Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cranial Nerve Examination
Hochgeladen von
laureeate0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten2 Seitennerve
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldennerve
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten2 SeitenCranial Nerve Examination
Hochgeladen von
laureeatenerve
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Cranial nerve examination.
Position: Sitting on the side of the bed or in chair.
General inspection of head and neck: scars, neurofibromas, facial asymmetry, ptosis,
proptosis, deviation of the eyes, equality of the pupils.
The first nerve (olfactory).
1. Ask the patient if he can smell normally.
2. If there is a problem with a smell, with the eyes closed test one nostril at a time with a
different aromatic materials.
The second nerve (optic).
1. Ask whether the patient normally wears spectacles?
2. Visual acuity with Snellen chart. Consider pin-hole do differentiate refractory error.
3. Visual field. (Always remove patients spectacles first. Examiners head should be
level with the patients head. Do it slowly! The doctor will close the same side, not the
same eye)
4. Fundoscopy (Do red reflex first, use the right eye to look in the patients right eye,
and vice versa.)
The third, fourth, sixth nerves (oculomotor, trochlear, abducens).
1. Look at the pupil (shape, size, associated ptosis)
2. Test direct and consensual response to light, check for afferent pupillary defect.
(Bring the light from the site.)
3. Test accommodation (look at the distance focus on the object -30cm distance from
the nose)
4. Assess the eye movements (start from the centre follow H pattern, ask about
diplopia, look for nystagmus and failure of movement). Lateral rectus (6th nerve)
can only move eyes horizontally outwards; while medial rectus (3d nerve) can only
move eyes horizontally inwards.
The fifth nerve (trigeminal).
1. Cornel reflex - light touch cornea, not conjunctiva; (sensory 5th nerve, motor 7th)
2. Test sensory: light touch and pain in 3 divisions (ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular).
3. 3 motor functions: ask to clench teeth + feel masseter muscles; open mouth against
resistance; jaw jerk.
The seventh nerve (facial)
1. Look up + wrinkle forehead push down against the corrugation on each side (spared
in UMN lesions)
2. Close eyes tightly - try to open.
3. Puff out cheeks with mouth closed.
4. Show teeth compare nasolabial folds.
The eighth nerve (acoustic).
1. Softly whisper a number 60cm away from each ear.
2. Otoscopy if indicated.
3. Perform Rinners (conduction deafness no note is audible at the external meatus)
and Webers tests (conduction deafness the sound is louder in the abnormal ear)
with 256 Hz tuning fork if partial deafness is suspected.
The ninth and tenth nerves (glossopharyngeal + vagus)
1. Note any displacement of the uvular (unilateral 10th nerve palsy - uvula is drawn
towards the normal side).
2. Look for symmetrical movements of soft palate as the patient says Ah.
3. Assess gag reflex.
4. Assess for voice hoarseness and cough.
The twelfth nerve (hypoglossal).
1. Inspect the tongue for wasting and fasciculation (Deviate towards the weaker side if
there is a unilateral LMN lesion).
2. Ask patient to protrude tongue and look for deviation.
The eleventh nerve (accessory).
1. Ask the patient to shrug shoulders and feel trapezius as you push down.
2. Ask the patient to turn head against resistance and feel bulk of sternocleidomastoid
muscle. (Right sternocleidomastoid muscle turns the head to the left!)
Reference: N. Talley and S. OConnor Clinical examination 6th edition
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- 341-Nac Asthma Action Plan Colour A4Dokument2 Seiten341-Nac Asthma Action Plan Colour A4laureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apply HMO Intern 2017Dokument3 SeitenApply HMO Intern 2017laureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes education for advairDokument62 SeitenDiabetes education for advairlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
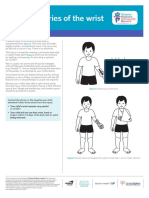
- Buckle Injuries VponDokument1 SeiteBuckle Injuries VponlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign - The Student Physical TherapistDokument1 SeiteHawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign - The Student Physical TherapistlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMO3 Medical 2016Dokument4 SeitenHMO3 Medical 2016laureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Review Clinical Medicine MRCP - 2Dokument433 SeitenRapid Review Clinical Medicine MRCP - 2Karen LooNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Rhythm Interpretation: Recognize Arrhythmias and Interpret ECGsDokument232 SeitenECG Rhythm Interpretation: Recognize Arrhythmias and Interpret ECGslaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Therapy FinalDokument3 SeitenFluid Therapy Finallaureeate100% (1)
- Health Services in WADokument10 SeitenHealth Services in WAlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Examine ThyroidDokument7 SeitenHow To Examine ThyroidlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMC 2 SamplesDokument2 SeitenAMC 2 Sampleschalak19800Noch keine Bewertungen
- Useful Website LinksDokument1 SeiteUseful Website LinkslaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System ExminationDokument3 SeitenRespiratory System ExminationlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency RegistrarDokument3 SeitenEmergency RegistrarlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Victorian HospitalsDokument55 SeitenVictorian Hospitalshadia_unitedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darbar e DilDokument156 SeitenDarbar e Dilapi-370666150% (2)
- Epidemiology of BPVC Clinical Features of BPVC: Gen Med C Presents . Benign Paroxysmal Vertigo of Childhood (BPVC)Dokument5 SeitenEpidemiology of BPVC Clinical Features of BPVC: Gen Med C Presents . Benign Paroxysmal Vertigo of Childhood (BPVC)laureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- TeriRahMainRulGayeeWe PDFDokument99 SeitenTeriRahMainRulGayeeWe PDFlaureeate100% (1)
- Obstetrics History - ExamDokument3 SeitenObstetrics History - ExamMavra zNoch keine Bewertungen
- PESCI /physical ExaminationsDokument5 SeitenPESCI /physical ExaminationslaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- 96 Sozani DarindaDokument64 Seiten96 Sozani DarindalaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To A The Child With A Fever and RashDokument7 SeitenApproach To A The Child With A Fever and RashlaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry: When Your Mood Is High?Dokument38 SeitenPsychiatry: When Your Mood Is High?Mavra zNoch keine Bewertungen
- 72 Surg Orth Sprained AnkleDokument3 Seiten72 Surg Orth Sprained AnkleMavra zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankle Brachial IndexDokument3 SeitenAnkle Brachial IndexMoe Zaw LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breaking Bad NewsDokument9 SeitenBreaking Bad NewslaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol Excess in PregnancyDokument3 SeitenAlcohol Excess in PregnancyMavra zNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCSC CounsellingDokument1 SeiteLCSC CounsellinglaureeateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Jurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan IndonesiaDokument6 SeitenJurnal Kesehatan Lingkungan IndonesiaNuriemayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dexamethasone implant for posterior uveitis in Behcet's diseaseDokument2 SeitenDexamethasone implant for posterior uveitis in Behcet's diseasehasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bellis Crosmodal 2011Dokument10 SeitenBellis Crosmodal 2011Letícia Amado PachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology MCQs Practice Test 1Dokument5 SeitenPsychology MCQs Practice Test 1Krishna Kanta BarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Skills in Correcting Astigmastism (Dr. Putri Hartini, Sp. M.)Dokument33 SeitenImproving Skills in Correcting Astigmastism (Dr. Putri Hartini, Sp. M.)Nisaa DwityarahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Sensorybiology Summer2017Dokument6 SeitenSyllabus Sensorybiology Summer2017api-321515818Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ent MCQ 1Dokument17 SeitenEnt MCQ 1sushil466Noch keine Bewertungen
- KARIKATURADokument35 SeitenKARIKATURAAndrea Rose Reyno100% (1)
- Avian SensesDokument23 SeitenAvian SensesB-vek GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sue Barry - 1 PDFDokument5 SeitenSue Barry - 1 PDFAnisha KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Prescribing of PrismDokument3 SeitenThe Prescribing of PrismJosepMolinsReixachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astigmatism 2Dokument35 SeitenAstigmatism 2Thanujaa Uvaraj0% (1)
- SENSORY BRAND EXPERIENCEDokument98 SeitenSENSORY BRAND EXPERIENCEBrownbrothaMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heep 116Dokument7 SeitenHeep 116pk2varmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ear - WikipediaDokument15 SeitenEar - WikipediadearbhupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MyopiaReportforWeb PDFDokument40 SeitenMyopiaReportforWeb PDFSiti KhodijahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDokument5 SeitenParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligibility of speech in hearing impaired childrenDokument11 SeitenIntelligibility of speech in hearing impaired childrenMaria P12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cdem 19december WebDokument32 SeitenCdem 19december WebRicardo Jonathan Ayala GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Human BehaviorDokument46 SeitenMechanism of Human BehaviorIsmaela BawicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 09 09Dokument13 SeitenCH 09 09ssoeliauwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Items QuestionsDokument22 Seiten100 Items Questionsdianneako100% (1)
- 07.02 Wiring DiagramDokument23 Seiten07.02 Wiring DiagramNazar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Accommodation & Pupillary Light ReflexDokument46 Seiten10 - Accommodation & Pupillary Light ReflexSugumar YathavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam in Gen Ed 6 2021'Dokument2 SeitenMidterm Exam in Gen Ed 6 2021'Bill Russell CecogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. - Montecalvo Prescribing PrismDokument187 SeitenDr. - Montecalvo Prescribing PrismVan KochkarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Script On AssessmentDokument14 SeitenScript On AssessmentissaiahnicolleNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Placement Test Reading PassageDokument2 SeitenIELTS Placement Test Reading PassageKayabwe GuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do You Know Me Flyer-Teacher VersionDokument1 SeiteDo You Know Me Flyer-Teacher VersionMaria Guy Del DucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noise Level Survey Report Provides Ambient Noise LevelsDokument1 SeiteNoise Level Survey Report Provides Ambient Noise LevelsVikas YamagarNoch keine Bewertungen