Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
QMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling: Chapter 1 What Is Statistics?
Hochgeladen von
Faith0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
8 Ansichten2 Seitenmath
Originaltitel
2014_Ch.1_Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenmath
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
8 Ansichten2 SeitenQMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling: Chapter 1 What Is Statistics?
Hochgeladen von
Faithmath
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
QMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling
Chapter 1 What is Statistics?
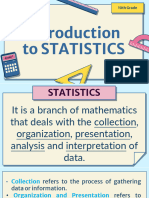
Statistics
Statistics is the science that deals with collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data.
Collection of data is the process of obtaining measurements or counts. Valid conclusions can
result from properly collected data.
Organization of data is the task of presenting the collected measurements or counts in a form
suitable for deriving logical conclusions. Representative methods of organizing and presenting
data by means of tables and graphs will be used.
Analysis of data is the process of extracting relevant information from the given measurements or
counts, from which a summarized and comprehensive numerical description can be tabulated.
Interpretation of data is the task of drawing conclusions from analysis of the data and usually
involves the formulation of predictions concerning a large collection of objects from information
available for a small collection of similar objects. This forms the most important topics in the
statistical inference.
Definition of Statistical Terms
A population is the complete collection of measurements, objects, or individuals under
consideration.
A sample is the portion of the population that is selected for analysis.
A parameter is a summary measure that describes a characteristic of an entire population.
A statistic is a summary measure that describes a characteristic of a sample.
The process of selecting a subset of data from the population of interest is called sampling.
Descriptive statistics is the science of describing the important aspects of a set of data. It can be
defined as those methods focusing on the collection, presentation, and characterization of a set of
data in order to describe properly the various features of that set of data.
Inferential statistics is the science of using sample data to make generalization about the
important aspects of population data. It can be defined as those methods that make possible the
estimation of a characteristic of a population or the making of a decision concerning a population
based only on sample results.
Chapter 2 Types of Data
Interval (quantitative or numerical) data are data values that are measured on a numerical scale.
Nominal (qualitative or categorical) data are data values, each of which can be classified into a
single category that belongs to a set of categories.
Ordinal data appear to be nominal but the difference is that the order of their values has meaning.
Discrete data result from a countable number of possible values that arise from a counting
process.
Continuous data result from infinitely many possible values that can be associated with points on
a continuous scale in such a way that there are no gaps or interruptions.
Review Problems: 1.4, 1.8, 2.2, 2.6, 2.8.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Business StatisticsDokument86 SeitenBusiness Statisticsmulu12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summarize Topic in StatisticalDokument5 SeitenSummarize Topic in StatisticalBanesa AsistioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic StatisticsDokument53 SeitenBasic Statisticsአንተነህ የእናቱNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scholarly Publication-CHAPTER 1 & 2.pdf261-1176727076Dokument25 SeitenScholarly Publication-CHAPTER 1 & 2.pdf261-1176727076lataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Statistics (SRWM)Dokument141 SeitenIntroduction To Statistics (SRWM)Suvankar NandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument20 SeitenCH 1kidanemariam teseraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of StatisticsDokument4 SeitenDefinition of StatisticsJulie ann YbanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One: 1.1definition and Classification of StatisticsDokument22 SeitenChapter One: 1.1definition and Classification of StatisticsasratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Chapter 1Dokument8 SeitenStatistics Chapter 1kasutaye192Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1: Introduction To Probability and Statistics For Civil EngineeringDokument18 SeitenChapter - 1: Introduction To Probability and Statistics For Civil Engineeringznour alyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive and Inferential StatisticDokument11 SeitenDescriptive and Inferential StatisticJanine Leigh BacalsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processing and Analyzing Data: Construction Management ChairDokument29 SeitenProcessing and Analyzing Data: Construction Management ChairhayelomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDokument9 SeitenChapter 1 IntroductionDinksrawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of StatisticsDokument10 SeitenFundamentals of StatisticsLucky GojeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stats and Proba 240878Dokument130 SeitenStats and Proba 240878bahru demekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Statistics For Analysis and Interpretation of Assessment DataDokument24 SeitenBasic Statistics For Analysis and Interpretation of Assessment DataIhsanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat 1-3 ChaptersDokument36 SeitenStat 1-3 ChaptersGizachew NadewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Introduction To StatisticsDokument9 SeitenLesson 1 Introduction To StatisticsFrancis OnyangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument6 SeitenUnit 1subhankar fcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Is The Study of The Collection, Organization, Analysis, and Interpretation of DataDokument1 SeiteStatistics Is The Study of The Collection, Organization, Analysis, and Interpretation of DataArbie FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument9 SeitenChapter 1Roha CbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDokument5 SeitenSSheila PalabayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability and StatisticsDokument6 SeitenProbability and Statisticssubhan sibghatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat I CH - IDokument19 SeitenStat I CH - Ibrucknasu279Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Statistics MastersDokument13 SeitenLesson 1 Statistics MastersNieva FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument16 SeitenChapter 1hussein mohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To StatisticsDokument24 SeitenIntroduction To Statisticssunhyep.kimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1define What Is StatisticDokument2 Seiten1define What Is StatisticJairah CammayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1 PDFDokument106 SeitenCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1 PDFMuket AgmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 CH 1 Up 9 Probability NoteDokument104 Seiten2013 CH 1 Up 9 Probability NoteZemenu mandefroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average: Sagni D. 1Dokument85 SeitenAverage: Sagni D. 1keebeekNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-1 Stat IDokument13 SeitenCH-1 Stat IFraol DabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Stat 1-2 PDF-1-1Dokument15 SeitenBasic Stat 1-2 PDF-1-1efrem atsbahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics IntroDokument5 SeitenStatistics IntroMai Mgcini BhebheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generalstatistics 091020092539 Phpapp01Dokument129 SeitenGeneralstatistics 091020092539 Phpapp01Penny BesidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability and Statistics Final-3Dokument106 SeitenProbability and Statistics Final-3Abel MaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec - Not On Statistics and ProbabilityDokument118 SeitenLec - Not On Statistics and ProbabilityBetsegaw DemekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Meaning, Types and Limitations of StatisticsDokument6 SeitenLesson 1 - Meaning, Types and Limitations of StatisticsrelebohilemochesaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 7-1Dokument4 SeitenChap 7-1Milkias MuseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educ 201Dokument2 SeitenEduc 201Neña Dela Torre GanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- StatisticsDokument3 SeitenStatistics11ABM Isamiel Grace MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAS 111 Week 1Dokument3 SeitenPAS 111 Week 1Franz PampolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-1 Introduction To StatisticsDokument5 SeitenCH-1 Introduction To StatisticsMelaku DegefuNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Book On Essentials of Business Analytics: Group 7Dokument6 SeitenE-Book On Essentials of Business Analytics: Group 7Mark Gabriel GerillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 Data Management (Statistics)Dokument116 SeitenTopic 5 Data Management (Statistics)Kimberly V. TumulakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 AND 2-b.s.Dokument9 SeitenChapter 1 AND 2-b.s.yahoshu.pandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Note (Chapter-I and II) PDFDokument26 SeitenLecture Note (Chapter-I and II) PDFabi adamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business StatisticsDokument506 SeitenBusiness StatisticsLokesh Baskaran100% (22)
- Principles of Statistical AnalysisDokument21 SeitenPrinciples of Statistical AnalysisKeithNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Exactly Is Data ScienceDokument15 SeitenWhat Exactly Is Data Sciences6652565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Ii PartialDokument106 SeitenQuantitative Ii PartialWendy CevallosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Definition of StatisticsDokument48 SeitenLesson 1 - Definition of StatisticsSERALDYN SAMSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business AnalyticsDokument40 SeitenBusiness Analyticsvaishnavidevi dharmarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4. Data ManagementDokument12 SeitenModule 4. Data ManagementHotaro OrekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Non Parametric Methods Through R SoftwareVon EverandIntroduction To Non Parametric Methods Through R SoftwareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Business Statistics Through R Software: SoftwareVon EverandIntroduction To Business Statistics Through R Software: SoftwareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning - A Complete Exploration of Highly Advanced Machine Learning Concepts, Best Practices and Techniques: 4Von EverandMachine Learning - A Complete Exploration of Highly Advanced Machine Learning Concepts, Best Practices and Techniques: 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biostatistics Explored Through R Software: An OverviewVon EverandBiostatistics Explored Through R Software: An OverviewBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- EELC131 - Week 4 Class 2Dokument8 SeitenEELC131 - Week 4 Class 2FaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- X X B X B X B y X X B X B N B Y: QMDS 202 Data Analysis and ModelingDokument6 SeitenX X B X B X B y X X B X B N B Y: QMDS 202 Data Analysis and ModelingFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Inference About A Population: QMDS 202 Data Analysis and ModelingDokument7 SeitenChapter 12 Inference About A Population: QMDS 202 Data Analysis and ModelingFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Ch.17 Example-3Dokument4 Seiten2014 Ch.17 Example-3FaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- QMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling: Chapter 15 Chi-Squared TestsDokument5 SeitenQMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling: Chapter 15 Chi-Squared TestsFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- QMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling: Chapter 14 Analysis of VarianceDokument7 SeitenQMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling: Chapter 14 Analysis of VarianceFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 Inference About Comparing Two Populations: QMDS 202 Data Analysis and ModelingDokument9 SeitenChapter 13 Inference About Comparing Two Populations: QMDS 202 Data Analysis and ModelingFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- QMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling Formula Sheet: N X N X N N X X X N X X S N X N XDokument4 SeitenQMDS 202 Data Analysis and Modeling Formula Sheet: N X N X N N X X X N X X S N X N XFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- EthicsDokument12 SeitenEthicsFaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Research Report: Please Refer To The Project OutlineDokument6 SeitenHow To Write A Research Report: Please Refer To The Project OutlineFaithNoch keine Bewertungen