Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
5.2 Background Information: 70 Chapter 5. Case Study
Hochgeladen von
Joao0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten1 SeiteOriginaltitel
Páginas de 44350 94.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten1 Seite5.2 Background Information: 70 Chapter 5. Case Study
Hochgeladen von
JoaoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
70
CHAPTER 5. CASE STUDY
Material law: Elasto-plastic for crash analysis and elastic for modal analysis.
Model options: Boundary conditions, rigid bodies, multiple nodes to one node constraint, dynamic loads, g-forces, gravity.
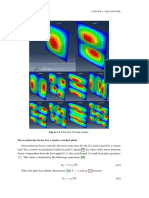
Key results: Stress distributions, displacements, natural frequencies and modal shapes.
5.2
Background information
Pre-processor, solver and post-processor software used:
ANSA: For the model mesh generation and other model geometric setups like weld
beads, rigid bodys, multiple nodes to one node constraint, springs, etc. .
Visual-Crash PAM: To set up the finite element model.
Analysis (PAM-CRASH explicit and implicit): To perform the crash simulation and the
modal analysis by the FEM.
Visual Viewer: Evaluating stress, deformations, natural frequencies and modal shapes
results.
5.3
Problem data and description
Units: kN, mm, kg, ms.
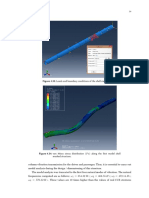
Description: Steel cross car beam structure with weld connections submitted to dynamic loading that simulate a frontal overlaped crash scenario.
Loading: Multiple loads on the structure simulating the impact and airbags explosion.
Material: FEP13 Steel (E = 205 kN /mm 2 (GPa) ; = 0.3; and = 7 .8 10 6
kg/mm3 ), [22]. For plasticity, the stress/plastic strain curve is defined in Table 5.1.
The FEP 13 hardening curve is defined in Figure 5.2. The BV226 parts material, available in the technical drawing (appendix 1), is not used in this analysis due to lack of
information.
5.3.1
Parts list
The BV226 model structure technical drawing is available in appendix 1. This cross car
beam FE model parts list is available in Table 5.2:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Non-Linear Structures: Matrix Methods of Analysis and Design by ComputersVon EverandNon-Linear Structures: Matrix Methods of Analysis and Design by ComputersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Metal Fatigue Analysis Handbook: Practical Problem-solving Techniques for Computer-aided EngineeringVon EverandMetal Fatigue Analysis Handbook: Practical Problem-solving Techniques for Computer-aided EngineeringBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (5)
- Composites MaterialsDokument21 SeitenComposites MaterialsMayra AmandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ructural Nalysis ND Esign Gram: ST A A D ProDokument31 SeitenRuctural Nalysis ND Esign Gram: ST A A D ProZarinaKhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ructural Nalysis ND Esign Gram: ST A A D ProDokument31 SeitenRuctural Nalysis ND Esign Gram: ST A A D ProCosminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nafems India Webinar Fem For Engineering Analysis PDFDokument27 SeitenNafems India Webinar Fem For Engineering Analysis PDFjohn_max03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Csi BridgesDokument24 SeitenManual de Csi Bridgessolucionessigloxxi100% (3)
- ProjectsDokument6 SeitenProjectsbaljinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hull Segment Test - 2003Dokument24 SeitenHull Segment Test - 2003ILya KryzhanovskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extreme Loading For StructuresDokument6 SeitenExtreme Loading For StructuresRavindra MRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural AnalysisDokument26 SeitenStructural Analysisafifa kausar100% (2)
- A General Procedure For Finite Element AnalysisDokument11 SeitenA General Procedure For Finite Element AnalysisBelagaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Structural Rigid and Flexible Bus Design in Air Insulated SubstationsDokument8 SeitenDynamic Structural Rigid and Flexible Bus Design in Air Insulated SubstationsnashapkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 3 1620Dokument38 Seiten24 3 1620Alexander ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Structures Using ANSYSDokument31 SeitenAnalysis of Structures Using ANSYSSaurabhMulayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shakedown and Plastic Design of Steel StructuresDokument2 SeitenShakedown and Plastic Design of Steel StructuresVedant MankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSM Flexure Presentation 19-3-2023Dokument35 SeitenCSM Flexure Presentation 19-3-2023Nora MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Plan Structural Engineering Design - II: Unit Description of Topics Assignments No of Lectures RequiredDokument2 SeitenTeaching Plan Structural Engineering Design - II: Unit Description of Topics Assignments No of Lectures RequiredkamalnitrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atkins QueriesDokument4 SeitenAtkins QueriesMuhammad ZeeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Body PDFDokument5 SeitenBus Body PDFjohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Design Lab: SAP 2000 DemonstrationDokument27 SeitenAdvanced Design Lab: SAP 2000 DemonstrationVijayKhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method For Evaluating The Structural Reliability of Radial Gates - Renewable Energy WorldDokument8 SeitenMethod For Evaluating The Structural Reliability of Radial Gates - Renewable Energy WorldWalterHuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Sem Course DiaryDokument68 Seiten6th Sem Course DiaryRaj ManovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic AnalysisDokument90 SeitenPlastic AnalysisBishanjit Singh Grewal100% (4)
- Alhorani (2020) - Mathematical Models For The Optimal Design of I - and H-Shaped Crane Bridge GirdersDokument16 SeitenAlhorani (2020) - Mathematical Models For The Optimal Design of I - and H-Shaped Crane Bridge GirdersGogyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijett V11P218Dokument6 SeitenIjett V11P218Mr ShrekNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cosmos Companion: Material Properties Used in CosmosworksDokument23 SeitenThe Cosmos Companion: Material Properties Used in Cosmosworksjontylee87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Explosive Testing of Open CylindersDokument27 SeitenExplosive Testing of Open CylindershaithamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project Finite Element AnalysisDokument41 SeitenFinal Project Finite Element AnalysisAkhil KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsional Stiffness - Formula SAE LeedsDokument8 SeitenTorsional Stiffness - Formula SAE LeedsBreno VieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Proceedings of The Institution of MechanicalDokument16 SeitenEngineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Proceedings of The Institution of MechanicalAvinash ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design II (ME-3217)Dokument12 SeitenMachine Design II (ME-3217)Somnath SomadderNoch keine Bewertungen
- StageDokument20 SeitenStageSnehal dhengleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ravi Resume PDFDokument2 SeitenRavi Resume PDFRavi Prakash M PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Stress-Strain Model and Damage Index FoDokument11 SeitenAnalytical Stress-Strain Model and Damage Index Fomhmdwalid95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis and Design of Steel ConnectionsDokument7 SeitenStructural Analysis and Design of Steel ConnectionsCarlos Julio Ramirez BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crash Analysis of An Impact Attenuator For Racing Car in Sandwich MaterialDokument6 SeitenCrash Analysis of An Impact Attenuator For Racing Car in Sandwich MaterialLeonardo GibranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Automobile & Mechanical Engineering: System Design and SimulationDokument12 SeitenDepartment of Automobile & Mechanical Engineering: System Design and Simulationanup chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM Analysis of Connecting Rod of Different Materials Using AnsysDokument20 SeitenFEM Analysis of Connecting Rod of Different Materials Using AnsysjeffNoch keine Bewertungen
- PME2011 Mechanical EngineeringDokument1 SeitePME2011 Mechanical EngineeringjvanandhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dump Truck SimulationDokument26 SeitenDump Truck SimulationIdwandi FedoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Linear Structural AnalysisDokument12 SeitenNon-Linear Structural AnalysisMohammed SallamNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Reliability Models For Bridge StructuresDokument9 SeitenSystem Reliability Models For Bridge StructuresCarlos GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A123 - Zhang & YeDokument25 SeitenA123 - Zhang & YeChangbum YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Validation of Eicher 11.10 ChassisDokument4 SeitenAnalysis and Validation of Eicher 11.10 ChassisdessaivipulNoch keine Bewertungen
- FeaDokument200 SeitenFeakarthipriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- This TwoDokument2 SeitenThis Twovigneshbabu1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chassis Design ImportantDokument27 SeitenChassis Design ImportantNandan PoojaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 1 - Mechanical Characterization of Selfcompacting Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete by Digital Image CorrelationDokument6 SeitenHW 1 - Mechanical Characterization of Selfcompacting Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete by Digital Image CorrelationAngie GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DME 1 Course ContentDokument12 SeitenDME 1 Course Content4NM19ME034 DIXIT HEGDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Design NotesDokument46 SeitenFatigue Design NotestehepiconeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS & STAAD ComparisonDokument70 SeitenETABS & STAAD Comparisonpido290% (1)
- Structural and Modal Analysis of Scooter Frame: D.Mohankumar, R. Sabarish, Dr. M. PremjeyakumarDokument10 SeitenStructural and Modal Analysis of Scooter Frame: D.Mohankumar, R. Sabarish, Dr. M. PremjeyakumarChu Ngọc TúNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: Design Optimization and Analysis of A Connecting Rod of A Vehicle Engine Using CAE ToolsDokument1 SeiteObjective: Design Optimization and Analysis of A Connecting Rod of A Vehicle Engine Using CAE ToolsNishikant KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research On Reverse Engineering of Mechanical Characteristic Parameters of Materials in Collision SimulationDokument8 SeitenResearch On Reverse Engineering of Mechanical Characteristic Parameters of Materials in Collision SimulationJOSE ZUBIETANoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Analysis and Design of Steel StructuresVon EverandPlastic Analysis and Design of Steel StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Viscoelastic Structures: Mechanics of Growth and AgingVon EverandViscoelastic Structures: Mechanics of Growth and AgingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel Structures: Materials, Connections, and ComponentsVon EverandDesign of Steel Structures: Materials, Connections, and ComponentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersVon EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 86 Chapter 5. Case Study: Passenger's Airbag Rigid Body. Table 5.5: A-Pillar LoadingDokument1 Seite86 Chapter 5. Case Study: Passenger's Airbag Rigid Body. Table 5.5: A-Pillar LoadingJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 78 Chapter 5. Case Study: Hole Feature Usefull Help in MeshingDokument1 Seite78 Chapter 5. Case Study: Hole Feature Usefull Help in MeshingJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 107 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 107 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 111 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 111 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 80 Chapter 5. Case Study: A-PILLAR LHS Meshing StepsDokument1 Seite80 Chapter 5. Case Study: A-PILLAR LHS Meshing StepsJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 87 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 87 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 103 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 103 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 84 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 84 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 82 Chapter 5. Case StudyDokument1 Seite82 Chapter 5. Case StudyJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 101 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 101 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 99 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 99 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 Case Study DescriptionDokument1 Seite5.1 Case Study DescriptionJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 74 Chapter 5. Case Study: Quality Criteria WindowDokument1 Seite74 Chapter 5. Case Study: Quality Criteria WindowJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 5.2: BV226 Parts List. Part Name Part Figure Part Name Part FigureDokument1 SeiteTable 5.2: BV226 Parts List. Part Name Part Figure Part Name Part FigureJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 76 Chapter 5. Case Study: Geometry CheckDokument1 Seite76 Chapter 5. Case Study: Geometry CheckJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 88 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 88 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 95 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 95 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 81 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 81 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 77 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 77 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 86 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 86 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Three Modes of Cracking, (18) .: 46 Chapter 4. Fem SoftwareDokument1 SeiteThe Three Modes of Cracking, (18) .: 46 Chapter 4. Fem SoftwareJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 65 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 65 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 76 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 76 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 82 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 82 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 83 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 83 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 71 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 71 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 66 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 66 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 73 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 73 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 78 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 78 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas de 44350 67 PDFDokument1 SeitePáginas de 44350 67 PDFJoaoNoch keine Bewertungen