Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CAMBRIDGE CHECKPOINT BIOLOGY EXAM
Hochgeladen von
rashmi_harryOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CAMBRIDGE CHECKPOINT BIOLOGY EXAM
Hochgeladen von
rashmi_harryCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 1 of 15
BOOK 2
NAME:
CHAPTER : 1 How Plants Grow
BOOK 3
CLASS:
CHAPTER : 1 Photosynthesis
Q.1
An investigation was carried out to find the best conditions for photosynthesis. Four similar sized
plants of the same species were placed in a dark cupboard for 24 hours. A leaf from each plant was
removed and tested for starch. The plants were then watered and placed in the apparatus shown
below. Each glass vessel was illuminated for 24 hours.
(a)
(b)
When the leaves from the plants were tested for starch at the start of the investigation all gave a
yellow-brown colour with iodine. Explain why.
What conditions for photosynthesis were lacking in :
(i)
vessel C? (ii) vessel D? ..
(c)
What would be the effect of the tracing paper covering vessel B?
Ans
(d)
After 24 hours leaves were removed from plant C and tested for starch with iodine solution. What
would be the expected result of this test?
Ans
Q.2
The diagram shows the apparatus used in an investigation.
(a)
An equal amount of a harmless blue indicator was added to each tube. The indicator changes from
blue in alkaline conditions to green in acid conditions. The pH of the pond water and the colour of
the indicator were recorded at the start and again after 6 hours.
The table shows some of the results.
(i)
(ii)
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water to form a weak acid.
State the colour of the pond water in tube 2 after 6 hours. ..
Give a reason for your answer.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 2 of 15
Ans
(iii)
(iv)
What was the pH of tube 3 after 6 hours? ..
State the colour and pH of the pond water in tube 5 after 6 hours. Give a reason for each answer.
Colour of tube 5 : .. Reason : ...
pH of tube 5 : ..Reason : ......
(b)(i)
In which of the tubes was photosynthesis taking place?
Ans
(ii)
In which of the tubes was respiration taking place?
Ans
Q.3
The diagram shows some apparatus used to investigate
photosynthesis.The water weed was exposed to three
different intensities of light, each for the same length of
time. The gas produced at each light intensity was
analysed.The results are shown in the table.
(a)
What happened to the percentage of carbon dioxide when
the light intensity was increased from 1 to 8 units?
Ans
(b)
Ans
What happened to the percentage of oxygen when the light intensity was increased from 1 to 8
units?
(c)
Explain why the percentage of carbon dioxide and oxygen changed as the light intensity increased.
Ans
Q.4
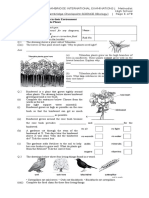
The drawings below show
trees in a woodland area at the
beginning of May and at the
end of May. The graph below
shows the amount of light
reaching the top of the trees
and the woodland floor over
one year.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 3 of 15
(a)
Why does the amount of light reaching the woodland floor decrease during May?
Ans
(b)
Ans
Plants grow on the woodland floor. Explain why these plants grow bigger and faster when there is
plenty of light.
(c)
Respiration takes place in the cells of all plants. Complete the word equation for respiration.
Q.5
Joe bought a potted plant. He kept it well watered but some of the leaves turned
yellow.
Joe thought that the plant did not have enough light for photosynthesis.
He moved the plant closer to the window but more leaves turned yellow.
He then thought that the plant did not have enough minerals. The table below
gives information about minerals.
Joes plant did not have enough of one of the minerals in the table.
Use the information in the table to suggest which mineral
this was.
(a)
(i)
Ans
(ii)
Ans
A plant growing in a pot is more likely to be affected by a
shortage of minerals than a plant growing in a garden.
Give the reason for this.
(b)
(i)
Joe bought some fertiliser for his plant.
The names and formulae of four
different fertilisers are shown below.
Give the letter of one box of fertiliser, A,
B, C or D, that would provide each of
the minerals in the table below. Write
the letters in the table.
(ii)
Easy Grow is ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3. How many different
elements are present in ammonium nitrate?
Ans
...
(iii)
How many atoms are present in the formula of ammonium nitrate?
Ans
...
Q.6
The diagram shows a pupils investigation of
photosynthesis.
Sodium hydrogencarbonate can be added to the water to
increase the concentration of dissolved carbon dioxide. A
group of pupils added measures of sodium
hydrogencarbonate to the water and counted the number
of gas bubbles given off by the pond weed. Their results
are shown in the table.
(a)
Plot a line graph using these results. Label the axes.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 4 of 15
(b)
Ans
How many bubbles would you expect to be given off per minute if the experiment was repeated
using 4 measures of sodium hydrogen carbonate?
(c)
What do these results suggest about the
composition of the water at the start of the
experiment?
Ans
Q.7
(a)
Look at the following diagram.
What is gas Y? ...
(b)
Where does gas Y enter the plant? .
(c)
What do plants use gas Y for?
(d)
In which process do animals use oxygen?
Ans
(e)
Name process A and B.
A : . B : ..
(f)
What does the arrow labelled X represent?
Ans
Q.8
The diagram shows the stages in testing a green leaf for starch.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 5 of 15
(a)
The stages are not in the correct order.
Place the letters of the stages in the correct order by writing the letters in the boxes. The last stage
has been completed for you.
(b)
(i)
Ans
Give the reason for each of the following stages:
stage C.
(ii)
Ans
stage B.
(iii)
Ans
stage E.
Q.9
An experiment was carried out to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of
photosynthesis of a water plant. The diagram below shows the apparatus used.
(a)
Suggest how you ensure that the plant had a good supply of carbon dioxide?
Ans
(b)(i)
Which gas is given off by the plant? ..
(ii)
How could you test for this gas?
Ans
(c)
How could you prevent the heat from the lamp affecting the experiment?
Ans
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 6 of 15
(d)
Ans
How would you use this apparatus to investigate the effect of increasing light intensity on the rate
of photosynthesis?
Q.10
A student carried out an experiment to find out if plants need light to make starch. The diagram
shows what the student did.
(a)
Why was the potted plant kept in a dark cupboard for 48 hours?
Ans
(b)
Why did the student cover part of one of the leaves with aluminium foil?
Ans
(c)
Stage 5 shows three areas on the leaf: A, B and C. Write down the colours these areas would be
stained after testing for starch.
Ans
Q.11
An investigation was set
up to find out if the
concentration of carbon
dioxide affected the rate
of photosynthesis. A
water plant was placed
in each of 6 test tubes
containing water and
different concentrations
of hydrogen carbonate.
The hydrogen carbonate
releases carbon dioxide
into the water. An
indicator was added to
each test tube. The indicator changes from yellow to green when oxygen is released. Each test tube
was illuminated by a lamp placed behind a measuring cylinder full of water. The time for the
indicator to change from yellow to green was recorded and plotted on a chart.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 7 of 15
(a)
What was the purpose of the measuring cylinder full of water?
Ans
(b)
What causes the indicator to change colour?
Ans
The bar chart shows the results of this investigation.
(c)
What was the effect of increasing the hydrogen carbonate concentration from 0.2 to 0.4%?
Ans
(d)(i)
At what concentration of hydrogen carbonate was the rate of photosynthesis highest?
Ans
(ii)
Give an explanation for your answer.
Ans
Q.12
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(b)
The diagram shows a section through a small part of a leaf.
Which of the structures labelled on the diagram :
is where most photosynthesis takes place?
forms a waterproof layer to the leaf?
controls the entry of carbon dioxide into the leaf?
Water is needed for photosynthesis in the leaf. Describe how
water is carried from the soil to the leaf.
Ans
.
.
(c)
One of the products of photosynthesis is sugar. In which tissue
is sugar transported? ..
Q.13
A student investigated the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis in a water plant.
The results are shown in the following table.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 8 of 15
Plot these results on the graph paper below.
(b)(i)
Describe the effect of temperature on the volume produced.
Ans
(ii)
Suggest an explanation for this effect.
Ans
(c)
What would have been the result if the experiment had been repeated at 70oC? Explain your
answer.
Result: ..................................................................................................................................................
Explanation: .........................................................................................................................................
(d) Name two other factors which influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Ans
Q.14
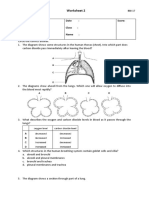
The diagram shows some of the processes which take place in a green plant.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 9 of 15
(a)
Name A, B and C.
A........................................... B................................................ C................................................
(b)
What is the function of the chlorophyll? ................................................
(c)
In what form do plants such as potatoes store sugar? ................................................
(d)
Which process releases energy in a plant? ................................................
Q.15
The diagram shows some of the ways in which plants use carbohydrates.
(a)
What is cellulose used for in a plant?
Ans
(b)
Why do plants need to produce amino acids?
Ans
(c)(i)
To produce amino acids, plants require a mineral. This is labelled X on the diagram.
(ii)
Name mineral X.
How does mineral X enter the plant?
(d)
Plants store carbohydrates as starch rather than sugar. Explain the reason for this.
Ans
Q.16
A student investigated the effect of mineral ions on the growth of plants. The diagram shows the
apparatus used.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 10 of 15
(a)
Tube A allowed air to be bubbled at intervals through the culture solution. What was the purpose?
Ans
(b)
Suggest a reason why was the glass tube covered with black paper.
Ans
(c)
Suggest one way of measuring the growth of the plant.
Ans
(d)
(i)
Ans
After 4 weeks, the plants were removed and examined. The plant from tube 1 showed normal
healthy growth. The plants in the other tubes showed symptoms of mineral deficiencies. Describe
the appearance of the plant in :
tube 2.
(ii)
Ans
tube 3.
(iii)
Ans
tube 4.
Q.17
The graph below shows the effect of increasing carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of
photosynthesis in an aquatic plant.
(a)
Explain why the rate of photosynthesis increases from point A to B on the graph.
Ans
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 11 of 15
(b)
Explain why the rate of photosynthesis remains the same between points B and C on the graph.
Ans
(c)
(i)
As a result of burning fossil fuels, atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide have increased in
this country. Suggest how this might lead to:
increased food production
Ans
(ii)
decreased food production in some areas.
Ans
Q.18
(a)
(i)
Scientists have attempted to increase food production by genetic engineering. However concern
about these genetically modified foods has resulted in some shops withdrawing them from sale.
Suggest how food production could be increased if scientists succeeded in inserting:
genes which control nitrogen fixation into cereal crops.
Ans
(ii)
genes which make plants drought resistant into cereal crops.
Ans
(b)
Suggest a reason why there is concern about genetically modified plants.
Ans
Q.19
Canadian pondweed is a common aquatic plant. A student investigated the production of starch in
Canadian pondweed using lengths of leafy stem which had previously been destarched. The pieces
of plant were placed in four flasks labelled A to D and treated as shown in the table below. The
flasks were kept at room temperature, and after 36 hours the pieces of plant were tested for starch.
(a)
How and why was the Canadian pondweed destarched?
Ans
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 12 of 15
(b)
Why were the water and glucose solutions enriched with carbon dioxide?
Ans
(c)
Suggest reasons for the results seen in each of the flasks A to D.
A: ...
B: ...
C: ...
Q.20
(a)
(i)
D: ...
The figure shows an apparatus used in an investigation
into transpiration. The cylinders were set up and left in
the same conditions for 24 hours.
The drop in the level of water in the cylinders is taken as
a measure of the rate of transpiration.
Complete the table.
(ii)
Which variable could account for the differences in the
results for cylinders A and B?
Ans
(iii)
Ans
Suggest a modification you could make to ensure that all the water lost from the cylinders is taken
up by the shoots.
(b)
State three environmental factors that can affect the rate of transpiration.
Ans
Q.21
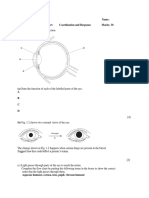
Fig. 4.1 shows a section through a leaf.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 13 of 15
(a)
(b)(i)
On Fig. 4.1, label a stoma, the cuticle and a vascular bundle. Use label lines and the words stoma,
cuticle and vascular bundle on Fig. 4.1
The upper layers of a leaf are transparent. Suggest an advantage to a plant of this feature.
Ans
(ii)
The cuticle is made of a waxy material. Suggest an advantage to a plant of this feature.
Ans
(iii)
State two functions of vascular bundles in leaves.
Ans
(c)
(i)
Most photosynthesis in plants happens in leaves.
Name the two raw materials needed for photosynthesis
(ii)
Photosynthesis produces glucose. Describe how plants make use of this glucose.
Ans
Q.22(a)Plants need nitrogen compounds for growth. Give the name of
the type of plant cell that absorbs water and nitrogen compounds
from the soil.
Ans
..
(b)
The photograph shows a pitcher plant. Pitcher plants get nitrogen
compounds from insects. They digest insects in leaves shaped
like containers called pitchers. In the bottom of the pitcher there
is a liquid. Insects are attracted to the plant. They fall into the
liquid. The inner surface of the pitcher is very smooth and
slippery with downward pointing hairs as shown below.
Suggest the function of the smooth, slippery surface with downward pointing hairs.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 14 of 15
Ans
(c)
There are useful bacteria living in the liquid. They produce enzymes to help digest the insects. Both
the bacteria and the pitcher plant absorb some of the products of digestion. How does the number of
insects that fall into the liquid affect the number of these useful bacteria?
Ans
(d)
(i)
Pitcher plants also have ordinary green leaves where photosynthesis takes place.
Complete the word equation for photosynthesis.
________________ + water glucose + ____________________
to provide energy
to provide liquid
to provide immunity
to provide minerals
(ii)
Glucose is a carbohydrate. Why are carbohydrates needed by
living things? Tick the correct box.
Q.23
Suzi investigated how temperature affects the number of bubbles produced by waterweed in one
minute. She set up the experiment as shown below.
(a)
Ans
When the temperature of the water was 10C the waterweed did not produce bubbles.
Suzi increased the temperature of the water in the water-bath to 20C. The waterweed started to
produce bubbles. She waited two minutes before starting to count the bubbles. Explain why she
waited for two minutes before she started to count the bubbles.
(b)
Suzi counted the number of bubbles produced at six different temperatures. Her results are shown
on the graph below.
(i)
(ii)
(c)
Draw a smooth curve on the graph.
Use your curve to find the temperature of water which produced the most bubbles per minute...
Suzi predicted that the higher the temperature the more bubbles would be produced. Which points
on the graph support Suzis prediction?
Ans
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS | Methodist High
School
Cambridge Checkpoint SCIENCE [Biology] | Page 15 of 15
(d)
Suzis data does not show clearly the exact temperature at which most bubbles were produced. How
could she improve the data she collects to find this temperature?
Ans
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- God of The Oppressed - James ConeDokument271 SeitenGod of The Oppressed - James ConeArun Samuel Varghese97% (29)
- Life Strategy 101: How To Live Live by Vision, Work With Purpose, and Achieve More SuccessDokument31 SeitenLife Strategy 101: How To Live Live by Vision, Work With Purpose, and Achieve More SuccessMichelle Casto100% (2)
- IGCSE Reproduction in Plants WsDokument4 SeitenIGCSE Reproduction in Plants WsAnand Kumar ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 9 Biology QuestionsDokument58 SeitenYear 9 Biology QuestionsDuong Kha NhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- S 495160Dokument4 SeitenS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Diaphragmatic Breathing - The Foundation of Core Stability PDFDokument7 SeitenDiaphragmatic Breathing - The Foundation of Core Stability PDFElaine CspNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 States of MatterDokument4 Seiten8 States of Matterrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesVon EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Court Document SummaryDokument15 SeitenCourt Document SummaryAkAsh prAkhAr vErmA100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeworks 1 eDokument8 SeitenHomeworks 1 eSumi VjNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemVon EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionDokument7 SeitenCHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (1)
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Von EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Septuagint A Critical AnalysisDokument76 SeitenThe Septuagint A Critical AnalysisscaunasNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions EcologyVon EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions EcologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Summative in Science 4-2nd QDokument2 Seiten3rd Summative in Science 4-2nd QERMIDA SANTOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turning Effect of Forces (Worksheet)Dokument3 SeitenTurning Effect of Forces (Worksheet)Usman Ameen100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision NotesDokument56 SeitenEdexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Notespepepepepepe30% (1)
- IGCSE Biology (O610) Workbook: Balanced DietDokument5 SeitenIGCSE Biology (O610) Workbook: Balanced DietPatrick Abidra100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions HomeostasisVon EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions HomeostasisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationVon EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions RespirationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Year 10 - CS Worksheet - MA 2Dokument6 SeitenYear 10 - CS Worksheet - MA 2manojNoch keine Bewertungen
- IG General PhyDokument155 SeitenIG General PhyJun QiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- (42 Marks) Answer All Question: Section ADokument15 Seiten(42 Marks) Answer All Question: Section AGie KieNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Dokument66 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Living Things in Their Environment - 6 - People and Planet - QueDokument9 Seiten5 Living Things in Their Environment - 6 - People and Planet - Querashmi_harry100% (1)
- Atomic BasicsDokument4 SeitenAtomic Basicsapi-169639475Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Grade 8 Gas ExchangeDokument4 SeitenWorksheet Grade 8 Gas ExchangeListya RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Catalog EnglishDokument32 SeitenProduct Catalog Englishrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- KARG - (Ravenloft) Quoth The Raven #10Dokument179 SeitenKARG - (Ravenloft) Quoth The Raven #10David CullifordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil ExperimentsDokument32 SeitenSoil Experimentsrashmi_harry100% (1)
- Epd-Lca Meranti Plywood-Final ReportDokument29 SeitenEpd-Lca Meranti Plywood-Final ReporttangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Grade 8 Gas ExchangeDokument4 SeitenWorksheet Grade 8 Gas ExchangeListya RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41Dokument16 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/41CindirllaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics & Classification of Living Organisms (Multiple Choice) 2 QPDokument8 SeitenCharacteristics & Classification of Living Organisms (Multiple Choice) 2 QPAdetohunNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology Worksheet - Coordination and ResponseDokument2 SeitenIGCSE Biology Worksheet - Coordination and ResponseAnand Kumar ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keys and Classifciation - Level 4 - QuestionsDokument31 SeitenKeys and Classifciation - Level 4 - QuestionsLovy Le Er100% (1)
- Grade 7 Biology revision worksheetDokument3 SeitenGrade 7 Biology revision worksheetRenee DisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BookletDokument110 SeitenBookletabc100% (1)
- Coordinated SciencesDokument166 SeitenCoordinated SciencesRaghadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binder1 MixturesDokument12 SeitenBinder1 Mixturesjomabi0% (1)
- Yr 8 Unit 1 Science Tests Plants - Photosynthesis Part ADokument3 SeitenYr 8 Unit 1 Science Tests Plants - Photosynthesis Part AQuang Nguyễn Thế Việt100% (1)
- QP 6 FellDokument464 SeitenQP 6 FellAliMushtaq0% (1)
- AQA Physics: 4 Waves Exam-Style QuestionsDokument8 SeitenAQA Physics: 4 Waves Exam-Style QuestionsMoses AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Biology Past PaperDokument8 SeitenCambridge Biology Past PaperHelpful HandNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReproductionDokument26 SeitenReproductionNicholas LeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 14 (Final) PDFDokument7 SeitenUnit 14 (Final) PDFआई सी एस इंस्टीट्यूटNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Chemistry A2 (Student Book) Examzone PDFDokument11 SeitenEdexcel Chemistry A2 (Student Book) Examzone PDFGhaith AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Revision - Structures in the Thorax and Respiration ProcessesDokument2 SeitenBiology Revision - Structures in the Thorax and Respiration ProcessesskeltenboiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcerptDokument4 SeitenExcerptGreeshma Kamat100% (1)
- Sunrise English School Physics Worksheet on Electricity CircuitsDokument2 SeitenSunrise English School Physics Worksheet on Electricity Circuitspinky100% (1)
- Properties of Matter and Materials WorksheetDokument16 SeitenProperties of Matter and Materials Worksheetrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working With Fractions Difficult: Easy: Question Paper 3Dokument7 SeitenWorking With Fractions Difficult: Easy: Question Paper 3farhathul afraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability of Combined Events - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDokument18 SeitenProbability of Combined Events - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper NumberAditiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Las Sci HS 062Dokument8 SeitenLas Sci HS 062Larry MarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1112 1mathsw00Dokument12 Seiten1112 1mathsw00Jessica AmandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Dokument16 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42afy100% (1)
- O.level Human Bio Edexcel Past Papers Paper 1 2019 - 2020Dokument68 SeitenO.level Human Bio Edexcel Past Papers Paper 1 2019 - 2020Tamer AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Otba Theme 1 TextDokument11 SeitenBiology Otba Theme 1 Textrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write-Up Rubric ChecklistDokument1 SeiteWrite-Up Rubric Checklistrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Otba 2016 Biology Theme 1Dokument11 Seiten11 Otba 2016 Biology Theme 1charulekhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Microscope: Summary of ExerciseDokument18 SeitenThe Microscope: Summary of Exerciserashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance Notes: in General You Should Be Able ToDokument3 SeitenGuidance Notes: in General You Should Be Able Torashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- x4 Objective x10 Objective x40 Objective x100 ObjectiveDokument1 Seitex4 Objective x10 Objective x40 Objective x100 Objectiverashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC Specimen 2015 Biology Paper 2Dokument5 SeitenISC Specimen 2015 Biology Paper 2rashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Sample LabDokument10 SeitenFood Sample LabNurulnameiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating Effect of Concentration On The Activity of TrypsinDokument4 SeitenInvestigating Effect of Concentration On The Activity of Trypsinrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: The Spit Lab: Teacher VersionDokument9 SeitenEnzymes: The Spit Lab: Teacher Versionrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sp11 1021 Breaking Down Starch Using Salivary EnzymesDokument7 SeitenSp11 1021 Breaking Down Starch Using Salivary EnzymescooldudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Book For Publication PDFDokument209 SeitenBiology Book For Publication PDFrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and FunctionDokument12 SeitenLab 1: The Microscope (10 Points) : Exercise 1.1: Microscope Structure and Functionrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Tests: A. Benedict's Test For Reducing SugarsDokument3 SeitenFood Tests: A. Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugarsrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules LabDokument21 SeitenMacromolecules Labrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Book For Publication PDFDokument209 SeitenBiology Book For Publication PDFrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Testing (1) : Student Safety Sheets 4Dokument1 SeiteFood Testing (1) : Student Safety Sheets 4rashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variables WorksheetDokument2 SeitenVariables Worksheetrashmi_harry0% (2)
- Lab 1: Learn Microscope Use and CareDokument8 SeitenLab 1: Learn Microscope Use and Carerashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Record AS/A Level Biology Candidate NameDokument2 SeitenStudent Record AS/A Level Biology Candidate Namerashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Support 9: Size and ScaleDokument3 SeitenPractical Support 9: Size and Scalerashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Respiration Rqandothermetabs PaxsonDokument3 SeitenCell Respiration Rqandothermetabs Paxsonrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating The Presence of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats in Different FoodsDokument4 SeitenInvestigating The Presence of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats in Different Foodsrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Testing (1) : Student Safety Sheets 4Dokument1 SeiteFood Testing (1) : Student Safety Sheets 4rashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio NotesDokument71 SeitenBio Notesrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2-Starch Hydrolysis by AmylaseDokument6 SeitenExp 2-Starch Hydrolysis by AmylaseDodi Ihsan TaufiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Download Cosmetic Injection Techniques A Text and Video Guide To Neurotoxins Fillers Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full ChapterDokument36 SeitenHow To Download Cosmetic Injection Techniques A Text and Video Guide To Neurotoxins Fillers Ebook PDF Docx Kindle Full Chapterkerri.kite140100% (24)
- Writing Statement of PurposeDokument1 SeiteWriting Statement of PurposeArunmani Arunachalam100% (1)
- Meena ResumeDokument3 SeitenMeena ResumeAnonymous oEzGNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys Geotechnical Geology - Finite Element ModelingDokument25 SeitenAnsys Geotechnical Geology - Finite Element ModelingvishnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Unpacking The SelfDokument13 Seiten1 Unpacking The SelfJEMABEL SIDAYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideation For Product Innovation What Are The BestDokument9 SeitenIdeation For Product Innovation What Are The BestLIVIA MARILIA CHIARINoch keine Bewertungen
- O'laco Vs Cocho ChitDokument16 SeitenO'laco Vs Cocho ChitAngel Pagaran AmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationDokument17 SeitenTwo Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationSharath KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alpha To Omega PPT (David & Krishna)Dokument11 SeitenAlpha To Omega PPT (David & Krishna)gsdrfwpfd2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2019-20Dokument33 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2019-20omvrat singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template For An Effective Statement of InterestDokument3 SeitenTemplate For An Effective Statement of InterestbabananakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 03Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 03Molto falsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function Point and Cocomo ModelDokument31 SeitenFunction Point and Cocomo ModelParinyas SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch5 Multivariate MethodsDokument26 SeitenCh5 Multivariate MethodsRikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Study 2 Ep. 5 AnswerDokument10 SeitenField Study 2 Ep. 5 AnswerShane Via CainticNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 7 1st Lesson Plan For 2nd QuarterDokument4 SeitenEnglish 7 1st Lesson Plan For 2nd QuarterDiane LeonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thank You LetterDokument2 SeitenThank You LetterFathina57% (7)
- Impact On Modern TechnologyDokument2 SeitenImpact On Modern TechnologyNasrullah Khan AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3-Euler's Equation PDFDokument6 Seiten4.3-Euler's Equation PDFRonald Cario SeguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Disabilities in The ClassroomDokument5 SeitenLearning Disabilities in The ClassroomekielaszekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gajendra-Moksha HTMLDokument7 SeitenGajendra-Moksha HTMLankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 SQL Complex QueriesDokument51 SeitenChapter 8 SQL Complex QueriesJiawei TanNoch keine Bewertungen