Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP Baby D
Hochgeladen von
Yna LafuenteCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NCP Baby D
Hochgeladen von
Yna LafuenteCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lafuente, Maryca Shaina M.
BSN 2-2
Pediatric Ward
CI: Professor Verame
Nursing Care Plan
Patients Name: Baby D
Initial Diagnosis: Severe Pneumonia
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired gas exchange r/t collection of secretions affecting oxygen exchange across alveolar membrane.
Short-term Goal: at the end of my shift, the patients condition will lighten and minimal formation of secretion will only occur.
Long-term Goal: after hospital confinement patient will be free of secretion enabling condition of oxygen exchange normally.
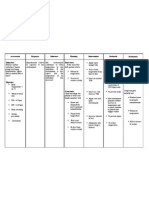
ASSESSMENT
>O:
- Dyspnea
-Shortness of
breath
-Wheezes upon
auscultation
-Nasal Flaring
-Altered Chest
Excursion
-Use of
accessory
muscles in
breathing
V/S taken as
follows:
T: 36.7 C
P: 138
R: 67
DIAGNOSIS
INFERENCE
PLANNING
>Impaired gas
Exchange
related to
alveolarcapillary
membrane
changes
(inflammatory
effects)
>Pneumonia is an
excess of fluid in the
lungs resulting from an
inflammatory process.
The inflammation is
triggered by many
infectious organisms
and by inhalation of
irritating agents.
Short term:
After 6 hours
of nursing
interventions the
patient will
demonstrate ease in
breathing.
Bronchospasm, which
occurs in many
pulmonary diseases,
reduces the caliber of
the small bronchi and
may cause dyspnea,
static secretions and
infections.
Bronchospasm can
sometimes be detected
by stethoscope when
wheezing or
diminished breath
sounds are heard.
Increase mucous
production along with
decrease mucous
ciliarys action,
contributes to further
Long term:
After 2-3 days
of nursing
interventions the
patients
S.O will verbalize
understanding
of the causative
factors that
could aggravate
the condition
and appropriate
factors that
could help the
patient relive
from gas
exchange
impairment
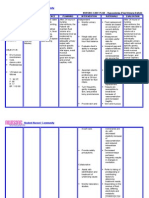
INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
>Administer Oxygen as ordered
> Improves gasexchange decrease
work of breathing.
> Position the patient in semi
fowlers position
>To facilitate lung
expansion to
enhance breathing.
>Administer antimicrobials as
prescribed.
>Suction as indicated.
>Assist with nebulizer treatments.
>Assess respiratory rate, depth and
>These drugs are
used to combat most
of the microbial
pneumonias.
>Stimulates cough or
mechanically clears
airway in patient
who is unable to
cough effectively.
>Facilitates
liquefaction and
removal of
secretions.
>Signs of
improvement in
EVALUATION
Short term:
The patient shall have
demonstrated ease in
breathing.
Long term:
The patients S.O
will
verbalize understanding
of the causative
factors that could
aggravate the
condition and
appropriate factors that
could help the patient
relive from gas exchange
impairment.
reduction in the caliber
of the bronchi and
results in decrease air
flow and decrease gas
exchange.
ease.
condition should
occur within 24- 48
hrs.
>This signs may indicate
hypoxia.
>Assess LOC, distress and irritability.
>Observe skin color and capillary refill.
>Monitor body temperature.
>Monitor effectiveness of
antimicrobial therapy.
>Determine
circulatory adequacy,
which is necessary for
gas exchange to
tissues.
>High fever greatly
increases metabolic
demands and oxygen
consumption and
alters cellular
oxygenation.
>Promotes
expectoration,
clearing or infection.
To facilitate lung
expansion to
enhance breathing.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCP For PCAPCDokument6 SeitenNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- Nicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)Dokument3 SeitenNicu NCP (Neo - Pnia)lorence_cachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDokument2 SeitenAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCP PDFFARAH MAE MEDINA100% (2)
- NCP PediaDokument2 SeitenNCP PediaJoey JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Rds 2Dokument1 SeiteNCP Rds 2Angelokeizer Gavino0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance: Nursing Care PlanJose Mari F. Esguerra0% (1)
- Altered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalDokument4 SeitenAltered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalAlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenActivity Intoleranceayra_alegreNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP InfectionDokument3 SeitenNCP InfectionPrince AhmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenNCP Pneumonia_garonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study in PneumoniaDokument17 SeitenDrug Study in PneumoniaKara Kathrina FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DiarrheaDokument2 SeitenNCP DiarrheaMiguelMartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - CapDokument4 SeitenNCP - CapSherryNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDokument3 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For InfectionDokument2 SeitenRisk For InfectionSuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- NCP PediaDokument2 SeitenNCP PediaJacinth Rizalino40% (5)
- Discharge Plan For TuberculosisDokument6 SeitenDischarge Plan For Tuberculosisploy8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDokument1 SeiteImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acutepain PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenAcutepain PneumoniaJoy SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationllianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identified Nursing Diagnoses and PrioritizationDokument4 SeitenIdentified Nursing Diagnoses and Prioritizationrheinz-marlon-m-carlos-7771Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument20 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- Health Teaching PlanDokument2 SeitenHealth Teaching PlanShedrann JohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teething:diaper Dermatitis NCPDokument2 SeitenTeething:diaper Dermatitis NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP ProperDokument5 SeitenNCP ProperRustan FrozenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altered Sleeping PatternDokument4 SeitenAltered Sleeping PatternIan Kenneth Da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Gastritis NewDokument3 SeitenNCP Gastritis NewNova Triska Purnama Sari0% (1)
- Pneumonia NCPDokument7 SeitenPneumonia NCPitsmeaya100% (3)
- NCP HyperthermiaDokument1 SeiteNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP HyperthermiaDokument6 SeitenNCP HyperthermiaGrax DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenNCP PneumoniaSteffanie Serrano100% (1)
- Deficit)Dokument2 SeitenDeficit)Lee DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefuroximeDokument1 SeiteCefuroximeRox SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument5 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument2 SeitenImpaired Skin IntegrityEli AyaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKhat100% (1)
- NCP UtiDokument1 SeiteNCP UtiElaisa Mae Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For ConcussionDokument3 SeitenNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- NCP MeningitisDokument2 SeitenNCP MeningitisARISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doenges, Et. Al, (2008) - Nurse's Pocket Guide. 11 Edition. F.A. Davis Company. P. 385Dokument3 SeitenDoenges, Et. Al, (2008) - Nurse's Pocket Guide. 11 Edition. F.A. Davis Company. P. 385Theresa AbrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Infection - NCPDokument3 SeitenRisk For Infection - NCPHamil BanagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDokument1 SeiteAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan2Dokument13 SeitenNursing Care Plan2Nna ANn CastleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Nursing Care PlansDokument58 SeitenLabor Nursing Care PlansMuhamad AriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preterm Labor - Prevention of DeliveryDokument10 SeitenPreterm Labor - Prevention of DeliveryLei OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Risk For ConstipationDokument1 SeiteNCP Risk For Constipationjorgeacct50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For FeverDokument2 SeitenNCP For FeverSherwin B. CaytapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Dokument1 SeiteAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DobDokument2 SeitenNCP DobIvy Mary Grace TanguiligNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)Dokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)kyaw100% (2)
- NCP PcapDokument2 SeitenNCP PcapGacutan Jonathan88% (26)
- NCP NminDokument5 SeitenNCP NminkrizziajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The BronchiDokument9 SeitenChronic Obstructive Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchiinamaliit100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDokument16 SeitenNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaAngel Cabatingan100% (4)
- Permission To Teach AftermidDokument1 SeitePermission To Teach AftermidYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Letter Templates (4th Year)Dokument49 SeitenSample Letter Templates (4th Year)Yna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lordosis Kyphosis DraftDokument2 SeitenLordosis Kyphosis DraftYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Letter (Sample)Dokument5 SeitenThesis Letter (Sample)Yna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal No. 1 Date: January 3, 2017Dokument3 SeitenJournal No. 1 Date: January 3, 2017Yna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter Template (College)Dokument1 SeiteLetter Template (College)Yna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- (University of The City of Manila) : Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Intramuros, ManilaDokument1 Seite(University of The City of Manila) : Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila Intramuros, ManilaYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia PA School AgedDokument8 SeitenPedia PA School AgedYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnoses Inference Implementation/ Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome/Evaluatio NDokument2 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnoses Inference Implementation/ Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome/Evaluatio NYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 Conclusion Physics LabDokument2 SeitenExperiment 4 Conclusion Physics LabYna Lafuente100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila (University of The City of Manila) Intramuros, Manila Telefax No. 526-68-82Dokument2 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila (University of The City of Manila) Intramuros, Manila Telefax No. 526-68-82Yna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promoting The PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenPromoting The PhilippinesYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systematic Review Pelaksanaan Programmatic Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Pada Pasien Tuberkulosis Resistan ObatDokument8 SeitenSystematic Review Pelaksanaan Programmatic Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Pada Pasien Tuberkulosis Resistan ObatAdinda Pramesthi RiadyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDF NAC ProtocolDokument247 SeitenCDF NAC ProtocolFrorefare LarcenerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Psychiatry WikipediaDokument153 SeitenGlossary of Psychiatry WikipediaAkio OzaragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Back To Basic Workbook UpdatedDokument68 SeitenBack To Basic Workbook UpdatedErna Andrea LipeczkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaDokument19 SeitenInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaCJ M. Pablo100% (1)
- IAPHD Hand Book On Palliative Care PDFDokument37 SeitenIAPHD Hand Book On Palliative Care PDFMohammed ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- South Carolina Maternal Morbidity and Mortality Review CommitteeDokument4 SeitenSouth Carolina Maternal Morbidity and Mortality Review CommitteeABC15 NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apothio Hemp LawsuitDokument58 SeitenApothio Hemp LawsuitLaw&CrimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BangkasDokument5 SeitenBangkasJulianne BangkasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Onbeing Ill: by Virginia WoolfDokument14 SeitenOnbeing Ill: by Virginia Woolf馬思宇Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prezentare AromaDokument56 SeitenPrezentare AromaMamaliga LizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Aortic Arches in VertebratesDokument2 SeitenEvolution of Aortic Arches in Vertebratesarbazkhan825lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Practice On: Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Risk ManagementDokument51 SeitenCode of Practice On: Workplace Safety and Health (WSH) Risk Managementaminul islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Dental Discussion 1) - Hesy ReDokument32 Seiten(Dental Discussion 1) - Hesy ReethanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Book Jicccim 2018Dokument171 SeitenScientific Book Jicccim 2018ngwinda90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Package Insert - 048437-01 - en - 422243Dokument22 SeitenPackage Insert - 048437-01 - en - 422243HadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Campbell Chapter 43 NotesDokument13 SeitenCampbell Chapter 43 NotesRyan LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type 1 Diabetes MellitusDokument4 SeitenType 1 Diabetes MellitusLaura Lhoeste100% (1)
- Performing Chest PhysiotherapyDokument14 SeitenPerforming Chest PhysiotherapyDivya Chauhan100% (1)
- Circadian RhythmsDokument6 SeitenCircadian Rhythmshafsa111100% (1)
- 074 Victor Babes PDFDokument1 Seite074 Victor Babes PDFCosminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare Associated InfectionsDokument17 SeitenHealthcare Associated InfectionsjahneeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoatlas of Ophthalmic Pathology PDFDokument177 SeitenStereoatlas of Ophthalmic Pathology PDFMihai CrișanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7.VARIETY OF LIFEDokument120 SeitenUnit 7.VARIETY OF LIFEPika PiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Biology Olympiad 2009Dokument41 SeitenAustralian Biology Olympiad 2009Science Olympiad Blog100% (1)
- Symptoms of ColitisDokument5 SeitenSymptoms of ColitisChatrina TandiloloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Caffeine On Voice A Systematic ReviewDokument13 SeitenThe Effects of Caffeine On Voice A Systematic ReviewChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Control For Plant Disease in Thailand: Watchalee SopinDokument80 SeitenMicrobial Control For Plant Disease in Thailand: Watchalee SopinImie S. Canaria100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical and Clinical Study of Kumkumadi Cream Prepared Using Kwath As Water Phase and Oil As Modern Phase On The Disease Vyanga'Dokument8 SeitenPharmaceutical and Clinical Study of Kumkumadi Cream Prepared Using Kwath As Water Phase and Oil As Modern Phase On The Disease Vyanga'freemoronsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CADASIL Management or What To Do When There Is Little One Can Do.Dokument14 SeitenCADASIL Management or What To Do When There Is Little One Can Do.eduardobar2000Noch keine Bewertungen