Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
72 HR Reviewer
Hochgeladen von
Astrid AmadorOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
72 HR Reviewer
Hochgeladen von
Astrid AmadorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
hr chick reviwer
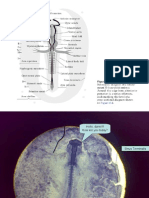
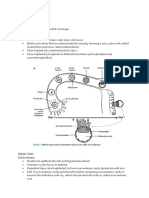
[EMBRYO LAB]
WHOLE MOUNT
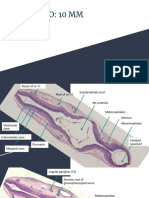
4 flexures:
o Cranial/ cephalic flexure
o Cervical/nuchal flexure (at the level of 1 st several somites)
o Tail flexure flexure
o Caudal flexure
Amnion and chorion enclosed the entire embryo
Paired wing & lung bud visible nut not sharply bounded
Allantois sac-like structure encircled by the tail
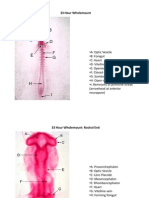
STRUCTURE
DESCRIPTION
TRANSVERSE SECtION
Anterior part of the hindbrain w/ thicker walls
than myelencephalon
The roof undergoes enlargement
Posterior part of the hindbrain
Thin roof plate lying freely within the cavity
Segmented enlargements in the walls of the
myelecephalon & metencephalon
11 neuromeres
Forebrain: 1st, 2nd, 3rd
Midbrain: 4th and 5th
Hindbrain: 6th 11th
Thin roof of myelencephalon which is folded in
the myelocoell
Where vascularization occurs
Small, thick-walled oval structure that appears
before the auditory vesicle (forerunner)
Located at the level of 10th neuromere on each
side of myelencephalon
Bigger than endolymphatic duct
Ganglia of VII (facial) & VIII (auditory) nerves
Mass of cells lying against the cranial wall of
auditory vesicles
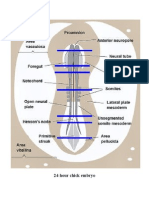
Spinal cord
Central cavity of spinal cord
Thin mid-dorsal wall of the spinal cord
Mid-ventral wall of the spinal cord
Lateral depression of the central canal about
midway between the floor and roof plates
Dorsolateral wings of the spinal cord
Between sulcus limitans & roof plate
Metencephalon
myelencephalon
Neuromeres
Posterior choroid
plexus
Endolymphatic duct
Auditory vesicles
syn: otic vesicle
otocyts
Acoustic-facialis
ganglia
Central canal
Roof plate
Floor plate
Sulcus limitans
Alar plates
cerebellum
roof of the medulla &
adjacent skin
ectoderm
hr chick reviwer
Basal plates
Marginal layer
Ependymal layer
Mantle layer
[EMBRYO LAB]
Ventrolateral wings of the spinal cord
Between sulcus limitans & floor plate
Outer region of the neural tube
Composed of several fibers & fewer nuclei
Single, innermost layer of cells
Adjacent to the central canal
Cells capable of mitosis
Wide heavily nucleated layer between marginal
& ependymal
Large mass anterior to the acoustic-facialis
ganglion
Subdivide into 3 branches
(branches of trigeminal nerve):
located w/in 1st branchial arch
Semilunar ganglion
Maxillary branch - medial branch
Ophthalmic branch lateral branch closest to
mesencephalon
Mandibular branch lateral branch above the
ophthalmic branch
syn: gasserian ganglion
Very small rounded accumulation of cells at the
caudal side of auditory vesicle
Glossopharyngeal nerves into 3rd branchial arch
Cell mass lying immediately lateral to
myelencephalon
Small rounded region beneath the
metencephalon & mesocoel
Becomes continuous w/ metencephalon
Cavity of mesencephalon
Found @ mesencephalon
Nerve fibers from the neural ectodermal cells
appearing as a pair of streaks from the floor of
mesencephalon
Will innervate 4 pairs of extrinsic eye muscles
Superior ganglion
Somite
Mesencephalon
mesocoel
Oculomotor nerve
(III)
Anterior cardinal
vein
syn: precardinal vein
notochord
Closing plates
Found laterally situated in the mesenchyme of
the floor of myelencephalon
Found between 2 regions of hindbrains or
between spinal cord & hindbrain
FOREGUT AND ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES
Double layered membranes formed by
endoderm of pharyngeal pouches & ectoderm
Cerebral aqueduct/
Aqueduct of sylvius
hr chick reviwer
Pharyngeal furrows
st
1 pharyngeal
furrow and pouch
nd
2 pharyngeal
furrow and pouch
Visceral arches
Mandibular arch
Maxillary arch
Hyoid arch
Symphysis of the
lower jaw
[EMBRYO LAB]
of pharyngeal furrows
Result of invagination of pharyngeal pouches
that are projected lateral from pharynx to
contact the adjacent region of skin ectoderm
Endodermal evagination which soon become
continuous with pharynx & open to the outside
via 1st pharyngeal furrow
Furrow V-shaped ectodermal indentation
Similar to 1st pharyngeal furrow & pouch but
towards spinal cord
Found between the adjacent pharyngeal
furrows
Greatly thickened & filled w/ mesenchymal cells
Mass of mesenchyme anterior to the 1st furrow
(towards mesencephalon)
Lobe-like mass of mesenchyme anterior to
stomodeum
Found where mesencephalon is
Mesenchyme between 1st (hyomandibular)
pouch & furrow and 2nd furrow
2 arches fuse ventrally (posterior of mandibular
arch)
Paired structures w/c are cut frontally (foregut)
Appear constricted into 2 parts of the level of 1st
pharyngeal pouch
Dorsal aorta
1st aortic arch
Lies within mandibular process
2nd, 3rd, & 4th aortic
arches
Extend from the dorsal aortae into 2nd, 3rd, & 4th
branchial arches
Continuous with 1st aortic arches (separate
vessels)
Ventral ends of 2nd & 3rd also unite in ventral
aorta
Result from the fusion of paired aortae
Posterior to 3rd pharyngeal pouch
Narrower vessel arises as a cranial extension
of dorsal aorta
Located medial to ant cardinal vein
Derived from group of neural crest cells
Lying posterior to IX nerve
Fades out w/in 4th branchial arch
Arise from the floor of pharynx as a median
diverticula/ depression bet. 1st and 2nd pair of
Ventral aorta
syn: aortic sac
Descending aorta
Internal carotid
artery
Jugular ganglion
Thyroid rudiments
jaws
hr chick reviwer
Oral plate
syn:pharyngeal
membrane
Pre-oral gut
stomodeum
Rathkes pouch
Laryngotracheal
groove
Trachea
Lung buds
[EMBRYO LAB]
pharyngeal pouches
Constituted by apposition of pharyngeal
endoderm & stomodeal ectoderm
Separates stomodeum from foregut
Ruptures to form mouth opening
Located cranial to the pharyngeal membrane
Less conspicuous after rupture of oral plate
Slitlike space lined by ectoderm
Lies bet 2 visceral masses next to foregut
Cavity lined with cuboidal epithelium opens in
more posterior sections into the stomodeum
Serves as rudiment of ant. pituitary gland
V-shaped ventralmost part of foregut (post.)
Seen at the level of 4th pharyngeal pouch
Arises with the lung buds as ventrocaudal
diverticulum of pharynx
Paired bilateral expansion of laryngotracheal
groove
Doughnut-like structure (when cut off from
laryngotracheal groove)
Pleural cavities
Esophagus
Coelomic cavities lateral to lung buds
Continuous w/ pericardial cavities
Rounded part of foregut
Contained w/in a thick mesentery of splanchnic
mesoderm
Whole mesenchymal mass where esophagus &
lung buds are embedded
Includes dorsal mesentery (mesoesophagus)
and ventral mesentery (dorsal mesocardium)
Mediastinum
Bulbus cordis
Endocardium & myocardium (present) indicates
the beginning of bulbus cordis
Large chamber lying to the left and caudally to
bulbus cordis
Has blood corpuscles in it
On the dorsal part of atrium
Attached to foregut by dorsal mesocardium
Separated from atrium by slight constriction
Continuous with common cardinal vein
Regions of heart where left and right fused
Thick wall
syn: conus arteriosus
Atrium
Sinus venosus
Ventricle
Ant. pituitary gland
bronchi
hr chick reviwer
Trabeculae
Pericardial cavity
Common cardinal
vein
syn:duct of Cuvier
Pleuropericardial
membrane
syn: lateral
mesocardium
Irregular projections of myocardium
Numerous in ventricular walls
Coelom surrounding the heart
Found continuous to sinus venosus
Lower vessel
Bridge of mesenchyme through which common
cardinal vein passes
Mesenchyme incompletely separates the
pericardial cavity from peritoneal cavity
Encloses the veins that enter the heart
Body cavity posterior to transverse septum
Continuous w/ pleural and pericardial cavity
Replaces the mesencephalon
Laterally compressed w/ thin walls
Posterior to oculomotor nerves
Long ventral outpocketing of diencephalon
Formed by invagination of optic vesicles
Inner layer of optic cup
Differentiates into:
Sensory retina thick layer of optic cup
next to lens vesicle
Pigmented retina thin external layer of
optic cup
Formed by ventral invagination of optic cups &
optic stalks
Seen as ventral gap in optic cup
Lens become freed from superficial skin
ectoderm
2 regions:
Elongated & centrally located will form
lens fibers
Outer & narrower cells will become
lens epithelium
Single layer of epithelial tissue covering the
lens of the eye
Transverse septum
Peritoneal cavity
Diencephalon
Infundibulum
Optic cup
Retina
Optic fissure
syn: choroid fissure
Lens vesicle
Corneal epithelium
[EMBRYO LAB]
Optic stalk
Connects optic ups with diencephalon
Postcardinal vein
Intersegmental vein
Lies dorsal to mesonephros
Appear as extensions of postcardinal vein
Drain blood from the dorsal organs like somites,
corneal epithelium
Layer: sclera &
choroid
hr chick reviwer
[EMBRYO LAB]
notochord, neural tube
Stomach
Lies medial to the pleural cavities
Dorsal mesogaster
Mesentery dorsal to the stomach
Hepatogastric
ligament
Mesentery ventral to stomach
Has become of sinus venosus
Liver diverticula are embedded in it
Lying above the ductus venosus
Seen when ant. liver diverticulum becomes
continuous with foregut
Mesentery lying dorsal to duodenum
Mesentery lying ventral to duodenum
Lies beneath the ductus venosus & connecting
duodenum
Small tubes found ventrolateral to the dorsal
aorta
Drains blood from allantois
Telencephalic vesicles oval-shaped
evagination
Cavity of telencephalon:
Median telocoel (ventricle III) connects
posteriorly w/ diocoele
2 lateral diocoele (ventricles 1 & 2)
connect with the median telocoel thru
foramen of Monro
syn:ventral mesogaster
Ductus venosus
Anterior liver
diverticulum
syn: cranial liver
diverticulum
duodenum
Mesoduodenum
Hepatoduodenal
ligament
syn:duodenohepatic
ligament
Posterior liver
diverticulum
syn: caudal liver
diverticulum
Pronephros
Allantoic veins
syn:umbilical vein
Telencephalon
Lamina terminalis
Thin section of snterior telencephalic wall
Cerebral hemispheres
hr chick reviwer
Nasal placodes
Thickened layer from skin ectoderm lateral to
telencephalon
Ectodermal invagination on each side of
telencephalon
2 big blood vessel on each side of cranial liver
dicerticulum
Level of gut
Level of duodenum
Ventral to ductus venosus
Caudal to cranial intestinal portal
Appear as conical bulges on each side of body
Composed of somatic mesoderm covered by
skin ectoderm
Thickened as apical ectodermal ridge
Small blood vessels continuous w/ dorsal aorta
syn: olfactory placode
Nasal pit
syn: olfactory pit
Vitelline veins
syn:
omphalomesenteric
vein
Cranial intestinal
portal
syn: anterior intestinal
portal
Wing buds
Intersegmented
arteries
Mesonephric duct
syn: Wolffian duct
Mesonephric
tubules
Mesonephric ridge
Subcardinal veins
Leg buds
Tail bud
Allantois
Chorio-allantoic
membrane
[EMBRYO LAB]
Yolk sac
UROGENITAL SYSTEM
Tiny duct w/ thin wall on each side
Level of wing buds
by cavitation of mesonephric duct rudiment
Paired S-shaped tubules medial to mesonephric
duct
Rounded bulge of dorsal body wall into peritoneal
cavity containing mesonephros
Small blood vessel lying beneath each
mesonephric kidney
Level of the posterior intestinal portal
Remnants of primitive streak and Hensens node
Large mass of undifferentiated cells
Dark mass w/ large irregular sacculation located
to the right of hindgut in extraembryonic coelom
Formed from splachnopleure
Store nitrogenous waste product
Serves as embryonic respiratory organs for birds
Lies beneath the inner shell membrane
For respiration & absorption of calcium for shell
Formed from splanchnopleure that overgrows
yolk
Endodermal cells of yolk sac digest yolk w/c are
External nares
Mesonephric kidneys
hr chick reviwer
Chorion
Amnion
Extraembryonic
coelom
syn: exocoel
Hindgut
Lateral body fold
cloaca
Cloacal membrane
syn: anal plate
Caudal intestinal
portal
syn: posterior intestinal
portal
[EMBRYO LAB]
transported to developing embryo via vitelline
veins
Outer wall of each amniotic fold
Ectoderm on outside w/ adjacent layer of
mesoderm inside
Inner wall of each amniotic fold
Consist of somatic mesoderm on outside and
ectoderm on inside
Somatic mesoderm lined cavity within each
amniotic fold
Continuous with intraembryonic coelom
Endoderm line cavity
Posterior region of the gut
Forms the boundary bet. Embryonic &
extraembryonic regions
Posterior portion of hindgut w/c continuous
ventrally w/ allantois & mesonephric ducts
Double-layered membrane
Ventral endoderm of cloaca fuses w/ ventral skin
ectoderm
Opening formed from hindgut into the
subgerminal cavity
Upon rupture:
anal opening
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)Von EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Development of The Pig EmbryoDokument12 SeitenDevelopment of The Pig EmbryoKarmina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72-HR ChickDokument16 Seiten72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDokument5 Seiten33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogDokument13 SeitenEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Hour ChickDokument13 Seiten48 Hour ChickJowi SalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Development of Pig EmbryoDokument4 SeitenPosterior Development of Pig EmbryoAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDokument9 SeitenBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 MM FrogDokument5 Seiten4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDokument7 SeitenEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDokument5 Seiten48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Chick EmbryoDokument74 SeitenEarly Chick EmbryoMinette EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Dokument6 SeitenANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick 33 HRDokument14 SeitenChick 33 HRaa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Hour Chick EmbryoDokument27 Seiten24 Hour Chick Embryoaa6280% (1)
- 33.48,72 From 2011Dokument63 Seiten33.48,72 From 2011aa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansDokument9 Seiten10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabDokument3 Seiten24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDokument8 Seiten24-Hr Chick EmbryopauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDokument4 SeitenExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDokument48 SeitenChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 MM FrogDokument28 Seiten7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Dokument16 SeitenExercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Gail AmuraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick EmbryoDokument24 SeitenChick Embryonabilalk100% (1)
- Chick 72 HR DDokument35 SeitenChick 72 HR Daa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ex. 9 Chick DevelopmentDokument7 SeitenEx. 9 Chick Developmentfrances agulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Dokument9 SeitenChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDokument14 SeitenEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- 72 HrsDokument35 Seiten72 HrsChristalie Bea FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick 48 HRDokument50 SeitenChick 48 HRaa628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Dokument17 SeitenEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2 4.1 1Dokument11 SeitenExp 2 4.1 1Carlo MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frog EmbryosDokument43 SeitenFrog EmbryosNics Martinez100% (7)
- Exercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDokument8 SeitenExercise 21 Serial Transverse Section of A 72 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 MM Frog EmbryoDokument20 Seiten7 MM Frog EmbryoCourtneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenChick Embryo DevelopmentPaula Manalo-SuliguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenEarly DevelopmentMarina of The SeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDokument18 Seiten24-Hr Chick: Structure Description FateDimple May Gianne DumaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Group Iv CationsDokument5 SeitenAnalysis of Group Iv CationsjudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDokument30 Seiten10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- Serial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoDokument41 SeitenSerial Sections of 10 MM Pig EmbryoChristalie Bea FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chick Embryo WMDokument6 SeitenChick Embryo WMdhyan_ajjah67% (3)
- 18 Hour Chick EmbryoDokument7 Seiten18 Hour Chick Embryoaa628100% (2)
- Chick Serial SectionsDokument74 SeitenChick Serial SectionsKazuki FuchoinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDokument34 Seiten48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDokument4 Seiten10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histo Ra 3 - Barbosa, Azenith VincentDokument7 SeitenHisto Ra 3 - Barbosa, Azenith VincentMinamiSapphire BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dumaguit (2021)Dokument12 SeitenDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenEarly DevelopmentyelloweverglowNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDokument18 Seiten72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Lab Org 2Dokument14 SeitenEmbryo Lab Org 2pauNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsDokument22 Seiten48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsNathan Bantayan100% (1)
- Development of Frog EmbryoDokument13 SeitenDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEVBIOLAB OogensisDokument91 SeitenDEVBIOLAB OogensisDimple May Gianne Dumaguit100% (1)
- Gastrulation and Formation of Germ Layers PDFDokument5 SeitenGastrulation and Formation of Germ Layers PDFElla LagramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24hr Chick Cross SectionsDokument16 Seiten24hr Chick Cross Sectionsaa628100% (9)
- 10 MM FrogDokument23 Seiten10 MM Frogfrances agulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDokument28 Seiten48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Embryology Week OneDokument14 SeitenEarly Embryology Week OnelukesqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48-Hour Chick ReviewerDokument5 Seiten48-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatrice100% (1)
- Circulatory ShockDokument9 SeitenCirculatory ShockTri UtomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- As To Number of People Exercising Government Powers: (Type The Document Title)Dokument2 SeitenAs To Number of People Exercising Government Powers: (Type The Document Title)Astrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo QuizDokument2 SeitenEmbryo QuizAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDokument12 SeitenSunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structures TalagaDokument8 SeitenStructures TalagaAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiscussionDokument1 SeiteDiscussionAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forms of GovernmentDokument2 SeitenForms of GovernmentAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Development of Pig EmbryoDokument4 SeitenPosterior Development of Pig EmbryoAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 HRDokument3 Seiten24 HRAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set On Membrane PotentialDokument1 SeiteProblem Set On Membrane PotentialAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 HR ReviewerDokument7 Seiten48 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxonomic Classification of Phylum Echinodermata PDFDokument1 SeiteTaxonomic Classification of Phylum Echinodermata PDFAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algae Taxonomic ClassificationDokument2 SeitenAlgae Taxonomic ClassificationAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To InvertebratesDokument1 SeiteIntroduction To InvertebratesAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ProtozoaDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To ProtozoaAstrid AmadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terex PPM Crane Att 400 3 Technical Electric Schematic Spare Pats CatalogDokument22 SeitenTerex PPM Crane Att 400 3 Technical Electric Schematic Spare Pats Catalogsharonflores100901san100% (105)
- Gambaran Anatomi Dan Histologi Ginjal Dan Vesika Urinaria PADA MUSANG LUWAK (Paradoxurus Hermaphroditus) DI PULAU TIMORDokument11 SeitenGambaran Anatomi Dan Histologi Ginjal Dan Vesika Urinaria PADA MUSANG LUWAK (Paradoxurus Hermaphroditus) DI PULAU TIMORSaadatulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aurora Poineeers Memeorial College Formerly: Cebuano Barracks Institute Aurora, Zamboanga Del Sur Final Examination College DepartmentDokument6 SeitenAurora Poineeers Memeorial College Formerly: Cebuano Barracks Institute Aurora, Zamboanga Del Sur Final Examination College DepartmentEvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdomen Practice Exam - 1Dokument11 SeitenAbdomen Practice Exam - 1Obinna Adolalom100% (1)
- ANAPHY Lec Session #22 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Dokument9 SeitenANAPHY Lec Session #22 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabiston Textbook of Surgery, 18th Ed. The Biological Basis of Modern Surgical PracticeDokument5 SeitenSabiston Textbook of Surgery, 18th Ed. The Biological Basis of Modern Surgical PracticeNunsio NallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevated Liver Enzymes PDFDokument63 SeitenElevated Liver Enzymes PDFPrakarsa Adi Daya NusantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorDokument14 SeitenNeurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorcindyucdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34-2 PowerPointDokument24 Seiten34-2 PowerPointLeo HellawellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Anatomy With Clinical CorrelationDokument27 SeitenBreast Anatomy With Clinical CorrelationDionix Cruz100% (2)
- Body Systems 6-11Dokument2 SeitenBody Systems 6-11Yelizaveta BondarenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Exam QuestionsDokument32 SeitenClinical Exam QuestionsAtiqah ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vagus Nerve StimulationDokument2 SeitenVagus Nerve StimulationMary Antonette100% (2)
- ImmunochemistryDokument44 SeitenImmunochemistryJowe VarnalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IiiiiiDokument8 SeitenIiiiiiAyusriwahyuni RambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bralette String Pattern PDFDokument3 SeitenBralette String Pattern PDFBelu Villamarin100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Section 3Dokument21 SeitenChapter 12 Section 3api-240305777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genesis Dav Jan 23Dokument7 SeitenGenesis Dav Jan 23Nazmul Alam FarukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Lecture On Cardiac Physiology by Dr. RoomiDokument11 Seiten3rd Lecture On Cardiac Physiology by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (2)
- Histologi KardiovaskularDokument32 SeitenHistologi KardiovaskularMochammad Fariz AmsalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transplantation ImmunologyDokument50 SeitenTransplantation ImmunologyОльга КоваленкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology vs. Anatomy: by Sarah C.P. Willaims Medically Reviewed by Minesh Khatri, MD On July 28, 2021Dokument2 SeitenPhysiology vs. Anatomy: by Sarah C.P. Willaims Medically Reviewed by Minesh Khatri, MD On July 28, 2021exo oxeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salivary GlandsDokument97 SeitenSalivary GlandsSwati George100% (2)
- EfnodipineDokument4 SeitenEfnodipineSAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Bagian-Bagian Nama PhantomDokument9 SeitenBagian-Bagian Nama PhantomAlviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pysiology Schedule 2020 2021Dokument3 SeitenPysiology Schedule 2020 2021MB MontalboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothlamic-Pituitary Physiology: Mona Abou Chebl MD. METABOLISM-2018 Lectures 1-2 March 14 2018Dokument213 SeitenHypothlamic-Pituitary Physiology: Mona Abou Chebl MD. METABOLISM-2018 Lectures 1-2 March 14 2018rachid09Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 06Dokument19 SeitenCH 06cyberyeung0% (1)
- Brain & Nervous System Health Center: Image Collection: Human AnatomyDokument1 SeiteBrain & Nervous System Health Center: Image Collection: Human AnatomyNica NebrejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science6 ST1 Q2Dokument2 SeitenScience6 ST1 Q2Joseph PederisoNoch keine Bewertungen