Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Descripción Prueba Cadmio y Plomo para Cerámicos
Hochgeladen von
Karlos Daniel BarrosOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Descripción Prueba Cadmio y Plomo para Cerámicos
Hochgeladen von
Karlos Daniel BarrosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LEAD AND CADMIUM RELEASE
This characteristic is required in the C marking of ceramic tiles intended for
claddings that are going to be in contact with food or in those applications where this is
required by national regulations.
Standard ISO 10545-15 establishes a method for the determination of the
quantity of lead and cadmium released by a ceramic tile glaze, through exposure of the
glazed surface to an acetic acid (vinegar) solution and measurement of the lead and
cadmium present in that solution.
This test method has been incorporated with a view to assuring that ceramic tiles
do not give off toxic and harmful substances to the environment, to people, and to other
materials that enter into contact with the tiles, in order to conform to European Directive
76/769/EEC.
The results of the test shall be specified in the C marking, in the form of mass
of lead and cadmium extracted per unit surface area (in milligrams per square
decimetre, mg/dm2) in tiles that will be in contact with food. It is assumed that the
national standards on food health will stipulate the maximum levels of lead and
cadmium release.
The determination of lead and cadmium release in ISO 10545-15
Principle
This part of standard ISO 10545 establishes a method for the determination of
the quantity of lead and cadmium given off by the glaze of a ceramic tile, through
exposure of the glazed surface to an acetic acid (vinegar) solution and measurement of
the dissolved lead and cadmium in that solution.
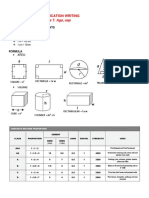
Procedure
Subject the glazed surface to
acetic acid attack in a solution at 4%
by volume for 24 hours and then
determine the quantity of lead and
cadmium present in the solution by
atomic
absorption
spectrometry
analysis. The result of the analysis is
put into the following formula, which
expresses the mass of lead (Pb) and
cadmium (Cd) given off per unit surface area (milligrams per square decimetre):
Physico-chemical characteristics
Lead and cadmium release
A (M) = (M)x
V
1
x
where
1000 A
M
is the extracted metal (Pb or Cd).
(M) is the concentration of metal M in the
solution after attack.
V
is the volume in millilitres (cm3) of the test
solution used.
A
is the area in square decimetres, of the
tested surface.
Comments
This test method has been incorporated with a view to assuring that ceramic tiles
do not give off toxic and harmful substances to the environment, to people, and to other
materials that enter into contact with these tiles, in order to conform to European
Directive 76/769/EEC.
Annex Q of EN 14411 establishes that this test method shall be taken into
account in ceramic tiles that are going to be in contact with food. This will be the case
for kitchen benchtops in domestic housing, and for ceramic tiles intended for the food
industry or for industrial kitchens; generally speaking, in applications where such
contact is expected.
On the one hand, the current formulation of glazes has eliminated or decreased
the presence of lead in glaze compositions. However, cadmium remains present in glaze
formulations and in colours ranging from orange to dark red for intermediate and low
temperatures. As a result, it is advisable to avoid that range of colours in the
applications mentioned above.
Physico-chemical characteristics
Lead and cadmium release
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Glazes For The Potter by Emmanuel Cooper, Dereck RoyleDokument199 SeitenGlazes For The Potter by Emmanuel Cooper, Dereck RoyleAdry B80% (5)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Ceramics NotesDokument11 SeitenCeramics Notesapi-26898561050% (2)
- DPWH Cost Estimate GuidelinesDokument101 SeitenDPWH Cost Estimate GuidelinesJohn75% (4)
- FiringTemperatures Cone EquivDokument1 SeiteFiringTemperatures Cone EquivPaul GhingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pricelist 1Dokument8 SeitenPricelist 1ChinangNoch keine Bewertungen
- GL 4Dokument12 SeitenGL 4Karlos Daniel BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 98 A 7 AaDokument80 Seiten98 A 7 AaKarlos Daniel BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instafloor Product Range Acoustic Performance v5Dokument2 SeitenInstafloor Product Range Acoustic Performance v5Karlos Daniel BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The GRO Green Roof Code 2011Dokument26 SeitenThe GRO Green Roof Code 2011Karlos Daniel BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020-05 Combo SW181 NightMothDokument2 Seiten2020-05 Combo SW181 NightMothVasiliy DyominNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Ancient Egyptian Faience With NanotechnologyDokument96 SeitenExploring Ancient Egyptian Faience With NanotechnologynaglaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceramic Tiles From Crassostrea Iredalei (Oyster) ShellsDokument85 SeitenCeramic Tiles From Crassostrea Iredalei (Oyster) ShellsAllen A. Espinosa95% (64)
- Ceramic IndustryDokument90 SeitenCeramic IndustrySalih MohayaddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paver Block Manufacturing UnitDokument12 SeitenPaver Block Manufacturing UnitMusic & ArtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porcelain Stoneware CLEOPATRADokument81 SeitenPorcelain Stoneware CLEOPATRAmagedshokryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceramic Insulator and Waste ManagementDokument18 SeitenCeramic Insulator and Waste ManagementVerry HendrawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jars Research EvaDokument67 SeitenJars Research EvaJohn Marion CapunitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitrified TilesDokument15 SeitenVitrified TilesVedika VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airbrush Step by Step - March 2015 EU PDFDokument72 SeitenAirbrush Step by Step - March 2015 EU PDFJesus GamiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Pro 44078Dokument8 SeitenRadio Pro 44078rajeshji_000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pottery Lessons 1 o 2Dokument8 SeitenPottery Lessons 1 o 2Ar FumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorants and Opacifiers PDFDokument7 SeitenColorants and Opacifiers PDFSiddharthapachisiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pottery Clays and ChemicalsDokument16 SeitenPottery Clays and ChemicalsDave SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medium and Technique in ArtDokument33 SeitenMedium and Technique in ArtGarnette A MalubayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burgio, L. Lustre Ceramics Analysis. 2005Dokument2 SeitenBurgio, L. Lustre Ceramics Analysis. 2005Trinidad Pasíes Arqueología-ConservaciónNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLAYDokument41 SeitenCLAYSwapna PandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 7 - TileworksDokument93 SeitenGroup 7 - TileworksPercival ArcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art 2704C Ceramic Figure Sculpture 2008 CtionsDokument13 SeitenArt 2704C Ceramic Figure Sculpture 2008 Ctionsterdahl100% (3)
- Estimates LectureDokument14 SeitenEstimates LectureTricia Infante100% (3)
- Ceramic Glaze - WikipediaDokument46 SeitenCeramic Glaze - WikipediaAna BarbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystalline Glaze Class Dan DermerDokument4 SeitenCrystalline Glaze Class Dan DermerJesus MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narumi Catalogue Vol 4 LightDokument124 SeitenNarumi Catalogue Vol 4 Lightlatavola100% (1)
- Update HS CODE TERBARU-2Dokument1 SeiteUpdate HS CODE TERBARU-2Ardi IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wight Pottery March 2023 MADDokument5 SeitenWight Pottery March 2023 MADJustin W. ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen