Boundaries of
Oxygenate Blended Fuel Samples
ALWAYS consult MSDS for both samples and reagents to familiarize yourself with chemical hazards before beginning a procedure.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CLEW German Parties Energy Climate Policy PositionDokument1 SeiteCLEW German Parties Energy Climate Policy PositionCarbon BriefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Servo RobotDokument40 SeitenMicro Servo Robotlokesh mahor0% (1)
- Astm d4945Dokument7 SeitenAstm d4945M.Malyadri ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Ace: Wheel Nut CrackedDokument8 SeitenSuper Ace: Wheel Nut CrackedScientific KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR - No Description Make Model No. Rating Qty.: E Cable Cables & Busbar RR/Polycab - 1Dokument1 SeiteSR - No Description Make Model No. Rating Qty.: E Cable Cables & Busbar RR/Polycab - 1Vaijayanti JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMG PIGA-31601-Process Audit Report After Start SOP Line Audit and During PPVTDokument15 SeitenSMG PIGA-31601-Process Audit Report After Start SOP Line Audit and During PPVTeddycul009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ivar Aasen Field Development Project PDQ: Dn02-S09011-E-Xk-6511-00Dokument27 SeitenIvar Aasen Field Development Project PDQ: Dn02-S09011-E-Xk-6511-00ayemyothantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental, Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental, Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemAsan IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualityprinciplesandconcepts 141214012537 Conversion Gate01 PDFDokument32 SeitenQualityprinciplesandconcepts 141214012537 Conversion Gate01 PDFSuhendi SSNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELEVATE - CSR Program and Service Provider OverviewDokument58 SeitenELEVATE - CSR Program and Service Provider OverviewHồng Thái Nguyễn MicroBiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gap Analysis ReportDokument23 SeitenGap Analysis ReportTaimur ShanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chennai Radha Engineering Works (P) LTD.: Near Miss / Incident Report & Investigation FormDokument2 SeitenChennai Radha Engineering Works (P) LTD.: Near Miss / Incident Report & Investigation FormsamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS-09-01 R0 Communication During ChangeDokument1 SeiteDS-09-01 R0 Communication During ChangeDhinakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality System Process Manual (In Accordance With ISO 9001:2015) Distribution & Change ControlDokument1 SeiteQuality System Process Manual (In Accordance With ISO 9001:2015) Distribution & Change Controlsasi10000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Salt Spray Test Report - SampleDokument8 SeitenSalt Spray Test Report - SamplearvindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zanini Social ResponsibilityDokument80 SeitenZanini Social ResponsibilityPiyush DikshitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report 2016 17 (Transpek)Dokument100 SeitenAnnual Report 2016 17 (Transpek)હિરેનપ્રફુલચંદ્રજોષીNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-2552310121752-Sirirat-1 Productivity Improvement Tools & StandardsDokument32 Seiten04-2552310121752-Sirirat-1 Productivity Improvement Tools & StandardsKampol HarnkittisakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Whistle Blower PolicyDokument2 SeitenSample Whistle Blower Policy4geniecivilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive Maintenance Check List: (Legend: / Due, X Done)Dokument2 SeitenPreventive Maintenance Check List: (Legend: / Due, X Done)Rohtash fastnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factories Act, 1948Dokument72 SeitenFactories Act, 1948Ansuman NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full and Final Settlement1Dokument4 SeitenFull and Final Settlement1Zaheer AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonus C Register 225Dokument2 SeitenBonus C Register 225boopathi.nNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMEDokument3 SeitenMMEMinoj SarasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rejection PPM - Forging (2019 20)Dokument7 SeitenRejection PPM - Forging (2019 20)Rohtash fastnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intertek Package Price For OrchestraDokument1 SeiteIntertek Package Price For OrchestraFerdous Khan RubelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindi ISO 22000 Nutshell FSMS Food Sfaety Management Systems Standard NoteDokument14 SeitenHindi ISO 22000 Nutshell FSMS Food Sfaety Management Systems Standard Notenallasivam vNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Operator InstructionDokument2 SeitenBoiler Operator Instructionmohamed.k.ismail6467100% (1)
- Bill of Material FormatDokument6 SeitenBill of Material FormatKDTNoch keine Bewertungen
- EQ-17 StackDokument6 SeitenEQ-17 StackSangam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Excel v3.0 - Part 1Dokument1.380 SeitenRPH Excel v3.0 - Part 1Hazimah AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lumax Quality System: Gauge TypeDokument4 SeitenLumax Quality System: Gauge TypeHarkesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Plan NDTDokument7 SeitenInspection Plan NDTEdison WalitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paretto (Defect Wise) FEB-2022Dokument2 SeitenParetto (Defect Wise) FEB-2022Bangali SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident MonitoringDokument3 SeitenAccident MonitoringRohtash fastnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Master List of Documents.r1Dokument23 Seiten2 Master List of Documents.r1chandrashekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.FPC BNG 06 F 0101 Certificate of Gauge InspectionDokument3 Seiten1.FPC BNG 06 F 0101 Certificate of Gauge InspectionSunil GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A00F100e Rv15 03.18 QuestionnaireDokument4 SeitenA00F100e Rv15 03.18 QuestionnaireShiella BagalacsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Satisfaction Measurment ProcedureDokument1 SeiteCustomer Satisfaction Measurment ProcedureAnkur GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINETURN Feasibility FormatDokument1 SeiteFINETURN Feasibility FormatAyush NarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agreement Between Alpha & Disposafe Health and Life CareDokument2 SeitenAgreement Between Alpha & Disposafe Health and Life CarePrakash RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS-04-02 R0 Annual Training PlanDokument13 SeitenDS-04-02 R0 Annual Training PlanDhinakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17.FPC BNG 06 F 0117 Noise Level Monitoring Sheet.Dokument10 Seiten17.FPC BNG 06 F 0117 Noise Level Monitoring Sheet.Sunil GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPV AQEMM 01 11 Turtle Diagram ProductionDokument4 SeitenIPV AQEMM 01 11 Turtle Diagram ProductionNurul NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohtas Fastener Pvt. LTD.: Internal Audit Plan (QMS)Dokument5 SeitenRohtas Fastener Pvt. LTD.: Internal Audit Plan (QMS)Rohtash fastnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shelf Life Management SystemDokument1 SeiteShelf Life Management Systemrajesh sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Shelf Life ItemsDokument2 SeitenList of Shelf Life ItemsDhinakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Productivity April 151Dokument1 SeiteProductivity April 151azadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRM Agenda April 2018-July 18Dokument4 SeitenMRM Agenda April 2018-July 18ukavathekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kansal Industries - Tool Development Plan Model 'N': Assy T0 SampleDokument2 SeitenKansal Industries - Tool Development Plan Model 'N': Assy T0 SampleajayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Capability Analysis: Rohtas Fasteners PVT - LimitedDokument2 SeitenProcess Capability Analysis: Rohtas Fasteners PVT - LimitedVikas KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAP Structure WorkDokument64 SeitenIAP Structure Workmanu_giteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Rule Sheet (Problem Solving Sheet) : 715-0030 GSR P-90Dokument4 Seiten5 Rule Sheet (Problem Solving Sheet) : 715-0030 GSR P-90Anonymous rqVd3slYDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Butterworth Feedmill SDN BHD: Toolbox Meeting RecordsDokument1 SeiteButterworth Feedmill SDN BHD: Toolbox Meeting RecordsNurul NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Plan: Pre-Launch Production PrototypeDokument1 SeiteControl Plan: Pre-Launch Production PrototypeAnkur DhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCP of HR Process-03Dokument2 SeitenOCP of HR Process-03sathyabalaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 9001:2008 ISO/TS 16949:2009 Added Requirement: 0.5 Goal of This Technical SpecificationDokument36 SeitenISO 9001:2008 ISO/TS 16949:2009 Added Requirement: 0.5 Goal of This Technical Specificationsupady5751Noch keine Bewertungen
- HLS and ISO 9001 - ISO 14001 - Key Changes and Transition (September 2015) - tcm8-12652Dokument18 SeitenHLS and ISO 9001 - ISO 14001 - Key Changes and Transition (September 2015) - tcm8-12652KumaravelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EF MR F 20 00 Training PlanDokument2 SeitenEF MR F 20 00 Training PlanManu SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fema Iso 14001Dokument1 SeiteFema Iso 14001unicdbestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 1 MW: Table 1 CAS: Table 2 RTECS: Table 2: Alcohols I 1400Dokument4 SeitenTable 1 MW: Table 1 CAS: Table 2 RTECS: Table 2: Alcohols I 1400cerbero36Noch keine Bewertungen
- H C O MW: 30.03 CAS: 50-00-0 RTECS: LP8925000: Formaldehyde 2016Dokument7 SeitenH C O MW: 30.03 CAS: 50-00-0 RTECS: LP8925000: Formaldehyde 2016Ahmet GezerNoch keine Bewertungen
- R5 - FCC Main Fractionator: Process DataDokument24 SeitenR5 - FCC Main Fractionator: Process Datanico123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rigaku Journal 33-2-26-28Dokument3 SeitenRigaku Journal 33-2-26-28Eduardo ArdilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Aisc Steel ToolsDokument4 Seiten2010 Aisc Steel Toolsmuh2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- F5 KSSM Tutorial 1.1 (Force and Motion Ii)Dokument13 SeitenF5 KSSM Tutorial 1.1 (Force and Motion Ii)Alia Qistina Mara KasmedeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve and Pipeline Design Notes - Part 1Dokument29 SeitenValve and Pipeline Design Notes - Part 1Anilduth Baldan100% (2)
- GS14 Industrial Geophone - GeoSpace TechnologiesDokument1 SeiteGS14 Industrial Geophone - GeoSpace TechnologieshectorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Definite Integral and Its ApplicationsDokument13 SeitenThe Definite Integral and Its Applicationsapi-312673653100% (1)
- Motion in A Straight Line PDFDokument32 SeitenMotion in A Straight Line PDFRohit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ixef 1032Dokument2 SeitenIxef 1032Michele RodriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage LawDokument7 SeitenVoltage LawSaddeg RaiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument8 SeitenThermodynamicsBasu SbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers: Issue 3Dokument10 Seiten50 Questions and Answers For Marine Engineers: Issue 3Tara Gonzales100% (3)
- Trial Mix Design Report PDFDokument38 SeitenTrial Mix Design Report PDFTimothy HughesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Several Problems of The Polish Physics Olympiad: Waldemar GorzkowskiDokument4 SeitenSeveral Problems of The Polish Physics Olympiad: Waldemar GorzkowskiVikram SaurabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- SETTLING VELOCITY 2.1 - Calculations of Sedimentation Velocity and Hindered Settling Rate of ParticlesDokument74 SeitenSETTLING VELOCITY 2.1 - Calculations of Sedimentation Velocity and Hindered Settling Rate of ParticlesSonu Singh100% (4)
- Cie - 462 - Test One.09.05.2022Dokument2 SeitenCie - 462 - Test One.09.05.2022Chris KapendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resummation and Renormalization in Eff Ective Theories of Particle PhysicsDokument229 SeitenResummation and Renormalization in Eff Ective Theories of Particle PhysicsDomenico Barillari100% (2)
- Workshop 3-3: Rectangular Patch Antenna: Introduction To ANSYS Electronics DesktopDokument21 SeitenWorkshop 3-3: Rectangular Patch Antenna: Introduction To ANSYS Electronics DesktopRodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frac To GraphyDokument639 SeitenFrac To GraphyBHARANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Olympic 2018 - Tien Giang 11Dokument17 SeitenOlympic 2018 - Tien Giang 11Trần Quốc ToảnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causality Bernhard SchölkopfDokument169 SeitenCausality Bernhard SchölkopfQingsong GuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture1426865066 PDFDokument53 SeitenLecture1426865066 PDFEhab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Velocity-Physics IGCSE NotesDokument4 SeitenSpeed Velocity-Physics IGCSE Notesismun nadhifah100% (1)
- Monitored Natural Attenuation Toolkit For Evaluation 1 and 2 - Combined FINAL PDFDokument176 SeitenMonitored Natural Attenuation Toolkit For Evaluation 1 and 2 - Combined FINAL PDFcaraballoaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Plan Instructor K S RajmohanDokument4 SeitenLecture Plan Instructor K S RajmohanSwapnil TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument4 SeitenLecture 5Faisal RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Trends in Microelectronics - 95 - KluwerDokument418 SeitenFuture Trends in Microelectronics - 95 - KluwerGlenn VirreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Exploration Into Wind Turbines Their Impacts and Potential SolutionsDokument6 SeitenAn Exploration Into Wind Turbines Their Impacts and Potential SolutionsFortune JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen