Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Hochgeladen von
Adithya ShourieCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Hochgeladen von
Adithya ShourieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
Helping you piece IT together
Computer Viruses
Threats & Solutions
2005 BH Consulting
Page 1 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
Copyright Notice
2005 BH Consulting IT Ltd. trading as BH Consulting, All rights reserved.
This whitepaper is protected by copyright. Any reproduction of material of this whitepaper
must be requested and authorised in writing from BH Consulting. Authorised reproduction
of material must include all copyright and proprietary notices in the same form and manner
as the original, and must not be modified in any way. Acknowledgement of the source of
the material must also be included in all references. BH Consulting reserves the right to
revoke such authorisation at any time, and any such use must be discontinued immediately
upon notice from BH Consulting.
Disclaimer:
BH Consulting has made every reasonable effort to ensure that information contained within
this document is accurate. However no representation or warranty, expressed or implied, is
given by BH Consulting as to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this
document or any information supplied. Recommendations outlined in this document are
based on accepted industry best practises.
The information contained in this document has been provided by BH Consulting for
information purposes only. This information does not constitute legal, professional or
commercial advice. While every care has been taken to ensure that the content is useful
and accurate BH Consulting gives no guarantees, undertakings or warranties in this regard,
and does not accept any legal liability or responsibility for the content or the accuracy of the
information so provided, or, for any loss or damage caused arising directly or indirectly in
connection with reliance on the use of such information. Any errors or omissions brought to
the attention of BH Consulting will be corrected as soon as possible.
Any views, opinions and guidance set out in this document are provided for information
purposes only, and do not purport to be legal and/or professional advice or a definitive
interpretation of any law. Anyone contemplating action in respect of matters set out in this
document should obtain advice from a suitably qualified professional adviser based on their
unique requirements.
The information in this document may contain technical inaccuracies and typographical
errors. The information in this document may be updated from time to time and may at
times be out of date. BH Consulting accepts no responsibility for keeping the information in
this document up to date or any liability whatsoever for any failure to do so.
BH Consulting are under no obligation to update this document or correct any inaccuracies
or omissions in it which may exist or become apparent.
2005 BH Consulting
Page 2 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
Table of Contents
1.
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions............................................................................. 4
2.
Contact Us ........................................................................................................................ 7
2005 BH Consulting
Page 3 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
1. Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Once the realm of IT Security Professionals, computer viruses are now becoming an issue
and concern for business people. Recent major computer virus outbreaks such as the
Sober, Mydoom and Sobig viruses have caused many hours of downtime for companies
throughout Ireland and the world. The resulting chaos meant many companies' computer
systems were offline until the infected systems were restored. Productivity was lost,
projects were delayed, important deadlines missed and management time diverted to deal
with frustrated customers and/or business partners.
Computer viruses are becoming more and more sophisticated and employ many different
methods of spreading. While email has been the primary method for the spread of these
recent computer viruses, it is not the only method. A computer virus can enter a network by
CD, floppy disk, Internet download, file transfer and file sharing programs, or by remote
users connecting directly to the corporate network with an infected PC. Once a computer
virus gets into a network it can spread from computer to computer in multiple ways.
Given the numerous ways a computer virus can spread, how can a company ensure that its
network is protected?
1. Install Anti-Virus Software.
Ensure that reputable anti-virus software is installed on all computers. This should
include all servers, PCs and laptops. If employees use computers at home for
business use or to remotely access the network, these PCs should also have antivirus software installed.
2. Ensure that the anti-virus software is up to date.
Everyday new computer viruses are being released and it is essential that business
is protected from these viruses by keeping the anti-virus software up to date. If
possible, companies should look at policies whereby computers that do not have
the most up to date anti-virus software installed are not allowed to connect to the
network.
3. Employ a firewall to protect networks.
As computer viruses can spread by means other than email, it is important that
unwanted traffic is blocked from entering the network by using a firewall. Sensitive
areas with a companys network should also be further segmented and protected
using additional firewalls.
For users that use computers for business away from the protection of the
company's network, such as home PCs or laptops, a personal firewall should be
installed to ensure the computer is protected.
4. Filter all email traffic.
All incoming and outgoing email should be filtered for computer viruses. This filter
should ideally be at the perimeter of the network to prevent computer viruses.
Emails with certain file attachments commonly used by computer viruses to spread
themselves, such as .EXE, .COM and .SCR files, should also be prevented from
entering the network.
5. Educate all users to be careful of suspicious e-mails.
Ensure that all users know to never open an email attachment they are not
expecting. Even when the email is from a known source, caution should be
exercised when opening attachments. Recent viruses have spread because they
appear to be from addresses familiar to the user.
2005 BH Consulting
Page 4 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
6. Scan Internet Downloads.
Ensure that all files downloaded from the Internet are scanned for computer viruses
before being used. Ideally this scanning should be done from one central point on
the network to ensure that all files are properly scanned.
7. Don't run programs of unknown origin.
It is important that a company establishes a trusted source for their software
requirements. This is to ensure that all software installed within the company can
be accounted for and that its sources can be confirmed to be legitimate. Apart from
ensuring that the correct licensing agreements are in place, using a trusted supplier
can help reduce the risk of software infected with a virus entering the companys
network. All users should be educated to never run a computer program unless the
source is known or has originated from a person or company that is trusted and has
been authorised by those responsible for managing the companys network.
8. Implement a vulnerability management program.
Most computer viruses and worms try to exploit bugs and vulnerabilities within the
operating system and applications that companies use. New vulnerabilities are
introduced into networks everyday, be that from installing new software and
services, making changes to existing systems or simply from previously
undiscovered vulnerabilities coming to light. It is important to regularly review your
network and the applications running on it for new vulnerabilities. In accordance
with your vulnerability management program, these vulnerabilities should be rated
and prioritised regarding their criticality and the potential business impact they could
have. Once this has been done, a plan on how to manage those vulnerabilities,
either by patching, upgrading, or managing the vulnerability using tools such as
firewalls or Intrusion Detection Systems should be put into place.
9. Make regular backups of critical data.
It is important to ensure that regular copies of important files are kept either on
removable media such as CD-ROM discs or tape to ensure a trusted source for
data in the event that the network is infected with a computer virus. Not only will
this ensure that important data is available in the event of a computer virus infecting
the companys network, backups will also enable the company to restore systems
to software that is known to be free from computer virus infection.
10. Develop an Information Security Policy.
The creation and publication of an Information Security Policy is key to ensuring
that information security receives the profile it requires in the organisation and is the
first critical step in securing the companys systems and data. It is important that
senior management support the Information Security Policy and that all users are
made aware of their roles and responsibilities under this policy.
11. Monitor logs and systems.
Regular monitoring of network and system logs can assist in the early identification
of a computer virus infecting the network. Unusual traffic patterns or log entries
could indicate that the network has been infected. As well as monitoring for
suspicious traffic and events, it is important that logs for other devices are checked
regularly to ensure that the network remains protected. Log files for the backups
should be checked regularly to ensure that the backups succeeded, likewise the log
files for anti-virus software deployed should be regularly checked to ensure that all
PCs are running the latest version of the anti-virus software.
2005 BH Consulting
Page 5 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
12. Develop an Incident Response Plan.
Knowing what to do when a computer virus enters the network is critical to minimise
the damage the virus may cause and to prevent it spreading further internally or
externally to customers and suppliers. The incident response plan should outline
the roles and responsibilities that people have in the event of a computer virus
infecting the network. This plan should be drawn up and agreed between all
relevant parties before an incident occurs. Remember, the worst time to develop a
security incident response plan is in the middle of such an incident.
13. Restrict end user access to systems
Where possible, end users should not be given administrative privileges to their
workstations. Most computer viruses can only run in the context of the user that is
logged into the system, i.e. they only have the same permissions as the user
running the program. If that user has their access restricted, then the virus will be
similarly restricted. Unfortunately many applications designed for the Windows
platform require the end user to have such privileges; however these users should
be the exception rather than the rule.
Computer viruses pose a very real and constant threat to every business. It is important that
businesses recognise this threat and take the appropriate steps, such as the above, to
reduce the likelihood and minimise the impact of being infected with a computer virus.
2005 BH Consulting
Page 6 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Computer Virus Threats and Solutions
Version 1.0
2. Contact Us
Helping you piece IT together
If you wish to contact us or provide any feedback on this whitepaper
you may do so using the following contact details.
Telephone :
Website :
:
2005 BH Consulting
+353-(0)1-4404065
http://www.bhconsulting.ie
info@bhconsulting.ie
Page 7 of 7
BH Consulting
18/05/2006
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PC Computer Security & Backup Guide: How to Secure & Backup Your PC with Antivirus & Malware SoftwareVon EverandPC Computer Security & Backup Guide: How to Secure & Backup Your PC with Antivirus & Malware SoftwareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: The Untold Origins of Cloud Computing (Manipulation, Configuring and Accessing the Applications Online)Von EverandCloud Computing: The Untold Origins of Cloud Computing (Manipulation, Configuring and Accessing the Applications Online)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Virus PolicyDokument4 SeitenAnti-Virus PolicyCaratekar TekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Guide: Quick Heal Antivirus 2010Dokument78 SeitenUser Guide: Quick Heal Antivirus 2010UDAY PRATAPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Lab ManualDokument3 SeitenStudent Lab ManualRafat BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing of Antivirus SoftwaresDokument17 SeitenMarketing of Antivirus SoftwaresBiswajit DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Major Crackdown Security Pros: When Antivirus Is A VirusDokument7 SeitenA Major Crackdown Security Pros: When Antivirus Is A VirusJaydenIanCarlBautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Basic and ITDokument9 SeitenSecurity Basic and ITNextLevel AkhyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Assurance AwarenessDokument4 SeitenInformation Assurance AwarenessJosé NatalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Virus Protection PolicyDokument3 SeitenAnti Virus Protection PolicyOmar AyoubNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO27k Model Security Policy On Malware PDFDokument5 SeitenISO27k Model Security Policy On Malware PDFeleazar_lostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stand and Deliver Your Money or Your Bytes: Ransomware Prevention GuidelinesDokument21 SeitenStand and Deliver Your Money or Your Bytes: Ransomware Prevention Guidelinesmadhav_maroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO27k Model Security Policy On MalwareDokument5 SeitenISO27k Model Security Policy On MalwareTahir100% (2)
- INSTRUCTION. Answer ALL Questions. (Total: 30 Marks)Dokument6 SeitenINSTRUCTION. Answer ALL Questions. (Total: 30 Marks)Dipu RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protect Your Business From Cyber Threats - Business - Gov.auDokument6 SeitenProtect Your Business From Cyber Threats - Business - Gov.augregoryhageNoch keine Bewertungen
- 65 4877 63283 40237296 11182022173909Dokument2 Seiten65 4877 63283 40237296 11182022173909fouad khouryNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Best Cyber Security Tips For Remote WorkersDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Best Cyber Security Tips For Remote Workersaariya goelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 AssignmentDokument5 SeitenModule 4 Assignmentapi-360051483Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument3 SeitenLab 6Anh DucNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT FP2250 KellyTravis Assessment6 1Dokument6 SeitenIT FP2250 KellyTravis Assessment6 1Anas ToufeeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security ProceduresDokument2 SeitenSecurity ProceduresАнна-Алина МикитюкNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cybersecurity Essentials Chapter 7Dokument13 SeitenCybersecurity Essentials Chapter 7Samuel AmureNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Programming Software? If You Were A Software Developer, What Kind of Software Would You Develop? ExplainDokument3 SeitenWhat Is A Programming Software? If You Were A Software Developer, What Kind of Software Would You Develop? ExplainKripesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Top Cyber Security Best Practices To Prevent A BreachDokument3 Seiten11 Top Cyber Security Best Practices To Prevent A BreachArmena BegradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1: Install Quality Antivirus: Download The PDF VersionDokument5 Seiten1: Install Quality Antivirus: Download The PDF VersionbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virus Protection Policy: Ymddiriedolaeth Gig Ceredigion A Chanolbarth Cymru Ceredigion and Mid Wales Nhs TrustDokument3 SeitenVirus Protection Policy: Ymddiriedolaeth Gig Ceredigion A Chanolbarth Cymru Ceredigion and Mid Wales Nhs TrustedwinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis - Computer-Security-Audit PDFDokument34 SeitenThesis - Computer-Security-Audit PDFLoverianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endpoint Security Best PracticesDokument8 SeitenEndpoint Security Best PracticesoliieNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR 1Dokument9 SeitenPR 1talrejaanish2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber Law and EthicsDokument50 SeitenCyber Law and EthicsVanshita PathareNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO27k Model Security Policy On MalwareDokument3 SeitenISO27k Model Security Policy On Malwarepenumudi233Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Secure ComputingDokument5 Seiten1.1 Secure ComputingHemanth N PoojariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Mobile Device Security PolicyDokument3 SeitenExample Mobile Device Security PolicyOmar AyoubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Virus PolicyDokument12 SeitenAnti Virus PolicyVic LogicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cybersecurity FCC's Cybersecurity Tips For Small Businesses Criterion 4.1Dokument1 SeiteCybersecurity FCC's Cybersecurity Tips For Small Businesses Criterion 4.1Juan JuárezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Computer Security in Organizations TodayDokument4 SeitenImportance of Computer Security in Organizations TodayDon Ozone Oscar Oluoch100% (2)
- Unit 1Dokument265 SeitenUnit 1arundhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Does Information AssuranceDokument11 SeitenWhat Does Information AssuranceDagim Fekadu AmenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntivirusDokument10 SeitenAntivirusGaurav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Virtualization A Black Hole in Your Security?: 5 Ways To Ensure It Isn'tDokument6 SeitenIs Virtualization A Black Hole in Your Security?: 5 Ways To Ensure It Isn'tsairvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.-Revised-Tle-As-Css-10-Q3-Installing AntivirusDokument4 Seiten5.-Revised-Tle-As-Css-10-Q3-Installing AntivirusJonald SalinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginners Guide To Firewalls 2012Dokument6 SeitenBeginners Guide To Firewalls 2012CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Crypto Locker WarningDokument29 SeitenNew Crypto Locker WarningAdin HujicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis AntivirusDokument8 SeitenThesis Antivirusfjebwgr4100% (2)
- ManualDokument74 SeitenManualprasenshyamaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pecha KuchaDokument3 SeitenPecha KuchaYuda BacasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Security: Ict - Css Third Quarter - Week 9 - Module 9Dokument12 SeitenNetwork Security: Ict - Css Third Quarter - Week 9 - Module 9Kaylene VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber SecurityDokument19 SeitenCyber SecurityRymar DabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spyware Term PaperDokument6 SeitenSpyware Term Paperfat1kifywel3100% (2)
- CIS 12 Computer Protection DOJDokument4 SeitenCIS 12 Computer Protection DOJAjay_mane22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Seurity EssentialDokument4 SeitenMicrosoft Seurity EssentialBilya LawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Security MeasuresDokument28 SeitenComputer Security Measuresrosemarie cabonegroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Exercise 1 & 2. Excercise 1Dokument4 SeitenAnswers To Exercise 1 & 2. Excercise 1Bree ElaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Security: Presented By: Luke SpeedDokument30 SeitenComputer Security: Presented By: Luke SpeedKevin SahalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Securiyt Ass 2 FinzlDokument90 SeitenIt Securiyt Ass 2 FinzlBehailu DemissieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finding Security VulnerabilitiesDokument19 SeitenFinding Security Vulnerabilitiesshafici DajiyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dsci Advisory: Work From Home - Best PracticesDokument4 SeitenDsci Advisory: Work From Home - Best PracticesVicky PanditaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antivirus Programs Research PaperDokument6 SeitenAntivirus Programs Research Paperh04pn7zr100% (1)
- User Guide: Quick Heal Technologies (P) LTDDokument119 SeitenUser Guide: Quick Heal Technologies (P) LTDips_pawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admin Consol 2008Dokument7 SeitenAdmin Consol 2008rushibmr19785604Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intake StructuresDokument14 SeitenIntake Structuresnimm1962100% (1)
- Plate 1 Analysis of Test Data For 28 Days Compressive Strength For The Month of April 2020 Meeting Acceptance CriteriaDokument4 SeitenPlate 1 Analysis of Test Data For 28 Days Compressive Strength For The Month of April 2020 Meeting Acceptance CriteriaAdithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of SWM Empanelled Agencies - 0Dokument6 SeitenList of SWM Empanelled Agencies - 0Adithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- EOI For Empanelment of Agencies For Preparation of Detail Project Report (DPR) Under HRIDAY SchemeDokument28 SeitenEOI For Empanelment of Agencies For Preparation of Detail Project Report (DPR) Under HRIDAY SchemeAdithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
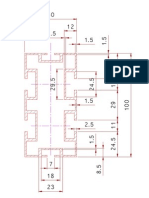
- Detailed Estimate of CC RoadDokument5 SeitenDetailed Estimate of CC RoadAdithya Shourie72% (25)
- DerivativesDokument20 SeitenDerivativesPerry LawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Complete Guide To Windows 8Dokument52 SeitenThe Complete Guide To Windows 8Robert SillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notification No 25 - 40 Service TaxDokument70 SeitenNotification No 25 - 40 Service TaxAdithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
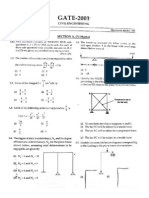
- Gate Ce 2007Dokument9 SeitenGate Ce 2007Adithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate 2001Dokument10 SeitenGate 2001tonykalladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Analysis: Doron LevyDokument112 SeitenNumerical Analysis: Doron LevyEhtisham Ul Haq Arshad100% (1)
- Getting Started STAAD 2005 PDFDokument570 SeitenGetting Started STAAD 2005 PDFbryan94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Analysis 1011Dokument129 SeitenPlastic Analysis 1011F Azam Khan Ayon100% (1)
- Mock Test - 1Dokument3 SeitenMock Test - 1kishangopi123Noch keine Bewertungen
- IS800 2007 Channel 1Dokument3 SeitenIS800 2007 Channel 1Adithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension Members: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDokument20 SeitenTension Members: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurAnonymous ptLRLiNNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of MN, P, S, SiDokument2 SeitenEffects of MN, P, S, SiAdithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP6-Steel Hand BookDokument209 SeitenSP6-Steel Hand BookAmit87% (15)
- Nokia Lumia 620 ManualDokument107 SeitenNokia Lumia 620 Manual303richycNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution AIEEE Mock Solved-1: N R R R NDokument3 SeitenSolution AIEEE Mock Solved-1: N R R R NAdithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citybus Info For HydDokument34 SeitenCitybus Info For Hydhow2knowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Purlin Model - pdf2Dokument1 SeiteAluminium Purlin Model - pdf2Adithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9013Dokument14 Seiten9013Sujoy RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture NumericalMethodsForODEDokument6 SeitenLecture NumericalMethodsForODEgtgreatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed End MomentsDokument1 SeiteFixed End MomentsHarold DeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TolerancesDokument2 SeitenTolerancesAdithya ShourieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barron's - GRE, 17th Edition, 2008Dokument537 SeitenBarron's - GRE, 17th Edition, 2008Vandana SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS: 8147 - Code of Practice For Use of Aluminium Alloys in StructuresDokument170 SeitenIS: 8147 - Code of Practice For Use of Aluminium Alloys in StructuresbccharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GUI Design in MIDP: Fenil Gandhi ROLL NO. 105 MBA Tech - I.TDokument37 SeitenGUI Design in MIDP: Fenil Gandhi ROLL NO. 105 MBA Tech - I.TFenilGandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems Question Bank and SolutionDokument32 SeitenOperating Systems Question Bank and SolutionMahesh S Gour50% (2)
- Plasma Donation System: A Project OnDokument29 SeitenPlasma Donation System: A Project OnArshiya Mobile ShopeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Linked ListDokument25 SeitenCircular Linked ListSarwat ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation Anywhere Certified Advanced RPA Professional (V11) - Advanced-RPA-Professional Exam Practice TestDokument4 SeitenAutomation Anywhere Certified Advanced RPA Professional (V11) - Advanced-RPA-Professional Exam Practice TestRanger rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12 SYAD-Implementation TestingDokument34 SeitenWeek 12 SYAD-Implementation TestingJonathan LawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy, Saves Time: Dataview Ii DisplayDokument2 SeitenEasy, Saves Time: Dataview Ii DisplayOscar Arturo Callirgos LozadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBMSDokument9 SeitenDBMSMohit SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Database and Web Database SystemsDokument49 SeitenDatabase and Web Database SystemsAiyas AboobakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Management SystemDokument31 SeitenStudent Management SystemSudhakar Reddy100% (2)
- Monitoring and Alerting For Azure Key VaultDokument5 SeitenMonitoring and Alerting For Azure Key VaultPoojith JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resigned Staff and Data BackupDokument18 SeitenResigned Staff and Data BackupBryan ChooiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solving: Chapter 2-Visual Basic Schneider 1Dokument18 SeitenProblem Solving: Chapter 2-Visual Basic Schneider 1dnlkabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AngleDokument6 SeitenAnglesreekanth kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument4 SeitenMultiple Choice Questionstimothyosaigbovo3466Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Databases and Database Users: Answers To Selected ExercisesDokument90 SeitenChapter 1: Databases and Database Users: Answers To Selected ExercisesPhúc HuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Software NotesDokument12 SeitenComputer Software NotesSimon Chege89% (9)
- Red Hat Process Automation Manager: Automate Business DecisionsDokument3 SeitenRed Hat Process Automation Manager: Automate Business DecisionsBaatar SukhbaatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gnu PemDokument2 SeitenGnu PemmontecchyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 1 - IntroductionDokument53 SeitenData Mining: Concepts and Techniques: - Chapter 1 - IntroductionXhy KatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Recovery PlanDokument11 SeitenData Recovery PlanCream FamilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument14 SeitenCloud ComputingLovedeep ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP B1 CCC Solution: Technical DatasheetDokument2 SeitenSAP B1 CCC Solution: Technical DatasheetWilliams CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Audit For Organizational Resilience: Balancing Assurance - Advisory-AnticipateDokument70 SeitenInternal Audit For Organizational Resilience: Balancing Assurance - Advisory-Anticipatemikael abubakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Data For CP - BD - Direct - Input - Plan PDFDokument6 SeitenTest Data For CP - BD - Direct - Input - Plan PDFgtipturnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Middleware TechnologiesDokument17 SeitenMiddleware TechnologiesArunachalam SelvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wowcoin LaunchDokument18 SeitenWowcoin LaunchVpsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.3.7 Lab - Use RESTCONF To Access An IOS XE DeviceDokument14 Seiten8.3.7 Lab - Use RESTCONF To Access An IOS XE DeviceWilly DinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Domanin Command GuideDokument448 SeitenData Domanin Command GuideGreivin ArguedasNoch keine Bewertungen
- rc218 CDW Jenkins Workflow PDFDokument8 Seitenrc218 CDW Jenkins Workflow PDFVictor SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen