Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ANatomy and Physiology Vocabulary
Hochgeladen von
yasiraCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ANatomy and Physiology Vocabulary
Hochgeladen von
yasiraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sivan Wilfred G.
Barbarona
Prof. Doctor
Anatomy and Physiology
18 Januarry, 2015
Vocabulary
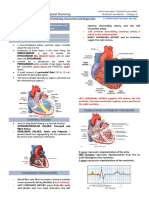
Heart
Cardiac arrhythmia (also known as irregular heartbeat) is any of a group of conditions
in which the electrical activity of the heart is irregular, faster, or slower than normal.
Sinus Tachycardia is a heart rate that exceeds the normal range. In general, a resting
heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia
Sinus bradycardia- a heart beat that is too slow - conventionally below 60 beats per
minute.
Sinus rhythm- means a normal heart beat, both with respect to the heart rate and rhythm.
Heart rate will fall between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Ectopic Pacemaker-is an excitable group of cells that causes a premature heart beat
outside the normally functioning SA node of the human heart.
Point of Maximal impulse-is the furthermost point outwards (laterally) and downwards
(inferiorly) from the sternum at which the cardiac impulse can be felt.
Palpitation- a noticeably rapid, strong, or irregular heartbeat due to agitation, exertion,
or illness.
Angina Pectoris-Chest pain due to an inadequate supply of oxygen to the heart muscle.
Angina can accompany or be a precursor of a heart attack.
Mycocardial Infarction-commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood stops
flowing properly to a part of the heart, and the heart muscle is injured because it is not
receiving enough oxygen. the coronary arteries that supplies blood to the heart develops a
blockage due to an unstable buildup of white blood cells, cholesterol and fat
Pericarditis- Inflammation of the lining around the heart (the pericardium) that causes
chest pain and accumulation of fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion).
Myocarditis-is a disease marked by inflammation and damage of the heart muscle.
Endocarditis- is an infection of the inner lining of your heart (endocardium).
Rheumatic heart disease- heart disorders that can occur as a result of rheumatic fever.
One common result of rheumatic fever is heart valve damage. This damage to the heart
valves may lead to a valve disorder.
Blood Pressure
Normotension- having or denoting a normal blood pressure.
Hypertension- abnormally high blood pressure.
Hypotension- abnormally low blood pressure.
Hypertensive crisis- when blood pressure reaches levels that are damaging
organs. Hypertensive emergencies generally occur at blood pressure levels exceeding 180
systolic OR 120 diastolic, but can occur at even lower levels in patients whose blood
pressure had not been previously high.
Systolic pressure- The blood pressure when the heart is contracting. It is specifically the
maximum arterial pressure during contraction of the left ventricle of the heart.
Diastolic pressure- when the heart is in a period of relaxation and dilatation (expansion).
Pulse pressure- is the difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure readings. It
represents the force that the heart generates each time it contracts.
Mean arterial pressure- is a term used in medicine to describe an average blood
pressure in an individual. It is defined as the average arterial pressure during a single
cardiac cycle.
Blood
Anemia- when your blood lacks enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin.
Sickle Cell Anemia- means that the red blood cells are shaped like a crescent. They tend
to block blood flow in the blood vessels of the limbs and organs
Polycythemia Vera- is a bone marrow disease that leads to an abnormal increase in the
number of blood cells. The red blood cells are mostly affected.
Plethora- an excess of blood.
Leukemia - the bone marrow and other blood-forming organs produce increased
numbers of immature or abnormal leukocytes. These suppress the production of normal
blood cells, leading to anemia and other symptoms.
Hemophilia- is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood doesn't clot normally.
Hypoxia- deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues.
Hypoxemia- A condition where the respiratory system fails in one or both of its gas
exchange functions (oxygenation and elimination of carbon dioxide from mixed venous
blood) is known as respiratory failure.
Thrombus- is a blood clot that forms in a vessel and remains there
Embolus- A blockage or plug that obstructs a blood 'vessel. Examples of emboli are
detached blood clots, clumps of bacteria, and clumps of other foreign material, such as
air.
Thrombosis- is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow
of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses
platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Anatomy of Circulatory SystemDokument56 SeitenAnatomy of Circulatory SystemLina Wijaya100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Concept MapDokument1 SeiteCongestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema Concept MapAndrew Godwin100% (5)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Question Bank For Pharmacology - WJP AnsweredDokument55 SeitenQuestion Bank For Pharmacology - WJP AnsweredGeorge MoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Summary Chapter 21Dokument5 SeitenPhysiology Summary Chapter 21gail018Noch keine Bewertungen
- Central Venous Pressure MonitoringDokument2 SeitenCentral Venous Pressure MonitoringpauchanmnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCI International Library of MeasuresDokument261 SeitenJCI International Library of Measuresh1m4w4n100% (4)
- Digital Clubbing in Pediatric Age GroupDokument33 SeitenDigital Clubbing in Pediatric Age GroupDeboprasad DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-5 Pharmacology of NeurosurgeryDokument12 SeitenUNIT-5 Pharmacology of NeurosurgeryFaizan Mazhar100% (1)
- CPAR MAS Preweek Quizzer May2004Dokument23 SeitenCPAR MAS Preweek Quizzer May2004kevinlim186100% (1)
- Lecture #5 - Circulatory DisturbanceDokument36 SeitenLecture #5 - Circulatory DisturbanceEl Farouk100% (1)
- Hemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedDokument60 SeitenHemiplegia Resource Book ModifiedAnonymous czrvb3hNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGD Aa PDFDokument11 SeitenSGD Aa PDFyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural Network - Your Text HereDokument2 SeitenNeural Network - Your Text HereyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRL InsertDokument19 SeitenRRL InsertyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tranzen1K BOIPEZADokument51 SeitenTranzen1K BOIPEZAyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check List: Your Title Text HereDokument2 SeitenCheck List: Your Title Text HereyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design - : Your Text HereDokument2 SeitenDesign - : Your Text HereyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicatio N: Your Subtitle Text HereDokument2 SeitenCommunicatio N: Your Subtitle Text HereyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Location - Your Text Here: Lorem Ipsum Is Simply Dummy Text of The Printing and Typesetting IndustryDokument2 SeitenLocation - Your Text Here: Lorem Ipsum Is Simply Dummy Text of The Printing and Typesetting IndustryyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 SlidesDokument2 Seiten2 SlidesyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- (-ENE) (-YNE) (-OL) (-OXY) (Benzene) : ChlorobenzeneDokument2 Seiten(-ENE) (-YNE) (-OL) (-OXY) (Benzene) : ChlorobenzeneyasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Review AnswerDokument8 SeitenGeneral Review AnsweryasiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DySAS General Review Acctg6 - AnsDokument11 SeitenDySAS General Review Acctg6 - Ansyasira0% (1)
- Pulse Oximeter Perfusion Index InfoDokument1 SeitePulse Oximeter Perfusion Index InfopavoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mean Arterial PressureDokument3 SeitenMean Arterial Pressureleslie vasquez lucumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extract Analysis T-Waves ECG Atrial Flutter VinetDokument9 SeitenExtract Analysis T-Waves ECG Atrial Flutter VinetAlex WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartDokument8 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartRoyce Vincent TizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening 65Dokument8 SeitenListening 65Sunrise 2587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Point-Of-Care Ultrasound in Cardiac ArrestDokument13 SeitenPoint-Of-Care Ultrasound in Cardiac ArrestEgorSazhaevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityDokument118 SeitenPharmacology For Nurses: The Islamic UniversityRojina AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseDokument28 Seiten1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseJavier Mora BaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Club: Presented by - Dr. Harshal Pamecha Resident in Cardiology CMCHDokument34 SeitenJournal Club: Presented by - Dr. Harshal Pamecha Resident in Cardiology CMCHlichumo murryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Case Study Homework Week 5Dokument4 SeitenCardiac Case Study Homework Week 5Study AssistantNoch keine Bewertungen
- kh7 CVPDokument50 Seitenkh7 CVPأبوأحمد الحكيمNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVT ClampsDokument112 SeitenCVT ClampsAmmoResearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- (KEL 1) Jurnal IMA (Pak Arif)Dokument8 Seiten(KEL 1) Jurnal IMA (Pak Arif)Nurul HendrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS and MegacodeDokument33 SeitenACLS and MegacodeMark Joseph100% (1)
- BCU 2022 First Announcement RevDokument14 SeitenBCU 2022 First Announcement RevAnggar KingStyle100% (1)
- Santa Monica Institute of Technology: Science 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grade (Biology and Chemistry)Dokument8 SeitenSanta Monica Institute of Technology: Science 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grade (Biology and Chemistry)Chapz PaczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiology EmqDokument8 SeitenCardiology EmqDenosshan SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 2022 (IAL) QPDokument28 SeitenJanuary 2022 (IAL) QPMaria Shabbir PanjiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument44 SeitenCase StudyMICHELLE MONTEBONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine Answers For ExamDokument94 SeitenAnesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine Answers For Exammichal ben meronNoch keine Bewertungen