Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
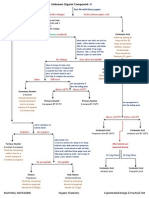
Table of The Simple Relationships Between The Basic Values Within An Electrolytic and Galvaic Cells in Respect To The Redox Half Equations
Hochgeladen von
Mark Riley0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten1 SeiteThis is handy because the knowledge that you should have from 1st semester redox chemistry should allow you to review the table and not have to much trouble at all thinking about why the values are on which side and correspond with other values below and above and why the values change for electyrolytic cells. And in senior chem where I made the table it helped me to first understand.
Originaltitel
Table of the simple relationships between the basic values within an electrolytic and galvaic cells in respect to the redox half equations
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis is handy because the knowledge that you should have from 1st semester redox chemistry should allow you to review the table and not have to much trouble at all thinking about why the values are on which side and correspond with other values below and above and why the values change for electyrolytic cells. And in senior chem where I made the table it helped me to first understand.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten1 SeiteTable of The Simple Relationships Between The Basic Values Within An Electrolytic and Galvaic Cells in Respect To The Redox Half Equations
Hochgeladen von
Mark RileyThis is handy because the knowledge that you should have from 1st semester redox chemistry should allow you to review the table and not have to much trouble at all thinking about why the values are on which side and correspond with other values below and above and why the values change for electyrolytic cells. And in senior chem where I made the table it helped me to first understand.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Annode Oxidation REDuction
Gain of oxygen CAThode
Loss of hydrogen Loss of oxygen
Loss of 𝒆 Gain of hydrogen
+𝑒 in products Gain of 𝒆
Oxidation +𝑒 in reactants
StrongestReductant Reduction
Anode StrongestOxident
Corrodes Faster Cathode
𝒆 →→
Voltaic Cell Spontaneous
Negative Electrode Positive Electrode
HASLower E0 HASHigest E0
E0 x-1
Solid forms (plating)
←← 𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝐼𝑜𝑛𝑠 (𝐶𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠) 𝐴+
𝐴−𝑁𝑒𝑔𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝐼𝑜𝑛𝑠 (𝐴𝑛𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠) →→
Zn s |Zn(NO3 )2 aq ||Cu(NO3 )2 aq |Cu(s)
Electrolytic Cells Non Spontaneous
Positive Electrode Negative
0
Highest E Electrode
E0 x-1 Lowest E0
Becomes basic 𝑝𝐻 ↑ GOES AS PREDICTED
Becomes acidic 𝑝𝐻 ↓
Solid forms on electrode
+
𝐴 𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝐼𝑜𝑛𝑠 (𝐶𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠) →→
←← 𝑁𝑒𝑔𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝐼𝑜𝑛𝑠 (𝐴𝑛𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠) 𝐴−
Cl=-1 Br=-1 H=+1 O=-2 Ag=+1
H2 O2 ∶ O = −1 CuH2 : H = −1
K Na Li Ba Ca Mg Al Zn Fe Ni Sn Pb H2 Cu Ag Hg
←strongest REDUCTANT weakest→
𝑤𝑜𝑛𝑡 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡 𝑤𝑖𝑡ℎ 𝑎𝑐𝑖𝑑 ← 𝐻2 → will react
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Optics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Dokument1 SeiteOptics Formula Sheet Study Sheet PhysicsA 2010Mark Riley100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Heat & Determining Enthalpy Change (Lab Assessment) Part I & Part 2Dokument8 SeitenHeat & Determining Enthalpy Change (Lab Assessment) Part I & Part 2Mark Riley81% (16)
- Fluids Dynamics Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenFluids Dynamics Formula SheetMark Riley88% (8)
- Small Changes - Errors Fixed - OutlineDokument1 SeiteSmall Changes - Errors Fixed - OutlineMark RileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 10 Op Amps Lab NotesDokument4 SeitenExp 10 Op Amps Lab NotesMark RileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab - Magnetic Field Strengths Practical Reports (REALLY BASIC)Dokument7 SeitenPhysics Lab - Magnetic Field Strengths Practical Reports (REALLY BASIC)Mark Riley100% (2)
- Physics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportDokument8 SeitenPhysics Lab Assessment 7 PARTA - The Conservation of Energy (Elastic Potential Energy) Practical ReportMark Riley67% (3)
- Dimensional Analysis: A Simple ExampleDokument10 SeitenDimensional Analysis: A Simple ExampleMark RileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - Relationships Between The Equations Linear and Angular Motion. Torque, Momentum, Angular Velocity EtcDokument2 SeitenPhysics - Relationships Between The Equations Linear and Angular Motion. Torque, Momentum, Angular Velocity EtcMark Riley100% (2)
- Senior Maths Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenSenior Maths Formula SheetMark Riley100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Dokument7 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Esters Lab & Lab Report (Making Scents of Esters)Mark Riley86% (14)
- Maths Assignment - With Roller Coaster QuestionDokument12 SeitenMaths Assignment - With Roller Coaster QuestionMark Riley100% (1)
- Missing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportDokument1 SeiteMissing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportMark RileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab8 Part I (Major Assessment) Design A Flow Chart To Determine An Unknown Organic Compound - (BEST FLOW CHART EVER)Dokument1 SeiteLab8 Part I (Major Assessment) Design A Flow Chart To Determine An Unknown Organic Compound - (BEST FLOW CHART EVER)Mark Riley50% (2)
- Common Reactions To Determine Unknown Organic CompoundsDokument1 SeiteCommon Reactions To Determine Unknown Organic CompoundsMark RileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab8 Part II (Major Assessment) Determine An Unknown Organic Substance. The ReportDokument10 SeitenLab8 Part II (Major Assessment) Determine An Unknown Organic Substance. The ReportMark RileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lab Assessment - Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenChemistry Lab Assessment - Oxidation & Reduction - Redox Reactions Lab ReportMark Riley100% (11)
- Chem - Redox Formula Sheet (Never Completely Finished), Electrolytic Cells, Voltaic Cells, Electric PotentialsDokument2 SeitenChem - Redox Formula Sheet (Never Completely Finished), Electrolytic Cells, Voltaic Cells, Electric PotentialsMark Riley100% (2)
- Quantum & Atomic Physics (Eg Photoelectric Affect) Formula Sheet & Study Tool Physics ADokument2 SeitenQuantum & Atomic Physics (Eg Photoelectric Affect) Formula Sheet & Study Tool Physics AMark Riley100% (2)