Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tube Welding 2
Hochgeladen von
Srinivasan RaviCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tube Welding 2
Hochgeladen von
Srinivasan RaviCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 1 of 8
E-mail This
To A Friend
Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Understanding the basic principles behind orbital tube welding may
help you arrive more rapidly at the optimum weld procedure for your
specific application.
Orbital welding was first used in the 1960's when the aerospace industry
recognized the need for a superior joining technique for aerospace hydraulic
lines. A mechanism was developed in which the arc from a tungsten electrode
was rotated around the tubing weld joint. The arc welding current was
regulated with a control system thus automating the entire process. The
result was a more precision and reliable method than the manual welding
method it replaced.
A typical orbital tube weld.
Orbital welding became practical for many industries in the early 1980's when N o t e t h e p u l s e d a r c f i n i s h
combination power supply/control systems were developed that operated
on the weld surface.
from 110 VAC and were physically small enough to be carried from place to
place on a construction site for multiple in-place welds. Modern day orbital welding systems offer
computer control where welding parameters for a variety of applications can be stored in memory and
called up when needed for a specific application. The skills of a certified welder are thus built into the
welding system, producing enormous numbers of identical welds and leaving significantly less room for
error or defects.
Orbital Welding Equipment
In the orbital welding process, tubes/pipes are clamped in place and an
orbital weldhead rotates an electrode and electric arc around the weld joint to
make the required weld. An orbital welding system consists of a power supply
and an orbital weldhead.
Power Supply: The power supply/control system supplies and controls the
welding parameters according to the specific weld program created or recalled
from memory. The power supply provides the control parameters, the arc
welding current, the power to drive the motor in the weld head and switches
the shield gas(es) on/off as necessary.
Weld Head: Orbital weld heads are normally of the enclosed type and provide
an inert atmosphere chamber that surrounds the weld joint. Standard
enclosed orbital weld heads are practical in welding tube sizes from 1/16 inch
(1.6mm) to 6 inches (152mm) with wall thickness' of up to .154 inches
(3.9mm) Larger diameters and wall thickness' can be accommodated with
open style weld heads.
Reasons for Using Orbital Welding Equipment
There are many reasons for using orbital welding equipment. The ability to
make high quality, consistent welds repeatedly at a speed close to the
maximum weld speed offer many benefits to the user:
l
Standard enclosed orbital
weld heads are practical
in welding tube sizes from
1/16 inch (1.6mm) to 6
inches (152mm) with wall
thickness' of up to .154
inches (3.9mm) Larger
diameters and wall
thickness' can be
accommodated with open
style weld head.
Productivity. An orbital welding system will drastically outperform manual
welders, many times paying for the cost of the orbital equipment in a
single job.
Quality. The quality of a weld created by an orbital welding system with
the correct weld program will be superior to that of manual welding. In
applications such as semiconductor or pharmaceutical tube welding, orbital welding is the only
means to reach the weld quality requirements.
Consistency. Once a weld program has been established an orbital welding system can repeatedly
perform the same weld hundreds of times, eliminating the normal variability, inconsistencies, errors
and defects of manual welding.
Skill level. Certified welders are increasingly hard to find. With orbital welding equipment you don't
need a certified welding operator. All it takes is a skilled mechanic with some weld training.
Orbital welding may be used in applications where a tube or pipe to be welded cannot be rotated or
where rotation of the part is not practical.
Orbital welding may be used in applications where access space restrictions limit the physical size of
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 2 of 8
the welding device. Weld heads may be used in rows of boiler tubing where it would be difficult for a
manual welder to use a welding torch or view the weld joint.
Many other reasons exist for the use of orbital equipment over manual welding. Examples are
applications where inspection of the internal weld is not practical for each weld created. By making a
sample weld coupon that passes certification, the logic holds that if the sample weld is acceptable,
that successive welds created by an automatic machine with the same input parameters should also
be sound.
Industries and Applications for Orbital Welding
Aerospace: As noted earlier, the aerospace industry was the first industry to recognize the requirement for
orbital welding. The high pressure systems of a single plane can have over 1,500 welded joints, all
automatically created with orbital equipment.
Boiler Tube: Boiler tube installation and repairs offer a perfect application for orbital welding. Compact
orbital weld heads can be clamped in place between rows of heat exchanger tubing where a manual
welder would experience severe difficulty making repeatable welds.
Food, Dairy and Beverage Industries: The food, dairy and beverage industries require consistent full
penetration welds on all weld joints. Most of these tubing/piping systems have schedules for cleaning
and sterilization in place. For maximum piping system efficiency the tubing must be as smooth as
possible. Any pit, crevice, crack or incomplete weld joint can form a place for the fluid inside the tubing to
be trapped and form a bacteria harbor.
Nuclear Piping: The nuclear industry with its severe operating environment and associated specifications
for high quality welds has long been an advocate of orbital welding.
Offshore Applications: Sub-sea hydraulic lines use materials whose properties can be altered during the
thermal changes that are normal with a weld cycle. Hydraulic joints welded with orbital equipment offer
superior corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Pharmaceutical process lines and piping systems deliver high quality water to
their processes. This requires high quality welds to ensure a source of water from the tubes that is
uncontaminated by bacteria, rust or other contaminant. Orbital welding ensures full penetration welds
with no overheating occurring that could undermine the corrosion resistance of the final weld zone.
Semiconductor Industry: The semiconductor industry requires piping systems with extremely smooth
internal surface finish in order to prevent contaminant buildup on the tubing walls or weld joints. Once
large enough, a build up of particulate, moisture or contaminant could release and ruin the batch
process.
Tube/Pipe Fittings, Valves and Regulators: Hydraulic lines, and liquid and gas delivery systems all require
tubing with connector fittings. Orbital systems provide a means to ensure high productivity of welding
and improved weld quality. Sometimes the tubing may be welded in place to a valve or regulator body.
Here the orbital weldhead provides the ability to produce high quality welds in applications with restricted
access to the weld joint.
General Guidelines for Orbital Tube Welding
For orbital welding in many precision or high purity applications, the base material to be welded, the tube
diameter(s), weld joint and part fit-up requirements, shield gas type and purity, arc length, and tungsten
electrode material, tip geometry and surface condition may already be written into a specification
covering the specific application.
Each orbital welding equipment supplier differs slightly in recommended welding practices and
procedures. Where possible, follow the recommendations of your orbital equipment supplier for
equipment set-up and use, especially in areas that pertain to warranty issues.
This section is intended as a guideline for those applications where no specification exists and the
engineer responsible for the welding must create the welding set-up, and derive the welding parameters
in order to arrive at the optimum welding solution.
Welding Basics and Set-Up
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 3 of 8
This weld profile shows a single level of weld time.
Orbital welding normally uses a minimum of 4
levels of weld time with each level decreasing in
weld amperage as the tube heats up during the
welding process.
The Physics of the GTAW Process
The orbital welding process uses the Gas Tungsten Arc Welding process (GTAW) as the source of the
electric arc that melts the base material and forms the weld. In the GTAW process (also referred to as
the Tungsten Inert Gas process - TIG) an electric arc is established between a Tungsten electrode and
the part to be welded. To start the arc, an RF or high voltage signal (usually 3.5 to 7 KV) is used to
break down (ionize) the insulating properties of the shield gas and make it electrically conductive in
order to pass through a tiny amount of current. A capacitor dumps current into this electrical path, which
reduces the arc voltage to a level where the power supply can then supply current for the arc. The power
supply responds to the demand and provides weld current to keep the arc established. The metal to be
welded is melted by the intense heat of the arc and fuses together.
Material Weldability
The material selected varies according to the application and environment the tubing must survive. The
mechanical, thermal, stability, and corrosion resistance requirements of the application will dictate the
material chosen. For complex applications a significant amount of testing will be necessary to ensure the
long term suitability of the chosen material from a functionality and cost viewpoint.
In general, the most commonly used 300 series stainless steels have a high degree of weldability with
the exception of 303/303SE which contain additives for ease of machining. 400 series stainless steels
are often weldable but may require post weld heat treatment.
Accommodation must be made for the potential differences of different material heats. The chemical
composition of each heat batch number will have minor differences in the concentration of alloying and
trace elements. These trace elements can vary the conductivity and melting characteristics slightly for
each heat. When a change in heat number is made a test coupon should be made for the new heat.
Minor changes in amperage may be required to return the weld to its original profile.
It is important that certain elements of the material be held to close tolerances. Minor deviations in
elements such as sulfur can vary the fluid flow in the weld pool thus completely changing the weld profile
and also causing arc wander.
Low Sulfur Content
(less than .01% - 100 PPM)
Surface tension temperature
coefficient negative
Normal Sulfur Content
(greater than .01% - 100 PPM)
Surface tension temperature
coefficient positive
Minor changes in sulfur content can change weld
pool flow characteristics with a dramatic effect on
penetration (the Maragoni effect)
Weld Joint Fit-Up
Weld joint fit-up is dependent on the weld specification requirements on tube straightness, weld
concavity, reinforcement and drop through. If no specification exists the laws of physics will require that
the molten material flow and compensate for tube mismatch and any gap in the weld joint.
Tubing is produced according to tolerances that are rigid or loose according to the application for which
the tube was purchased. It is important that the wall thickness is repeatable at the weld joint from part
to part. Differences in tube diameter or out-of-roundness will cause weld joint mismatch and arc gap
variations from one welding set up to another.
Tube and pipe end prep facing equipment is recommended in order to help ensure end squareness and
end flatness. Both the ID and OD should be burr free with no chamfer.
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 4 of 8
When two tubes are butted together for welding, two of the main considerations are mismatch and gaps.
In general, the following rules apply:
l
Any gap should be less than 5% of the wall thickness. It is possible to weld with gaps of up to 10%
(or greater) of wall thickness, but the resultant quality of weld will suffer greatly and repeatability
will also become a significant challenge.
Wall thickness variations at the weld zone should be +/- 5% of nominal wall thickness. Again, the
laws of physics will allow welding with mismatch of up to 25% of wall thickness if this is the only
challenge but again, the resultant quality of weld will suffer greatly and repeatability will also
become a significant issue.
Alignment mismatch (high-low) should be avoided by using engineering stands and clamps to align
the two tubes to be welded. This system also removes the mechanical requirement of aligning the
tubes from the orbital weldhead.
Shield Gas(es)
An inert gas is required on the tube OD and ID during welding to prevent the molten material from
combining with the oxygen in the ambient atmosphere. The objective of the welder should be to create a
weld which has zero tint at the weld zone ID.
Argon is the most commonly used shield gas (for the OD of the tube)and the purge gas (for the ID of
the tube). Helium is often used for welding on copper material. Mixed gases such as 98% Argon/2%
Hydrogen, 95% Argon/5% Hydrogen, 90% Argon/10% Hydrogen or 75% Helium/25% Argon my be used
when the wall thickness to be welded is heavy (.1" or above). Using mixtures of 95% Argon/5%
Hydrogen is incompatible with carbon steels and some exotic alloys, often causing hydrogen
embrittlement in the resultant weld. As a general rule, for simplicity and reduction of shield gas cost, use
100% argon gas.
Gas purity is dictated by the application. For high purity situations where the concern for microcontamination is paramount, such as semiconductor and pharmaceutical applications, the shield and
purge gases must minimize the heat tint that could otherwise be undesirable. In these applications,
ultra high purity gas or gas with a local purifier are employed. For non-critical applications, commercial
grade argon gas may be used.
Tungsten Electrode
The tungsten welding electrode, the source of the welding arc, is one of the most important elements of
the welding system that is most commonly ignored by welding systems users. While no one would refute
the importance of the ignition device on an automobile airbag, the rip cord for a parachute, or quality
tires for automobiles, the importance of tungsten electrode for quality welding is often overlooked. Users
continue to manually grind and wonder why they produce inconsistent results. Whether in manual or
automatic welding, this is the area where manufacturing organizations can improve the consistency of
their welding output with minor effort.
The objective for the choice of tungsten parameters is to balance the benefits of a clean arc start and
reduced arc wander with good weld penetration and a satisfactory electrode life.
Electrode Materials: For quite some time, tungsten manufacturers have added an oxide to pure tungsten
to improve the arc starting characteristics and the longevity of pure tungsten electrodes. In the orbital
welding industry, the most commonly used electrode materials are 2% thoriated tungsten and 2%
ceriated tungsten.
Safety: The safety issues of tungsten electrode material are now being looked at more closely. Many
users of the Tig welding process do not realize that the welding electrode they use contains Thorium, a
radioactive element added to the tungsten. While the radioactivity is of a low level, it brings an issue of
danger especially with the radioactive dust generated when grinding the electrodes to a point for welding.
Alternative, non-radioactive tungsten materials are now available, such as 2% ceriated electrodes, which
often offer superior arc welding. While these materials are commercially available they have been largely
ignored until recently.
Recommended Electrode Materials: Cerium, as a base material, has a lower work function than thorium,
thus it offers superior emission characteristics. Thus, not only do ceriated electrodes offer an advance in
electrode safety, they also improve the arc starting ability of the orbital equipment. However, as
mentioned earlier, it is always best to follow the advice of your orbital equipment manufacturer. 2%
ceriated and 2% thoriated electrodes are the most commonly recommended materials for orbital welding
equipment.
Electrode Tip Geometry: Given the ever increasing weld quality requirements of the final weld, more and
more companies are looking for ways to ensure that their weld quality is up to par. Consistency and
repeatability are key to welding applications. The shape and quality of the tungsten electrode tip is
finally being recognized as a vital process variable. Once a weld procedure has been established, it is
important that consistent electrode material, tip geometry and surface condition be used.
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 5 of 8
Welding Basics and Set-Up
To produce high consistent welds the Tungsten
electrode must provide the following:
1. H i g h q u a l i t y e l e c t r o d e m a t e r i a l
2. T h e e l e c t r o d e t i p d i m e n s i o n s s h o w n m u s t b e
held to close tolerances
3. T h e s u r f a c e f i n i s h ( g r o u n d o r p o l i s h e d ) o f t h e
electrode grind must be consistent.
Welders should follow an equipment supplier's suggested procedures and dimensions first, because they
have usually performed a significant amount of qualifying and troubleshooting work to optimize
electrode preparation for their equipment. However, where these specifications do not exist or the welder
or engineer would like to change those settings to possibly improve and optimize their welding, the
following guidelines apply:
A. Electrode Taper - This is usually called out in degrees of included angle (usually anywhere between
14 and 60). Below is a summary chart that illustrates how different tapers offer different arc
shapes and features:
Sharper Electrodes
Blunter Electrodes
Easy arc starting
Usually harder to start the arc
Handle less amperage
Handle more amperage
Wider arc shape
Narrower arc shape
Good arc stability
Potential for more arc wander
Less weld penetration
Better weld penetration
Shorter electrode life
Longer electrode life
In addition, to demonstrate graphically how the taper selection will effect the size of the weld bead
and the amount of penetration, below is a drawing that shows typical representations of the arc
shape and resultant weld profile for different tapers.
B. Electrode Tip Diameter - Grinding an electrode to a point is sometimes desirable for certain
applications, especially where arc starting is difficult or short duration welds on small parts are
performed. However in most cases it is best for a welder to leave a flat spot or tip diameter at the
end of electrode. This reduces erosion at the thin part of a point and reduces the concern that the
tip may fall into the weld. Larger and smaller tip diameters offer the following trade-offs:
Smaller Tip
Larger Tip
Easier arc starting
Usually harder to start the arc
Potential for more arc wander
Good arc stability
Less weld penetration
More weld penetration
Shorter electrode life
More electrode life
Tungsten Electrode Grinders and Pre-Ground Electrodes: Using electrodes pre-ground to requirements or a
dedicated commercial electrode grinder to provide electrode tip quality and consistency offers the
following benefits to the user in their welding process:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Improved arc starting, increased arc stability and more consistent weld penetration.
Longer electrode life before electrode wear or contamination.
Reduction of tungsten shedding. This minimizes the possibility of Tungsten inclusions in the weld.
A dedicated electrode grinder helps ensure that the welding electrodes will not become
contaminated by residue or material left on a standard shop grinder wheel.
5. Tungsten electrode grinding equipment requires less skill to ensure that the tungsten electrode is
ground correctly and with more consistency.
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 6 of 8
Pre-Ground Electrodes: Rather than risk electrode radioactivity issues and also
constantly endure the variability of each operator grinding the electrodes with
a slightly different touch, many manufacturing organizations have chosen to
purchase electrodes pre-ground. In addition, since a small difference in the
dimensions of an orbital electrode can produce a big difference in the weld
results, pre-ground electrodes are the preferred electrode choice to maintain
the consistency of your welding. This low cost option ensures that the
electrode material quality, tip geometry and ground electrode surface input to
the welding process is constant. Consult electrode charts or a pre-ground
electrode supplier to obtain the electrode diameter and tip geometry that is
most suitable for your welding application.
Welding Parameter Development
Many welding equipment suppliers offer a series of pre-calculated weld
programs for a variety of tube diameters, wall thicknesses and materials.
Welders should always follow an equipment supplier's suggested procedures
first, because they have usually performed a significant amount of qualifying
and troubleshooting work to optimize electrode preparation for their
equipment.
Using pre-ground
electrodes ensures that
the electrode material
quality, tip geometry and
ground electrode surface
input to the welding
process is constant
However, it is impossible for the equipment suppliers to have welding procedures for every welding
application and there will always exist a trade off in maximum weld speed possible versus weld quality
and repeatability. Where weld parameter specifications do not exist or the welder or engineer would like
to change those settings to possibly improve or optimize their welding, the guidelines noted below give
information on how to modify the welding parameters for a desired result.
Note: The "rules of thumb" noted below are general guidelines only and will not apply to every
welding application and mix of parameters chosen. Although the welding parameters are often
chosen and changed according to the specific needs of the application, there are some
industry standards that have been developed as starting points. Experimentation and
experience will determine the final weld parameters.
Arc Length
The arc gap setting is dependent on weld current, arc stability and tube concentricity/ovality. The
objective of the welding engineer is to keep the electrode at a constant distance from the tube surface
with sufficient gap to avoid stubbing out.
As a "rule of thumb" use a base arc gap of 0.010" and add to this half the penetration required (usually
the tube wall thickness) expressed in thousandths of an inch. Thus if the tube wall is .030" then a good
starting arc gap would be 0.010" + 0.015" = .025". For a wall thickness/penetration requirement of .154"
the arc gap would be 0.010" + .070" = 0.080"
Weld Speed
The weld speed is dependent on flow rate of material to be welded, and wall thickness. The objective is
to weld as fast as possible while still yielding a quality output.
As a starting point the tungsten surface speed should be 4 - 10 inches per minute with the faster welding
speeds used for thinner wall materials and the slower welding speeds used for heavy wall thickness. As a
good starting point, use 5 inches per minute.
Welding Current
The welding current is dependent on the material to be welded, wall thickness, weld speed, and the
shield gas chosen. The objective is to achieve full penetration, defect free welds.
As a starting point use 1 average current per 0.001" wall thickness if the material is stainless steel. Thus
for a 0.030" wall tubing the average weld current will be 30 amps in the first level.
Weld Current Levels
Orbital welding normally uses multiple levels of weld current to compensate for heat building up in the
tube during the welding process. If the weld current used to initially penetrate the tubing was held at the
same level for the complete weld, the weld penetration would increase as the weld progressed around
the tube, producing too much penetration.
Normally orbital welding uses a minimum of 4 levels of weld time with each level decreasing in weld
amperage
Starting parameters: Set weld level 4 to be at 80% of weld level 1 amperages. Set weld level 2 and weld
level 3 to gradually decrease the current from level 1 to level 4.
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 7 of 8
Arc Pulsing
Arc pulsing involves using the welding power supply to rapidly alternate the weld current from a high
(peak current) to a low (background current) value. This creates a seam of overlapping spot welds. This
technique reduces the overall heat input to the base material and can also allow for increases in weld
speed. This welding technique brings many benefits to the welding procedure, often improving weld
quality and repeatability. In some cases materials and weld joints with poor fit-up that are difficult to
successfully weld with a non-pulsed arc can easily be welded with a pulsed arc technique. The result is
improved weld quality and increased output.
In orbital welding, arc pulsing also offers another advantage due to the fact that the gravity pulls the
weld puddle in different directions as the weld is created around the tube. When pulsing at peak current
the base material(s) melt and flow together, at the lower background current the puddle can solidify
before becoming liquid at the next peak current pulse. This diminishes the effect of gravity on the
molten weld, minimizes the weld sagging at the 12 and 6 o clock positions, and reduces the molten weld
puddle running/slumping downhill at the 3 and 9 o'clock positions and effectively alters the electrode to
weld puddle distance. The arc pulsing technique thus becomes more advantageous as the wall thickness
increases resulting in a larger weld puddle.
Arc Pulsing Parameters: Arc pulsing involves four welding parameters: peak current, background current,
pulse width (duty cycle), and pulse frequency. Here again, opinions vary from one welding organization
to another and indeed from welder to welder. Many welders arrive at the same welding result having
somewhat different welding parameters.
It is important to understand how to choose convenient weld development starting parameters and the
effect on the weld by changing each parameter.
The primary objective is to use the benefits of weld pulsation to improve weld quality and output.
Peak/Background Current Ratios: The peak to background current ratios basically provide a means for the
welding current to pulse from one level to another. Industry usage generally varies from 2:1 ratios to
5:1 ratios. A good starting point is to use 3:1 ratios, make the required weld and test other parameters
to see if any benefit can be gained.
Pulse Frequency: The pulse frequency is dependent on spot overlap required. Good starting parameters
are to attempt for a 75% spot overlap. Pulse rate for thin wall tube is often equal to the weld speed in
ipm (5 ipm = 5 pps)
Pulse Width: The pulse width (the percentage of time spent on the peak current) is dependent on heat
sensitivity of material and available current from power supply. Higher heat sensitivity requires lower
pulse width % on peak current. Standard pulse widths are often 20% to 50%. A good starting parameters
would be to set a pulse width of 35%.
Free arc pulsation software is available from the internet that pre-calculates a variety of arc pulsation
parameters for any given amperage of an application. In this fashion, welders can arrive at an
acceptable weld program and quickly obtain a variety of alternative arc pulsation options to examine
without requiring lengthy calculations or tedious empirical "try it and see" test welding.
Conclusion
One of the best methods for a company to assume a superior position in the marketplace is to develop
a competitive advantage by optimizing the welding process in manufacturing. This will improve weld
quality, increase weld speed, and reduce scrap and rework costs. From this, a company can realize lower
costs per unit of product, quicker delivery of product, and less defects in workmanship. All of this can be
accomplished through the use of orbital welding systems using the consistency and repeatability of finetuned weld programs, control of input material and shield gas quality, and properly prepared pre-ground
electrodes.
Pro-Fusion Technologies provides pre-ground tungsten electrodes for orbital and tube mill applications.
The company offers free access to a welding web site with over 75% of the site dedicated to offering
information on welding processes and even allows the user to input data on what they are welding and
receive welding parameters. The site also gives information on various welding applications with
recommendations on the best techniques to use and handbooks for troubleshooting welding systems.
The web site may be accessed at www.Pro-fusionOnline.com
For free sample Tungsten electrodes, or more information on any of the above contact Pro-Fusion, 1090
Lawrence Drive #104, Newbury Park, CA 91320 U.S.A. Tel (805) 376-8021 Fax (805) 376-0619 Email:
Sales@Pro-FusionOnline.com
Welding Parameter Development Example
For 1" Tube/.030" Tube Wall Thickness:
1. Arc Length/Gap = .010" + (0.5 x penetration required)
Starting Parameters: .010" + (0.5 x .030") = .025"
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
17-09-2002
Pro-Fusion: Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding
Page 8 of 8
2. Weld Speed = 5 ipm surface speed
RPM = ipm/(3.1415 x dia.)
Starting Parameters: 5/(3.1415 x 1") = 1.59 RPM
3. Welding Current Levels
Level 1 = 1 amp per .001" of wall thickness for level 1 current
Level 4 = 80% of Level 1 current
Levels 2 and 3 gradually decrease the current from Level 1 to Level 4
Starting Parameters:
Level 1 Peak Current = .030" wall thickness = 30 amps
Level 4 Peak Current = 30 amps x 80% = 24 amps
Level 2 Peak Current = 28 amps
Level 3 Peak Current = 26 amps
Background Current will be 1/3rd of peak current. Pulse width/duty cycle is 35%
4. Tungsten Electrode Diameter & Tip Geometry - Use your equipment manufacturer's specifications
or consult your pre-ground electrode supplier
The above data gives starting parameters. On completion of the first test weld, the parameters will be
modified to obtain the final result desired.
We can provide free samples of various tungsten materials, electrode tip geometries, and surface
finishes for you to test. Call or e-mail to review your specific application and to obtain the most suitable
samples for your needs.
-
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Return to Top
A b o u t P r o -F u s i o n
file://A:\Pro-Fusion Fundamentals of Orbital Tube Welding.htm
C o p y r i g h t 2 0 0 1 P r o -F u s i o n T e c h n o l o g i e s , I n c .
3825 Old Conejo Road
Newbury Park, CA 91320 USA
T e l ( 8 0 5 ) 3 7 6 -8 0 2 1
F a x ( 8 0 5 ) 3 7 6 -0 6 1 9
e m a i l : sales@pro-fusiononline.com
17-09-2002
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Vedanta SutrasDokument399 SeitenThe Vedanta Sutrasapi-3716165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zero Air For Gas Chromatography: Market Application PublicationDokument2 SeitenZero Air For Gas Chromatography: Market Application PublicationSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Control - In.spiritual - Practice ImersonDokument98 SeitenSelf Control - In.spiritual - Practice ImersonTodorov Shabanski TodorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ab HumidityDokument1 SeiteAb HumiditySrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm Standards: S. NO. Description Standard No. No. of CopiesDokument1 SeiteAstm Standards: S. NO. Description Standard No. No. of CopiesSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashtavakra Gita EbookDokument60 SeitenAshtavakra Gita EbookJayraj08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Tooth Lockwasher SpecificationDokument2 SeitenInternal Tooth Lockwasher Specificationsharkdude1134100% (1)
- Ab HumidityDokument1 SeiteAb HumiditySrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Days ShiftDokument8 Seiten2 Days ShiftSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate ValveDokument3 SeitenGate ValveSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPR Vs EPDMDokument1 SeiteEPR Vs EPDMSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 38 Study On Corrosion Failure Analysis and Mechanism of Stainless Steel Pipe Welding Joint in Seawat PDFDokument6 Seiten38 Study On Corrosion Failure Analysis and Mechanism of Stainless Steel Pipe Welding Joint in Seawat PDFSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Leakage RedDokument10 Seiten07 Leakage RedSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arunakirinatar Aruliya "Tiruppukaz" Part 1 (Verses 1-330)Dokument259 SeitenArunakirinatar Aruliya "Tiruppukaz" Part 1 (Verses 1-330)StallinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 MicrobiallyInfluencedCorrosionDokument5 Seiten5 MicrobiallyInfluencedCorrosionSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Washer Lock HicollarsplitDokument1 SeiteWasher Lock HicollarsplitSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- True Love is Accepting What IsDokument4 SeitenTrue Love is Accepting What IsSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashtavakra Gita EbookDokument60 SeitenAshtavakra Gita EbookJayraj08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiesel: An Alternative Fuel Made From Plants and AnimalsDokument8 SeitenBiodiesel: An Alternative Fuel Made From Plants and AnimalsSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Days ShiftDokument8 Seiten2 Days ShiftSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- LappingDokument25 SeitenLappingSrinivasan Ravi100% (1)
- Washer Lock HicollarsplitDokument1 SeiteWasher Lock HicollarsplitSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Washer Lock Hicollarsplit PDFDokument1 SeiteWasher Lock Hicollarsplit PDFSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Tooth Lockwasher SpecificationDokument2 SeitenInternal Tooth Lockwasher Specificationsharkdude1134100% (1)
- A Guide To Shaft SealsDokument5 SeitenA Guide To Shaft SealsSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Washer Lock HicollarsplitDokument1 SeiteWasher Lock HicollarsplitSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Days ShiftDokument8 Seiten2 Days ShiftSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er.Sulthan's Ayurvedic Home RemediesDokument321 SeitenEr.Sulthan's Ayurvedic Home Remediesarunram86100% (2)
- Er.Sulthan's Ayurvedic Home RemediesDokument321 SeitenEr.Sulthan's Ayurvedic Home Remediesarunram86100% (2)
- Cathodic ProtectionDokument2 SeitenCathodic ProtectionSrinivasan RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Bob L200Dokument12 SeitenBob L200LucyPher_Comte_7563Noch keine Bewertungen
- Otis Relay Coils SpecificationsDokument1 SeiteOtis Relay Coils SpecificationsDamian Alberto EspositoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NACA Report 184 The Aerodynamic Forces On Airship HullsDokument16 SeitenNACA Report 184 The Aerodynamic Forces On Airship Hullsshatal16Noch keine Bewertungen
- En 818-6 PDFDokument5 SeitenEn 818-6 PDFlub007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Pipe FittingsDokument12 SeitenAluminium Pipe Fittingsrahult19Noch keine Bewertungen
- VAS5054ADokument3 SeitenVAS5054AKarim ElmahrokyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Chemistry PDFDokument213 SeitenIndustrial Chemistry PDFLucio Peña Zarate100% (1)
- Faa Gleim Outlines Instrument PilotDokument130 SeitenFaa Gleim Outlines Instrument PilotTalaat SalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Hemant ChaurasiaDokument3 SeitenResume Hemant Chaurasiachaurasia_hNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHG 25 3000 SeriesDokument23 SeitenSHG 25 3000 Seriesjpsingh75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aiwa NSX-VC58Dokument41 SeitenAiwa NSX-VC580000AbdielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco SD-WAN Intro SOLRST-2006 PDFDokument10 SeitenCisco SD-WAN Intro SOLRST-2006 PDFffusaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 Drawing Operations: Need To See If It Really Works For All Tasks, and If Not Then Get Rid of ItDokument1 Seite2.3 Drawing Operations: Need To See If It Really Works For All Tasks, and If Not Then Get Rid of ItTrogo BoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Fabrication of a Solar-Assisted Air DehumidifierDokument17 SeitenDesign & Fabrication of a Solar-Assisted Air DehumidifierSree NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA SymbolsDokument2 SeitenISA Symbolsmahesh009Noch keine Bewertungen
- FC100 ServiceManual MG90L102Dokument209 SeitenFC100 ServiceManual MG90L102Said BoubkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypergraphDB: A Graph-Oriented DatabaseDokument20 SeitenHypergraphDB: A Graph-Oriented DatabaseandresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ship Stability 5Dokument31 SeitenShip Stability 5jeaneva guiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 07 Digital Modulations - EEE309Dokument13 SeitenPart 07 Digital Modulations - EEE309elon muskNoch keine Bewertungen
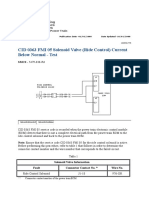
- 363-5 Machine Ride Control Actuator - Current Below NormalDokument3 Seiten363-5 Machine Ride Control Actuator - Current Below NormalArtin HykoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVDokument3 SeitenCVDhiraj Patra100% (1)
- What is an electrostatic shieldDokument3 SeitenWhat is an electrostatic shieldsujaraghupsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAP Demo ExercisesDokument34 SeitenMAP Demo ExercisesNancy HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FESCO Consumer Service Manual OverviewDokument60 SeitenFESCO Consumer Service Manual OverviewMus'ab FarouqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hands-On Exercise Oracle 10g PL SQL - v1 0Dokument24 SeitenHands-On Exercise Oracle 10g PL SQL - v1 0pavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Writer Is A Young Boy Who Is Taken To The Railway Station To See Soldiers Departing For The Second World WarDokument2 SeitenThe Writer Is A Young Boy Who Is Taken To The Railway Station To See Soldiers Departing For The Second World WarFariha RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRC800 Remote Control UserGuideDokument2 SeitenDRC800 Remote Control UserGuideLuis MurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hex Head AVD 780 Installation Manual WEB PDFDokument77 SeitenHex Head AVD 780 Installation Manual WEB PDFdasdsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On The Unique Features of The Leading Database SystemsDokument2 SeitenA Case Study On The Unique Features of The Leading Database SystemsLiezheel Mynha AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super PaveDokument20 SeitenSuper PaveHashem EL-MaRimeyNoch keine Bewertungen