Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
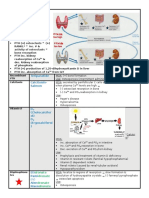
Hypothalamus & Pituitary
Hochgeladen von
Zagros MotamedOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hypothalamus & Pituitary
Hochgeladen von
Zagros MotamedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GH Somatropin / Somatrem
Prader-Willi syndrome
Noonans syndrome
Turner syndrome
CKD (chronic kidney disease)
IGF-1 Mecasermin
-
Used when treatment when GH is not
responding
Can cause HYPOglycemia (need to take in some CHO after
administration)
GH Antagonists (cant use Somatostatin due to short half-life)
(somatostatin = from pancreas)
1. Octreotide inhibits the release of GH
o Carcinoid syndrome (decreases serotonin release)
o WDHA (watery diarrhea/hypokalemia/achlorohydria)
o Bleeding esophageal varices (decreases portal venous pressure)
2. Pegvisomant GH hormone RECEPTOR antagonist (no effect on
GH release)
o Indication = acromegaly
Gonadotropins
Clinical uses:
1. Ovulation induction in women with anovulation due to:
o Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (2nd hypothyroidism)
o Polycystic ovary syndrome
o Obesity
Starting from the 3rd day of the menstrual cycle, give daily FSH
for 7-12 days
2. Controlled ovarian hyper stimulation in IVF
3. Male infertility
8-12 weeks of FSH/LH/HCG to help sperm production
Toxicity:
1. Ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome
o Ovarian enlargement leads to rupture leading to:
Ascites
Hydrothorax
Hypovolemia
2. Multiple pregnancies
FSH
1. Urofollitropin / Follitropin alfa / Follitropin beta
LH
1. Lutropin
a. Female ovulation in women / formation of corpus luteum
b. Male stimulates formation of Testosterone
hCG produced by the human placenta
Oxytocin
1. Induces labor; useful in:
o Post maturity
o Health risk to mom (diabetes, preeclampsia)
o Premature rupture of membrane
2. Augment delayed labor
a. Baby that is not born by week 41
3. Control uterine hemorrhage after birth
Toxicity:
Dont give it to a pregnant person because it will cause uterine contractions
before birth. Also will cause fluid retention and water intoxication.
Contraindicated in:
-
Fetal distress / Prematurity / Cephalopelvic disproportion
Prolactin
Hyperprolactinemia can be due to DRUGS or ADEMONAs
Women amenorrhea / galactorrhea
Men decreased libido / infertility
Dopamine Agonists
- Mostly used in cases of microadenoma (<1cm). Macro-adenoma
would require surgery.
- Can cause Huntington like
symptoms
1. Bromocriptine
2. Cabergoline
3. Pergolide
Clinical:
-
These can be used in cases of prolactin secreting tumors / lower
circulating prolactin levels and restoring ovulation
Sheehans Syndrome: major hemorrhage or hypotension during the
peripartum period, can result in ischemia of the affected pituitary
regions leading to necrosis.
o Need hormone replacement with:
Prolactin
Corticosteroids
Vasopressin (ADH)
V1: vascular smooth muscle cells vasoconstriction
V2: renal tubule cells reduce diuresis
Deficiency leads to Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
Central desmopressin
Nephrogenic diuretics (thiazide) = helps with loss of Na+ (balancing
blood osmolality)
Desmopressin synthetic ADH
-
Used for central diabetes insipidus
o Injection with this drug will cause >50% change in urine
osmolality (diagnosis)
Conivaptan / Tolvapatan ADH antagonists
-
Used for hyponatremia/heart
failure
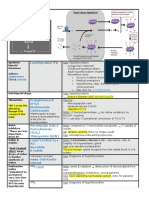
Hypothalamic Hormones
(GnRH)
Natural versions of the hormone is
called Gonadorelin but its a huge
peptide and hard to administer.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Goserelin
Histrelin
Leuprolide
Naferelin
The effect of these drugs will depend on the mode of administration due to
physiological mechanisms of action:
-
Pulsatile will stimulate FSH and LH secretions (simulates normal
physiological release)
Continued inhibits release of FSH and LH
Clinical:
1. Stimulation of gonadotropin production is useful for:
o Female / Male infertility
2. Suppression of gonadotropin production is useful for:
o Assisted reproductive technologies
You dont want to do IVF & have a normal ovulation
because that increases the chance of having multiple
babies at once.
o Endometriosis (presence of endometrial tissue outside the
uterus)
Reduces estrogen and progesterone concentrations
o Uterine Leiomyoma (fibroids) reduce the size by GnRH
agonists
o Prostate Cancer
Combined antiandrogen therapy with continuous GnRH
agonist & androgen receptor antagonist
o Central Precocious Puberty when puberty occurs <8 in girls /
<9 in boys
Adverse effect:
Continuous use of GnRH analogs in women typical symptoms of
menopause
- These can be fixed by using GnRH receptor antagonists:
1. Ganirelix
2. Cetrorelix
These two drugs prevent the LH surge from occurring during controlled
ovarian hyper stimulation (for example when you are doing IVF; can be used
instead of dopamine agonists with less side effects)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pe TempDokument1 SeitePe TempZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE: Problem Focused HPI AbdomenDokument6 SeitenOSCE: Problem Focused HPI AbdomenZagros Motamed100% (1)
- PTH & CalciumDokument2 SeitenPTH & CalciumZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThyroidDokument2 SeitenThyroidZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCM Block 1 Exam Notes - ShailDokument10 SeitenFCM Block 1 Exam Notes - ShailZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE Component PhysicalsDokument13 SeitenOSCE Component PhysicalsZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM DrugsDokument3 SeitenDM DrugsZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSK TumorsDokument3 SeitenMSK TumorsZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive and restrictive lung diseases and lung tumorsDokument6 SeitenObstructive and restrictive lung diseases and lung tumorsZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive and restrictive lung diseases and lung tumorsDokument6 SeitenObstructive and restrictive lung diseases and lung tumorsZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 2012 Von Willebrand Disease Pocket GuideDokument4 Seiten2012 Von Willebrand Disease Pocket GuideAnonymous T1fOfQfqRBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemophilia: Factor IX (Hemophilia B)Dokument38 SeitenHemophilia: Factor IX (Hemophilia B)Jhvhjgj JhhgtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ButlerDokument9 SeitenButlerHepicentar NišaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes InsipidusDokument60 SeitenDiabetes Insipidusperie_md100% (1)
- Medicine & Surgery MCQs With Answers Feb 20Dokument21 SeitenMedicine & Surgery MCQs With Answers Feb 20sb medexNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 116 Endocrine DisordersDokument106 SeitenNCM 116 Endocrine DisordersAnthony Seth AguilandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of Adults: Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersDokument134 SeitenNursing Care of Adults: Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersMary Ann Pardilla Alcober100% (4)
- Diabetes InsipidusDokument48 SeitenDiabetes InsipidusAhmed Fraz MamoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System Nursing ReviewDokument7 SeitenEndocrine System Nursing ReviewMeiJoyFlamianoIINoch keine Bewertungen
- DesmopresinDokument9 SeitenDesmopresinNARESH JANDIALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desmopressin Clinical PREADokument15 SeitenDesmopressin Clinical PREAjoelrequenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Diabetes InsipidusDokument16 SeitenWhat Is Diabetes InsipidusllianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidiuretic HormoneDokument1 SeiteAntidiuretic HormoneFalaq2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Hemophilia A and B PDFDokument268 SeitenTreatment of Hemophilia A and B PDFYusry SuryawiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endo Diseases Oralrev Part IDokument28 SeitenEndo Diseases Oralrev Part IRafi AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1 ExplanationDokument16 SeitenQuestion 1 ExplanationAnna Mae LumioNoch keine Bewertungen
- JAY VILLASOTO - Prelude To Endocrine BlockDokument3 SeitenJAY VILLASOTO - Prelude To Endocrine BlockJay VillasotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Clotting Mechanism ExplainedDokument63 SeitenBlood Clotting Mechanism ExplainedRahul PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- OsmometryDokument6 SeitenOsmometryVERMADEEN0% (1)
- ICU Reading on Pathophysiology and Management of Posttraumatic Diabetes InsipidusDokument24 SeitenICU Reading on Pathophysiology and Management of Posttraumatic Diabetes Insipidus駱品全Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENN PHARMACOLOGY BUNDLE PrintDokument142 SeitenENN PHARMACOLOGY BUNDLE Printronique reid75% (4)
- Diabetes Insipidus Journal ReadingDokument13 SeitenDiabetes Insipidus Journal ReadingnadiyasyadinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enuresis in ChildrenDokument42 SeitenEnuresis in ChildrenJood AL AbriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - The Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis)Dokument23 SeitenChapter 5 - The Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis)張宏軒Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine AgentsDokument10 SeitenEndocrine AgentsWendy VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garrahy 2020Dokument13 SeitenGarrahy 2020Ana Elizabeth Gangotena CoralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemophilia and Von Willebrand Disease EmergenciesDokument13 SeitenHemophilia and Von Willebrand Disease EmergenciesDobrila SimonovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acquired Factor VIII Inhibitors: Pathophysiology and TreatmentDokument6 SeitenAcquired Factor VIII Inhibitors: Pathophysiology and TreatmentSakinah Mar'ie SanadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Review AIPGMEE, 2011Dokument44 SeitenRapid Review AIPGMEE, 2011basic80% (5)
- Vidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014Dokument51 SeitenVidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014naltrisilvianNoch keine Bewertungen