Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
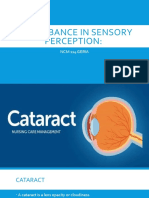
Cataracts (Rationale)
Hochgeladen von
Joseph Wilson Macasa0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
56 Ansichten2 SeitenCataracts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCataracts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
56 Ansichten2 SeitenCataracts (Rationale)
Hochgeladen von
Joseph Wilson MacasaCataracts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
CATARACTS (Rationale):
1. ANSWER C. A gradual, painless blurring of central vision is the chief
clinical manifestation of a cataract. Early symptoms include slightly
blurred vision and a decrease in color perception.
2. ANSWER C. The most appropriate nursing diagnosis for the client
scheduled for cataract surgery is Disturbed sensory perception
(visual) related to lens extraction and replacement. Although the
other options identify nursing diagnoses that may be appropriate,
they are not related specifically to cataract surgery.
3. ANSWER C. A mydriatic medication produces mydriasis or dilation
of the pupil. Mydriatic medications are used preoperatively in the
cataract client. These medication act by dilating the pupils. They
also constrict blood vessels. An osmotic diuretic may be used to
decrease intraocular pressure. A miotic medication constricts the
pupil. A thiazide diuretic is not likely to be prescribed for a client
with a cataract.
4. ANSWER A. Severe pain or pain accompanied by nausea is an
indicator of increased intraocular pressure and should be reported to
the physician immediately. The other options are inappropriate.
5. ANSWER C. The client is instructed to wear a metal or plastic shield
to protect the eye from accidental and is instructed not to rub the
eye. Glasses may be worn during the day. Aspirin or medications
containing aspirin are not to be administered or taken by the client
and the client is instructed to take acetaminophen as needed for
pain. The client is instructed not to sleep on the side of the body on
which the operation occurred. The client is not to lift more than 5
pounds.
6. ANSWER D. Surgical removal is the only treatment used at this
time for cataracts; no medical treatment is available to prevent or
treat them. Surgical removal of the cataract and lens is indicated
when the cataract has developed to the point that vision and
activities of daily living are affected. If the patient presents with
bilateral cataracts, surgery is only performed on one eye at a time.
Complications from cataract surgery are unusual, and occur in less
than 1% of the surgeries.
7. ANSWER C. The nurse should reinforce any limitation, such as
avoiding reading, lifting, and strenuous activity, and sleeping on the
operative side. The patient also needs to understand the importance
of not disturbing the eye dressing, of follow-up appointments, and of
manifestations of complications such as eye pain, change in vision,
headache, or nausea.
8. ANSWER D. Prolonged use of steroidal anti-inflammatory agents is
a risk factor for cataracts. The other risk factors dont contribute to
the development of cataracts.
9. ANSWER B. Pain shouldnt be present after cataract surgery. The
client should be told the other symptoms might be present.
10.
ANSWER D. The client should report a noticeable or sudden
decrease in vision to the physician. The eye may be slightly
reddened postoperatively, but this should gradually resolve. The
client is taught to take acetaminophen, which is usually effective for
relieving discomfort. Small amounts of dried material may be
present on the lashes after sleep; this is expected and should be
removed with a warm facecloth.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Human Body WorkbookDokument25 SeitenHuman Body Workbookjk centralNoch keine Bewertungen
- SA Anesthesia Drug Dosages 2022Dokument3 SeitenSA Anesthesia Drug Dosages 2022KRLITHIU Borja100% (1)
- Eye and Vision 7th EditionDokument35 SeitenEye and Vision 7th EditionCrystal LynaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retina Detachment, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionVon EverandRetina Detachment, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otalgia & TinnitusDokument19 SeitenOtalgia & Tinnitushonda matizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take One Nursing Final Coaching Ms CriticalDokument29 SeitenTake One Nursing Final Coaching Ms Criticalnot your medz duranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endo Gi QuestionerDokument26 SeitenEndo Gi QuestionerRymmus Asuncion100% (1)
- Case Studies - Apollo Hospitals, DhakaDokument7 SeitenCase Studies - Apollo Hospitals, Dhakasakil khan100% (1)
- NURSING PRACTICE TEST I - Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice General InstructionsDokument9 SeitenNURSING PRACTICE TEST I - Foundation of PROFESSIONAL Nursing Practice General InstructionsjcruzadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Practice Guidelines - 2017Dokument54 SeitenClinical Practice Guidelines - 2017Cem ÜnsalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NP 5Dokument26 SeitenNP 5Allaiza CristilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncology QuestionsDokument3 SeitenOncology QuestionsWilma BaludoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avastin Injection ConsentDokument4 SeitenAvastin Injection ConsentSaumya SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rationale of Ms Exam October 18, 2022Dokument15 SeitenRationale of Ms Exam October 18, 2022Felimon BugtongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sas 38Dokument2 SeitenSas 38Gwenn SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glaucoma, Cataract, Otitis Lippincot Questions-1Dokument3 SeitenGlaucoma, Cataract, Otitis Lippincot Questions-1Rammy KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract: Presented By: HomipalDokument12 SeitenCataract: Presented By: Homipalankita singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbance in Sensory PerceptionDokument48 SeitenDisturbance in Sensory PerceptionKristine Louise JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The EyeDokument16 SeitenDisorders of The Eyelisette_sakuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology MCDokument6 SeitenOphthalmology MCyodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pterygium and Pterygium Surgery: Patient InformationDokument11 SeitenPterygium and Pterygium Surgery: Patient InformationAnna ListianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student's Name: - Roll No: - Date: - Subject: Special Senses Class: 2Dokument4 SeitenStudent's Name: - Roll No: - Date: - Subject: Special Senses Class: 2Priya bhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postoperative Comanagement ProtocolDokument3 SeitenPostoperative Comanagement ProtocolNeva ArsitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicDokument18 SeitenNCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicDiego DumauaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Problems On ExpeditionsDokument7 SeitenEye Problems On ExpeditionsjustanothergunnutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eent Post Test Final DipologDokument6 SeitenEent Post Test Final DipologJan Joseph BanzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toophtj 8 1Dokument2 SeitenToophtj 8 1SusPa NarahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JaniceDokument2 SeitenJaniceCrystal Ivy AgpaoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of GlaucomaDokument7 SeitenManagement of GlaucomaAlbertus Bayu KristiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med Surg3Dokument17 SeitenMed Surg3Hasan A AsFourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample QuestionareDokument4 SeitenSample QuestionareJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 8 Edition: Chapter 21: Nursing Assessment: Visual and Auditory Systems Test BankDokument8 SeitenLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 8 Edition: Chapter 21: Nursing Assessment: Visual and Auditory Systems Test BankMonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract SurgeryDokument14 SeitenCataract SurgeryRenato AbellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye SurgeryDokument1 SeiteEye SurgerySewyel GarburiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocols For Injuries To The EyeDokument11 SeitenProtocols For Injuries To The EyeSteve D'HamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CATARACT Case Senario No.1 (Tapel, Joyce T. - BSN3-E)Dokument4 SeitenCATARACT Case Senario No.1 (Tapel, Joyce T. - BSN3-E)SIJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye BulletsDokument3 SeitenEye BulletsDonaJeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical ProceduresDokument20 SeitenSurgical ProceduresfheisanzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Evaluation: Techniques IncludeDokument4 SeitenDiagnostic Evaluation: Techniques IncludeDelvimalakianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye and Ear Disorders CompiledDokument93 SeitenEye and Ear Disorders CompiledJonamae Flor DagumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizDokument22 SeitenGlaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizGabrielle G. MaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 DamageEye2017Dokument6 Seiten05 DamageEye2017sudhirksingh27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Meq Ss OncoDokument10 SeitenFinal Meq Ss OncoRoadtogot 2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Katarak 2Dokument6 SeitenKatarak 2Indra Jati LaksanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DDokument7 SeitenCataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DKismet SummonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CataractDokument15 SeitenCataractNiningRahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract Information For Patients PDFDokument4 SeitenCataract Information For Patients PDFMohammad Abdullah BawtagNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPhtoDokument9 SeitenOPhtoEkoy TheRealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes/Risk Factors: ModifiableDokument5 SeitenCauses/Risk Factors: ModifiableDelvimalakianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 17 NCS POST TEST Group 2Dokument3 SeitenWEEK 17 NCS POST TEST Group 2Karenkaren BescaserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Although Some Vision As Been Lost and Cannot Be Restored, Further Loss May Be Prevented by Adhering To The Treatment Plan.Dokument8 SeitenAlthough Some Vision As Been Lost and Cannot Be Restored, Further Loss May Be Prevented by Adhering To The Treatment Plan.Juma Sammy100% (1)
- Diabetic Eye DiseaseDokument3 SeitenDiabetic Eye DiseaseRabiu Hassan MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MX of Patients With Senile CataractDokument6 SeitenMX of Patients With Senile CataractzusehenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glucoma Cyclodiode LaserDokument2 SeitenGlucoma Cyclodiode LaserMido KimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs and Symptoms of GlaucomaDokument15 SeitenSigns and Symptoms of Glaucomayangi dokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report of Diethyl Carbamazine Induced Anterior Uveitis With Raised Intraocular Pressure in Known Case of Lymphatic FilariasisDokument4 SeitenCase Report of Diethyl Carbamazine Induced Anterior Uveitis With Raised Intraocular Pressure in Known Case of Lymphatic FilariasisIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicDokument18 SeitenNCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicSIJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of The EYESDokument64 SeitenAssessment of The EYESAlliah Marie CababarosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ini Cet 22ND July 2021Dokument8 SeitenIni Cet 22ND July 2021gksah711Noch keine Bewertungen
- Michael Chuka OkosaDokument5 SeitenMichael Chuka OkosaKaisun TeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract Discharge PlanDokument2 SeitenCataract Discharge PlanLeah GordoncilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataract CasestudyDokument3 SeitenCataract CasestudyJamal AgontongNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP Factsheet - Steroids and The EyeDokument6 SeitenGP Factsheet - Steroids and The EyeBima RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set CDokument25 SeitenSet CImraan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)Dokument13 SeitenImmunization Schedule in India 2017 (Latest !!)rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201 Lecture 32010 Dissociative DisordersstudentDokument18 Seiten201 Lecture 32010 Dissociative DisordersstudentCatherine Omondang PascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Female Genitalia, Anus, and RectumDokument27 SeitenAssessing Female Genitalia, Anus, and RectumCrestyl Faye R. CagatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Session Adult I-1 3Dokument34 SeitenClinical Session Adult I-1 3Juan LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outcome BarthelDokument5 SeitenOutcome BarthelEncep Ivan SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Blood BankingDokument4 SeitenHistory of Blood BankingShaira AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submental Abscess After Deoxycholic Acid Injection: ReferenceDokument1 SeiteSubmental Abscess After Deoxycholic Acid Injection: Referencechash75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Davars LOM Vol 2Dokument163 SeitenDavars LOM Vol 2Sridhar SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrochureDokument2 SeitenBrochureZubair ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin ConditionsDokument11 SeitenSkin ConditionsElza ShainidzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankle SprainDokument3 SeitenAnkle SpraindrakbarbabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Monitoring RecordDokument4 SeitenLabor Monitoring RecordFrancis PeterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sage Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology - I36172Dokument5 SeitenThe Sage Encyclopedia of Abnormal and Clinical Psychology - I36172Rol AnimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Evaluation Report For Trilogy Evo Ventilator: Prepared For: Respironics, IncDokument79 SeitenClinical Evaluation Report For Trilogy Evo Ventilator: Prepared For: Respironics, Incdaphnestc0211Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pengaruh Inisiasi Menyusu Dini Terhadap Jumlah Perdarahan Pasca PersalinanDokument10 SeitenPengaruh Inisiasi Menyusu Dini Terhadap Jumlah Perdarahan Pasca Persalinanstasebolen asikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 20Dokument2 SeitenSession 20Bernadeth Barrientos ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief Intervention: Mhgap-Ig Base Course - Field Test Version 1.00 - May 2012 1Dokument16 SeitenBrief Intervention: Mhgap-Ig Base Course - Field Test Version 1.00 - May 2012 1TEOFILO PALSIMON JR.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piles Treatment-Simple Safe Sure Painless Cure-Just 30 Minutes Kshar Sutra Therapy & Go Home.Dokument51 SeitenPiles Treatment-Simple Safe Sure Painless Cure-Just 30 Minutes Kshar Sutra Therapy & Go Home.FISTULA IN ANO-SIMPLE SAFE SURE PAINLESS CURE100% (2)
- Vaginal MicrobiomeDokument9 SeitenVaginal MicrobiomeRika Yulizah GobelNoch keine Bewertungen
- TH Participant-Guide WebDokument5 SeitenTH Participant-Guide WebYarden ShneyourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleDokument12 SeitenIndian Perspective For Probiotics: A Review: ArticleMurali DathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConsultsDokument16 SeitenConsultsRaq KhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NormaltestreportDokument3 SeitenNormaltestreportcslpc01Noch keine Bewertungen
- HTTPSWWW - whc.SgDocumentsWH Allied20Health and Pharmacy PDFDokument5 SeitenHTTPSWWW - whc.SgDocumentsWH Allied20Health and Pharmacy PDFAndrew LimNoch keine Bewertungen