Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Math Notes
Hochgeladen von
Cesal100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
248 Ansichten1 Seite1) The document covers various mathematical concepts including the Pythagorean theorem, trigonometric functions, properties of parallel lines, systems of equations, and quadratic functions.
2) Key formulas are presented for trigonometric ratios, the quadratic formula, laws of sines and cosines, and calculating distances on a coordinate plane.
3) Different types of angles are defined including corresponding, complementary, linear pairs, vertical, and supplementary angles based on their geometric relationships.
Originalbeschreibung:
A bunch of al/trig notes
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1) The document covers various mathematical concepts including the Pythagorean theorem, trigonometric functions, properties of parallel lines, systems of equations, and quadratic functions.
2) Key formulas are presented for trigonometric ratios, the quadratic formula, laws of sines and cosines, and calculating distances on a coordinate plane.
3) Different types of angles are defined including corresponding, complementary, linear pairs, vertical, and supplementary angles based on their geometric relationships.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
248 Ansichten1 SeiteMath Notes
Hochgeladen von
Cesal1) The document covers various mathematical concepts including the Pythagorean theorem, trigonometric functions, properties of parallel lines, systems of equations, and quadratic functions.
2) Key formulas are presented for trigonometric ratios, the quadratic formula, laws of sines and cosines, and calculating distances on a coordinate plane.
3) Different types of angles are defined including corresponding, complementary, linear pairs, vertical, and supplementary angles based on their geometric relationships.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
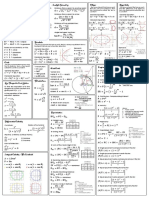
~Triangles~ ht=-16t2+24t d=x1-x2)2+ (y1+y2)2
Pathagoreom Theorem: a2+b2=c2 h=height t= time Rational
Inverse Pathagorem Theorem: -16=force of gravity Radius of a circle:r2=(x-h)2+(y-k)2
b=√c2-a2 Domain=x
h and k= center
a=c2-b2 Range=y Integers
Rise over run: y2-y1x2-x1
Law of Sines: Sin Aa=Sin Bb=Sin 0 product Property whole
Cc if a×b=0 then either a=0 or
Only if you know a side the b=0 Natural
Numbers 12345
opposite angle, and another when you find 0’s find average of 2 numbers then
part. substitute top find maximum
Law of Cosines: c2=a2+b2- Irrational
2abCosC Quadratic Formula: -b2a=b2-4ac2a 01234
^
b2=a2+c2- (min/max) ∛5 π e √2
2acCosB ~Mathematical Reasoning~ -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
Inductive: Observing patterns and making a
a2=b2+ c2- conclusion based on the patterns
2bcCosA Deductive: Trying to prove based on what’s given -4 131.7 12 -3.9
Inverse Law of Cosines:
c2-a2-b2- ~Mathematical Reasioning~
2ab=CosC Tips: When proving, think about the conclusion
b2-a2-c2- and everything that makes it true. Go back to the
given
2ac=CosB
a2-b2-c2- p=>q if p then q
2bc=CosA Converse: q=>p no conclusion
Area of a Triangle:12abSinC ~q=>~p true
12 bcSinA statement
12acSinB Inverse:
30-60-90 Triangle: ~p=>~q no
Short=12of hypotenuse conclusion
Hypotenuse=2Short
Long=Short∛ ~Lines~
Sinθ=oh Parallel lines: lines on a plane that never intersect
Cosθ=ah
Transversal lines: intersects parallel lines
Tanθ=oa
Corresponding angles: angles in the same relative
Height of a Triangle: b2-x2=h2 position in respect to the parallel and transverse
lines.
c2-(a-x)2
~Inverse Operations~
Corresponding angles are ≅
p+q=r is equivalent to p=r-q
p÷q=r is equivalent to Converse 2 parallel lines cut by a transverse so that
p=r×q the corresponding angles have equal measure
if q≠0 Parallel lines property: 2 lines cut by a transversal
if p≥0 then ps=p are parallel if and only if corresponding angles
have the same measure.
~Properties of Equations~
if p=q and p&q≥0 then Complementary: the sum of 2 angles = 90°
p=√q Linear pairs: angles along the same line. Together
p+r=q+r =180°
p-r=q-r
Vertical angles: angles across from each other.
p×r=q×r Both the same degrees.
p÷r=q÷r if r≠0
Linear pair property: if 2 angles are a linear pair
~Systems of Equations~ then the sum of their measures is 180°
Graphing Matrices
Substitution Elimination Vertical angles: share only a vertex (across from
• When dividing/multiplying my a each other)
negative you must change your
inequality symbol Linear pair: share vertex on one side (adjacent to
each other)
~Linear Programming~
1.Determine Variables (always 2) Supplementary angles: 2 angles that add up to be
2. State Constraints 180° (don’t have to be linear)
-one at a time
3.Define objective
~Miscellaneous equations~
~Quadratic Functioning~
Distance on a coordinate plane:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sec 4. MathematicsDokument1 SeiteSec 4. MathematicshuangchasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus I Exercise 4.7.67 Fall 2017 SolutionDokument3 SeitenCalculus I Exercise 4.7.67 Fall 2017 SolutionMarris BaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Straight LineDokument1 SeiteThe Straight LineFATIN NOORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curvature Functions On A One-Sheeted Hyperboloid: Boris OdehnalDokument17 SeitenCurvature Functions On A One-Sheeted Hyperboloid: Boris OdehnallucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenFormula SheetSEOW INN LEENoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector and Calculus: Sin Sin SinDokument2 SeitenVector and Calculus: Sin Sin SinAyush TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- ( + 2 Ab+b ( 2ab+b: A+b) A A B) ADokument5 Seiten( + 2 Ab+b ( 2ab+b: A+b) A A B) AsiewthiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- A, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaDokument2 SeitenA, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaLean Amara VillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaDokument2 SeitenA, B, and C Are Real Numbers and A and B Are: C. by Quadratic FormulaLean Amara VillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATHEMATICSDokument2 SeitenMATHEMATICSLean Amara VillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenAlgebra Formula Sheettishaoppong452Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vector & Basic Maths - Short Notes - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2024Dokument2 SeitenVector & Basic Maths - Short Notes - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2024Comical comicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cartesian CoordinatesDokument3 SeitenCartesian CoordinatesmahitumikoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conic Sections FormulasDokument2 SeitenConic Sections FormulasMulti talented IndiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1Dokument1 SeiteACTMathFormulaSheetFREE 1segun shonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math III SolutionSet PDFDokument4 SeitenMath III SolutionSet PDFqwertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area of Part of A CircleDokument4 SeitenArea of Part of A CircleAshutosh papelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE Formes Et ContoursDokument7 SeitenBE Formes Et ContourszuiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- KCF 1Dokument17 SeitenKCF 1vinod1577Noch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Line - 2: Normal FormDokument11 SeitenStraight Line - 2: Normal FormakshitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 10C - Unit 1 WorkbookDokument44 SeitenMath 10C - Unit 1 WorkbookjimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 102 Recitation Sol 1Dokument4 Seiten102 Recitation Sol 1omar msmqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double: Cheat Sheet - Straight LineDokument1 SeiteDouble: Cheat Sheet - Straight Linearnab dasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Special AnglesDokument9 SeitenChapter 8 Special AnglesShina GalvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmathDokument9 SeitenAmathAnnette ChiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mathematics: Co-Operative Arts & Science College, MadayiDokument2 SeitenDepartment of Mathematics: Co-Operative Arts & Science College, MadayiShijina ChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Equations - CharacteristicsDokument5 SeitenClassification of Equations - CharacteristicsAmit JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGO ACT3solDokument15 SeitenTRIGO ACT3solMaevin WooNoch keine Bewertungen
- APPENDIX B【Mathematics Review】Dokument4 SeitenAPPENDIX B【Mathematics Review】陳慶銘Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Quick Revision NoteDokument12 SeitenMaths Quick Revision NoteRohan JeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulas and Properties 9th GradeDokument4 SeitenFormulas and Properties 9th Gradedgjdf hgjhdgNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLUTION SET Math IIIDokument4 SeitenSOLUTION SET Math IIIMichael ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 08 Solving For PotentialsDokument20 SeitenNotes 08 Solving For PotentialsSofía Rodas VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE C222/ME C237 - Spring'18 - Lecture 3 Notes: Murat Arcak January 24 2018Dokument5 SeitenEE C222/ME C237 - Spring'18 - Lecture 3 Notes: Murat Arcak January 24 2018SBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conic Optimization: Conic Linear Program Examples Modeling DualityDokument40 SeitenConic Optimization: Conic Linear Program Examples Modeling Dualityanish_iyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Maths Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenSenior Maths Formula SheetMark Riley100% (2)
- Solving Quadratic Equations by The Quadratic Formula: Objectives 1Dokument11 SeitenSolving Quadratic Equations by The Quadratic Formula: Objectives 1Joy CloradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathematicsDokument7 SeitenMathematicsJay LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Math Applications and Interpretations Summer PacketDokument21 SeitenIb Math Applications and Interpretations Summer Packetapi-327140356Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review GeometryDokument1 SeiteReview GeometryGabby LabsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exerciselist5 Eja2022 Physics SolutionsDokument4 SeitenExerciselist5 Eja2022 Physics SolutionsfelicioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Revision in P1, P2, P3Dokument26 SeitenQuick Revision in P1, P2, P3surendrakumar.adhikari2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- PPSC Mock Test 2 Akhtar AbbasDokument4 SeitenPPSC Mock Test 2 Akhtar AbbasUmair AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Class Maths FormulasDokument5 Seiten10th Class Maths FormulasashwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Notes 2Dokument3 SeitenVector Notes 2Sofea GhafranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Quarter Pre-Calculus Reviewer. AY 2019-2020: Prepared by Leo Matthew SarneDokument6 Seiten2 Quarter Pre-Calculus Reviewer. AY 2019-2020: Prepared by Leo Matthew SarneAmiel MonsantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Coordinate GeometryDokument4 Seiten7 Coordinate GeometryRoses Are RosieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 10 - Straight LinesDokument3 SeitenUnit 10 - Straight LinesRaffaella LaxaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Formula SheetDokument8 SeitenMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteMath 2 PDFRimar LiguanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2Dokument1 SeiteMath 2Edmar TabinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2Dokument1 SeiteMath 2Jaypee BucatcatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteMath 2 PDFJads CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Formulas PDFDokument1 SeiteMathematics Formulas PDFStevenAronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteMath 2 PDFChloe OlazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2Dokument1 SeiteMath 2Ronna Mae De AsisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteMath 2 PDFRJNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Once The Game Is Over, The King and The Pawn Go Back in The Same Box.Dokument1 SeiteOnce The Game Is Over, The King and The Pawn Go Back in The Same Box.Cesal50% (2)
- Chem VocabDokument3 SeitenChem VocabCesalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab WriteDokument1 SeiteLab WriteCesalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railroads and Impact On WashingtonDokument8 SeitenRailroads and Impact On WashingtonCesal100% (1)
- RUNNING LOG 2006-2007: Total MileageDokument6 SeitenRUNNING LOG 2006-2007: Total MileageCesal100% (1)
- Mileage Log2Dokument4 SeitenMileage Log2CesalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3dmark ResultsDokument81 Seiten3dmark ResultsCesalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railroads Impact On WashingtonDokument9 SeitenRailroads Impact On WashingtonCesal50% (2)
- Physical Injury - AssaultDokument12 SeitenPhysical Injury - AssaultCesalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Along A Straight LineDokument11 SeitenMotion Along A Straight LineBrandy Swanburg SchauppnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Linear RegressionDokument24 SeitenSimple Linear Regressionইশতিয়াক হোসেন সিদ্দিকীNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Dokument4 SeitenMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4Ashmal ShazNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL DatatypeDokument7 SeitenSQL Datatypetesting engNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 Mathematics Investigation - The Cartesian Plane and Pythagorean TriplesDokument6 SeitenYear 8 Mathematics Investigation - The Cartesian Plane and Pythagorean TriplesRishitha DurgiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRES CODE Project05 - 2upDokument3 SeitenTRES CODE Project05 - 2upMourad BenzianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grobler AJ Chapter4Dokument14 SeitenGrobler AJ Chapter4hieuhuech1Noch keine Bewertungen
- FactoringDokument13 SeitenFactoringglebe myrtle belnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument23 SeitenTopologyAnotherZoruaAmongUsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan DivisionDokument12 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan DivisionDarlin Shane SanguirNoch keine Bewertungen
- (NEW) History of Mathematics in ChinaDokument20 Seiten(NEW) History of Mathematics in ChinaSJK(C) PHUI YINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuzzy Hungarian Method For Solving Intuitionistic FuzzyDokument7 SeitenFuzzy Hungarian Method For Solving Intuitionistic Fuzzybima sentosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Order Ordinary Differential Equations (1 Order - ODE)Dokument3 SeitenFirst Order Ordinary Differential Equations (1 Order - ODE)Naga MerahNoch keine Bewertungen
- D2-03Dokument18 SeitenD2-03yashika bairwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 978 3 642 35858 6 - Book - OnlineDokument341 Seiten978 3 642 35858 6 - Book - OnlineIvn TznNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TestDokument9 SeitenChapter TestkokonyinyichitchitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsDokument5 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsAnand TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 257 Signature AssignmentDokument7 SeitenMath 257 Signature Assignmentapi-434808297Noch keine Bewertungen
- Harcourt CompleteDokument498 SeitenHarcourt CompleteAkjafndjkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing Practice, Developing PractitionersDokument30 SeitenDeveloping Practice, Developing PractitionersAlonso GaxiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Reasoning AbilitiesDokument7 SeitenLogical Reasoning AbilitiesGulEFarisFarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.08 Binomial Distribution - Examples Moments PDFDokument4 Seiten3.08 Binomial Distribution - Examples Moments PDFDeepak ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMMSDokument302 SeitenMMMSAllen100% (1)
- Class 11C - Maths P2Dokument20 SeitenClass 11C - Maths P2St. Andrew's High School KarachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 SNM - New (Compatibility Mode) Solved Hypothesis Test PDFDokument50 SeitenUnit 1 SNM - New (Compatibility Mode) Solved Hypothesis Test PDFsanjeevlrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee 326 Lecture Notes 1Dokument38 SeitenEee 326 Lecture Notes 1Barış DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices and Matrix Operations PDFDokument23 SeitenMatrices and Matrix Operations PDFPranaykumar PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Today Utopia or DystopiaDokument30 SeitenTechnology Today Utopia or DystopiaDiego HDZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Determinants & Matrices: B C C B B C D A B CDokument2 SeitenAnswer Key Determinants & Matrices: B C C B B C D A B CElbert EinsteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Geometry (1) : LessonDokument4 SeitenAnalytical Geometry (1) : Lessongemgirl6686Noch keine Bewertungen