Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Procedure For QA
Hochgeladen von
WaqarAhmedButtOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Procedure For QA
Hochgeladen von
WaqarAhmedButtCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
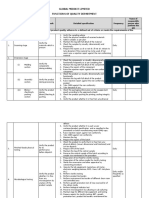
Procedure for Quality Assurance
1.0
PURPOSE
The purpose of this procedure is to ensure that all testing activities
carried out at ENTERPRISE Labs meet requirements to assure the quality
of test results and that the results are accurate and precise.
2.0
SCOPE
This procedure is applicable to ENTERPRISE Labs where testing is being
conducted.
3.0
RESPONSIBILITY
3.1Management Representative (MR) is responsible to:
3.1.1
3.1.2
3.1.3
3.1.4
Ensure coordination for Proficiency testing (PT).
Approve Quality Assurance Program for the lab.
Ensure that the developed program is followed.
Approve list of selected PT providers.
3.2Deputy Management Representative (DMR) is responsible to:
3.2.1
Register Lab with finalized PT Providers.
3.2.2
Develop Quality Assurance Plan for the lab.
3.2.3
Develop list of selected PT providers.
3.2.4
Ensure execution of the plan and maintain documentary evidence of
its implementation.
3.2.5
Compile and store all the results and records that are generated
from Quality assurance activities.
4.0
PROCEDURE
In order to assure the Quality of tests being performed, lab management
is to make dedicated efforts to ensure strict compliance through Quality
Assurance Program. Laboratory quality control is an essential aspect
of ensuring that data released is fit for the purpose determined by the
quality objectives (i.e. accuracy and precision). Lab Quality Assurance
Program includes:
a.
b.
c.
d.
Participation in PT
Replicate Testing
Retesting
Estimation of Uncertainty
4.1Proficiency Testing (PT)
4.1.1
Selection Process for PT providers
DMR is primarily responsible for searching of suitable PT providers
especially for the tests in the accreditation scope. DMR in consultation
with MR short lists the PT providers and form initial contact via email, fax
or telephone. In case of more than one PT providers then DMR in
consultation with MR selects the PT provider considering the following;
a. International / Domestic Recognition of the PT provider
Procedure for Quality Assurance
b. Appropriateness of the PT scheme to parameters in the scope of
accreditation
c. Financial considerations
d. Suitability of program (time, parameter)
NOTE: Quality Assurance Program will be developed in accordance with
schedule provided by the PT provider.
4.1.2
a.
b.
Registering in a PT Program
DMR is responsible to identify PT providers for tests in the scope of
accreditation. Upon finalization of PT provider, DMR enters its details
in the List of Selected PT Providers and make preparations s per
the instructions provided by the PT provider.
DMR is responsible to store all communication records.
4.1.3
Managing PT Process for Participation and Test Result
Submission
a. Upon receiving Blind Samples, DMR inspects the following before
accepting it:
i. Packaging of the sample for any physical damage or tampering
ii. Sample container, and sample itself for any physical / visible
damage, leak, tampering, etc.
b. In case of any nonconformity, PT provider is immediately notified and
test on the sample is not performed until and unless PT provider gives
a go-ahead or re-issues a new sample (this step is also performed in
case sample is damaged by the lab itself).
c. If the sample is found to be in acceptable state, its acceptance is
reported to PT by DMR, while ensuring that date is noted to estimate
the total time available for performance of test and delivery of test
result (timeline is provided by PT service provider).
d. DMR ensures the following before performance of the test on blind
sample is initiated:
i. Analyst to perform the test is identified on the basis of his/her
authorization and expertise (supervisor level recommended).
ii. Test Method is available.
iii. Equipment is ready.
e. Analyst ensures the following before starting the test performance:
i. Availability of lab note book for documentation of activity.
ii. Availability of appropriate test method.
iii. Equipment and required additional apparatus is ready for use, and
work instruction available.
iv. Environmental conditions (if any) are in compliance with test
requirement and not exceeding the defined limits.
Procedure for Quality Assurance
v. Any additional documents or forms required for test are available
(based on test requirement or requirements by PT service
providers).
f. When everything mentioned above is confirmed and ready, Analyst
starts the performance of test.
g. DMR ensure monitoring while the test is being performed and ensure
fulfillment of required documentation requirements for submission of
test results to PT provider.
h. DMR will ensure that results are documented as per PT provider
instructions.
i. The results are communicated to PT provider utilizing the medium of
service providers preference.
j. Remaining sample is stored in a controlled environment for future
references and activities (where possible).
4.1.4
a.
PT Result Analysis
After receiving the result from PT service provider, it is determined
whether QA/QC results have been considered Satisfactory or NonSatisfactory (Questionable).
No further actions required in case of satisfactory result, DMR can
now initiate new program for PT, or start communication for next due
round.
In case of Unsatisfactory results, lab will follow these steps:
b.
c.
i. DMR initiate CPA form and investigate for identification of root
cause behind the issue following Procedure for Corrective and
Preventive Action.
ii. DMR also involves PT provider to collect their expert opinion.
iii. Based on the result of investigation, DMR decides to rectify the
problem as well as re-initiates PT process
iv. In case of unsatisfactory result of investigation (unable to discover
the actual cause of unsatisfactory test result), DMR will register PT
program with a new service provider.
4.2Retesting & Replicate Testing of Samples
4.2.1
Retesting
Retesting is a planned activity and performed at periodic intervals to
verify previously performed tests. It must be understood here that
retesting a sample because of a nonconformity or because of an
ongoing investigation or complaint is not the same. ISO 17025 asks for
retesting of samples as a QA/QC measure. It is a procedure of repeating
test on already tested samples. All such samples are kept in storage
under acceptable conditions. The intention is to get the same result as of
the first performance. It can also be adopted in case; an analysis is not
giving the required result. In Short:
Retesting means same person performing the same test
repeatedly under same conditions
Procedure for Quality Assurance
4.2.2
Replicate testing
Replicate testing is also a planned activity and performed at periodic
intervals to verify previously performed tests. It is performing tests on a
volume of sample after replicating it and distributing it to different staff
members. The intention is to get the same results out of each of them,
but lab supervisors must ensure that all sample replicates carry the
same characteristics/ In short:
Replicate testing means different persons performing same
tests under same conditions
Replicate / Retesting will be performed as per the formulated Quality
Assurance Program / Plan. Retesting is performed by rechecking
results by the same method and analyst whereas Replicate Testing is
performed by rechecking results by the same method but by a second
analyst.
a.
Selection of Personnel
Before finalizing Lab staff members to contribute in this activity (at
least 2), DMR should ensure the following;
i. Performer is fully trained in the selected testing activity and has
training records available to justify this statement.
ii. Performer is available on the required date/time for performance
iii. He has good practice on the equipment / apparatus being used.
iv. He understands the requirements of the replicate / retesting
activities and its importance in Lab Management System
v. He is capable of providing data that is relevant to testing report
vi. He is capable of highlighting weak areas and also can address
corrective actions
b.
Sample Preparation and Distribution Control
DMR is responsible for finalizing sample preparation procedure and
shall appoint a person (or perform himself) the activities and give
each sample a unique ID, e.g. REP-TEST-01 / RETEST-01, REP-TEST-02 /
RETEST-02, etc. This data shall be recorded in Replicate Testing /
Retesting Report, so that related data is available at one place.
c.
Result Compilation and Analysis
After collecting all results from staff members involved, DMR should
develop Replicate / Retesting Report which should include the
following;
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
v.
d.
Dates / Time
Name of Personnel Involved
Sample results with their Unique IDs
Calculation of Average (based on Results)
Standard Deviation (based on Results)
Corrective Action and Its Follow up (Wherever Applicable)
Procedure for Quality Assurance
In case results or any condition varies and difference at some level is
very high, activity should be rescheduled for the same type of
sample. If the difference persists then corrective action should be
initiated to address the problem.
4.3Estimation of Uncertainty
It is the uncertainty of the personnel performing the test, as a
personnels error it cannot be calculated in the form of numerical values
but estimated by determining the combined estimation of Repeatability
and Reproducibility through the test result.
ENTERPRISE Lab performs uncertainty of tests in the accreditation scope
as per the Quality Assurance Program. Furthermore, lab will perform
uncertainty each time when any of the following happens;
a. Amendment in the Test Method
b. Change in Lab Authorizations (addition / deletion of test performers
for particular test)
c. Calibration or recalibration of equipment
d. Allocation of new equipment for particular test
Please refer Procedure for Estimation of Uncertainty
5.0
ASSOCIATED DOCUMENTS & FORMATS
5.1Procedure for Estimation of Uncertainty
5.2PT Correspondence & Communication File
5.3Quality Assurance Program
5.4Quality Assurance Plan
5.5Replicate / Retesting Report
5.6 List of selected PT providers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Quality ManualDokument43 SeitenQuality ManualsolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- QSP-006 R0 QSP For Non-Conformance Product ControlDokument13 SeitenQSP-006 R0 QSP For Non-Conformance Product ControljennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Validation A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandSoftware Validation A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier Audits and SurveysDokument13 SeitenSupplier Audits and SurveysBighneswar PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 质量过程审核 Quality Process Audit: 修订履历 Revision HistoryDokument42 Seiten质量过程审核 Quality Process Audit: 修订履历 Revision HistoryphamtienkhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA/QCDokument2 SeitenQA/QCapi-78981986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Current Area Item Assembly Process Production Qa CheckingDokument32 SeitenCurrent Area Item Assembly Process Production Qa Checkingteresa100% (1)
- Quality Audit (QAP GTL 05) Rev.Dokument12 SeitenQuality Audit (QAP GTL 05) Rev.GV Narayana ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 17025 QuestionDokument5 SeitenIso 17025 QuestionTalal HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boeing-Tasl: Strategic AlliancesDokument16 SeitenBoeing-Tasl: Strategic AlliancesSanchit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure 01 - Control of Documents and RecordsDokument6 SeitenProcedure 01 - Control of Documents and Recordssuhara hussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- VAL - 170401 - BMAA VAL Activity 3 URS - TemplateDokument10 SeitenVAL - 170401 - BMAA VAL Activity 3 URS - TemplateEcolor SRL100% (1)
- Supplier Auditpak 2000Dokument52 SeitenSupplier Auditpak 2000Adrian AustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance For Service IndustriesDokument16 SeitenQuality Assurance For Service IndustriesDr Srinivasan Nenmeli -K100% (11)
- Guidance For Preparing Standard Operating Procedures (Sops) : Epa Qa/G-6Dokument60 SeitenGuidance For Preparing Standard Operating Procedures (Sops) : Epa Qa/G-6rai_khan_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1.1 Control Inspection, Measuring and Test EquipmentDokument3 Seiten3.1.1 Control Inspection, Measuring and Test EquipmentStephen David GozunNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO Quality Manual v0.7Dokument27 SeitenISO Quality Manual v0.7adarshdk1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Certified Quality Assurance ProfessionalDokument4 SeitenCertified Quality Assurance Professionalismaeel247Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1A. Vendor Pre Qualification & Registration Form (HKG)Dokument3 Seiten1A. Vendor Pre Qualification & Registration Form (HKG)Arun Raj Arun RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form - Supplier Quality Survey - Rev 0Dokument3 SeitenForm - Supplier Quality Survey - Rev 0Selvaraj SimiyonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProQC ExampleReport Initial Supplier EvaluationDokument12 SeitenProQC ExampleReport Initial Supplier EvaluationMohammad Faraz Akhter100% (1)
- Project Quality Plan 8 7 2012 PDFDokument26 SeitenProject Quality Plan 8 7 2012 PDFtalhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure For Control of Non Confirming ProductDokument7 SeitenProcedure For Control of Non Confirming ProductAvijit DebnathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance Manual Oct-18Dokument176 SeitenQuality Assurance Manual Oct-18Ayush SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QC Example Resume.01Dokument4 SeitenQC Example Resume.01Guru SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance PlanDokument2 SeitenQuality Assurance PlanKarmyog Hi-Tech Machineries InfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QSV 2 Product Release Procedure EN 01Dokument6 SeitenQSV 2 Product Release Procedure EN 01prashanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration ListDokument2 SeitenCalibration ListCemang AmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality ManualDokument4 SeitenQuality ManualAli IrvaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality PlanningDokument10 SeitenQuality Planningkaushalsahu2332Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Quality PlanDokument110 SeitenProject Quality PlanJoseph Allan TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QAQCDokument15 SeitenQAQCflawlessy2k100% (1)
- Control of Non-ConformanceDokument6 SeitenControl of Non-ConformanceLawzy Elsadig Seddig100% (1)
- Specification For QMS Requirements 6-78-0001 - Rev. 1Dokument7 SeitenSpecification For QMS Requirements 6-78-0001 - Rev. 1Ayush Choudhary100% (1)
- MAI 07 - Control of Insp Measuring and Testing Equipment - DJ - v1Dokument9 SeitenMAI 07 - Control of Insp Measuring and Testing Equipment - DJ - v1IT Support - FernanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QCS 2010 Section 5 Part 2 AggregatesDokument9 SeitenQCS 2010 Section 5 Part 2 Aggregatesbryanpastor106Noch keine Bewertungen
- QMS ProceduresDokument1 SeiteQMS Proceduressurenu89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Monitoring and Measuring Equipment: Engineering Services Division Ministry of HealthDokument6 SeitenControl of Monitoring and Measuring Equipment: Engineering Services Division Ministry of Healthsyedfahadraza627Noch keine Bewertungen
- KQP 16 Inspection & Testing Rev 04Dokument11 SeitenKQP 16 Inspection & Testing Rev 04Mohd Isa HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional SummaryDokument3 SeitenProfessional SummaryVijay LS SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Execution Template - Quality Management ProcessDokument8 SeitenExecution Template - Quality Management ProcessAzza ShoukrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certified ISO 9001 Lead Implementer - Two Page BrochureDokument2 SeitenCertified ISO 9001 Lead Implementer - Two Page BrochurePECBCERTIFICATIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07.01.05 Fabrication Galvanizing R1Dokument11 Seiten07.01.05 Fabrication Galvanizing R1Bhanu Pratap ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9001 Audit Checklist - Quality Planning and DesignDokument14 Seiten9001 Audit Checklist - Quality Planning and DesignAmer RahmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Complaint ProcedureDokument4 SeitenCustomer Complaint ProcedureTomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drone Delivery Risk Analysis ReportDokument16 SeitenDrone Delivery Risk Analysis Reportfamily imtiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Karthik QaDokument3 SeitenResume Karthik QaYuvan Karthik MechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Plan: (Type The Document Subtitle)Dokument11 SeitenQuality Plan: (Type The Document Subtitle)ahmed hamed0% (1)
- Inspection and Test: Submitted To: Prepared By: Dr. Archana Gandhi Shrey Sharma Anmol JainDokument17 SeitenInspection and Test: Submitted To: Prepared By: Dr. Archana Gandhi Shrey Sharma Anmol JainAnmol JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document Control System Procedures: Prepared By: Wael ElsayedDokument13 SeitenDocument Control System Procedures: Prepared By: Wael ElsayedHadj Ali BoumedieneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of Quality DepartmentDokument5 SeitenFunctions of Quality DepartmentsachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managment Review Meeting 2012 Presentation Rev. 3Dokument37 SeitenManagment Review Meeting 2012 Presentation Rev. 3Hesham badawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP - Vendor Induction & Approval Procedure 062Dokument1 SeiteSOP - Vendor Induction & Approval Procedure 062ASIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAL-000 Test and Calibrated EquipmentDokument6 SeitenCAL-000 Test and Calibrated EquipmentEllis HowardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buhler Global Quality Manual V1.0Dokument35 SeitenBuhler Global Quality Manual V1.0JOECOOL67Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On QA QC Faisal Ali ShaikhDokument14 SeitenPresentation On QA QC Faisal Ali ShaikhFaisal Ali ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Quality KPIDokument1 SeiteExample of Quality KPISanjeev NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecom Quality Plan Sample PDFDokument24 SeitenTelecom Quality Plan Sample PDFTarek Tarek El-safrani100% (1)
- HALAL Internal AuditDokument34 SeitenHALAL Internal AuditWaqarAhmedButt100% (4)
- Procedure For SamplingDokument3 SeitenProcedure For SamplingWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSE GuideDokument15 SeitenHSE GuideWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- ILC Registration Form: Organization / Lab DetailsDokument1 SeiteILC Registration Form: Organization / Lab DetailsWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Description CompendiumDokument185 SeitenJob Description CompendiumWaqarAhmedButt100% (1)
- Punjab Food Authority Act 2011Dokument15 SeitenPunjab Food Authority Act 2011WaqarAhmedButt100% (1)
- SOPs For Food Business OperatorsDokument29 SeitenSOPs For Food Business OperatorsWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health: Hygiene Sanitation ExposureDokument3 SeitenHealth: Hygiene Sanitation ExposureWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Validation CIPACDokument11 SeitenMethod Validation CIPACWaqarAhmedButt0% (1)
- West Pakistan Hazardous Occupations (Lead) Rules, 1963Dokument7 SeitenWest Pakistan Hazardous Occupations (Lead) Rules, 1963WaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sr. No. Test Title Remarks: List of Accredited Tests (Rev01)Dokument1 SeiteSr. No. Test Title Remarks: List of Accredited Tests (Rev01)WaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter Lab Comparison Test Result SheetDokument2 SeitenInter Lab Comparison Test Result SheetWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation in Manufacturing Systems Trends in Industry: The ObjectiveDokument70 SeitenAutomation in Manufacturing Systems Trends in Industry: The ObjectiveWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Approach To Management: Group MembersDokument5 SeitenQuantitative Approach To Management: Group MembersWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalibrationDokument25 SeitenCalibrationWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalibrationDokument25 SeitenCalibrationWaqarAhmedButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ludwig Van Beethoven: Für EliseDokument4 SeitenLudwig Van Beethoven: Für Eliseelio torrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SME-Additional Matter As Per Latest Syllabus Implementation WorkshopDokument14 SeitenSME-Additional Matter As Per Latest Syllabus Implementation WorkshopAvijeet BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sweet Biscuits Snack Bars and Fruit Snacks in MexicoDokument17 SeitenSweet Biscuits Snack Bars and Fruit Snacks in MexicoSantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Volt Battery ChargerDokument5 Seiten48 Volt Battery ChargerpradeeepgargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Article: Finite Element Simulation of Medium-Range Blast Loading Using LS-DYNADokument10 SeitenResearch Article: Finite Element Simulation of Medium-Range Blast Loading Using LS-DYNAAnonymous cgcKzFtXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Report On Customer Relationship Management On SubwayDokument16 SeitenPresentation Report On Customer Relationship Management On SubwayVikrant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check Fraud Running Rampant in 2023 Insights ArticleDokument4 SeitenCheck Fraud Running Rampant in 2023 Insights ArticleJames Brown bitchNoch keine Bewertungen
- A PDFDokument2 SeitenA PDFKanimozhi CheranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Address MappingDokument26 SeitenAddress MappingLokesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forecasting of Nonlinear Time Series Using Artificial Neural NetworkDokument9 SeitenForecasting of Nonlinear Time Series Using Artificial Neural NetworkranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Fly Ash Conveying0 PDFDokument1 SeitePneumatic Fly Ash Conveying0 PDFnjc6151Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3125 Vitalogic 4000 PDFDokument444 Seiten3125 Vitalogic 4000 PDFvlaimirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Star Hotels in Portugal Leads 1Dokument9 Seiten5 Star Hotels in Portugal Leads 1Zahed IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building New Boxes WorkbookDokument8 SeitenBuilding New Boxes Workbookakhileshkm786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8: ACCG3001 Organisational Planning and Control Tutorial In-Class Exercise - Student HandoutDokument3 SeitenWeek 8: ACCG3001 Organisational Planning and Control Tutorial In-Class Exercise - Student Handoutdwkwhdq dwdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument3 SeitenUnit 1beharenbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expectation Vs Reality: Job Order and Contract of ServiceDokument10 SeitenExpectation Vs Reality: Job Order and Contract of ServiceMikee Louise MirasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Himachal Pradesh Important NumbersDokument3 SeitenHimachal Pradesh Important NumbersRaghav RahinwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form16 2018 2019Dokument10 SeitenForm16 2018 2019LogeshwaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 Social Responsibility and EthicsDokument54 SeitenCHAPTER 3 Social Responsibility and EthicsSantiya Subramaniam100% (4)
- Chapter 5Dokument3 SeitenChapter 5Showki WaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment ReportDokument1 SeiteAccomplishment ReportMaria MiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraftdesigngroup PDFDokument1 SeiteAircraftdesigngroup PDFsugiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Specifications: Fire Investigation and Failure Analysis (E901313)Dokument2 SeitenCourse Specifications: Fire Investigation and Failure Analysis (E901313)danateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions For Microsoft Teams Live Events: Plan and Schedule A Live Event in TeamsDokument9 SeitenInstructions For Microsoft Teams Live Events: Plan and Schedule A Live Event in TeamsAnders LaursenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gardner Denver PZ-11revF3Dokument66 SeitenGardner Denver PZ-11revF3Luciano GarridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 066 RC - LuelcoDokument11 Seiten2016 066 RC - LuelcoJoshua GatumbatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRT Mrte MRTFDokument24 SeitenMRT Mrte MRTFJonathan MoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity 10thDokument45 SeitenElectricity 10thSuryank sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Avanzado 1 Trabajo FinalDokument4 SeitenIngles Avanzado 1 Trabajo FinalFrancis GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesVon EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsVon EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemVon EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersVon EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityVon EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersVon EverandFundamentals of Risk Management for Process Industry EngineersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisVon EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersVon EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesVon EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Epidemiology and Demography in Public HealthVon EverandEpidemiology and Demography in Public HealthJaphet KillewoBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyVon EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesVon EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EVon EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (6)
- Plutopia: Nuclear Families, Atomic Cities, and the Great Soviet and American Plutonium DisastersVon EverandPlutopia: Nuclear Families, Atomic Cities, and the Great Soviet and American Plutonium DisastersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (32)
- Culture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsVon EverandCulture, Health and Illness: An Introduction for Health ProfessionalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesVon EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignVon EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsVon EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeVon EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Tensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesVon EverandTensor Technology Guide: Tensor Ring Benefits and UsesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsVon EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- What Went Wrong?: Case Histories of Process Plant Disasters and How They Could Have Been AvoidedVon EverandWhat Went Wrong?: Case Histories of Process Plant Disasters and How They Could Have Been AvoidedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)