Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chap 1 Science Form 2
Hochgeladen von
Yobal YeuOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chap 1 Science Form 2
Hochgeladen von
Yobal YeuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SCIENCE FORM 2: MODULE CHAPTER 1:THE WORLD THROUGH OUR SENSES
B4 Relationship between sensory organs and their stimuli.
B4
1. Complete the table on the senses, sensory organs and stimuli detected.
Senses
Sensory Organ
Stimuli
eye
sound
chemical vapour
chemical substances
touch
sight
touch
tongue
nose
ear
hearing
smell
light
taste
skin
2. Complete the path of an impulse after a stimulus is received by the receptor in a sensory organ.
Stimulus
_____________________________
(In Sensory Organ)
_________________ (Example: muscle)
B2
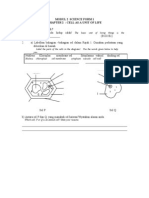
B2 Hearing Mechanism
1. Label parts of ear below.
1
auditory canal
semicircular canal
oval window
ear drum
ear pinna
Eustachian tube
cochlea
ossicles
auditory nerve
2. What is the function of the ear?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
3. State the parts of the ear which carry out the function stated in the table.
Parts of the ear
Outer Ear
Function
(a)
collects and directs sound waves into the ear
(b)
channels sound waves to the eardrum
(c)
vibrates when it is hit by sound waves
Middle
Ear
(d)
amplify sound vibrations
(e)
sends vibrations from the middle ear into the inner ear
Inner Ear
(f)
converts sound vibrations into nerve impulses
(g)
sends nerve impulses to the brain for interpretation
(h)
equalises air pressure on both sides of eardrum
(i)
controls body balance
4. Tick () two structures of the ear which do not play a part in hearing.
ear pinna
semicircular canal
Eustachian tube
2
5. Complete the path of a sound wave in the hearing mechanism.
Ear Pinna
Oval window
Brain
B2 Sight Mechanism
B2
Label parts of eye below.
aqueous humour
eye lens
blind spot
yellow spot
cornea
iris
suspensory ligaments
optic nerve
retina
conjuctiva
pupil
ciliary muscle
vitreous humour
choroid
sclera
1. What is the function of the eye?
_______________________________________________________________________________________
2. State the parts of eye which carry out the functions stated in the table.
Parts of Eye
Function
refracts light and helps to focus light on to the retina
3
focuses light onto the retina
controls the size of pupil
allows light to enter the eye
change the thickness of the lens
hold the eye lens
maintains the shape of the eye and helps to refract and focus light onto the
retina
protects and gives the shape of the eyeball
prevents reflection of light in the eye and supplies oxygen and nutrients to the
eye
detects light and converts it into nerve impulses
the part of eye that is most sensitive to light stimulus
sends nerve impulses from retina to the brain for interpretation
3. Complete the path of light in the eye.
Cornea
Vitreous humour
Brain
4. Choose the correct answers to explain the change in the size of the pupil in different situation.
(a) When we move from a dark place to a bright place, the pupils (constrict / enlarge) to (allow / prevent)
more light from entering our eyes.
(b) When we move from a bright place to a dark place, the pupils (constrict /enlarge) to (allow / prevent)
more light to enter our eyes.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Performance STD Science Yr 1 KSSRDokument7 SeitenPerformance STD Science Yr 1 KSSRsyazalina83Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Revision WritingDokument5 SeitenSPM Revision WritingShafizamra Hj Anuar100% (3)
- Modul 2 Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell As A Unit of Life What Is Cell?Dokument22 SeitenModul 2 Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell As A Unit of Life What Is Cell?Nurhuda MitieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dont Think About A ZebraDokument2 SeitenDont Think About A ZebraD2WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox ExperimentsDokument12 SeitenRedox Experimentsryder1man6433100% (1)
- Blood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansDokument14 SeitenBlood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansJames WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upsr ScienceDokument30 SeitenUpsr ScienceShyweyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 4 Chapter 5 5.2Dokument38 SeitenScience Form 4 Chapter 5 5.2KSSM TSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1Dokument2 SeitenScience Form 3 Chapter 1Mazidah MokhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 5 Chapter 6Dokument44 SeitenScience Form 5 Chapter 6Ashwin Josiah Samuel100% (1)
- Sept Break SPM ModuleDokument17 SeitenSept Break SPM Modulehumbra22100% (4)
- Chapter 8 Basic MeasurementsDokument2 SeitenChapter 8 Basic Measurementscikguanuar75% (4)
- Science F3 Chapter 8 Generation of Electricity-Paper 2 AnswersDokument1 SeiteScience F3 Chapter 8 Generation of Electricity-Paper 2 AnswersRebecca Choong Xin HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo chemistry: Exothermic vs Endothermic ReactionsDokument20 SeitenThermo chemistry: Exothermic vs Endothermic ReactionsAzie Nurul Akhtar100% (1)
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction GuideDokument23 SeitenSexual and Asexual Reproduction GuideHazira HaidzirNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Air Tawar Microorganisms Form 5 Science NotesDokument235 SeitenSMK Air Tawar Microorganisms Form 5 Science Noteskembara08100% (1)
- Mind Map Upsr-CompleteDokument89 SeitenMind Map Upsr-CompleteAziah AwanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced & Unbalanced Forces Practice 2012Dokument2 SeitenBalanced & Unbalanced Forces Practice 2012ibnurasheeda100% (1)
- Tangent and Secant SegmentsDokument9 SeitenTangent and Secant SegmentsJahariah Paglangan CernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nor Diana Binti HassanDokument2 SeitenNor Diana Binti HassanFazwadi Haliah100% (1)
- M013-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Dokument5 SeitenM013-Consumer Mathematics (Taxation)Tan Jun YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microorganism Science Year 5Dokument5 SeitenMicroorganism Science Year 5usemyknow.blogspot.com100% (1)
- Science Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFDokument4 SeitenScience Form 3 Chapter 2 - Blood Circulation PDFFarah Sofea Razali91% (11)
- Mathematics Form 3Dokument24 SeitenMathematics Form 3Amal SufiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Science Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenForm 4 Science Chapter 3Suryakala Sundram Sivaananda Sundram75% (8)
- Section A (10 MARKS) : Teliti Nota Di Bawah Dan Gunakan Maklumat Yang Diberi Untuk Melengkapkan TeksDokument7 SeitenSection A (10 MARKS) : Teliti Nota Di Bawah Dan Gunakan Maklumat Yang Diberi Untuk Melengkapkan TeksGee Yoke TingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Circulation and TransportDokument15 SeitenBlood Circulation and TransportSENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Chapter 2 Form 4Dokument16 SeitenScience Chapter 2 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin75% (4)
- SPM Biology Chapter 6Dokument32 SeitenSPM Biology Chapter 6birinthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tips and Guidelines for PMR Paper 2 WritingDokument40 SeitenTips and Guidelines for PMR Paper 2 Writingrmakunsai100% (1)
- Science Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentDokument8 SeitenScience Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Science Pt3Dokument11 SeitenModule Science Pt3lccjane8504Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 5Dokument3 SeitenChemistry Form 5alliey75% (8)
- Science Form 4 Chapter 5Dokument7 SeitenScience Form 4 Chapter 5Suryakala Sundram Sivaananda Sundram100% (2)
- Chapter 6Dokument1 SeiteChapter 6cikguanuar100% (1)
- Sce Form 2Dokument22 SeitenSce Form 2williamkong123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Kbat Sains MagnetDokument3 SeitenSoalan Kbat Sains MagnetSithira Devi Sabaratnam100% (1)
- English SPMDokument18 SeitenEnglish SPMSiti Norazliza Ramli100% (1)
- Science Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2 NotesDokument6 SeitenScience Form 1 KSSM Chapter 2 NotesNisa Muhd0% (2)
- Biology Form 4 RevisionDokument18 SeitenBiology Form 4 RevisionAyu YunusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 4 ThermochemistryDokument4 SeitenShort Note Chemistry Form 5-Chapter 4 Thermochemistrysalamah_sabri100% (2)
- Carbon Compounds ChapterDokument2 SeitenCarbon Compounds ChapterAngie Kong Su Mei67% (3)
- Solid Geometry 2 AnswerDokument15 SeitenSolid Geometry 2 AnswerHazri Mohd HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pt3 B. Inggeris Pertengahan Tahun 2015 LatestDokument12 SeitenPt3 B. Inggeris Pertengahan Tahun 2015 LatestScRembauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living Things ModuleDokument17 SeitenLiving Things ModuleZulkifli BudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- There Are Three Sections in This Paper: Section A, Section B and Section C. Answer All QuestionsDokument6 SeitenThere Are Three Sections in This Paper: Section A, Section B and Section C. Answer All QuestionsNur Aleeza June ZakeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Form 4 Exercise Periodic Table of ElementsDokument3 SeitenSPM Form 4 Exercise Periodic Table of Elementsasparagus1996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Upsr Volume 2 Module Task Force Seremban PDFDokument121 SeitenEng Upsr Volume 2 Module Task Force Seremban PDFJantai Jubin100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Solid Geometry 1Dokument2 SeitenChapter 12 Solid Geometry 1cikguanuar67% (3)
- Module Chapter 3Dokument32 SeitenModule Chapter 3Miz MiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Processes of PlantsDokument2 SeitenLife Processes of PlantsChomp Stad100% (1)
- Sentence RearrangementDokument22 SeitenSentence RearrangementKNOWLEDGE CREATORSNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDokument5 SeitenThe Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsHafiy Yusoff100% (1)
- English Year 4 Paper 2Dokument6 SeitenEnglish Year 4 Paper 2Tom Kurtis YorkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Social Studies Yr 4Dokument8 SeitenExam Social Studies Yr 4Afezz greenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Through Our SensesDokument14 SeitenThe World Through Our SensesamyryuzainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ls2 Our Sense OrganDokument12 Seitenls2 Our Sense OrganHeart Trixie Tacder SalvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One: Learning Area: The World Through Our Senses Learning ObjectivesDokument21 SeitenChapter One: Learning Area: The World Through Our Senses Learning ObjectivesMona MohtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Science F3 DLPDokument36 SeitenModul Science F3 DLPChuahSiewHoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Nervous SystemDokument6 SeitenManual Nervous SystemVynz Morales CosepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 4 Science Form 2Dokument9 SeitenChap 4 Science Form 2Yobal Yeu80% (5)
- Biodiversity Form 2 Module Chapter 3Dokument2 SeitenBiodiversity Form 2 Module Chapter 3Yobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - 4 Solution and SolubilityDokument3 Seiten5 - 4 Solution and SolubilityYobal Yeu100% (1)
- 5 - 4 Solution and Solubility (E)Dokument6 Seiten5 - 4 Solution and Solubility (E)Yobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDokument18 SeitenChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesYobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - 2 Composition of Water (A) - (B)Dokument4 Seiten5 - 2 Composition of Water (A) - (B)Yobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Chapter 5 - Motions Objective QuestionsDokument4 SeitenForm 5 Chapter 5 - Motions Objective QuestionsYobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - 4 Solution and Solubility (A) (B)Dokument6 Seiten5 - 4 Solution and Solubility (A) (B)Yobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - 4 Solution and Solubility (G)Dokument4 Seiten5 - 4 Solution and Solubility (G)Yobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDokument18 SeitenChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesYobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Chapter 5 - Motions Objective QuestionsDokument4 SeitenForm 5 Chapter 5 - Motions Objective QuestionsYobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunityDokument32 SeitenImmunityYobal YeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDokument17 SeitenScience Form 2 Notes on Water Solutions Acids and AlkalisDhiipagesan Muniandy100% (1)
- f2 Worksheet 6.2 2Dokument7 Seitenf2 Worksheet 6.2 2Yobal Yeu0% (1)
- f2 Revision Chapter 10 PDFDokument6 Seitenf2 Revision Chapter 10 PDFIzudin HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz # 50-100Dokument6 SeitenQuiz # 50-100Jhunjhun SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 3Dokument62 SeitenEnglish 3Danica BarbaronaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADE-3-2nd Quarter RDokument9 SeitenGRADE-3-2nd Quarter RCharmaine Paragas GalleneroNoch keine Bewertungen
- UHVPE Q&A Unit 2Dokument18 SeitenUHVPE Q&A Unit 2Tanishq SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature's Superheroes: Animals with Amazing AbilitiesDokument11 SeitenNature's Superheroes: Animals with Amazing AbilitiesNurul MuslimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archaeology and The Senses - Human Experience, Memory, and AffectDokument272 SeitenArchaeology and The Senses - Human Experience, Memory, and Affectachour100% (1)
- PERDEV CompleteDokument273 SeitenPERDEV CompleteKen Walker100% (1)
- Behavioural Sciences in Medical Practice, 2nd Ed Manju MehtaDokument268 SeitenBehavioural Sciences in Medical Practice, 2nd Ed Manju Mehtashafijan100% (1)
- LISSKA, Anthony J. - Aquinas's Theory of Perception. An Analytic ReconstructionDokument372 SeitenLISSKA, Anthony J. - Aquinas's Theory of Perception. An Analytic ReconstructionCaio Cézar Silva100% (1)
- Considerations: Social and PsychologicalDokument19 SeitenConsiderations: Social and PsychologicalRalph Vincent Valdez TamangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 4 3 2 1 Sensory Grounding Exercise PDFDokument4 Seiten5 4 3 2 1 Sensory Grounding Exercise PDFtaurusho100% (1)
- How Generation Z Learns Better PDFDokument11 SeitenHow Generation Z Learns Better PDFJosh A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 3Dokument18 SeitenTest 3Robert ChiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Remedies of Dr. John Henry ClarkeDokument247 Seiten13 Remedies of Dr. John Henry ClarkeNadeem Akhter100% (1)
- Is Psychology A ScienceDokument17 SeitenIs Psychology A ScienceDavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Film Director Interview QuestionsDokument10 SeitenFilm Director Interview QuestionsMùi ThúyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educ 3 Modyul FOR STUDENTDokument67 SeitenEduc 3 Modyul FOR STUDENTThereze CedeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Five Senses Lp2Dokument2 SeitenFive Senses Lp2aputtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Imagery: Shane Mharey R. Noble Manuel Francis Aino M. GealanDokument14 SeitenSensory Imagery: Shane Mharey R. Noble Manuel Francis Aino M. GealanRafael DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Cranial Nerves: Functions and LocationsDokument3 Seiten12 Cranial Nerves: Functions and LocationsPam ZingapanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANIG 1624 Animal EthologyDokument15 SeitenANIG 1624 Animal EthologyNanelo MzileniNoch keine Bewertungen
- English 10 Q 1 Week 4Dokument24 SeitenEnglish 10 Q 1 Week 4John Carlo Gonzales100% (1)
- sCARF: A Brain-Based Model For Collaborating With and Influencing OthersDokument10 SeitensCARF: A Brain-Based Model For Collaborating With and Influencing OthersyamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- HowtospeakmermaidDokument65 SeitenHowtospeakmermaidRaquel Lara RezendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 - Number Series For Psychological Normalization - Book1Dokument208 Seiten2004 - Number Series For Psychological Normalization - Book1Carla Perin67% (3)
- Ricci Psichiatriabun - It.enDokument122 SeitenRicci Psichiatriabun - It.enCosmin DeaconuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensation and Perception: PsychologyDokument92 SeitenSensation and Perception: Psychologysummer rrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eclipse Phase 2 - PsiDokument14 SeitenEclipse Phase 2 - PsiJaviergvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptability of Musa Balbisiana (Saba Banana) and Ipomea Batatas (Sweet Potato) Flavored Ice CreamDokument4 SeitenAcceptability of Musa Balbisiana (Saba Banana) and Ipomea Batatas (Sweet Potato) Flavored Ice CreamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Six Ways To Values - Philosphy PDFDokument312 SeitenSix Ways To Values - Philosphy PDFVarun DevNoch keine Bewertungen