Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Wireless
Hochgeladen von
Amro GoneimCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Wireless
Hochgeladen von
Amro GoneimCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
Type text to search here...
Page 1 of 7
Submit Query
Home > Wireless Tutorial
Wireless Tutorial
August 12th, 2011 Go to comments
In this article we will discuss about Wireless technologies mentioned in CCNA.
Wireless LAN (WLAN) is very popular nowadays. Maybe you have ever used some wireless
applications on your laptop or cellphone. Wireless LANs enable users to communicate without the need
of cable. Below is an example of a simple WLAN:
Each WLAN network needs a wireless Access Point (AP) to transmit and receive data from users.
Unlike a wired network which operates at full-duplex (send and receive at the same time), a wireless
network operates at half-duplex so sometimes an AP is referred as a Wireless Hub.
The major difference between wired LAN and WLAN is WLAN transmits data by radiating energy
waves, called radio waves, instead of transmitting electrical signals over a cable.
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
Page 2 of 7
Also, WLAN uses CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) instead of
CSMA/CD for media access. WLAN cant use CSMA/CD as a sending device cant transmit and
receive data at the same time. CSMA/CA operates as follows:
+ Listen to ensure the media is free. If it is free, set a random time before sending data
+ When the random time has passed, listen again. If the media is free, send the data. If not, set another
random time again
+ Wait for an acknowledgment that data has been sent successfully
+ If no acknowledgment is received, resend the data
IEEE 802.11 standards:
Nowadays there are three organizations influencing WLAN standards. They are:
+ ITU-R: is responsible for allocation of the RF bands
+ IEEE: specifies how RF is modulated to transfer data
+ Wi-Fi Alliance: improves the interoperability of wireless products among vendors
But the most popular type of wireless LAN today is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, which is known
informally as Wi-Fi.
* 802.11a: operates in the 5.7 GHz ISM band. Maximum transmission speed is 54Mbps and
approximate wireless range is 25-75 feet indoors.
* 802.11b: operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Maximum transmission speed is 11Mbps and
approximate wireless range is 100-200 feet indoors.
* 802/11g: operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Maximum transmission speed is 54Mbps and
approximate wireless range is 100-200 feet indoors.
ISM Band: The ISM (Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band, which is controlled by the FCC in the
US, generally requires licensing for various spectrum use. To accommodate wireless LANs, the FCC
has set aside bandwidth for unlicensed use including the 2.4Ghz spectrum where many WLAN products
operate.
Wi-Fi: stands for Wireless Fidelity and is used to define any of the IEEE 802.11 wireless standards. The
term Wi-Fi was created by the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA). Products certified as
Wi-Fi compliant are interoperable with each other even if they are made by different manufacturers.
Access points can support several or all of the three most popular IEEE WLAN standards including
802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g.
WLAN Modes:
WLAN has two basic modes of operation:
* Ad-hoc mode: In this mode devices send data directly to each other without an AP.
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
Page 3 of 7
* Infrastructure mode: Connect to a wired LAN, supports two modes (service sets):
+ Basic Service Set (BSS): uses only a single AP to create a WLAN
+ Extended Service Set (ESS): uses more than one AP to create a WLAN, allows roaming in a larger
area than a single AP. Usually there is an overlapped area between two APs to support roaming. The
overlapped area should be more than 10% (from 10% to 15%) to allow users moving between two APs
without losing their connections (called roaming). The two adjacent APs should use non-overlapping
channels to avoid interference. The most popular non-overlapping channels are channels 1, 6 and 11
(will be explained later).
Roaming: The ability to use a wireless device and be able to move from one access points range to
another without losing the connection.
When configuring ESS, each of the APs should be configured with the same Service Set Identifier
(SSID) to support roaming function. SSID is the unique name shared among all devices on the same
wireless network. In public places, SSID is set on the AP and broadcasts to all the wireless devices in
range. SSIDs are case sensitive text strings and have a maximum length of 32 characters. SSID is also
the minimum requirement for a WLAN to operate. In most Linksys APs (a product of Cisco), the default
SSID is linksys.
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
Page 4 of 7
In the next part we will discuss about Wireless Encoding, popular Wireless Security Standard and some
sources of wireless interference.
Pages: 1 2
Comments (58) Comments
Comment pages
Previous 1 2 787
1. John
August 12th, 2015
Can anybody tell us what to expect on CCNA wireless exam 640-722? I want to use PL dump
and request assistance narrowing down PL questions that are on exam. x152005@yahoo.com
2. Valentin
August 13th, 2015
Will Wi-Fi theme be on CCNA exam?
3. Anonymous
August 13th, 2015
fabulous
4. Tony
September 4th, 2015
Hi 9tut, I will be taking the 640-722. Can you send me the latest dump for CCNA_Wireless?
Appreciate it aeaster235@yahoo.com
5. nhial
September 29th, 2015
can anyone send me CD video of CCNAjuniornhial@gmail.comi will be grateful
6. WIRE
October 25th, 2015
Get Latest Update 100% VALID DUMPS here:
Remove asterisk
wireless-tut.blog*s*p*o*t*.*c*o*m
7. Anonymous
November 5th, 2015
any labs for the 640-722 exam please send to juka1@ayhoo.com
thank you
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
Page 5 of 7
8. ciscozel
November 16th, 2015
passed ccna wireless easy email massimokaba@gmail.com
Comment pages
Previous 1 2 787
Add a Comment
Name
Submit Comment
Subscribe to comments feed
Frame Relay Tutorial Frame Relay GNS3 Lab
Premium Membership
Become a member to interact with all questions and read all tutorials, labs!
Find out more or Sign In
CCNA 200-120
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
CCNA Lab Sim
CCNA Basic Questions
CCNA OSI & TCP/IP Model
CCNA IOS Questions
CCNA WAN Questions
CCNA Switch Questions
CCNA Switch Questions 2
CCNA VLAN Questions
CCNA Trunking Questions
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
Page 6 of 7
CCNA Trunking Questions 2
CCNA EtherChannel
CCNA InterVLAN Questions
CCNA STP
CCNA STP 2
CCNA RSTP
CCNA Access list Questions
CCNA Subnetting
CCNA Subnetting 2
CCNA IP Routing Questions
CCNA IP Routing 2
CCNA Frame Relay
CCNA Frame Relay 2
CCNA NAT PAT Questions
CCNA OSPF Questions
CCNA OSPF Questions 2
CCNA EIGRP Questions
CCNA DHCP Questions
CCNA HSRP VRRP GLBP
CCNA SNMP Questions
CCNA NetFlow Questions
CCNA Syslog Questions
CCNA Security Questions
CCNA Operation Questions
CCNA Operation 2
CCNA Show commands
CCNA Troubleshooting
CCNA IPv6
CCNA IPv6 Questions 2
CCNA Drag and Drop 1
CCNA Drag and Drop 2
CCNA Drag and Drop 3
CCNA Drag and Drop 4
CCNA Drag and Drop 5
CCNA FAQs & Tips
Share your CCNA Experience
CCNA Self-Study
z
z
z
Practice CCNA GNS3 Labs
CCNA Knowledge
CCNA Lab Challenges
Network Resources
z
Free Router Simulators
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
CCNA Training Wireless Tutorial
ICND1/ICND2 Website
CCNP - ROUTE Website
CCNP - SWITCH Website
CCNP - TSHOOT Website
CCNA Security Website
CCNA Voice Website
CCNA Wireless Website
CCIE Website
Page 7 of 7
Top
Copyright 2010-2013 CCNA Training
Site Privacy Policy. Valid XHTML 1.1 and CSS 3.BH
http://www.9tut.com/wireless-tutorial
12/15/2015
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 22 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 22 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Table 5.2.2.1.1/1: Insert Subscriber Data RequestDokument1 SeiteTable 5.2.2.1.1/1: Insert Subscriber Data RequestAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 23 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 23 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Table 5.2.1.1.1/2: Update Location Answer: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 14 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteTable 5.2.1.1.1/2: Update Location Answer: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 14 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 5.2.2 Subscriber Data Handling Procedures: 5.2.1.3.3 Detailed Behaviour of HSSDokument1 Seite5.2.2 Subscriber Data Handling Procedures: 5.2.1.3.3 Detailed Behaviour of HSSAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2 Mobility Services: 5.2.1 Location Management ProceduresDokument1 Seite5.2 Mobility Services: 5.2.1 Location Management ProceduresAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 15 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 15 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- 7 Protocol Specification and Implementation ........................................................................................... 37Dokument1 Seite7 Protocol Specification and Implementation ........................................................................................... 37Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 5 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 5 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Table 5.2.1.1.1/1: Update Location Request: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 13 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteTable 5.2.1.1.1/1: Update Location Request: ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 13 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 10 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 10 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Definitions and AbbreviationsDokument1 Seite3 Definitions and AbbreviationsAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
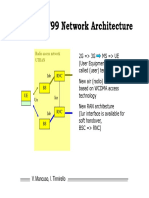
- GSM/GPRS Network GSM/GPRS Network Architecture Architecture: Radio Access Network BSSDokument1 SeiteGSM/GPRS Network GSM/GPRS Network Architecture Architecture: Radio Access Network BSSAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Spec EEEN60141Optical Com and Adhoc Updated June213Dokument30 SeitenUnit Spec EEEN60141Optical Com and Adhoc Updated June213Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Intellectual Property RightsDokument1 SeiteIntellectual Property RightsAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 3 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 3 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- ETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 1 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Dokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272 V9.13.0 (2014-07) 1 3GPP TS 29.272 Version 9.13.0 Release 9Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- LearnEnglish EfE Unit 4 Support PackDokument3 SeitenLearnEnglish EfE Unit 4 Support PackAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- ETSI TS 129 272: Technical SpecificationDokument1 SeiteETSI TS 129 272: Technical SpecificationAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
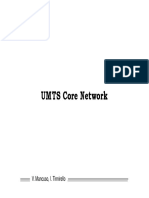
- 5 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreDokument1 Seite5 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- 4 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreDokument1 Seite4 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreDokument1 Seite3 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreDokument1 Seite1 PDFsam 13 Umts CoreAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS Network Planning Optimization and Inter Operation With GSM - p26Dokument1 SeiteUMTS Network Planning Optimization and Inter Operation With GSM - p26Amro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSOFTX3000 RNC ConfigurationDokument17 SeitenMSOFTX3000 RNC ConfigurationAmro GoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrayMfg ESD Catalog 2015Dokument12 SeitenTrayMfg ESD Catalog 2015Nicholas FlandinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cours de Géographie de L'habitat 2 Année Semestre Quatre Responsable de La Matière: Mme: Tebbi HafidaDokument22 SeitenCours de Géographie de L'habitat 2 Année Semestre Quatre Responsable de La Matière: Mme: Tebbi HafidaAmina AminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-Gothic Arch TracingDokument44 Seiten6-Gothic Arch TracingArun Kumar100% (2)
- Practical 5 - Timothy WellsDokument34 SeitenPractical 5 - Timothy WellsTimothy Alexander WellsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
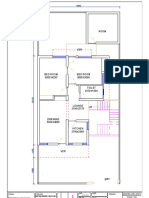
- Plan - Vikas NagarDokument1 SeitePlan - Vikas NagarPrakhar AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyfin Ag PDFDokument4 SeitenPolyfin Ag PDFvranceanu.ovidiu-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1-L Shaped LED SCAFFOLD - Copy-ModelDokument1 Seite1-L Shaped LED SCAFFOLD - Copy-ModelAbdul HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceh Chap8 QuizletDokument2 SeitenCeh Chap8 QuizletlynnverbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renaissance in FranceDokument23 SeitenRenaissance in FranceNihal Singh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel APHDokument2 SeitenOpen Channel APHponmanikandan1Noch keine Bewertungen
- NEU - Statement of PurposeDokument2 SeitenNEU - Statement of PurposeAkash WaradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Storey Residential Research Paper PDFDokument12 Seiten2 Storey Residential Research Paper PDFJayson Malaa100% (1)
- 02 - Occupant Load General ConditionsDokument5 Seiten02 - Occupant Load General ConditionsLean Liganor100% (1)
- C V AnglaisDokument3 SeitenC V AnglaisEric TamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Eats EatonDokument2 SeitenEats Eatonapi-356873137Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ac 133Dokument7 SeitenAc 133thirumalaichettiar100% (2)
- Med2 PC Building Uk HR PDFDokument1 SeiteMed2 PC Building Uk HR PDFfiorenzorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZALUX Protected LED Luminaires WEB PDFDokument64 SeitenZALUX Protected LED Luminaires WEB PDFopplusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonry Information: Masonry Cement: Product Data SheetDokument4 SeitenMasonry Information: Masonry Cement: Product Data SheetarylananylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Essay On The Architectural Sojourn in ManilaDokument4 SeitenAn Essay On The Architectural Sojourn in ManilaMae Francis V. MiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permalife Louver VentsDokument6 SeitenPermalife Louver VentsarchitecturalelementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterasys BasicDokument774 SeitenEnterasys Basicdiego valladolidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 978 3 86644 515 4 - PdfaDokument194 Seiten978 3 86644 515 4 - PdfacenabettinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConstructionDokument38 SeitenConstructionChakravarthi NagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Commands For Powershell: Configuring Windows PowerShell and Working With Basic CommandsDokument14 SeitenBasic Commands For Powershell: Configuring Windows PowerShell and Working With Basic CommandsDr. Hitesh Mohapatra100% (2)
- San Luis Reservoir State Recreaion Area Campground MapDokument2 SeitenSan Luis Reservoir State Recreaion Area Campground MapCalifornia State ParksNoch keine Bewertungen
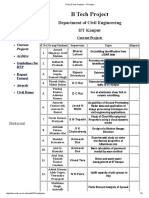
- CIVIL B Tech Projects - IIT KanpurDokument2 SeitenCIVIL B Tech Projects - IIT Kanpurjayaram miryalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Re-Homing ProcessDokument17 SeitenRe-Homing ProcessKuldeep SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full World of Art 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank PDFDokument35 SeitenDwnload Full World of Art 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank PDFoctopodatomjohnnh73100% (7)
- Price ListDokument1 SeitePrice ListKeh En YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (543)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxVon EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (67)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonVon EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceVon EverandThe Journeyman Electrician Exam Study Guide: Proven Methods for Successfully Passing the Journeyman Electrician Exam with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen