Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Vector - Mechanics (Compatibility Mode) PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ramu VasaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Vector - Mechanics (Compatibility Mode) PDF
Hochgeladen von
Ramu VasaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Vectors
Vector classifications:
- Fixed or bound vectors have well defined points of
application that cannot be changed without affecting
an analysis.
- Free vectors may be freely moved in space without
changing their effect on an analysis.
Equal vectors have the same magnitude and direction.
Negative vector of a given vector has the same magnitude
and the opposite direction.
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Addition of Vectors
Parallelogram rule for vector addition
Triangle rule for vector addition
Law of cosines,
C
B
C
R 2 P 2 Q 2 2 PQ cos B
R PQ
Law of sines,
B
sin A sin B sin C
Q
R
P
Vector addition is commutative,
PQ Q P
Vector subtraction
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Addition of Vectors
Addition of three or more vectors through
repeated application of the triangle rule
The polygon rule for the addition of three or
more vectors.
Vector addition is associative,
P Q S P Q S P Q S
Multiplication of a vector by a scalar
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Addition of Vectors
A quantity which has magnitude and
direction, but doesnt follow parallelogram
law, cannot be a vector.
Can you name such a quantity?
Think in terms of commutative property!!
Answer: Finite Rotation
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Resultant of Several Concurrent Forces
Concurrent forces: set of forces which all
pass through the same point.
A set of concurrent forces applied to a
particle may be replaced by a single
resultant force which is the vector sum of the
applied forces.
Vector force components: two or more force
vectors which, together, have the same effect
as a single force vector.
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Rectangular Components of a Vector
May resolve a vector into perpendicular components
so
that the resulting parallelogram is a rectangle. Fx and Fy
are referred to as rectangular vector components and
F Fx F y
Define perpendicular unit vectors i and j which are
parallel to the x and y axes.
Vector components may be expressed as products of
the unit vectors with the scalar magnitudes of the
vector components.
F Fx i Fy j
Fx F cos
Fy F sin
Fx and Fy are referred to as the scalar components of F
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Addition of Concurrent Forces
Wish to find the resultant of 3 or more
concurrent forces,
R P Q S
Resolve each force into rectangular components
R x i R y j Px i Py j Q x i Q y j S x i S y j
Px Q x S x i Py Q y S y j
The scalar components of the resultant are
equal to the sum of the corresponding scalar
components of the given forces.
R x Px Qx S x
R y Py Q y S y
Fx
Fy
To find the resultant magnitude and direction,
Ry
R R x2 R y2
tan 1
Rx
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
Two structural members A and B are bolted to
a bracket as shown. Knowing that both
members are in compression and that the force
is 20 kN in member A and 30 kN in member B,
determine, using trigonometry, the magnitude
and direction of the resultant of the forces
applied to the bracket by members A and B.
SOLUTION KEY
o Construct the force triangle
and apply the sine and
cosine rules.
Example of a timber truss joint
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
SOLUTION
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
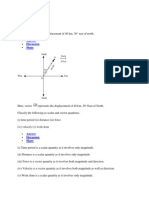
A collar that can slide on a vertical rod is subjected to
the three forces shown. Determine (a) the value of the
angle for which the resultant of the three forces is
horizontal, (b) the corresponding magnitude of the
resultant.
SOLUTION KEY
o Since the resultant (R) is to be
horizontal, sum of the vertical
comp. of the forces, i.e., Ry = 0.
Example of an Umbrella
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
SOLUTION
(a)
Since R is to be horizontal, Ry = 0
Then,
Ry Fy 0
90 lb 70 lb sin 130 lb cos 0
13 cos 7 sin 9
13 1 sin 2 7 sin
Squaring both sides:
169 1 sin 2 49 sin 2 126 sin 81
218 sin
Solving by quadratic formula:
126 sin 88 0
sin 0.40899
or,
24 .1
1 - 11
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example-2
or, R 117.0 lb
1 - 12
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Rectangular Components of a Vector in Space
Components of the vector F
Fx F cos x F y F cos y Fz F cos z
F Fx i F y j Fz k
F cos x i cos y j cos z k
cos x i cos y j cos z k
is a unit vector along the line of action of F
and cos x , cos
y , and cos z are the direction
cosines for F
cos 2 x cos 2 y cos 2 z 1
F Fx2 Fy2 Fz2
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Rectangular Components of a Force Vector in Space
The magnitude of the force vector is
F and the direction of the force is
defined by the location of two
points,
M x1 , y1 , z1 and N x 2 , y 2 , z 2
d vector joining M and N
d xi d y j d zk
d x x2 x1 d y y 2 y1 d z z 2 z1
F F
d xi d y j d z k
d
Fd y
Fd x
Fd z
Fx
Fy
Fz
d
d
d
d d x2 d y2 d z2
cos x
d
dx
d
; cos y y ; cos z z
d
d
d
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
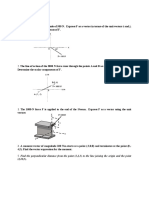
Example
SOLUTION:
Based on the relative locations of the
points A and B, determine the unit
vector pointing from A towards B.
Apply the unit vector to determine the
components of the force acting on A.
The tension in the guy wire is 2500 N.
Determine:
Noting that the components of the unit
vector are the direction cosines for the
vector, calculate the corresponding
angles.
a) components Fx, Fy, Fz of the force
acting on the bolt at A,
b) the angles qx, qy, qz defining the
direction of the force (the direction
cosines)
2 - 15
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
SOLUTION:
Determine the unit vector pointing from A
towards B.
AB 40m i 80m j 30m k
AB 40m 2 80m 2 30m 2
94.3 m
40 80 30
i
j
k
94.3 94.3 94.3
0.424 i 0.848j 0.318k
Determine the components of the force.
FF
2500 N 0.424 i 0.848j 0.318 k
1060N i 2120 N j 795 N k
2 - 16
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
Noting that the components of the unit vector are
the direction cosines for the vector, calculate the
corresponding angles.
cos x i cos y j cos zk
0.424 i 0.848 j 0.318 k
x 115.1
y 32.0
z 71.5
2 - 17
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
SOLUTION:
FBA
FAB
Since the force in the guy wire must be
the same throughout its length, the force
at B (and acting toward A) must be the
same magnitude but opposite in
direction to the force at A.
FBA FAB
1060N i 2120 N j 795 N k
What are the components of the
force in the wire at point B? Can
you find it without doing any
calculations?
2 - 18
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Scalar Product of Two Vectors
The scalar product or dot product between
two vectors P and Q is defined as
P Q PQ cos scalar result
Scalar products:
- are commutative,
- are distributive,
- are not associative,
P Q Q P
P Q1 Q2 P Q1 P Q2
P Q S undefined
Scalar products with Cartesian unit components,
P Q Px i Py j Pz k Qx i Q y j Qz k
i i 1 j j 1 k k 1 i j 0
j k 0 k i 0
P Q Px Qx Py Q y Pz Qz
P P Px2 Py2 Pz2 P 2
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Applications: Scalar Product of Two Force Vectors
Angle between two force vectors:
P Q PQ cos Px Qx Py Q y Pz Qz
cos
Px Qx Py Q y Pz Qz
PQ
Projection of a force vector on a given axis:
POL P cos projection of P along OL
P Q PQ cos
P Q
P cos POL
Q
Note:
- For an axis defined by a unit vector (): Q
Q
POL P
Px cos x Py cos y Pz cos z
10
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Vector Product of Two Vectors
Vector product of two vectors P and Q is defined
as the vector V which satisfies the following
conditions:
1. Line of action of V is perpendicular to plane
containing P and Q.
2. Magnitude of V is V PQ sin
3. Direction of V is obtained from the right-hand
rule.
Vector products:
- are not commutative, Q P P Q
- are distributive,
P Q1 Q2 P Q1 P Q2
- are not associative, P Q S P Q S
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Vector Products: Rectangular Components
Vector products of Cartesian unit vectors,
i i 0
j i k k i j
i j k
j j 0
k j i
i k j j k i
k k 0
Vector products in terms of rectangular
coordinates
V Px i Py j Pz k Qx i Q y j Qz k
Py Qz Pz Q y i Pz Qx Px Qz j
Px Q y Py Qx k
i
j
k
Px Py Pz
Q x Q y Qz
11
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Moment of a Force About a Point
Moment of a force produces a turning action on a
rigid body
The moment of a force F about O is defined as
MO r F
r is the position vector of A from O
The moment vector MO is perpendicular to the
plane containing O and the force F.
Magnitude of MO measures the tendency of the force
to cause rotation of the body about an axis along MO.
M O rF sin Fd
d is the perpendicular distance of the line of action
of Force F from O. The sense of the moment may be
determined by the right-hand rule.
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Moment of a Force About a Point
Two-dimensional structures have length and breadth but
negligible depth and are subjected to forces contained
only in the plane of the structure.
The plane of the structure contains the point O and the
force F. MO, the moment of the force about O, is
perpendicular to the plane.
If the force tends to rotate the structure clockwise, the
sense of the moment vector is out of the plane of the
structure and the magnitude of the moment is positive.
If the force tends to rotate the structure counterclockwise,
the sense of the moment vector is into the plane of the
structure and the magnitude of the moment is negative.
3 - 24
12
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Examples: Application of moments
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Varignons Theorem
The moment about a give point O of the
resultant of several concurrent forces is equal
to the sum of the moments of the various
forces about the same point O.
r F1 F2 r F1 r F2
Varignons Theorem makes it possible to
replace the direct determination of the
moment of a force F by the moments of two
or more component forces of F.
13
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Rectangular Components of the Moment of a Force about origin
The moment of force F applied at A about O,
M O r F , r xi yj z k
F Fx i Fy j Fz k
M O M xi M y j M zk
x
Fx
y
Fy
z
Fz
yFz zF y i zFx xFz j xFy yFx k
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Rectangular Components of the Moment of a Force about an
Arbitrary Point
The moment of force F applied at A about B,
M B rA / B F
rA / B rA rB
x A xB i y A yB j z A z B k
F Fx i Fy j Fz k
M B x A xB
Fx
j
y A yB
k
z A zB
Fy
Fz
14
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Rectangular Components of the Moment of a Force
For two-dimensional structures,
M O xFy yFx k
MO MZ
xFy yFx
M B x A x B Fy y A y B Fx k
MB MZ
x A x B Fy y A y B Fx
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
A 500-N vertical force is applied to the end of a lever
which is attached to a shaft (not shown) at O.
Determine:
0.6 m
500 N
a) the moment about O,
b) the horizontal force at A which creates the same
moment,
c) the smallest force at A which produces the same
moment,
d) the location for a 1200-N vertical force to
produce the same moment
15
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
0.6 m
500 N
a) Moment about O is equal to the product of the
force and the perpendicular distance between the
line of action of the force and O. Since the force
tends to rotate the lever clockwise, the moment
vector is into the plane of the paper which, by our
sign convention, would be negative or
counterclockwise.
M O Fd
d 0.6 m cos 60 0.3 m
M O 500 N 0.3 m 150 N.m
M O 150 N m
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
b) Horizontal force at A that produces the same
moment,
0.6 m
d 0.6 m sin 60 0.52 m
M O Fd
150 N m F 0.52 m
150 N m
F 288.5 N
F
0.52 m
Why must the direction of this F be to the right?
16
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
F(min) ?
What is the smallest force at A which produces
the same moment?
0.6 m
c) The smallest force at A to produce the same
moment occurs when the perpendicular distance is
a maximum or when F is perpendicular to OA.
M O Fd
150 N m F 0.6 m
150 N m
F
0.6 m
F 250 N
30o
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
d) To determine the point of application of a 1200 N
force to produce the same moment,
1200 N
M O Fd
150 N m 1200 N d
150 N m
d
0.125 m
1200 N
d OB cos 60
OB 0.25 m
17
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
A 36-N force is applied to a wrench to
tighten a showerhead. Knowing that the
centerline of the wrench is parallel to the x
axis. Determine the moment of the force
about A.
SOLUTION KEY
o Find out the position vector of the
point C .
o Get the components of the applied
force (F) along X, Y and Z directions.
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
SOLUTION
M A rC/ A F
where rC / A 215 mm i 50 mm j 140 mm k
Fx 36 N cos 45 sin12, Fy 36 N sin 45 ,
Fz 36 N cos 45 cos12
F 5.2926 N i 25.456 N j 24.900 N k
and M A
0.215
0.050
0.140
N m
5.2926 25.456 24.900
4.8088 N m i 4.6125 N m j 5.7377 N m k
M A 4.81 N m i 4.61 N m j 5.74 N m k
18
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Mixed Triple Product of Three Vectors
Mixed triple product of three vectors,
S P Q scalar result = volume of parallelepiped
The six mixed triple products formed from S, P, and
Q have equal magnitudes but not the same sign,
S P Q P Q S Q S P
S Q P P S Q Q P S
Evaluating the mixed triple product,
S P Q S x Py Q z Pz Q y S y Pz Q x Px Q z
S Q
P
S z Px Q y Py Qx
Sx
Sy
Sz
Px
Qx
Py
Qy
Pz
Qz
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Moment of a Force About an Axis Passing Through the Origin
Moment MO of a force F applied at the point A
about a point O,
MO r F
Scalar moment MOL about an axis OL is the
projection of the moment vector MO onto the
axis,
M OL M O r F
Moments of F about
the coordinate axes
(components of M O )
M x yFz zFy
r xi y j zk
M y zFx xFz
M z xFy yFx
19
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Application: Moment of a Force About an Arbitrary Axis
Moment of a force about an arbitrary axis,
M BL M B
rA B F
rA B rA rB
The result is independent of the location
of point B along the given axis!!
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
The frame ACD is hinged at A and D and is supported by a cable that
passes through a ring at B and is attached to hooks at G and H. Knowing
that the tension in the cable is 1125 N, determine the moment about the
diagonal AD of the force exerted on the frame by portion BH of the cable.
SOLUTION KEY
o Find unit vector along AD.
o Find the force vector BH.
o Choose either point A or D , get the
position vector AB or DB
M AD AD rB/ A TBH
20
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Example
M AD AD rB/ A TBH
AD
0.8 m i 0.6 m k
0.8 m 2 0.6 m 2
0.8 i 0.6 k
rB/ A 0.4 m i
TBH TBH
0.3 m i 0.6 m j 0.6 m k
BH
1125 N
2
2
2
BH
0.3 0.6 0.6 m
0.8
0.6
M AD 0.4
180 N m
375 750 750
M AD 180.0 N m
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Moment of a Couple Couple Moment
Two forces F and -F having the same magnitude,
parallel lines of action, and opposite sense are said
to form a couple.
Moment of the couple,
M rA F rB F
rA rB F
Special Notation
r F C
M rF sin Fd C
The moment vector of the couple is
independent of the choice of the origin of the
coordinate axes, i.e., it is a free vector that can
be applied at any point with the same effect.
21
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Moment of a Couple
Two couples will have equal moments if
F1d1 F2 d 2
the two couples lie in parallel planes, and
the two couples have the same sense or
the tendency to cause rotation in the same
direction.
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Addition of Couples
Consider two intersecting planes P1 and
P2 with each containing a couple
M 1 r F1 in plane P1
M 2 r F2 in plane P2
Resultants of the vectors also form a
couple
M r R r F1 F2
Sum of two couples is also a couple that is equal
to the vector sum of the two couples
M r F1 r F2
M1 M 2
22
11/26/2013
Engineers Mechanics- Review of Vector Algebra/Applications
Summary Couple
A couple can be represented by a vector with magnitude
and direction equal to the moment of the couple.
Couple vectors obey the law of addition of vectors.
Couple vectors are free vectors, i.e., the point of application
is not significant.
Couple vectors may be resolved into component vectors.
23
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2.1 Terms of Sizes: Limit and FitsDokument10 Seiten2.1 Terms of Sizes: Limit and FitsRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Terms of Sizes: Unit 1 Limit and FitsDokument20 Seiten2.1 Terms of Sizes: Unit 1 Limit and FitsRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear & Angular Measurement: Course ContentsDokument26 SeitenLinear & Angular Measurement: Course ContentsRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1: Tutorial-1 SolutionDokument5 SeitenProblem 1: Tutorial-1 SolutionRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Solution Equivalent System PDFDokument3 SeitenQuiz Solution Equivalent System PDFRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Problem - 1Dokument2 SeitenQuiz Problem - 1Ramu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - Equivalent - System (Compatibility Mode) PDFDokument8 SeitenLecture - Equivalent - System (Compatibility Mode) PDFRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Week ISTE Workshop: Engineers MechanicsDokument11 Seiten2-Week ISTE Workshop: Engineers MechanicsRamu VasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Matrices and Basic Calculus For Non Majors-MT161Dokument19 SeitenMatrices and Basic Calculus For Non Majors-MT161Hamisi MzariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Review Activity WordDokument6 SeitenChapter 8 Review Activity WordsaramafareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsDokument26 Seiten1 Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated in D IcialDokument21 SeitenUpdated in D IcialLuis NoveloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Analysis: Multivector Review and Training CenterDokument10 SeitenVector Analysis: Multivector Review and Training CenterMark FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-2.PDF Version 1Dokument32 SeitenChapter-2.PDF Version 1make handNoch keine Bewertungen
- USS Physics Part 1 PDFDokument766 SeitenUSS Physics Part 1 PDFNikhill SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 8. Vector & 3-D (Math +2)Dokument66 SeitenCH 8. Vector & 3-D (Math +2)Dinesh BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Dokument5 SeitenHSC 11 Scalars and Vectors Ch2Snehal PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 1Pravat Kumar SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Analysis: By: Ivan Sutresno Hadi SujotoDokument15 SeitenVector Analysis: By: Ivan Sutresno Hadi SujotoBagoes Budi LaksonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors Live Class 1 NotesDokument40 SeitenVectors Live Class 1 NotesKushagra TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths ProjectDokument15 SeitenMaths Projectvinith gomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics-Vector CalculusDokument53 SeitenEngineering Mathematics-Vector CalculusNurul Hanifah0% (2)
- Appendix A Vector Notation: Vector Notation Is Based On The Physical Laws of StaticsDokument6 SeitenAppendix A Vector Notation: Vector Notation Is Based On The Physical Laws of StaticsCielito MaligaligNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC420 Chapter 1Dokument10 SeitenMEC420 Chapter 1MohdFirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-1 - Engg Mech-1Dokument5 SeitenAssignment-1 - Engg Mech-1NiteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Signals: Engr. Mark Jefferson A. Arellano, Ect, VCP, RtaDokument52 SeitenElectromagnetic Signals: Engr. Mark Jefferson A. Arellano, Ect, VCP, RtaMark ArrelanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Vector Differentiation, 2010Dokument11 SeitenChapter 3 - Vector Differentiation, 2010mohamed fanouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.1 - Vector Calculus - Div & CurlDokument29 Seiten15.1 - Vector Calculus - Div & Curlkhanshaheer477Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Discussion Share: VectorDokument51 SeitenAnswer Discussion Share: Vectorneela94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors and ScalarsDokument26 SeitenVectors and ScalarsYob YnnosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector DifferentiationDokument33 SeitenVector DifferentiationShawkat Khanz TuhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated in D IcialDokument21 SeitenUpdated in D IcialLuis NoveloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Class 11 Vector Board Assignment PDFDokument2 SeitenAssignment Class 11 Vector Board Assignment PDFmihirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Class 11th HandPickedDokument71 SeitenComplete Class 11th HandPickedSamyak Jain100% (1)
- Chapter 06 PDFDokument29 SeitenChapter 06 PDFMA. CARMELA REBUYASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Answer SchemeDokument4 SeitenPhysics Answer SchemeBENNY LAU XUE ZHENG MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 2. ELMAG - 1 - Vector AlgebraDokument43 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - 2. ELMAG - 1 - Vector AlgebraDeni Ristianto100% (1)
- Yasir Ali Vector CalculusDokument42 SeitenYasir Ali Vector CalculusCh Abdul HadiNoch keine Bewertungen