Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Recycled Aggregate Concrete
Hochgeladen von
Eng Abdikarim WalhadOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Recycled Aggregate Concrete
Hochgeladen von
Eng Abdikarim WalhadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The International Reviewer
Volume 1 | Issue 2 | July - December 2014 | pp. 30-33 | ISSN 2395-1575
RECYCLED AGGREGATE CONCRETE
(Received: 23 October 2013; Revised: 22 December 2013; Accepted: 20 June 2014)
(Article Type: Research, Theme: Concrete Technology/Construction & Demolition Waste Management)
Sunil
A. U. Ravishankar
Department of Civil Engineering
M. S. Ramaiah Institute of Technology
Bangalore-560054, Karnataka, India
E-mail: sunil.patil959@gmail.com
Department of Civil Engineering
National Institute of Technology Surathkal
Mangalore-575025, Karnataka, India
S. M. Naik
Suresha S. N.
Department of Civil Engineering
M. S. Ramaiah Institute of Technology
Bangalore-560054, Karnataka, India
Department of Civil Engineering
National Institute of Technology Surathkal
Mangalore-575025, Karnataka, India-575025
Abstract - A Comparative analysis of the experimental results of
the properties of fresh and hardened concrete with different
replacement ratios of natural with recycled aggregate is
presented in the paper. Recycled aggregate was made by
crushing the waste concrete of laboratory test cubes and precast
concrete columns. In this project, the different tests are carried
out on recycled aggregates and Mix design of concrete of grade
M20 by using IS1260:2009 and IS456:2000. Compare the strength
of recycled aggregate concrete for 100% and 75% of recycled
aggregates for 7, 14, 21 days and also find the Modulus of
Elasticity and Splitting Tensile Strength of test specimens Load
testing of reinforced concrete beams made of the investigated
concrete types is also presented in the paper. Regardless of the
Replacement ratio, recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) had a
satisfactory performance, which did not differ significantly from
the performance of control concrete in this experimental
research. However, for this to be fulfilled, it is necessary to use
quality recycled concrete coarse aggregate and to follow the
specific rules for design and production of this new concrete
type.
Keywords- recycled; aggregate; concrete; properties; mix.
I.
INTRODUCTION
Recycled aggregate are comprised of crushed, graded
inorganic particles processed from the materials that have
been used in the construction and demolition debris. These
materials are generally from buildings, roads, bridges, and
sometimes even from catastrophes, such as wars and
earthquakes. Recycled aggregate is generally produced by
two stages crushing of demolished concrete, screening and
removal of contaminants such as reinforcement, plastic etc.
Concrete made with such aggregates is called as
Recycled aggregate Concrete (RAC). Demolition of old and
deteriorated buildings and traffic infrastructure, and their
substitution with new ones, is a frequent phenomenon
today in a large part of the world.
Reuse of waste concrete is beneficial from the view point
of environmental protection and resources reservation. The
most common method of managing this material has been
through its disposal in landfills. In this way, huge deposits of
construction waste are created, consequently becoming a
special problem of human environment pollution.
For this reason, in developed countries, laws have been
brought into practice to restrict this waste: in the form of
prohibitions or special taxes existing for creating waste
areas.
II.
LITERATURE SURVEY
Limbachiya and Leelawat (2000) found that recycled
aggregate concrete had 7 to 9% lower relative density and 2
times higher water absorption than natural aggregate.
According to Bodin and Zaharieva, precautions must also
be taken of pathological reactions such as alkali aggregate
reaction and sulphate reaction in the industrially produced
recycled aggregate.
For the undying research spirit within you.
30
www.theinternationalreviewer.info
Copyright 2013 All rights reserved
theinternationalreviewer@gmail.com
The International Reviewer
Volume 1 | Issue 2 | July - December 2014 | pp. 30-33 | ISSN 2395-1575
Sunil et al., Recycled Aggregate Concrete
III.
EXPERIMENTAL METHODOLOGY: PROCESSING OF RAC
In this project, the recycled concrete aggregates are
obtained from the big concrete blocks which are kept in
Structural Lab, NITK Surathkal. These blocks are first crushed
by using Hammer to a size of 40mm or less then it is crushed
by using Crusher. Due to this the recycled aggregates of size
10mm to 20mm are obtained. These recycled aggregates are
wet they are dried by keeping in oven for 24 days. The
different tests are carried out on finally obtained recycled
aggregates and Mix design of concrete of grade M20 by
using IS 1260:2009 and IS 456:2000.
Table 2: Properties of RAC.
Properties
Specific gravity
Recycled Aggregate
Concrete
2.57
Water absorption
1.21%
Aggregate Impact Value
30.69%
Aggregate Crushing Value
29.86%
ii) Mix Proportions
The compressive strength increased with a decrease in
w/c ratio and is directly proportional to strength of blended
aggregate. However, when used at higher level of
replacement, the high water absorption ability of recycled
aggregate resulted in the higher total water demand. We
Know that, Target Strength for M20 Mix proportion is 20 +
(1.65x4) as equal to 26.6MPa and the Ratio of
Cement:Sand:aggregate was arrived at as 1:2.65:3.92. The
results are tabulated under Table3.
Table 3: Mix Proportion.
Cement
Water
Fine aggregate
Coarse aggregate
Water Cement ratio
Fine aggregate to Cement ratio
Coarse aggregate to Cement ratio
Slump
Fig. 1: Particle size distribution [Photo taken by Author].
IV.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
i) Properties of RAC
Sum of Cumulative Percentage Retained = 533.8
Fineness Modulus = 533.8/100 = 5.338
iii) Slump Test
Table 1: Particle Size Distribution.
IS Sieve
40mm
20mm
10mm
4.75mm
2.36mm
1.18mm
600micron
150micron
Weight
Retained
(kg)
Cumulative
Weight
Retained
(kg)
0
0.1750
2.475
1.806
0.23
0.15
0.10
0.05
0
0.170
2.645
4.451
4.681
4.831
4.931
4.981
300kg/m3
148.8 kg/m3
796kg
1173.462kg
0.50
2.65
3.92
50mm
Cumulative
Percentage
Weight
Retained
(%)
0
3.4
52.9
89.02
93.62
96.62
98.62
99.62
Cumulative
Percentage
Passing
(%)
100
96.6
47.1
10.98
6.38
3.38
1.38
0.38
Table 4: Variation of Slump with Percentage of RAC.
Percentage of Recycled Aggregate (%)
Slump (mm)
100% recycled aggregate
48
75% recycled aggregate
55
Slump test was used to determine the workability of
fresh concrete. The slump less than 25mm indicates a very
stiff concrete and a slump that more than 125mm indicates
a running concrete. The results indicated 48mm for 100%
recycled aggregate and 55 mm for 75% recycled aggregate.
The results are tabulated under Table 4.
For the undying research spirit within you.
31
www.theinternationalreviewer.info
Copyright 2013 All rights reserved
theinternationalreviewer@gmail.com
The International Reviewer
Volume 1 | Issue 2 | July - December 2014 | pp. 30-33 | ISSN 2395-1575
Sunil et al., Recycled Aggregate Concrete
IV) Compression Test
V) Modulus of Elasticity Test
A Concrete mix having cement, fine aggregate and coarse
aggregate in the ratio of 1:2.65:3.92 was prepared. The
components were mixed using machine in adding water
cement ratio of 0.50 during the process. The concrete mix
was filled in 9 cube moulds kept for 24 hours. After 24 hours,
the specimens were demoulded and kept immersed in water
for 7, 14 and 21 days after which they were removed for
testing. The results are tabulated under Table 5.
Moulded test specimens (cylinders) were of the size
150x300mm. 3 such specimens were prepared using same
concrete mix design as compressive strength and tested
after 21 days of curing. The results are presented under
Chart 1.
Fig. 4: Specimen in Compression Testing Machine
Fig. 2: Test Specimen in Compression Testing Machine.
Chart 1: Specimen Load Variation (KN) with Deflection (cm)
vi) Splitting Tensile Strength Test of Concrete.
Table 6: Variation of Splitting Tensile Strength with Ultimate Load.
Fig. 3: Test Specimen at Failure.
Specimens
Table 5: Variation of Compressive Strength.
Weight of
Cylinder (kg)
Ultimate Load
Split Tensile
Strength (MPa)
P (KN)
Percentage of
Recycled
Aggregate
Concrete
Compressive
Strength for
7days
(MPa)
Compressive
Strength for
14days
(MPa)
Compressive
Strength for
21days
(MPa)
100%
21.24
23.62
24.88
75%
23.70
24.98
25.99
2P/ (DL)
1
2
3
12.56
12.46
12.60
190
180
195
190
2.54
2.75
For the undying research spirit within you.
32
www.theinternationalreviewer.info
Copyright 2013 All rights reserved
theinternationalreviewer@gmail.com
The International Reviewer
Volume 1 | Issue 2 | July - December 2014 | pp. 30-33 | ISSN 2395-1575
Sunil et al., Recycled Aggregate Concrete
Moulded test specimens (cylinders) are of the size
150x300mm. 3 such specimens were prepared using same
concrete mix design and tested after 21days of curing. The
results are tabulated under Table 6.
By using Recycled aggregates in construction it will
maximize the economic and environmental benefits. The
Compressive Strength of Concrete will decreases with
increase in Percentage of Recycled Aggregates for 7, 14, 21
days. The Modulus of Elasticity of Concrete is an important
property in Mix Design. The modulus of elasticity of concrete
also affects its strength. Characteristic Strength of concrete
is E=5000fck. Splitting Tensile Strength Test is simple and
gives uniform results. The Average Tensile Strength is
2.65MPa for 21 days test specimen. Average Compressive
Strength for 100% of Recycled aggregate at 21days specimen
is 24.98MPa. Average Compressive Strength for 75% of
Recycled aggregate at 21days specimen is 25.99MPa.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Fig. 5: Concrete Specimen in Splitting Tensile Testing Machine .
I would like to express my deep sense of gratitude to
Prof. Katta Venkataramana, Head of the Department, Civil
Engineering, NITK, Surathkal, whose encouragement has
made me to do so far.
REFERENCES
[1]
Limbachiya M.C., Leelawat T. and Dhir R.K.; Use of recycled
concrete aggregate in high-strength concrete, Materials and Structures,
Vol. 33, pp. 574-580, 2000.
[2]
Buyle-Bodin F. and Hadijieva-Zaharieva R.; Influence of
industrially produced recycled aggregates on flow properties of
concrete, Materials and Structures, Vol. 35, pp. 504-509, 2002.
Fig. 6: Test Specimen in Failure.
V.
CONCLUSION
Using Recycled fine aggregates in concrete can prove to
be better however in less quantity and can be
recommended for lower grade applications like lower layers
of roads such Sub base course and base course.
For the undying research spirit within you.
33
www.theinternationalreviewer.info
Copyright 2013 All rights reserved
theinternationalreviewer@gmail.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- As 2528-1982 Bolts Studbolts and Nuts For Flanges and Other High and Low Temperature ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenAs 2528-1982 Bolts Studbolts and Nuts For Flanges and Other High and Low Temperature ApplicationsSAI Global - APAC67% (3)
- ACI 216.1-07 Code Requirements For Determining Fire Resistance of Concrete and Masonry Construction Assemblies - MyCivil - IrDokument32 SeitenACI 216.1-07 Code Requirements For Determining Fire Resistance of Concrete and Masonry Construction Assemblies - MyCivil - IraliNoch keine Bewertungen
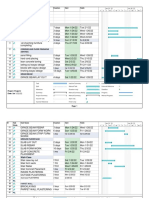
- Gantt ChartDokument6 SeitenGantt ChartSanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Guidelines For HydroPlast U-PVC FittingsDokument20 SeitenTechnical Guidelines For HydroPlast U-PVC FittingsOsama AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arup FSDokument8 SeitenArup FSGan Chin PhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastics Study MaterialDokument44 SeitenPlastics Study MaterialSri NavinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets and Institutions 8th Edition Mishkin Eakins Solutions Manual Instant DownloadDokument6 SeitenFinancial Markets and Institutions 8th Edition Mishkin Eakins Solutions Manual Instant DownloadEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Mix Ratio PDFDokument7 SeitenConcrete Mix Ratio PDFEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual DemandDokument5 SeitenSolution Manual DemandEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDokument5 SeitenFinancial Markets and InstitutionsEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRSLPII W10 Bidding Forms - 20-MayDokument124 SeitenDRSLPII W10 Bidding Forms - 20-MayEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drinking Water Through Recycling - Appendix BDokument72 SeitenDrinking Water Through Recycling - Appendix BEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules For Soil Management and Excess Soil Quality StandardsDokument201 SeitenRules For Soil Management and Excess Soil Quality StandardsEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA Table of ContentsDokument1 SeiteAPA Table of ContentsEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turkey Alumni Association of Somaliland (TAASO) The ConstitutionDokument4 SeitenTurkey Alumni Association of Somaliland (TAASO) The ConstitutionEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaba: 1500 MM 800 MM 2000 MM 800 MM 1000 MMDokument1 SeiteShaba: 1500 MM 800 MM 2000 MM 800 MM 1000 MMEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- W10 - Specific Procurement Notice v20.05Dokument2 SeitenW10 - Specific Procurement Notice v20.05Eng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix e Geology Terrain and Soils of The Refinery and RSFDokument49 SeitenAppendix e Geology Terrain and Soils of The Refinery and RSFEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix e Geology Terrain and Soils of The Refinery and RSF 2Dokument49 SeitenAppendix e Geology Terrain and Soils of The Refinery and RSF 2Eng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masjid Finshing: Coridor and Floor Finishing (Wayso)Dokument6 SeitenMasjid Finshing: Coridor and Floor Finishing (Wayso)Eng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOQ - Proposed Dhusamareeb Secondary School Boundary Masonry WallDokument3 SeitenBOQ - Proposed Dhusamareeb Secondary School Boundary Masonry WallEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract For ZEILA-WRDILDokument34 SeitenContract For ZEILA-WRDILEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Commercial Construction Timeline Template Updated 8847Dokument11 SeitenIC Commercial Construction Timeline Template Updated 8847Eng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Construction Schedule - TemplateLabDokument2 SeitenCommercial Construction Schedule - TemplateLabEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting Workbook StudentDokument37 SeitenCost Accounting Workbook StudentEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Eight: Credit Analysis and Financial StartupsDokument7 SeitenLesson Eight: Credit Analysis and Financial StartupsEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financed by LectureDokument5 SeitenFinanced by LectureEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generally Accepted Accounitng Princinples (GAAP)Dokument8 SeitenGenerally Accepted Accounitng Princinples (GAAP)Eng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior A: Period I Period 2 Afternoon EveningDokument7 SeitenSenior A: Period I Period 2 Afternoon EveningEng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Problems of Chapter-Two Ch-2 Tension Members: R L A I R Mpa F Mpa FDokument7 SeitenExercise Problems of Chapter-Two Ch-2 Tension Members: R L A I R Mpa F Mpa FEng Abdikarim Walhad100% (1)
- 022 PCRDokument46 Seiten022 PCREng Abdikarim WalhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- fm2798 818 819 820 PDFDokument4 Seitenfm2798 818 819 820 PDFOrellana Zeballos Luis CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 135 TPH Boiler-2. Erection ReportDokument12 Seiten135 TPH Boiler-2. Erection ReportVijay RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 219 Â " 02 QZIXOS0WMGDokument3 SeitenC 219 Â " 02 QZIXOS0WMGSebastián RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Research Paper STRENGTH AND SERVICEABILITY OF FRP GRIDDokument10 Seiten7 Research Paper STRENGTH AND SERVICEABILITY OF FRP GRIDMuhammad DaniyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 419 MosDokument2 Seiten419 MosTomtom YabayabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Spec - KSDokument76 SeitenProduct Spec - KSLeo HarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Material Classes Job SpecificationDokument6 SeitenPiping Material Classes Job SpecificationGERAILLYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromate-Free Coated Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet JCDokument2 SeitenChromate-Free Coated Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet JCaries26marchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet For Steel Grades Structure Steel 36crnimo4Dokument2 SeitenDatasheet For Steel Grades Structure Steel 36crnimo4Alexander ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LiveWall Reveal DIY Living Wall Kit Installation InstructionsDokument15 SeitenLiveWall Reveal DIY Living Wall Kit Installation InstructionsLiveRoof Green Roofs and LiveWall Vertical GardensNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESR 1056 Titen HeadDokument6 SeitenESR 1056 Titen HeadSandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Material - To Construct New HouseDokument136 SeitenBuilding Material - To Construct New HouseVenkata Ramanaiah KokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating Wood For Aircraft Use: FIGURE 3-2 Nomenclature For WoodsDokument4 SeitenEvaluating Wood For Aircraft Use: FIGURE 3-2 Nomenclature For Woodsomereh73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of JointsDokument8 SeitenTypes of JointsVeronica Zandra L. De Jesus-SowakenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grinding Machine: Grinding Machine, Often Shortened To G Rinder, Is Any of VariousDokument16 SeitenGrinding Machine: Grinding Machine, Often Shortened To G Rinder, Is Any of VariousMudassar AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WN SA-105 B16 5 TT Rev0Dokument2 SeitenWN SA-105 B16 5 TT Rev0Aço SalgueiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- NYC DOB Fire Escape Guidelines Per MDL (1 RCNY 15-10)Dokument12 SeitenNYC DOB Fire Escape Guidelines Per MDL (1 RCNY 15-10)John DoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yanbu: Export Refinery ProjectDokument8 SeitenYanbu: Export Refinery ProjectJanakiraman MalligaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fly Ash FTIRDokument14 SeitenFly Ash FTIRpriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rir Csfyyr Eè E, Oa MPP Ru RK Osq Lajpuk Blikr Fof'Kf"V: HKKJRH EkudDokument13 SeitenRir Csfyyr Eè E, Oa MPP Ru RK Osq Lajpuk Blikr Fof'Kf"V: HKKJRH EkudAnuradhaPatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part%203 1 ConcreteDokument37 SeitenPart%203 1 ConcreteShabir TrambooNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME.S.008 Piping Material - ASL - 2012Dokument3 SeitenME.S.008 Piping Material - ASL - 2012Ahmed AbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubber Hose ManufacturingDokument4 SeitenRubber Hose ManufacturingHue Trang Nguyen ThiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Res Eb Ec 015Dokument8 SeitenManual Res Eb Ec 015Levina YosheNoch keine Bewertungen