Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Trusts Review Notes
Hochgeladen von
ignorantlainey0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
90 Ansichten2 SeitenNotes based on the Civil Code of the Philippines Annotated by Edgardo Paras - Book 4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenNotes based on the Civil Code of the Philippines Annotated by Edgardo Paras - Book 4
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
90 Ansichten2 SeitenTrusts Review Notes
Hochgeladen von
ignorantlaineyNotes based on the Civil Code of the Philippines Annotated by Edgardo Paras - Book 4
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
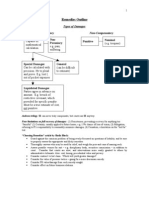
Trust the right to the beneficial enjoyment of property, the legal title
to which is vested in another.
Characteristics of a trust:
1.
2.
3.
Fiduciary
Created by law or agreement
Legal title is held by one, equitable title is held by another
Parties to a trust:
1.
2.
3.
Trustor or settler establishes the trust
Trustee holds the property in trust for the benefit of
another
Beneficiary or cestui que trust person for whose benefit
the trust is created
The trustor may at the same time be the beneficiary.
Trustor and trustee must be legally capacitated to convey property or
hold property and enter into contracts, respectively.
Beneficiary need not be capacitated, but must be capacitated to
receive gratuitously from the trustor.
Elements of a trust:
1.
2.
Parties
Subject matter of the trust
How express trusts are ended:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
Mutual agreement of all parties
Expiration of term
Fulfilment of a resolutory condition
Rescission or annulment
Loss of subject matter
Order of the court
Merger
Accomplishment of the purpose of the trust
2.
Implied trust created by operation of law (founded on
equity)
Implied trust may prescribe in 10 years from the
repudiation of the trust by the trustee.
Repudiation of resulting implied trust (and
express trust) must be made known to the
beneficiary.
Prescription supervenes in a constructive trust
even if the trustee does not repudiate the
relationship.
The existence of co-ownership argues against
the theory of implied trust (thus no prescription
can be considered).
May be proved by oral evidence, whether subject
matter is real or personal property
a.
Classifications of trusts:
1.
Express trust created by the parties or by the intention
of the trustor
If subject matter is an immovable or right over an
immovable, may not be proved by parol (oral
evidence).
Express trust with immovable or right thereto
must be in writing for enforceability only, not
validity.
As to third persons, the trust must be in public
instrument and registered in the Registry of
Property is the subject matter is a real property.
b.
a.3. Land passes by succession to any person and he
causes the legal title to be put in the name of another,
the former being the beneficiary and the latter the
trustee (Art. 1451)
By conveyance to the trustee by an act inter vivos or mortis
causa
By admission of the trustee that he holds the property only
as trustee
a.4. Two or more persons purchase property, the legal
title of which is under the name of one of them, the
latter is the trustee of others in proportion of the
interest of each (Art. 1452)
Administration of the trust by the trustee:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
File a bond
Make an inventory of the real and personal property in trust
Manage and dispose of the estate and faithfully discharge
his trust in relation thereto
Render a true and clear account
Cannot acquire the property held in trust by prescription as
long as the trust is admitted. If he repudiates and this is
made known to the party involved, prescription is permitted.
A trustee may sue or be sued alone as a trustee if the trust is
express.
In the absence of an express stipulation in a contract entered into by
a trustee for a corporation that the trust estate is liable on the
contract, the trustee is liable in its individual capacity.
Acceptance by the beneficiary is necessary, but acceptance is
presumed it the trust imposes no onerous condition.
If the person to whom the title is conveyed is
a child, no trust is implied as it is a gift
a.2. Donation is made a person and although legal
estate is transmitted to him, he has no beneficial
interest or only part thereof (Art. 1449)
How an express trust is created:
a.
Resulting trust intent to create a trust but it is not
effective as an express trust
a.1. Legal estate is granted to one party but the price
is paid by another (Art. 1448). Former is trustee, latter
is beneficiary.
The presumption is that interest of coowners are equal.
a.5. When property is conveyed to a person for him to
hold it or transfer it to another. Former is the trustee of
the property. (Art. 1453)
b.
Constructive trust no intention to create a trust but a
trust is nevertheless created by law to prevent unjust
enrichment or oppression
b.1. Property is loaned or paid by one person for the
benefit of another and conveyance of the property to
the former (i.e. by registering in his name the property)
as security for the loan. Creditor is the trustee and
debtor is the beneficiary who may redeem the property
(Art. 1450).
Example:
Trust receipt a security
transaction intended to aid in financing
importers and retail dealers who do not have
sufficient funds or resources to finance the
importation or purchase of merchandise, and
who may not be able to acquire credit except
thru utilization as collateral of the
merchandise imported or purchased.
b.2. Absolute conveyance of property is made in order to
secure performance (Art. 1454)
b.3. Trustee, guardian or other person holding a fiduciary
relationship uses trust funds for the purchase of property
and causes the conveyance to be made to him or a third
person (Art. 1455)
b.4. Property is acquired through mistake or fraud (Art
1456)
Mistake is made by a third person
Fraud is extra-contractual fraud
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Week 7 - Unincorporated AssociationDokument23 SeitenWeek 7 - Unincorporated AssociationJake Tahal100% (1)
- Assurance FundDokument3 SeitenAssurance FundRuth Hazel GalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salao V SalaoDokument21 SeitenSalao V SalaoJm CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRUSTS (Art. 1440 - 1457)Dokument8 SeitenTRUSTS (Art. 1440 - 1457)AvaSheryl Catapusan- TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glenn A. Howard 3000 W. Mac Arthur BLVD., #412 Santa Ana, CA 92704Dokument8 SeitenGlenn A. Howard 3000 W. Mac Arthur BLVD., #412 Santa Ana, CA 92704Turqueza Mariano Benzon Avila Law FirmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles Law On TrustsDokument3 SeitenPrinciples Law On TrustsAnthony Yap100% (1)
- Power of Attorney General - PDF BlankDokument3 SeitenPower of Attorney General - PDF BlankJennifer PartidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remedies FlowDokument44 SeitenRemedies Flowzeebeelo100% (1)
- Effect On Agreement, of Misrepresentation or Fraud by AgentDokument11 SeitenEffect On Agreement, of Misrepresentation or Fraud by AgentMitaliKshatriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nominal DamagesDokument16 SeitenNominal DamagesCharlie PeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trusts ReviewerDokument8 SeitenTrusts Reviewerroansalanga100% (9)
- Trust - NotesDokument2 SeitenTrust - NotesWinnie Ann Daquil Lomosad-Misagal100% (1)
- Reviewer TrustDokument4 SeitenReviewer TrustJoshuaGomez100% (4)
- Powers & Authority of The Commissioner of Internal Revenue Under Sec. 4-7, Title 1 of The Tax CodeDokument24 SeitenPowers & Authority of The Commissioner of Internal Revenue Under Sec. 4-7, Title 1 of The Tax CodeRovi PatinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trusts and PowerDokument20 SeitenTrusts and PowerChina WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current I-9 FormDokument4 SeitenCurrent I-9 Formlegiziano100% (4)
- Consensus Ad Idem Between The Parties. A Trust May Arise by Agreement, ForDokument4 SeitenConsensus Ad Idem Between The Parties. A Trust May Arise by Agreement, ForDane LRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trust NotesDokument3 SeitenTrust NotesEunice Nicee100% (1)
- TrustsDokument7 SeitenTrustsredenbidedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rule 102 - Habeas Corpus CoverageDokument3 SeitenRule 102 - Habeas Corpus CoverageIan Joshua RomasantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guaranty & Suretyship - CasesDokument361 SeitenGuaranty & Suretyship - CasesClarice Joy Sj100% (1)
- Deposits Notes CreditDokument7 SeitenDeposits Notes CreditMa. Goretti Jica GulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissolution Deed FormatDokument2 SeitenDissolution Deed FormatMuslim QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trust Reviewer P. 677-693Dokument2 SeitenTrust Reviewer P. 677-693Diane Uy100% (1)
- Sec 39conditio Nal IndorsementDokument10 SeitenSec 39conditio Nal IndorsementgoerginamarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trust ReviewerDokument4 SeitenTrust ReviewerFaustine Mata100% (1)
- Legal Issues Chapter 2Dokument8 SeitenLegal Issues Chapter 2sdfghjkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offer and AcceptanceDokument5 SeitenOffer and AcceptancePrithvi NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mananquil Vs Moico-ReadDokument4 SeitenMananquil Vs Moico-ReadPatrick James TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On TrustDokument12 SeitenNotes On TrustRoy Samuel HalasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARP Coverage Protest - Heirs of Ramiro JocsonDokument5 SeitenCARP Coverage Protest - Heirs of Ramiro JocsonKara Gonzaga Cuarom100% (1)
- Barrister J. AshrafDokument13 SeitenBarrister J. AshrafJennifer AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECHEGARAY v. SECRETARY OF JUSTICEDokument2 SeitenECHEGARAY v. SECRETARY OF JUSTICEGilbert John LacorteNoch keine Bewertungen
- All About TrustsDokument8 SeitenAll About TrustsJaysonmaleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD 115 Trust Receipt LawDokument5 SeitenPD 115 Trust Receipt LawDenise LabagnaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IV Agency and Business OrganizationDokument90 SeitenUnit IV Agency and Business OrganizationParina ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arbitration Complaint: Indicate The Corporationõs Legal Name As A Separately Named Respondent.)Dokument3 SeitenArbitration Complaint: Indicate The Corporationõs Legal Name As A Separately Named Respondent.)April Enrile-MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trust ReviewerDokument5 SeitenTrust ReviewerJaime Alfonso AloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negotiable InstrumentDokument19 SeitenNegotiable InstrumentPaul Angelo 黃種 武Noch keine Bewertungen
- TRUSTS PresentationDokument47 SeitenTRUSTS Presentationnegotiator100% (1)
- Roa, Jr. vs. Court of AppealsDokument1 SeiteRoa, Jr. vs. Court of AppealsPio Guieb AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TermpaperonpropertylawDokument10 SeitenTermpaperonpropertylawsanjog DewanNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Academy V LittonDokument4 SeitenInternational Academy V LittonDominic EstremosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Araneta Vs GatmaitanDokument1 SeiteAraneta Vs GatmaitanXyra Krezel GajeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abc New World V AMADokument3 SeitenAbc New World V AMARuth TenajerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liwat MoyaDokument9 SeitenLiwat MoyaKyle BanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Relief ActDokument7 SeitenSpecific Relief Actankit rocksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Law On TrustsDokument3 SeitenPhilippine Law On TrustsKayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parties To A Negotiable InstrumentDokument4 SeitenParties To A Negotiable InstrumentAamir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Letters Ofcredit and Trust Receipts 2019Dokument5 SeitenI. Letters Ofcredit and Trust Receipts 2019Jayson AbabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Beneficial Interest Insurance ProceedsDokument2 SeitenAssignment Beneficial Interest Insurance ProceedsrvisconteNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Case:: FactsDokument6 SeitenFirst Case:: FactsERICKSKIE23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syndicated Loan Agreement: PartiesDokument10 SeitenSyndicated Loan Agreement: PartiesAleezah Gertrude RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transpo CasesDokument53 SeitenTranspo CasesJoanna Paula P. SollanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Taxation of Estates and Trusts LlamadoDokument7 SeitenChapter 11 Taxation of Estates and Trusts LlamadoLiana Monica LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bill of ExchangeDokument15 SeitenBill of ExchangeArjun SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negotiable InstrumentsDokument52 SeitenNegotiable InstrumentsHp AmpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letters of CreditDokument20 SeitenLetters of CreditA.T.Comia100% (3)
- Exhaustion of Administrative RemediesDokument14 SeitenExhaustion of Administrative RemediestigerholmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Negotiable InstrumentsDokument23 SeitenChapter 6 Negotiable InstrumentsKristelJaneDonaireBihagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implied Authority of PartnerDokument1 SeiteImplied Authority of PartnerFrank NobodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accepted Offer Addendum-CounterDokument16 SeitenAccepted Offer Addendum-Counterrealestate6199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rescission of Contract3Dokument6 SeitenRescission of Contract3maheshdeshmukh402Noch keine Bewertungen
- TrustDokument4 SeitenTrusteldene tampicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 TrustDokument2 Seiten3 TrustKrissy PepsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On TrustsDokument6 SeitenNotes On TrustsJeff LambayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1456 To 1457 ReportDokument2 Seiten1456 To 1457 ReportNicole Dagohoy TaytayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trust Reviewer P 677 693Dokument2 SeitenTrust Reviewer P 677 693Jenny VallesteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agency, Trusts, Partnerships & Joint Ventures Atty. Jose U. Cochingyan IIIDokument46 SeitenAgency, Trusts, Partnerships & Joint Ventures Atty. Jose U. Cochingyan IIIjames lebronNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH Civil Law On TrustsDokument4 SeitenPH Civil Law On TruststransitxyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Legal System: Introduction To The English Legal System Basic Concepts in Law Suggested ReadingDokument34 SeitenEnglish Legal System: Introduction To The English Legal System Basic Concepts in Law Suggested ReadingRapstar VyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyuthi T0063 PDFDokument255 SeitenDyuthi T0063 PDFkeerthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Natural JusticeDokument33 SeitenPrinciples of Natural JusticeAAKANKSHA BHATIANoch keine Bewertungen
- J 2022 SCC OnLine SC 46 20bal073 Nirmauniacin 20220625 061602 1 40Dokument40 SeitenJ 2022 SCC OnLine SC 46 20bal073 Nirmauniacin 20220625 061602 1 40yashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernas V ReyesDokument4 SeitenBernas V ReyesDhin CaragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sherter Lies - 1st Rough DraftDokument12 SeitenSherter Lies - 1st Rough Drafttheplatinumlife7364Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sazon V Vasquez and Petron V Joven & ErmaDokument18 SeitenSazon V Vasquez and Petron V Joven & ErmaAngelo Lajarca100% (1)
- Employee Suspension Order Can Be Passed Considering The Gravity of The Alleged Misconduct I.E. Serious Act of Omission. Supreme Court of IndiaDokument36 SeitenEmployee Suspension Order Can Be Passed Considering The Gravity of The Alleged Misconduct I.E. Serious Act of Omission. Supreme Court of IndiaAbdul HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torres V NLRCDokument7 SeitenTorres V NLRCcha chaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajiv Gandhi School of Intellectual Property Law, Iit KharagpurDokument14 SeitenRajiv Gandhi School of Intellectual Property Law, Iit Kharagpurnidhi_anand_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trust NotesDokument5 SeitenTrust NotesAishwaryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trump Response To Govt Motion To StayDokument21 SeitenTrump Response To Govt Motion To StayFile 411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mactan-Cebu International Airport Authority & Air Transportation Office vs. LozadaDokument1 SeiteMactan-Cebu International Airport Authority & Air Transportation Office vs. LozadaErika Mariz CunananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canon Law and Common Sense - Rev. Anthony CekadaDokument13 SeitenCanon Law and Common Sense - Rev. Anthony CekadaMDStevensNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of London La3002 OctoberDokument4 SeitenUniversity of London La3002 OctoberJUNAID FAIZANNoch keine Bewertungen
- REM BaropsDokument302 SeitenREM BaropsRoxane Mae Villena100% (1)
- 2020LHC3566 High Court RulingDokument14 Seiten2020LHC3566 High Court RulingUmer MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- LachesDokument5 SeitenLachesNik AdilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- David Reyes vs. Jose Lim, Et Al. (G.R. No. 134241, August 11, 2003)Dokument12 SeitenDavid Reyes vs. Jose Lim, Et Al. (G.R. No. 134241, August 11, 2003)Fergen Marie WeberNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Court of Appeals, Second Circuit.: No. 336, Docket 94-7120Dokument13 SeitenUnited States Court of Appeals, Second Circuit.: No. 336, Docket 94-7120Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen