Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jaja Pagawa
Hochgeladen von
Dan Zky0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
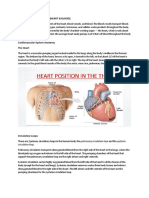
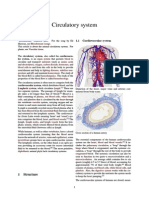
8 Ansichten1 SeiteThe circulatory system circulates blood and lymph through the body using the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph vessels and glands. The heart is a hollow muscular organ that pumps blood through the body in a rhythmic contraction and dilation. Blood is the red liquid that circulates through the arteries and veins, carrying oxygen to tissues and carbon dioxide away from tissues. Key components of blood include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. The circulatory system is divided into pulmonary circulation, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart, and systemic circulation, which then pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body before returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe circulatory system circulates blood and lymph through the body using the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph vessels and glands. The heart is a hollow muscular organ that pumps blood through the body in a rhythmic contraction and dilation. Blood is the red liquid that circulates through the arteries and veins, carrying oxygen to tissues and carbon dioxide away from tissues. Key components of blood include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. The circulatory system is divided into pulmonary circulation, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart, and systemic circulation, which then pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body before returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
8 Ansichten1 SeiteJaja Pagawa
Hochgeladen von
Dan ZkyThe circulatory system circulates blood and lymph through the body using the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph vessels and glands. The heart is a hollow muscular organ that pumps blood through the body in a rhythmic contraction and dilation. Blood is the red liquid that circulates through the arteries and veins, carrying oxygen to tissues and carbon dioxide away from tissues. Key components of blood include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. The circulatory system is divided into pulmonary circulation, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart, and systemic circulation, which then pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body before returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
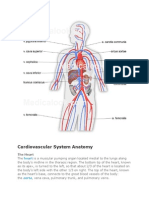
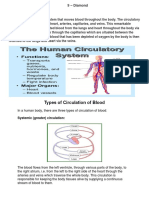
Circulatory system is the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart,
blood vessels, blood,
lymph, and the lymphatic vessels and glands.
Heart is a hollow muscular organ that pumps the blood through the circulatory system by rhythmic contraction and dilation. In
vertebrates there may be up to four chambers (as in humans), with two atria and two ventricles.
Blood is a hollow muscular organ that pumps the blood through the circulatory system by rhythmic contraction and dilation. In
vertebrates there may be up to four chambers (as in humans), with two atria and two ventricles.
Blood vessels the red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins of humans and other vertebrate animals, carrying oxygen to and
carbon dioxide from the tissues of the body.
Atria is a tubular structure carrying blood through the tissues and organs; a vein, artery, or capillary.
Ventricles is an open-roofed entrance hall or central court in an ancient Roman house.
Valves is a device for controlling the passage of fluid through a pipe or duct, especially an automatic device allowing movement in
one dire ction only.
Red blood cells is less technical term for erythrocyte.
White bloods cells is less technical term for leukocyte.
Platelets is a small colorless disk-shaped cell fragment without a nucleus, found in large numbers in blood and involved in clotting.
Ateries is any of the muscular-walled tubes forming part of the circulation system by which blood (mainly that which has been
oxygenated) is conveyed from the heart to all parts of the body.
Veens is any of the tubes forming part of the blood circulation system of the body, carrying in most cases oxygen-depleted blood
toward the heart.
Capellaries is any of the fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules.
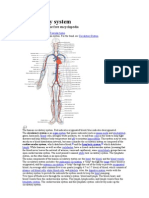
Pulmonary circulation is the portion of the cardiovascular system which carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the
lungs, and returns oxygenated (oxygen-rich) blood back to the heart.
Systemic circulation is the part of the cardiovascular system which carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and
returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. PubMed Health Glossary. (Source: Wikipedia) Related terms: Blood circulatory
system.
Anemia is a condition marked by a deficiency of red blood cells or of hemoglobin in the blood, resulting in pallor and weariness.
Heart attack is a sudden and sometimes fatal occurrence of coronary thrombosis, typically resulting in the death of part of a heart
muscle.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionVon EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SysDokument10 SeitenCirculatory SysnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Psychology Notes 2Dokument8 SeitenBio Psychology Notes 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDokument4 SeitenSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood CirculationDokument8 SeitenBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Science Part 2Dokument21 SeitenMedical Science Part 2Gauge FalkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADokument6 SeitenCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument71 SeitenCirculatory SystemAnas Mustafa HashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory Word OfficeDokument6 SeitenCirculatory Word OfficeMaria Christina CaceresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument111 SeitenCirculatory SystemYounas Bhatti100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument17 SeitenCardiovascular SystemPoojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Dokument4 SeitenRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)Dokument111 SeitenThe Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)brdaisyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Hollow Muscular Organ That Pumps The Blood Through The Circulatory System by Rhythmic Contraction and DilationDokument1 SeiteA Hollow Muscular Organ That Pumps The Blood Through The Circulatory System by Rhythmic Contraction and Dilationamber_harthartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument7 SeitenCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDokument16 SeitenCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDokument13 SeitenCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDokument3 SeitenCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemGodsend OparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Enrichment Activity For Term 2Dokument5 SeitenSubject Enrichment Activity For Term 2AADITRYA JAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartSyafiq RozaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cardiovascular SystemDokument8 SeitenThe Cardiovascular Systemsri samrithikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory SystemDokument8 SeitenThe Circulatory SystembysshelarbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeartDokument1 SeiteHeartVanessa Plata Jumao-asNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12, BioDokument26 SeitenChapter 12, BioRylee LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Circulatory SystemsDokument8 SeitenTypes of Circulatory SystemsJanis Micaela EsmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System Vascular TissueDokument8 SeitenCirculatory System Vascular TissueDrSachin SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument5 SeitenCirculatory System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBruce WayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course of Circulation Through Human Heart: Lymphatic SystemDokument4 SeitenCourse of Circulation Through Human Heart: Lymphatic Systemvishal pundirNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 2a CirculationDokument8 SeitenWEEK 2a Circulationdoodle dangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem Peredaran Darah ResumeDokument10 SeitenSistem Peredaran Darah Resumeilham ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- BookDokument8 SeitenBookmohamed aweys abuukarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in AnimalsDokument12 SeitenTransport in AnimalsJedidiah DickNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument8 Seiten6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDwnya S HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Circulation of BloodDokument5 SeitenTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Circulation of BloodDokument4 SeitenTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument44 SeitenCirculatory SystemAdonai Jireh Dionne BaliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- About The Circulatry System 001Dokument46 SeitenAbout The Circulatry System 001gaboelgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDokument39 SeitenScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument12 SeitenCirculatory SystemDipanshu JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Cardiovascular SystemDokument6 Seiten1 Cardiovascular SystemWaltz PadlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio & LymphaticDokument13 SeitenCardio & LymphaticJoan GalarceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02Dokument75 SeitenCardiovascularsystem 090820055728 Phpapp02muhammad ijazNoch keine Bewertungen
- M10 Myself - JawapanDokument4 SeitenM10 Myself - JawapanSteven OwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument1 SeiteCirculatory Systemandrzej36Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Systems Objective 2-1Dokument4 SeitenTransport Systems Objective 2-1darielleollivierreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System: FunctionsDokument12 SeitenCirculatory System: FunctionsAngelica Raquel Diaz CorralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General.: Blood CirculationDokument3 SeitenGeneral.: Blood CirculationJessica MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SystemDokument63 SeitenSystemBeth Rubin RelatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory System of Fish Is Quite SimpleDokument3 SeitenThe Circulatory System of Fish Is Quite SimpleEarl John Fajarito RafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsDokument17 SeitenTransport and Circulation in Plants and AnimalsTekomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Closed Circulatory SystemDokument8 SeitenClosed Circulatory Systemfardhu91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Dokument13 SeitenBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument9 SeitenPregnancy Induced HypertensionRiazell Antonio DungcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE Circulatory SystemDokument76 SeitenTHE Circulatory SystemJerickson Javier VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System SummaryDokument3 SeitenCirculatory System SummaryNiel S. DefensorNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcknowledgementDokument9 SeitenAcknowledgementJovin AshickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Circulatory SystemDokument9 SeitenHuman Circulatory SystemHimanshu JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Notes - Circulatory SystemDokument6 SeitenStudent Notes - Circulatory SystemJanith VimukthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ticket SheetDokument1 SeiteTicket SheetDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bethany Christ Church - Solicitation LetterDokument1 SeiteBethany Christ Church - Solicitation LetterDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signature Card - Aline AsuncionDokument1 SeiteSignature Card - Aline AsuncionDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSNSNSNDokument2 SeitenNSNSNSNDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cannot Print in ExcelDokument1 SeiteCannot Print in ExcelDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Compounds Defined1Dokument6 SeitenChemical Compounds Defined1Dan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAPPyDokument1 SeiteHAPPyDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massage TherapyDokument7 SeitenMassage TherapyDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bir DeadlinesDokument1 SeiteBir DeadlinesDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filing Reference No.: Bureau of Internal RevenueDokument1 SeiteFiling Reference No.: Bureau of Internal RevenueDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 30 17Dokument104 Seiten09 30 17Dan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Perfect Guide To Understanding Diabetes: Monica Danforth BSC 1008 24 July 2011 Professor RiveroDokument17 SeitenThe Perfect Guide To Understanding Diabetes: Monica Danforth BSC 1008 24 July 2011 Professor RiveroDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angel Kylie M. Romero Angel Kylie M. Romero: Awarded To Awarded ToDokument2 SeitenAngel Kylie M. Romero Angel Kylie M. Romero: Awarded To Awarded ToDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Spring - Is A Produced by The Emergence of Geothermally Heated GroundDokument2 SeitenHot Spring - Is A Produced by The Emergence of Geothermally Heated GroundDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative ReportDokument1 SeiteNarrative ReportDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Studies of Educational SystemsDokument6 SeitenComparative Studies of Educational SystemsDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProgrammeDokument2 SeitenProgrammeDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screening Grade 6 EnglishDokument3 SeitenScreening Grade 6 EnglishDan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Grade 5 English11Dokument4 SeitenDLL Grade 5 English11Dan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Cut A Square From ADokument1 SeiteHow To Cut A Square From ADan ZkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Grade 5 EnglishDokument10 SeitenDLL Grade 5 EnglishDan Zky0% (1)
- Pentra 120 DX PrintDokument6 SeitenPentra 120 DX Printnbiolab6659Noch keine Bewertungen
- NERVOUS TISSUE HandoutDokument6 SeitenNERVOUS TISSUE HandoutAkemi100% (1)
- Sysmex CA-1500 System Reference Guide 3.05 DXDCM 0900ac6d8005f093-1421696006187Dokument209 SeitenSysmex CA-1500 System Reference Guide 3.05 DXDCM 0900ac6d8005f093-1421696006187Evgeniy KaluhNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On The Correlation of ABO Blood Group System and HypertensionDokument4 SeitenA Study On The Correlation of ABO Blood Group System and HypertensionHema SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Groups Assignment AaaDokument3 SeitenBlood Groups Assignment AaaLoro JDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Flow Sheet: Hematology Blood ChemistryDokument2 SeitenLaboratory Flow Sheet: Hematology Blood ChemistrytrialqwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thromboembolic Disease PDFDokument5 SeitenThromboembolic Disease PDFBáĦẳá Y. Ẳl-mársǾúmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ananya Deb - 18IUT0290004Dokument26 SeitenAnanya Deb - 18IUT0290004subankar NagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Groups - ABO & RH - Draw It To Know ItDokument1 SeiteBlood Groups - ABO & RH - Draw It To Know ItDuy LuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Storage at Room and Refrigerator Temperatures On Sprague-Dawley Rat Hematology Blood Parameters and Peripheral Blood Smear FindingsDokument1 SeiteEffects of Storage at Room and Refrigerator Temperatures On Sprague-Dawley Rat Hematology Blood Parameters and Peripheral Blood Smear FindingsraysellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLOODTYPING lABORATORY REPORTDokument12 SeitenBLOODTYPING lABORATORY REPORTAdrian BabantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec - M4. Post Task I - Cardiovascular SystemDokument2 SeitenLec - M4. Post Task I - Cardiovascular SystemEmily BernatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System VCE BiologyDokument6 SeitenCirculatory System VCE BiologyCallum KennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy - QuizDokument2 SeitenAnatomy - Quizloan kimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Package Insert - SurgiscreenDokument5 SeitenPackage Insert - SurgiscreenAhmed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 Blood Component SeparationDokument8 Seiten4.1 Blood Component Separationayan CustodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAS - BC - Microtainer Tubes Order of Draw Poster - IM - ENDokument1 SeitePAS - BC - Microtainer Tubes Order of Draw Poster - IM - ENJeanneRoseBlancaflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connective Tissue ImagesDokument54 SeitenConnective Tissue ImagesSaaraAlleyahAlAnaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.Dokument2 SeitenCHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.MAHESH GAUTAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Group SerologyDokument89 SeitenBlood Group SerologynelsonlaizerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscular SystemDokument11 SeitenMuscular SystemGerarld Agbon100% (1)
- 1956 Pritchard JJ, Scott JH, Girgis FG. The Structure and Development ofDokument17 Seiten1956 Pritchard JJ, Scott JH, Girgis FG. The Structure and Development ofplayer osamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Phlebotomy EquipmentDokument10 Seiten4 Phlebotomy Equipmentmarche malnegroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oleh: DR Hudiarso SPPD Finasim Rs Puriasih SalatigaDokument38 SeitenOleh: DR Hudiarso SPPD Finasim Rs Puriasih Salatigaade ayuningsih utamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Blood Pressure Palpatory MethodDokument2 Seiten1-Blood Pressure Palpatory MethodUsama100% (1)
- Inventory Management of Blood ComponentsDokument20 SeitenInventory Management of Blood ComponentsNallagondla ThulasiramNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataSheet CoaLAB 1000 EN 11-2017 PDFDokument4 SeitenDataSheet CoaLAB 1000 EN 11-2017 PDFAgnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Adults - UpToDateDokument48 SeitenApproach To Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding in Adults - UpToDateDũng Hoàng Nghĩa TríNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions: CLS 422 Clinical Immunohematology I Absorption and ElutionDokument6 SeitenDefinitions: CLS 422 Clinical Immunohematology I Absorption and ElutionTrang HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - WBC Abnormalities: 3.1 NeutrophiliaDokument25 SeitenChapter 3 - WBC Abnormalities: 3.1 NeutrophiliaShishir AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen