Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
X1 Stair Balustrade
Hochgeladen von
aikalessCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
X1 Stair Balustrade
Hochgeladen von
aikalessCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
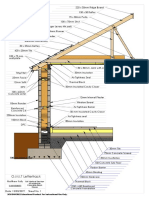
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
X1
design elements
A recurrent theme in modern
design is to let the structure
speak for itself, and X1
staircase stringer design is
an example of how effective
this can be in creating visual
appeal.
R
300
Support ribs for landing plate
300 max
Infill glass balustrade with blade
stanchions supportedby patch fittings
shown. A variety of balustrade styles
may be applied to this stringer design.
Plate steel stringer laser cut to
form simple crank into landing.
Nosing line
1A
20
300
Continuous through the
landing, this style of
stringer allows for a floating
appearance as it can span
from the upper flight to an
opposing wall or column
without the need for
intermediate landing supports.
These design methods
generate a light and open
feeling, well-suited to many
contemporary office layouts.
Landing support plate
30
The X1 is designed to create a
high degree of openness and
an impression of lightness.
Plate steel stringers support
an open tread and landing
design, relying on the
strength of complete laser
cut section and generating
a self-supporting structure.
Welded tread plates crossbrace the stringers.
Folded tread plate shown. Other tread
designs available
20
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
design
300 max
Figure 1. Stringer detail
30
0
1A. Simple crank into landing
1B. Complex crank into landing
1B
X1
2
www.arden.net.au
Plate steel stringer laser cut to
form complex crank to project
under landing.
Concrete Wall
2A. Engineering overview
2B. Side elevation
2C. Front elevation
A
C
Stringer cut away and continue
beneath landing
(Near side support and wall structure
not shown in this view)
Landing support plate stiffeners
reduce bounce
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
Figure 2. Plate stringer. The U
configuration shown is just one
example of the many configurations
possible with the X1 design.
Upper Floor Structure
B
F indicated on dimensions denotes a nominal
dimension that typically varies according to
specific application, engineering requirements
or client preferences.
2A
Lower Floor Structure
The narrow frontal profile
Overall structural rise
Overall structural rise
of The
the stringer
combines
narrow frontal
profile
wellofwith
treads
to
the open
stringer
combines
createwell
a design
with that
openopens
treads to
up lines
of vision
and
create
a design
that
opens
light.
upaccess
lines oftovision
and
access to light.
Overall going of
lower flight determined
Overall
by
tread going
going of
lower flight determined
by tread going
Steel plate stringers are ideal
for large unsupported spans.
Steel plate stringers are ideal
for large unsupported spans.
2B
250 nominal
tread going
250 nominal
tread going
2C
X1
design elements
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
technical
Stringers typically constructed
from 200-400 x 12-200mm
mild steel depending on span
and load rating. Minimal plate
steel dimensions that satisfy
engineering requirements
for design load are generally
selected, reducing the bulk of
the staircase and increasing
the impression of lightness
and openness.
In some of the examples
shown, the lower stringers
of the upper flight continue
beyond the landing to
concealed columns in the wall.
Regardless of the wall
coverings (i.e. plaster, stone,
shiplap), the penetration of
blade-like plate stringers
into the wall presents a
highly effective and modern
appearance. This is one of
the primary advantages of
laser cut plate steel over other
stringer types.
Three alternatives for tread
designs applicable to the X1
are shown. If these do not suit,
a wide variety of custom tread
assembly options are also
possible.
The X1 suits virtually any
configuration of straight
landings and flights: the
illustrations use a particular
configuration as an example.
X1
4
www.arden.net.au
M16 rods chemically bonded into floor structure.
Void edge fixing located on rods using 2 nuts.
The fixing assembly is covered by void edge
treatment stucture.
3A
10mm steel fixing plate shown as rebated into
floor to allow floor cover to go over. Other options
available to suit customer and site requirements.
3B
Figure 3. Typical fixing methods
3A. Fixing to upper structural floor
3B. Fixing to lower structural floor
3C. Fixing to structural wall
3D. View from underneath an upper
landing illustrating support method
for treads and landings
M16 rods chemset into wall
Welded steel tread plates add lateral
and torsional strength to the stringers
as well as supporting the treads.
10mm plate steel fixing plate rebated into
wall and plastered over for flush finish.
3C
3D
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
Landing plates strengthened with support ribs.
May be left exposed or enclosed in tread/landing
finish materials.
X1
design elements
Nosing line
4A. Tread option A: Monolithic timber
treads supported by welded steel
tags
Solid timber tread
Nominal going
Rebated
non-slip strip
42
4B. Tread option B: Composite timber
treads with non-slip strips supported
by internal steel plates welded to
stringer
4C. Tread option B: Isometric crosssection illustrating the internal MDF
stiffener, non-slip strip and side
laminate components
Gap between
treads must
not excede
125mm
270
23
Screws secure tread
to support tags
Mild steel support tag
welded to steel stringer
4A
Resilient insert for
high traffic stairs
50 Tread overlap
Internal MDF stiffener
Going
Rebated non-slip strip
Rise
4D. Tread option C: Composite timber
treads with non-slip strips supported
by exposed folded steel plates welded
to stringer
Nominal rise
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
Figure 4. Tread options
30 Nosing
inset from line
of stringer
Dress timber
back nosing
Ply core
Dress timber
bottom veneer
8mm steel plate tread support
welded to stringer
Dress Timber
Front Nosing
4B
Line of stringer
Timber edge laminate
10
0
Internal MDF stiffener
Applied rubber
tread surface
X1
4C
Selected non-slip strip
Dress timber nosing
253 mm
Rubber or vinyl
top covering
2 mm
25 mm
68 mm
F indicated on dimensions denotes a nominal
dimension that typically varies according to
specific application, engineering requirements
or client preferences.
www.arden.net.au
4D
32 mm
6mm Folded tread plate
welded to stringer
Intellectual property is copyright Archstairs
Pty Ltd unless otherwise agreed in writing. All
rights to the document are retained. Any use
of the document by clients or third parties,
unless specifically authorised by Archstairs
Pty Ltd, are at their own risk and the user
releases and indemnifies Archstairs Pty Ltd
from and against all loss or damage arising
from such use.
Inline laser cut plate steel stringer
About this document
compliance
Arden is a BSA licensed contractor for carpentry, joinery, glass, glazing
and aluminium as well as structural metal fabrication and erection. Arden
supplies a Form 16 (Licensed Contractor) on all projects. In design and
construct contracts, a Form 15 (Design Engineer) certification is supplied
upon request. For products and services incorporating the X1 system, this
table shows compliance with relevant codes and standards.
Key
full compliance with the code
can comply (see note for details)
not applicable to this element
Code
Title
BCA
The Building Code of Australia
Applicability
AS NZS 1170.1-2002
Structural Design Actions Permanent, imposed and other actions
AS 1288-2006
Glass in Buildings. Selection and installation.
AS NZS 1554.1-2004
Structural steel welding - Welding of steel structures
AS 1554.6-1994
Welding stainless steels for structural purposes
AS NZS 4586-2004
Slip resistance classification of new pedestrian surface materials
AS 1428.1-2009
Design for access and mobility
AS 1657-1992
Fixed platforms, walkways, stairways & ladders. Design, construction and installation
1. The incorporation of risers into the tread design is required for full compliance with AS 1428.1-2001
X1
design note
For all commercial applications, it is important that sufficient space
for the stairwell cavity be allowed to satisfy Australian Standards
and BCA requirements.
The footprint is primarily driven by the floor to floor rise, as well as the
staircase configuration chosen. However, stringer and balustrade style design
may increase the amount of space required. Allowing too small a cavity can
restrict the design options of the staircase. Also, points at where the staircase
interacts with other structures are best addressed early in the design cycle.
Consultation with Arden early on will help ensure that these design issues
can be addressed in a cost-effective manner.
design elements
www.arden.net.au
phone (07) 3267 6100 | fax (07) 3267 6500 | email admin@arden.net.au
Office & factory: 46 Radley Street Virginia Qld 4014 Australia
Postal address: PO Box 317 Virginia Qld 4014 Australia
Version 1.0. Design by www.cazazz.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Structural Inspection ChecklistsDokument57 SeitenStructural Inspection Checklistsaikaless100% (1)
- Structural Steel Det Train ManualDokument100 SeitenStructural Steel Det Train Manualsuperpiojo86% (22)
- Retaining Wall DetailDokument9 SeitenRetaining Wall DetailRonald KahoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cladding Systems: Manufactured Aluminum and Steel CladdingDokument32 SeitenCladding Systems: Manufactured Aluminum and Steel CladdingsalmaMB50% (2)
- Preliminary Structural DesignDokument8 SeitenPreliminary Structural Designaikaless100% (1)
- Metal Spiral Stairs Install ManualDokument36 SeitenMetal Spiral Stairs Install ManualPeter Jean-jacquesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing Checklist PDFDokument3 SeitenDrawing Checklist PDFaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Appraisal ReportDokument14 SeitenStructural Appraisal ReportaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Facade WP1 ReportDokument151 SeitenBest Facade WP1 Reporthienarch89Noch keine Bewertungen
- ProtaStructure QSG enDokument64 SeitenProtaStructure QSG enHenry67% (3)
- Astm E331-00Dokument4 SeitenAstm E331-00ELENA NAVASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin Glass 6 PDFDokument6 SeitenFin Glass 6 PDFEIWAA100% (1)
- ST Wa BraDokument20 SeitenST Wa BrakjdaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCW 14-Us HalfenDokument36 SeitenHCW 14-Us HalfenALBERT100% (1)
- Alessio Zenaro - Portfolio 2011 2MBDokument34 SeitenAlessio Zenaro - Portfolio 2011 2MBAlessio Zenaro MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weldlok GratingDokument16 SeitenWeldlok Gratingnovadistributors100% (3)
- Foundation Systems.Dokument9 SeitenFoundation Systems.PRECIOUS AMY TITIWANoch keine Bewertungen
- Bailey Load Table PDFDokument72 SeitenBailey Load Table PDFnumber_25Noch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION 03490 Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC)Dokument17 SeitenSECTION 03490 Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC)SunilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company ProfileDokument33 SeitenCompany ProfileGic LandscapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 4012 00 PDFDokument38 Seiten04 4012 00 PDFrmdarisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portal Frames Final - 2Dokument19 SeitenPortal Frames Final - 2Ar Vivek KareliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspended SlabDokument2 SeitenSuspended SlabaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Stud Solutions Product CatalogDokument15 SeitenSteel Stud Solutions Product CatalogDGWNoch keine Bewertungen
- St-006 - Block Wall Restraint Details and Lintel Schedule Sheet-1Dokument1 SeiteSt-006 - Block Wall Restraint Details and Lintel Schedule Sheet-1MØhãmmed ØwięsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Façade Treatment: Submitted To:-Submitted ByDokument17 SeitenFaçade Treatment: Submitted To:-Submitted ByShivam ShanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- False Ceiling: MMBC 7Th SemDokument54 SeitenFalse Ceiling: MMBC 7Th SemBmssa 2017BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel StaircaseDokument24 SeitenSteel StaircaseKanak Yadav100% (1)
- Steel Decking Revised PDFDokument26 SeitenSteel Decking Revised PDFcrimsonbunnie60% (5)
- Architectural AbbreviationsDokument15 SeitenArchitectural AbbreviationsMohamed AjeemusshaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal StairsDokument6 SeitenMetal Stairssks_242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 3-Design Requirements of BMUsDokument37 SeitenSession 3-Design Requirements of BMUsRanjit Singh100% (1)
- Design of Timber Floor JoistsDokument5 SeitenDesign of Timber Floor JoistsPaulius VasiliauskasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gang-Nail Connectors - How They Work Gang-Nail Truss SystemDokument5 SeitenGang-Nail Connectors - How They Work Gang-Nail Truss SystemAnonymous acaD5VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facade-Alumimum & Glazing Works Scope-Technical SpecificationsDokument5 SeitenFacade-Alumimum & Glazing Works Scope-Technical SpecificationsHasnain SafdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Loft Conversions SampleDokument18 SeitenUnderstanding Loft Conversions SampleElZahraa SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loft Conversion 1Dokument16 SeitenLoft Conversion 1Марко НакићNoch keine Bewertungen
- En Downloads Brochures TexlonHSP ETFE Brochure enDokument4 SeitenEn Downloads Brochures TexlonHSP ETFE Brochure ennubis_zionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition Nature and Scope of Urban GeographyDokument4 SeitenDefinition Nature and Scope of Urban Geographysamim akhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-General Part DetailDokument24 Seiten02-General Part DetailVinh HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- LysaghtArchitecturalDetailingManualRoofWallFlashingApril14 PDFDokument40 SeitenLysaghtArchitecturalDetailingManualRoofWallFlashingApril14 PDFthailanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining Wall CalculationDokument4 SeitenRetaining Wall CalculationaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lysaght Bondek Design and Construction Guide July 2016Dokument48 SeitenLysaght Bondek Design and Construction Guide July 2016Octavianus ManoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing Stress GlassDokument4 SeitenBearing Stress GlasslingchenhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiDokument48 SeitenPesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiAndi HafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alubond Tech - Brochure PDFDokument8 SeitenAlubond Tech - Brochure PDFLjubisa TopicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross Beam Cross Beam: Fitting 30 ° Fitting 30 °Dokument1 SeiteCross Beam Cross Beam: Fitting 30 ° Fitting 30 °jeacovjeceNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS ISO 5455 Scale PDFDokument8 SeitenBS ISO 5455 Scale PDFaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ead 020002 00 0404 Balcony and Terrace Glazing System Without Vertical Frames 2016Dokument9 SeitenEad 020002 00 0404 Balcony and Terrace Glazing System Without Vertical Frames 2016bmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design in Brickwork Non Load BearingDokument4 SeitenDesign in Brickwork Non Load Bearingharicv019Noch keine Bewertungen
- VetraFin Glass Fin SystemDokument24 SeitenVetraFin Glass Fin SystemPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balcony Detail-EVEN PLANDokument1 SeiteBalcony Detail-EVEN PLANAyushi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long SpanDokument113 SeitenLong SpanHasan KazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toaz - Info Design Calculation Skylight Structure PRDokument7 SeitenToaz - Info Design Calculation Skylight Structure PRAbdul khaliquNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 24 - Glass and Glazing PDFDokument14 SeitenChapter 24 - Glass and Glazing PDFpokemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Composite Panel Manufacturers IndiaDokument12 SeitenAluminium Composite Panel Manufacturers IndiaEurobondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3.8 - Window U-ValueDokument46 SeitenModule 3.8 - Window U-ValueSze Yan LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greatminds Architectural SpecificationDokument6 SeitenGreatminds Architectural SpecificationAr John Bernard AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glass Fixing DetailsDokument16 SeitenGlass Fixing Detailsprasaddha100% (2)
- W 36Dokument12 SeitenW 36matsiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction MaterialsDokument20 SeitenConstruction MaterialsmariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive Block Foundation DrawingDokument1 SeitePassive Block Foundation Drawingapi-426990805100% (1)
- Flat Roof 1Dokument10 SeitenFlat Roof 1agent206Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jordahl Jva enDokument48 SeitenJordahl Jva engasparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cantilever Curtain WallDokument18 SeitenCantilever Curtain WallkingdbmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Report Format Sample For Old BuildingsDokument5 SeitenAssessment Report Format Sample For Old BuildingsAndrew Araha0% (1)
- Stick Curtain Wall Installation-Hidden Frame WallDokument2 SeitenStick Curtain Wall Installation-Hidden Frame WallHan JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wade ChannelDokument24 SeitenWade ChannelAbdul NabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument7 Seiten4Malith De SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storage FacilitiesDokument32 SeitenStorage FacilitiesaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Country Value (Icv) - Entrepreneurial Opportunities in The Companies of OmanDokument17 SeitenIn-Country Value (Icv) - Entrepreneurial Opportunities in The Companies of OmanaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Download: Tunnel A Hard Day Aquaman Alone 1BRDokument1 SeiteTo Download: Tunnel A Hard Day Aquaman Alone 1BRaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design (Moment and Shear Check) (For Simply Supported)Dokument8 SeitenSteel Design (Moment and Shear Check) (For Simply Supported)aikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unbroken - SH Omar SuleimanDokument6 SeitenUnbroken - SH Omar SuleimanaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moh New Requirements For Foreign Workers ContractDokument3 SeitenMoh New Requirements For Foreign Workers ContractaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled Artwork 23Dokument1 SeiteUntitled Artwork 23aikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Trial InstallationDokument5 SeitenFree Trial InstallationAnonymous W6WPVDkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION 2 - Design Criteria For Water Distribution Systems - 201304251344365252Dokument16 SeitenSECTION 2 - Design Criteria For Water Distribution Systems - 201304251344365252aikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 2 - Design Criteria For Water Distribution SystemsDokument8 SeitenSection 2 - Design Criteria For Water Distribution SystemsKishan ChandrasekaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan SketchDokument43 SeitenPlan SketchIngenieria Estructural AplicadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Practical Approach To Design and Construction Detailing For Road, Industrial and Aircraft PavementsDokument15 SeitenA Practical Approach To Design and Construction Detailing For Road, Industrial and Aircraft PavementsaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Paper 0.25 inDokument1 SeiteGraph Paper 0.25 inmailbocks96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full ThesisDokument136 SeitenFull ThesisAlemayehu DargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 211ce2028 PDFDokument88 Seiten211ce2028 PDFaikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cantilever Retaining Wall - Metric PDFDokument16 SeitenCantilever Retaining Wall - Metric PDFJebin JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Presentation (Concrete Terrace Structure)Dokument62 SeitenFinal Presentation (Concrete Terrace Structure)aikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforcement Detailing For Openings in Beams 103Dokument5 SeitenReinforcement Detailing For Openings in Beams 103stefengoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Water Tank PDFDokument31 SeitenDesign of Water Tank PDFabdulqader100% (2)
- spch2 ch4 PDFDokument42 Seitenspch2 ch4 PDFAbu BiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intensity Duration FrequencyDokument1 SeiteIntensity Duration FrequencyYee Mon Ne WinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and DemonstratedDokument4 SeitenHybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and Demonstratedmohamad theibechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Terms 2nd PartDokument2 SeitenGlossary of Terms 2nd Part2DJoyce D.N CapacieteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Regional PlanningDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Regional Planningadeeba siddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Dokument3 SeitenENGLISH 4 (General & Specific Sentence, Main Idea & Key Sentence) )Analiza Dequinto BalagosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Lab Manual Main Ars 200280705008Dokument6 SeitenFinal Lab Manual Main Ars 200280705008shalini pathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme Bladder Accumulator DatasheetDokument3 SeitenAsme Bladder Accumulator DatasheetSamad A BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper DementiaDokument1 SeiteReaction Paper DementiaElla MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Dimmer CircuitsDokument14 SeitenLight Dimmer CircuitskapilasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- BF254 BF255Dokument3 SeitenBF254 BF255rrr2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 08Dokument32 SeitenLecture 08SusovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- El Nino 3Dokument8 SeitenEl Nino 3nisAfiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyse Bacterologique de L EauDokument6 SeitenAnalyse Bacterologique de L Eaupeguy diffoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCG Damri SurabayaDokument11 SeitenGCG Damri SurabayaEndang SusilawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Mathematics Checkpoint Booklet AY 23-24Dokument270 SeitenGrade 8 Mathematics Checkpoint Booklet AY 23-24Arta riaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)Dokument10 SeitenExam C - HANATEC142: SAP Certified Technology Associate - SAP HANA (Edition 2014)SadishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clepsydra - PesquisaDokument2 SeitenClepsydra - PesquisaJose Maria SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Government Employees Housing FoundationDokument2 SeitenFederal Government Employees Housing FoundationMuhammad Shakil JanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The King's Avatar - Chapter 696 - Guild Feature - Gravity TalesDokument5 SeitenThe King's Avatar - Chapter 696 - Guild Feature - Gravity TalesMayhaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AR Financial StatementsDokument281 SeitenAR Financial StatementsISHA AGGARWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyler & Wheeler Curriculum ModelDokument8 SeitenTyler & Wheeler Curriculum Modelliliyayanono100% (1)
- Augmentation of Labour: Nabhan A, Boulvain MDokument8 SeitenAugmentation of Labour: Nabhan A, Boulvain MMade SuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsDokument7 SeitenA Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsAhmed ShoeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- FL Switch 2000Dokument124 SeitenFL Switch 2000marcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Review A2-B1Dokument5 SeitenGrammar Review A2-B1Lena Silva SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Defining and Non Relative Clauses XII (I)Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Defining and Non Relative Clauses XII (I)mariaalexeli0% (1)
- Edug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - CompletedDokument37 SeitenEdug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - Completedapi-241358660Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rotc Reviewer FinalsDokument11 SeitenRotc Reviewer FinalsAngel Atienza100% (1)
- APS PresentationDokument32 SeitenAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNoch keine Bewertungen