Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CAD Question
Hochgeladen von
bhargav5508Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CAD Question
Hochgeladen von
bhargav5508Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6 Th Sem ester (M ech)
Computer Aided Design
Un it -5: Finite Element A nalysis
Uk a T arsa dia Univers ity, B ardol i
1 Marks Question
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What are the important sources of errors in FEA solutions?
Name some FEA packages widely used.
Sketch Eight-node quadrilateral element.
Draw Six-node triangular element.
Apart of linear interpolation, what are the other types of interpolation in FEM?
What is your opinion if element has aspect ratio slightly greater than 3 in FEM analysis?
Which industry is widely using 2D Finite element analysis (triangular and quadrilateral
elements)?
8. Define: FEM
9. What do you understand by natural coordinate system?
10. Write equation of surface traction on body
2 Marks Question
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
What do you understand by Shape functions in Finite Element analysis?
Write down the FEA Applications in engineering point of view.
Explain Elimination approach in FEA.
What functions Node serve in FEM?
What is node and element in FEM?
What are limitation of FEM List different FEM software available in market?
3 Marks Question
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Explain the concepts of FEM. Discuss the different steps involved in FEA in detailed.
Describe the procedure of formulating plane stress problems by finite element method.
Discuss different types of analysis for FEM, also mention advantages and limitations of FEM.
Explain 2-D and 3-D elements used in finite element analysis.
Explain elimination approach used in FEM.
Explain Rayleigh-Ritz and Garlekin method for finding an approximate solution to the
engineering problem.
7. Derive the equation [K].[Q] = [F] for elimination approach method in FEM.
8. Draw higher order 2D and 3D elements. Name the element type. Also show the nodes.
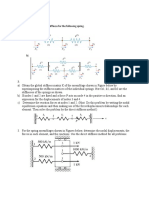
9. Figure -1 shows the compound section fixed at both ends. Estimate the reaction forces
at the supports and the stresses in each material when a force of 200 kN is applied at
the change of cross section.
Figure-1
Preparaed by: bhargav Patel (Mechanical/Automobile
Dept.) C. G. Patel Institute of Technology, Bardoli
Maliba Campus
6 Th Sem ester (M ech)
Computer Aided Design
Un it -5: Finite Element A nalysis
Uk a T arsa dia Univers ity, B ardol i
10. Use elimination approach to find the stress in all elements for 1-D problem shown in
Fig.4. Prepare the figure showing the elements and nodes clearly. Consider point load
only.
11. Use Penalty approach to find the stress in 1-D (X-Axis) problem shown in Fig. 5 in all
elements.Prepare the figure showing the elements and nodes clearly. Avoid body loads
and traction loads. The point load P is acting at 45 with X-Axis as shown in figure.
12. Figure below shows the bar with dimensions and loads. Determine the nodal
displacements, if the temperature rises by 600 C.
Assume the modules of elasticity for the complete bar as 200 GPa and Coefficient thermal
expansion as 12 x 10-6 per C.
c/s area = 250 mm2
c/s area = 400 mm2
F1 = 30 kN
F2= 60 kN
13. An axial stepped bar as shown in figure is subjected to an axial pull of 50 kN. If the
material of the bar is uniform and has a modulus of elasticity as 200 GPa. Determine the
displacement of each section. Also find the reaction.
Preparaed by: bhargav Patel (Mechanical/Automobile
Dept.) C. G. Patel Institute of Technology, Bardoli
Maliba Campus
6 Th Sem ester (M ech)
Computer Aided Design
Un it -5: Finite Element A nalysis
Uk a T arsa dia Univers ity, B ardol i
14. A two-step as shown in figure is subjected to thermal loading conditions. An axial load P = 200 x
103 N applied 20 C to the end. The temperature of the bar is raised by 50 C. Calculate: (i)
Element stiffness matrix (ii) Global stiffness matrix Consider E1 = 70 x 103 N/mm2 , E2 = 200 x
103 N/mm2 , A1 = 700mm2 , A2 = 1000mm2 , 1 = 23 x 10-6 per C and 2 = 11.7 x 10-6 per C
15. Axial load P = 300 KN is applied at 20 C to the rod as shown in fig. The temperature is then raised
to 60 C. The coefficient of thermal expansion for Aluminium is 23 x10-6 per C and Steel is
11.7x10-6 per C. AAl = 900 mm2 , ASteel = 1200 mm2 , EAl = 70 x 109 N/m2 , ESteel = 200 x 109 N/m2 .
Using FEM, (1) Determine the nodal displacement and element stresses. (2) The reaction forces
at the supports.
Preparaed by: bhargav Patel (Mechanical/Automobile
Dept.) C. G. Patel Institute of Technology, Bardoli
Maliba Campus
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Vallurupalli Nageswara Rao Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDokument48 SeitenVallurupalli Nageswara Rao Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering and TechnologyRathod VakilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument18 SeitenQuestion Bankbalajeemech2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Me 6603 Finite Element Analysis Question BankDokument18 SeitenMe 6603 Finite Element Analysis Question BankDineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Analysis On CrankshaftDokument5 SeitenStress Analysis On CrankshaftChanduReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6603 Finite Element AnalysisDokument18 SeitenME6603 Finite Element Analysissanthanam102Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5.accidental Car Impact Analysis and CFDDokument6 Seiten5.accidental Car Impact Analysis and CFDprojectzfourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me8692 Fea Question BankDokument15 SeitenMe8692 Fea Question Bankparandaman.mechNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6603 Finite Element Analysis PDFDokument18 SeitenME6603 Finite Element Analysis PDFAham GtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fem Assignment 2 and 3Dokument7 SeitenFem Assignment 2 and 3Aravind PhoenixNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEA TutorialsDokument14 SeitenFEA Tutorialsbalusharma1212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1. Find Element and Global Stiffness For The Following Spring. A)Dokument5 SeitenExercise 1. Find Element and Global Stiffness For The Following Spring. A)Selemon AssefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05-Bar Element DuzeltilmisDokument56 Seiten05-Bar Element Duzeltilmismmk111Noch keine Bewertungen
- ME 751 - Group 3 - Project 2Dokument24 SeitenME 751 - Group 3 - Project 2Steve SchwadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall 2011 Lab332a8Dokument4 SeitenFall 2011 Lab332a8Allen 艾倫 EgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fem Question BankDokument1 SeiteFem Question Banksan patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Proposed Experiments For Simulation Lab Updated-30th SepDokument4 SeitenList of Proposed Experiments For Simulation Lab Updated-30th SepSachi DhanandamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW1 Fem 2012Dokument3 SeitenHW1 Fem 2012greatkuroshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAE Lab ManualDokument30 SeitenCAE Lab Manualsyampnaidu100% (1)
- HW2 Fem 2012Dokument4 SeitenHW2 Fem 2012greatkuroshNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2-Computer Aided Design-QPDokument3 SeitenS2-Computer Aided Design-QPbhargav5508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation Lab-2022-23-ManualDokument22 SeitenSimulation Lab-2022-23-ManualChiru MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shown x10 Cartesian System Given: Experiment No. 9Dokument4 SeitenShown x10 Cartesian System Given: Experiment No. 9Maria MeharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture11 AllDokument32 SeitenLecture11 Alladeelyj100% (1)
- Fixtures - FEADokument5 SeitenFixtures - FEAMohammedRafficNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fracture Specimen Stree AnalysisDokument15 SeitenFracture Specimen Stree AnalysisGaurav PundirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys PZTDokument28 SeitenAnsys PZTQuoc LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced - Springs and JointsDokument8 SeitenAdvanced - Springs and Jointsgustavo5150Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element MethodsDokument12 SeitenFinite Element Methodspraneeth4a100% (1)
- Dynamic Load Analysis and Optimization of Connecting Rod of Samand EngineDokument9 SeitenDynamic Load Analysis and Optimization of Connecting Rod of Samand EnginecamiloromezNoch keine Bewertungen
- St7201 Finite Element MethodDokument11 SeitenSt7201 Finite Element MethodFinney WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM&BestpracticesDokument293 SeitenFEM&BestpracticesHem ANoch keine Bewertungen
- NozzleproDokument20 SeitenNozzleprossmith2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mtech. Finite Element AnalysisDokument11 SeitenMtech. Finite Element Analysissimalaravi100% (2)
- 03 Radioss BITSDokument6 Seiten03 Radioss BITSSharada GunjalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cama Lab 10mel68 PDFDokument63 SeitenCama Lab 10mel68 PDFshreedharkolekar50% (2)
- Global Institute of Engineering and Technology Melvisharam-Vellore-632 509Dokument6 SeitenGlobal Institute of Engineering and Technology Melvisharam-Vellore-632 509sathishneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me309 h05Dokument15 SeitenMe309 h05rksomepalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Spreadsheet in Mechanical EngineeringDokument11 SeitenExcel Spreadsheet in Mechanical EngineeringShaleh AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me6603 QB RejinpaulDokument18 SeitenMe6603 QB RejinpaulAravindhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kings: College of EngineeringDokument10 SeitenKings: College of Engineeringmanivannan_mageshNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM-Question BankDokument5 SeitenFEM-Question BankAthresh SudhindraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes For FemDokument35 SeitenNotes For FemG. Somasekhar SomuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Systems Laboratory User Manual: Revised: July 22, 2008Dokument40 SeitenPower Systems Laboratory User Manual: Revised: July 22, 2008prakashkmrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW6 - Problem Sheet - LSTDokument1 SeiteHW6 - Problem Sheet - LSTEntertainment GeneralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Analyses of Structural Systems: Opengl Opengl AutocadDokument1 SeiteLinear Analyses of Structural Systems: Opengl Opengl AutocadAy ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEA 2 CopyDokument13 SeitenFEA 2 CopyJo JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Model Question PaperDokument4 SeitenFinite Element Model Question PaperSrinivasan SriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abaqus Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenAbaqus Assignment 1Flávia de Souza BastosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST7201-Finite Element MethodDokument11 SeitenST7201-Finite Element MethodAshok AmmaiyappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Automatic Drain Cleaning SystemDokument30 SeitenReport On Automatic Drain Cleaning Systemtvishalkumar425Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Analysis AE2351Dokument5 SeitenFinite Element Analysis AE2351Aghil BuddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.FiniteElementAnalysisinAutomobileChassisDesign AMM.889.461 BookVolume889.page461Dokument8 Seiten1.FiniteElementAnalysisinAutomobileChassisDesign AMM.889.461 BookVolume889.page461PrimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LabManual PSBook2006 Revised Sept2010Dokument53 SeitenLabManual PSBook2006 Revised Sept2010boopelectraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Objectives Reactive Dispatch Optimization of An Electrical NetworkDokument14 SeitenMulti Objectives Reactive Dispatch Optimization of An Electrical NetworkSlim SaloumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar ApplicationDokument108 SeitenSolar Applicationbhargav5508Noch keine Bewertungen
- S2-Computer Aided Design-QPDokument3 SeitenS2-Computer Aided Design-QPbhargav5508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To FEMDokument47 SeitenIntroduction To FEMbhargav5508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Car BodyDokument67 SeitenCar Bodybhargav550850% (2)
- Aerodynamic Drag of Car BriefDokument80 SeitenAerodynamic Drag of Car Briefbhargav550850% (2)
- Dolan Springs AZ BusDefintionsDokument9 SeitenDolan Springs AZ BusDefintionsbhargav5508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reusable Firmware DevelopmentDokument321 SeitenReusable Firmware DevelopmentOsayd Mohamed100% (5)
- GSM GPRS GNSS HAT User Manual ENDokument32 SeitenGSM GPRS GNSS HAT User Manual ENvinod kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downgrade Request Form - Cesareo Angelo Banol 09202022Dokument2 SeitenDowngrade Request Form - Cesareo Angelo Banol 09202022Cesareo Angelo BanolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secospace USG2110 V100R001C03SPC200 User Guide (English Document)Dokument10 SeitenSecospace USG2110 V100R001C03SPC200 User Guide (English Document)Subarna GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cx93010-2X Ucmxx: Usb V.92/V.34/V.32Bis Controllered Modem With Cx20548 SmartdaaDokument62 SeitenCx93010-2X Ucmxx: Usb V.92/V.34/V.32Bis Controllered Modem With Cx20548 SmartdaaInquiryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS350 Technical CatalogueDokument20 SeitenACS350 Technical CatalogueJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4 OOSD NoteDokument32 SeitenUnit-4 OOSD Noterajputakshay8940Noch keine Bewertungen
- ICT X Practice QuestionsDokument3 SeitenICT X Practice QuestionsYash KohaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tally Prime Course Account and IntroDokument15 SeitenTally Prime Course Account and IntroAnkit Singh100% (1)
- Advanced Scan I21no2Dokument29 SeitenAdvanced Scan I21no2Jaiber SosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilyin2016 PDFDokument6 SeitenIlyin2016 PDFAnonymous fqHGrbwxeFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule For Theory Examination (Even Sem.) - 2011-2012 B.Tech., First Year-Ii SemesterDokument66 SeitenSchedule For Theory Examination (Even Sem.) - 2011-2012 B.Tech., First Year-Ii SemesterSheetal P. ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installed Files ProductDokument6 SeitenInstalled Files ProductCharlie ZulfikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silumin Catalogo Lutec PVP 2021Dokument186 SeitenSilumin Catalogo Lutec PVP 2021VEMATELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Import The Database File in OralceDokument5 SeitenImport The Database File in OralcewesternrailwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- G. Gevorgyan, M.markosyan+ C++Dokument229 SeitenG. Gevorgyan, M.markosyan+ C++HaykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sage X3 Partner Learning Catalog - 2020 - FINAL OctDokument50 SeitenSage X3 Partner Learning Catalog - 2020 - FINAL OctDinesh PandianNoch keine Bewertungen
- OLA - DPO Review & Clearance - 1678945432Dokument2 SeitenOLA - DPO Review & Clearance - 1678945432Reinier EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Sim TemplateDokument1 SeiteMicro Sim TemplateNikhil GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Add A Node To An HACMP ClusterDokument6 SeitenHow To Add A Node To An HACMP ClusterSenthil GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5Dokument23 SeitenLec 5Sama Atif Abdel-LatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMC Series - Driver ReadMe - 2019 04 02 PDFDokument3 SeitenUMC Series - Driver ReadMe - 2019 04 02 PDFLeo Do Monte0% (1)
- CMT Eh15Dokument50 SeitenCMT Eh15Eletrônica Maia Comércio e ServiçosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies 12 00446Dokument35 SeitenEnergies 12 00446Vimal SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bicsi Icttoday 20170708Dokument60 SeitenBicsi Icttoday 20170708saldivaroswaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 SO2 Curs-06 Kernel DebuggingDokument39 Seiten15 SO2 Curs-06 Kernel DebuggingAlla MstislavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Seven Capacitors and InductorsDokument10 SeitenChapter Seven Capacitors and InductorsVimala ElumalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eagle Point Tutorial - Cross SectionDokument9 SeitenEagle Point Tutorial - Cross Sectionqadiradnan7177100% (6)
- Dashboards Help FileDokument127 SeitenDashboards Help FilerameshvarkutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Programming Simple Word ProblemsDokument2 SeitenLinear Programming Simple Word ProblemsWendy Millheiser Menard0% (1)