Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mathematics Class 12 Syllabus For Session 2016-2017: Unit I: Relations and Functions
Hochgeladen von
mrrakeshkumar8100 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
8 Ansichten3 SeitenMathematics Class 12 syllabus for session 2016-2017. Unit I: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS (Periods 10) types of relations: Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto,functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations. Unit two: algebra. Unit three: Three-dimensional Geometry. Unit four: Differential Equations. Unit five: algebra, calculus. Unit six: trigonometry.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Mathematics Class 12 Syllabus for Session 2015
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMathematics Class 12 syllabus for session 2016-2017. Unit I: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS (Periods 10) types of relations: Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto,functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations. Unit two: algebra. Unit three: Three-dimensional Geometry. Unit four: Differential Equations. Unit five: algebra, calculus. Unit six: trigonometry.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
8 Ansichten3 SeitenMathematics Class 12 Syllabus For Session 2016-2017: Unit I: Relations and Functions
Hochgeladen von
mrrakeshkumar810Mathematics Class 12 syllabus for session 2016-2017. Unit I: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS (Periods 10) types of relations: Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto,functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations. Unit two: algebra. Unit three: Three-dimensional Geometry. Unit four: Differential Equations. Unit five: algebra, calculus. Unit six: trigonometry.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Mathematics Class 12 syllabus for session 2016-2017
UNIT I: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
1. Relations and Functions (Periods 10)
Types of relations: Reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and
onto ,functions, composite functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations
2. Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Periods 12)
Definition, range, domain, principal value branches. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions.
Elementary properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
1. Matrices (Periods 18)
Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero matrix, transpose of a matrix,
symmetric..
2. Determinants (Periods 20)
Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 3 matrices), properties of determinants, minors,
..
UNIT III: CALCULUS
1. Continuity and Differentiability (Periods 18)
Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of 2.
..
Applications of Derivatives (Periods 10)
Applications of derivatives: Rate of change, increasing/decreasing functions, tangents and
normals,)
3. Integrals (Periods 20)
Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by
substitution
4. Applications of the Integrals (Periods 10)
Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, arcs of
circles/parabolas/ellipses.
5. Differential Equations (Periods 10)
Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation.
Formation of
UNIT IV: VECTORS AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY
1. Vectors (Periods 10)
Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines/ratios of vectors.
Types.
2. Three-dimensional Geometry (Periods 12)
Direction cosines/ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian and vector equation of a line,
Unit V: Linear Programming (Periods 12)
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, different
types.
Unit VI: Probability (Periods 18)
Multiplications theorem on probability. Conditional probability, independent events, total
Detail analysis of Mathematics Course Structure
Analysing of course structure is very important for any student to do better in the exam . Good
analysis can increase the marks of student . Here is presenting the course outline of Mathematics
syllabus.
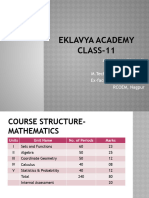
Course structure marks wise
Topics
Linear Programming
Marks
06
Relations and Functions
10
Probabiity
10
Algebra
13
Vectors and 3D geometry
17
Calculus
44
Course structure period wise
Topics
Periods
Linear Programming
Relations and Functions
12
22
Probabiity
18
Algebra
38
Vectors and 3D geometry
22
Calculus
68
Total Periods
180
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Class Xii: Unit I. Relations and FunctionsDokument3 SeitenClass Xii: Unit I. Relations and Functionsficky_iitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Cbse Maths Syllabus 2010-11Dokument3 SeitenClass 12 Cbse Maths Syllabus 2010-11Sunaina RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Mathematics 1Dokument3 Seiten2 Mathematics 1pathir KroNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Paper Time: 3 Hrs. Max Marks. 100 Units No. of Periods MarksDokument5 SeitenOne Paper Time: 3 Hrs. Max Marks. 100 Units No. of Periods MarksBharatPrajapatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum & Syllabus for Math Classes XI & XIIDokument6 SeitenCurriculum & Syllabus for Math Classes XI & XIIShivamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics SR - Sec 2020-21Dokument14 SeitenMathematics SR - Sec 2020-21Vandana GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi-Xii: Mathematics (C No. 041)Dokument6 SeitenXi-Xii: Mathematics (C No. 041)Bhatnagar Suraj MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 MathematicsDokument11 Seiten6 Mathematicsapi-352990570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 MathematicsDokument10 SeitenClass 12 Mathematicsanand maheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Xii: Unit I. Relations and FunctionsDokument4 SeitenClass Xii: Unit I. Relations and Functionsapi-243565143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class-Xii (2018-19) : One Paper Time: 3 Hrs. Max Marks. 100Dokument8 SeitenClass-Xii (2018-19) : One Paper Time: 3 Hrs. Max Marks. 100RishabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Mathematics 2022-23Dokument9 SeitenClass 11 Mathematics 2022-23Kapil ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument7 SeitenMathSudha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Maths Ro Jaipur FinalDokument140 SeitenXi Maths Ro Jaipur FinalHARSH VARDHAN 38 10C100% (1)
- Class XI Math Course Structure and Exam PatternDokument5 SeitenClass XI Math Course Structure and Exam Patternjaya prasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Syllabus For Class 10 MathsDokument4 SeitenNCERT Syllabus For Class 10 MathsPrash S100% (1)
- CBSE Grade XII Maths Supplementary Material 2017-18Dokument203 SeitenCBSE Grade XII Maths Supplementary Material 2017-18vyom911100% (1)
- Math Syllabus for Classes 9-10Dokument7 SeitenMath Syllabus for Classes 9-10Lyngdoh DamelamanbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths SrSec 2023-24Dokument3 SeitenMaths SrSec 2023-24ADITI CHOUHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Standard: Reduced SyllabusDokument5 SeitenMathematics Standard: Reduced SyllabusOP GAMERZ100% (2)
- SM 12 Math Eng 201617Dokument192 SeitenSM 12 Math Eng 201617Bhavesh DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus30 Class 10thengDokument20 SeitenSyllabus30 Class 10thengSANTHOSH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class: 12 Subject: Mathematics: Almost 30% Reduced SyllabusDokument36 SeitenClass: 12 Subject: Mathematics: Almost 30% Reduced SyllabusDeepam MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12Dokument5 SeitenClass 12Aryan GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC D0 M OPSyk UEB5 LTO6 EuDokument6 SeitenPC D0 M OPSyk UEB5 LTO6 EuAtul Vikash Kumar AnshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Second YearDokument3 SeitenMathematics Second YearSwapan DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOLDEN CBSE Board Sample Paper 2020-2021 Mathematics-XDokument92 SeitenGOLDEN CBSE Board Sample Paper 2020-2021 Mathematics-XAnnesha MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksDokument6 SeitenCourse Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksGfl• TaneeshTM100% (1)
- Mathematics General: Part-IDokument3 SeitenMathematics General: Part-IZA INNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phpu FD 5 EZDokument9 SeitenPhpu FD 5 EZSiddhi NagvekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Maths Good NotesDokument208 Seiten12 Maths Good NotesMohammad ShoebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure Class - X: 1. Real NumberDokument5 SeitenCourse Structure Class - X: 1. Real NumbersasyedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Class 12Dokument10 SeitenMathematics: Class 12SURYA KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 MathsDokument166 SeitenClass 10 MathsDeepankar Singh100% (2)
- Mathematics 11 2021-22 Term 1 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenMathematics 11 2021-22 Term 1 SyllabusBetaBeast12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths SyllabusDokument5 SeitenMaths SyllabusSRISTI GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics (Xi-Xii) (Code No. 041) Session - 2022-23Dokument11 SeitenMathematics (Xi-Xii) (Code No. 041) Session - 2022-23Ja SioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths CBSE 2022-23Dokument11 SeitenMaths CBSE 2022-23Vijay SNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus BreakdownDokument6 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus BreakdownShivani MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015-16 - Senior School MathematicsDokument11 Seiten2015-16 - Senior School MathematicsJyoti BholaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse 12th Class Maths SyllabusDokument7 SeitenCbse 12th Class Maths Syllabusaldrin9bNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument2 SeitenPhysicsRAUSHAN KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 MathematicsDokument9 SeitenClass 11 Mathematicsanand maheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics First Year SyllabusDokument3 SeitenMathematics First Year SyllabusAnuskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Download CBSE Class 11 Maths Syllabus 2022-23Dokument9 SeitenDownload CBSE Class 11 Maths Syllabus 2022-23cakravartin servicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 2011 Syllabus MathematicsDokument4 Seiten11 2011 Syllabus MathematicscerlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus Mathematics 2020-21 PDFDokument6 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Syllabus Mathematics 2020-21 PDFParth GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Math Eng 2018Dokument231 Seiten11 Math Eng 2018Karuna SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2019 20 PDFDokument6 SeitenCbse Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2019 20 PDFwhat can we do?Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus & Exam PatternDokument7 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus & Exam PatternDibyasha DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksDokument5 SeitenCourse Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksTarun GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Syllabus 2024Dokument5 SeitenMathematics Syllabus 2024C1B-33-AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper CBSE CLASS 12th Mathematics Sample Paper 2012-13-10Dokument21 SeitenQuestion Paper CBSE CLASS 12th Mathematics Sample Paper 2012-13-10Vishu KukkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Matrices and Their Applications in Numerical Mathematics: Second EditionVon EverandSpecial Matrices and Their Applications in Numerical Mathematics: Second EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Vectors and Matrices for Geometric and 3D ModelingVon EverandVectors and Matrices for Geometric and 3D ModelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital SAT Math Prep For Dummies, 3rd Edition: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatVon EverandDigital SAT Math Prep For Dummies, 3rd Edition: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Higher Geometry: An Introduction to Advanced Methods in Analytic GeometryVon EverandHigher Geometry: An Introduction to Advanced Methods in Analytic GeometryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Time Mathematics: For aspirants of mathematical olympiads, NTSE, and students of all age groupsVon EverandQuiz Time Mathematics: For aspirants of mathematical olympiads, NTSE, and students of all age groupsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Active Maths 3 Leaving Cert Ordinary Level Old Strand 5 BookletDokument50 SeitenActive Maths 3 Leaving Cert Ordinary Level Old Strand 5 BookletmatholemewofNoch keine Bewertungen
- O 0, Find X.: 1st PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 2020-21Dokument4 SeitenO 0, Find X.: 1st PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 2020-21Kartikey PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential EquationsDokument1 SeiteDifferential EquationsConan EdogawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEAMS - Unit 3 Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic FormulaeDokument42 SeitenBEAMS - Unit 3 Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulaerea007988% (8)
- HW2Dokument3 SeitenHW2당근으로만든무말랭이Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 09Dokument114 SeitenCH 09ddubbah100% (2)
- AlgebraDokument9 SeitenAlgebraJunaid K JumaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.pharmacy - R09 - Regulations SyllabusDokument164 SeitenB.pharmacy - R09 - Regulations SyllabusManoj MallakuntlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Differential Equations 6th EditionDokument645 SeitenElementary Differential Equations 6th EditionRakesh Sarma67% (3)
- CMO 87, S. 2017 - PSG FOR BSCpE-final PDFDokument85 SeitenCMO 87, S. 2017 - PSG FOR BSCpE-final PDFRoman MarcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptation of The Carter-Tracy Water Influx Calculation: To Groundwater Flow SimulationDokument6 SeitenAdaptation of The Carter-Tracy Water Influx Calculation: To Groundwater Flow SimulationAndrés Eduardo Guzmán VelásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiffeqDokument126 SeitenDiffeqRaghavendra GondabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Pile Driving by FEMDokument11 SeitenDynamics of Pile Driving by FEMDiana Alice SugunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gridding in Reservoir SimulationDokument7 SeitenGridding in Reservoir SimulationOvaid MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Sheet For Students Entering in 12th Class PDFDokument8 SeitenAssessment Sheet For Students Entering in 12th Class PDFKushagra SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Extract - Maths Class 11 & 12Dokument301 SeitenNcert Extract - Maths Class 11 & 12Krittika AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim1Dokument3 Seiten2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim1focuscharade_8247490Noch keine Bewertungen
- NASA/Army Rotorcraft Technology: NI/SIDokument594 SeitenNASA/Army Rotorcraft Technology: NI/SI雷黎明Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.2Dokument6 SeitenNCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 4 – Quadratic Equations Exercise 4.2NINJA GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP-8 Week 4 Day 4Dokument7 SeitenDLP-8 Week 4 Day 4Francisco Rosellosa LoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2024Dokument5 SeitenMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2024sagarbnekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Linear and Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations Using Mixture of Elzaki Transform and The Projected Differential Transform MethodDokument10 SeitenSolution of Linear and Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations Using Mixture of Elzaki Transform and The Projected Differential Transform MethodAlexander DeckerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit RPR Ma201Dokument2 SeitenIit RPR Ma201atggregNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ'S GRADE 10 MATHEMATICSDokument7 SeitenMCQ'S GRADE 10 MATHEMATICSMuhammadTariqKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSP-Math 1 October 1, 2014Dokument3 SeitenSSP-Math 1 October 1, 2014MirnaKamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock C4 Paper Key ConceptsDokument4 SeitenMock C4 Paper Key ConceptsWojtek BażantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling Rockfall Protection Fences (Cantarelli Et Al.)Dokument6 SeitenModelling Rockfall Protection Fences (Cantarelli Et Al.)massimo.bochioloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gre Powerprep PDFDokument9 SeitenGre Powerprep PDFShahidul Islam SandwipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Build-Up in Wells: HornerDokument19 SeitenPressure Build-Up in Wells: HornerandriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histeresis EmtpDokument6 SeitenHisteresis EmtpJavo CoreNoch keine Bewertungen