Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fluid Mosaic Model
Hochgeladen von
api-292439032Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fluid Mosaic Model
Hochgeladen von
api-292439032Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
You are made up of trillions and trillions of cells, and each one is separated
from its surroundings by a cell membrane. Learn about the structure and
functions of the cell membrane in this lesson.
The Cell Membrane is a Fluid Mosaic
A cell is the basic unit of life, and all organisms are made up of one or
many cells. One of the things that all cells have in common is a cell
membrane. It is a barrier that separates a cell from its surrounding
environment. This outer boundary of the cell is also called the plasma
membrane. It is composed of four different types of molecules:
1. Phospholipids
2. Cholesterol
3. Proteins
4. Carbohydrates
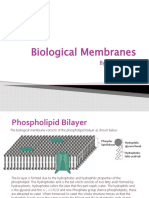
The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of a cell membrane. It
indicates that the cell membrane is not solid. It is flexible and has a similar
consistency to vegetable oil, so all the individual molecules are just
floating in a fluid medium, and they are all capable of moving sideways
within the cell membrane. Mosaic refers to something that contains many
different parts. The plasma membrane is a mosaic of phospholipids,
cholesterol molecules, proteins and carbohydrates.
Phospholipids
Phospholipids make up the basic structure of a cell membrane. A single
phospholipid molecule has two different ends: a head and a tail. The head
end contains a phosphate group and is hydrophilic. This means that it
likes or is attracted to water molecules.
The tail end is made up of two strings of hydrogen and carbon atoms
called fatty acid chains. These chains are hydrophobic, or do not like to
mingle with water molecules. This is just like what happens when you pour
vegetable oil in water. The vegetable oil will not mix with the water.
The phospholipids of a cell membrane are arranged in a double layer
called the lipid bilayer. The hydrophilic phosphate heads are always
arranged so that they are near water. Watery fluids are found both inside a
cell (intracellular fluid) and outside a cell (extracellular fluid). The
hydrophobic tails of membrane phospholipids are organized in a manner
that keeps them away from water.
This arrangement of phospholipid molecules makes up the lipid bilayer.
Cholesterol, Proteins and Carbohydrates
When you hear the word cholesterol, the first thing you probably think of is
that it is bad. However, cholesterol is actually a very important component
of cell membranes. Cholesterol molecules are made up of four rings of
hydrogen and carbon atoms. They are hydrophobic and are found among
the hydrophobic tails in the lipid bilayer.
Cholesterol molecules are important for maintaining the consistency of the
cell membrane. They strengthen the membrane by preventing some small
molecules from crossing it. Cholesterol molecules also keep the
phospholipid tails from coming into contact and solidifying. This ensures
that the cell membrane stays fluid and flexible.
Some plasma membrane proteins are located in the lipid bilayer and are
called integral proteins. Other proteins, called peripheral proteins, are
outside of the lipid bilayer. Peripheral proteins can be found on either side
of the lipid bilayer: inside the cell or outside the cell. Membrane proteins
can function as enzymes to speed up chemical reactions, act as receptors
for specific molecules, or transport materials across the cell membrane.
Carbohydrates, or sugars, are sometimes found attached to proteins or
lipids on the outside of a cell membrane. That is, they are only found on
the extracellular side of a cell membrane. Together, these carbohydrates
form the glycocalyx.
The glycocalyx of a cell has many functions. It provides cushioning and
protection for the plasma membrane, and it is also important in cell
recognition. Based on the structure and types of carbohydrates in the
glycocalyx, your body can recognize cells and determine if they should be
there or not. The glycocalyx can also act as a glue to attach cells together.
This is the fluid mosaic model of a cell membrane
Cell Membrane Functions
The plasma membrane of a cell has two main roles:
1. It is a physical barrier.
2. It regulates exchange of materials with its surroundings.
The cell membrane is important because it separates and protects a cell
from its surroundings. This allows the intracellular conditions of a cell to be
very different from the extracellular conditions. For example, nerve cells in
your body will maintain a high concentration of potassium inside. Outside,
in the extracellular fluid, there is very little potassium and lots of sodium.
These concentration differences are absolutely necessary for the function
of nerve cells, which is to send signals or nerve impulses.
A cell membrane's structure and properties, like having hydrophilic outer
areas and hydrophobic inner regions, prevents many substances from
entering or leaving a cell. This is good because it means that unwanted
materials don't accidentally get inside a cell. However, many materials,
like the nutrient glucose, do need to cross the cell membrane. Also, waste
substances need to get out of a cell. If they did not, the wastes would
build up and become toxic to the cell.
The cell membrane is able to regulate what comes in and what goes out of
a cell. This is called selective permeability. Only very small molecules,
such as water, oxygen or carbon dioxide, can easily pass through the lipid
bilayer of a cell membrane. Any other substances that must cross the cell
membrane must pass through the transport proteins. These proteins are
very specific about what they transport. For example, your cell
membranes have transporters that will only allow for the movement of
glucose molecules. There are others with different structures that only
transport sodium.
The selective permeability of a cell membrane: Some molecules can pass
through the phospholipid layer. Those that cannot, must have their own
transport proteins.
Lesson Summary
The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, surrounds and protects the
internal environment of a cell; however, this is not its only function. A cell
membrane also determines what materials enter or leave the cell. This
ensures that the cells will be able to get rid of wastes and take up
important nutrients and gases.
The plasma membrane is a fluid mosaic. This means that it is flexible and
made up of many different types of molecules. Phospholipids form the
basic structure of a cell membrane, called the lipid bilayer. Scattered in
the lipid bilayer are cholesterol molecules, which help to keep the
membrane fluid consistent. Membrane proteins are important for
transporting substances across the cell membrane. They can also function
as enzymes or receptors. On the extracellular fluid side of a cell
membrane, you find carbohydrates. They help a cell to be recognized as
a certain type of cell and are important for holding cells together.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Control of Environmental Parameters in A Green HouseDokument46 SeitenControl of Environmental Parameters in A Green Housekenbobalaji100% (1)
- Do Now:: - Complete The CH 8 Prior Knowledge WorksheetDokument27 SeitenDo Now:: - Complete The CH 8 Prior Knowledge Worksheetapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
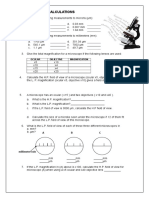
- Microscope CalculationsDokument2 SeitenMicroscope Calculationsapi-292439032100% (1)
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDokument3 SeitenCell Membrane Structure and FunctionLalata, Bianca Nicole D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Dokument24 SeitenAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembraneDokument2 SeitenCell MembranegrxcieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic of LifeDokument21 SeitenThe Basic of LifeJALAL JAMINoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane TransportDokument3 SeitenCell Membrane TransportHarry TeasdaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- q1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditDokument13 Seitenq1 Genbio1 Slkweek6 EditInele Ellia AgReNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of LifeDokument11 SeitenLecture 3 Notes Cellular Basis of Lifeochienganthony001Noch keine Bewertungen
- BiotechnologyDokument14 SeitenBiotechnologyLian Gwyneth TomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytoplasm and Plasma Membrane FunctionsDokument5 SeitenCytoplasm and Plasma Membrane FunctionsHamza MaqboolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Struct-Function Cell OrgaDokument30 SeitenStruct-Function Cell OrgaSiaw Sing OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share Cell Structure and FunctionsDokument47 SeitenShare Cell Structure and FunctionszzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 CellsDokument17 SeitenModule 1 CellsLara C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mosaic Model NotesDokument4 SeitenFluid Mosaic Model NotesanzalnaamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembraneDokument4 SeitenCell MembraneAbdi Majid Mohamed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Biological Membranes and Transports - Chapter-5 - Part 3Dokument27 Seiten5 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Biological Membranes and Transports - Chapter-5 - Part 3MD. SAJID GHUFRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanation and Acceptable Reason YeahDokument3 SeitenExplanation and Acceptable Reason YeahMj DeguzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembraneDokument7 SeitenCell MembraneRishikesh BhintadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE CELL STRUCTUREDokument93 SeitenTHE CELL STRUCTURERonald BakangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembraneDokument10 SeitenCell Membraneharshika tembhurneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell 1Dokument7 SeitenThe Cell 1Eniola DaramolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1Dokument7 SeitenLec 1dhoha alawsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADOCS1002 - Course NotesDokument12 SeitenADOCS1002 - Course NotesMostafa MansourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Section 2 OutlineDokument5 SeitenChapter 7 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455051100% (1)
- The Cell MembraneDokument36 SeitenThe Cell Membraneanulorance98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane in Transport MechanismsDokument29 SeitenCell Membrane in Transport MechanismsAnnie LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Midterm ReviewDokument49 SeitenBio Midterm ReviewLinh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell and Its FunctionsDokument71 SeitenThe Cell and Its FunctionsMirema CyberNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideDokument6 SeitenThis Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideZuzuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument7 SeitenCellPrashant PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of A CellDokument4 SeitenFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How eukaryotic cells organize into specialized structuresDokument6 SeitenHow eukaryotic cells organize into specialized structuresjuan mondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembraneDokument3 SeitenCell MembranesajmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Dokument6 SeitenCell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Rica NorcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of MicroorganismsDokument42 SeitenChemistry of MicroorganismsJisan RaihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma MembraneDokument6 SeitenPlasma Membraneparashakthi PRNoch keine Bewertungen
- SF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaDokument10 SeitenSF - MD.0145.T.22 Ally Omary MwambelaAlly OmaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1Dokument39 SeitenLec 1Hussain AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Functions & Organelles in 40 CharactersDokument14 SeitenCell Functions & Organelles in 40 Charactersamber tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDokument35 SeitenFull Download Zoology 9th Edition Miller Solutions Manualcaveneywilliams100% (14)
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsDokument5 SeitenChapter 3: Cell Structure and Internal Compartments: Key ConceptsFrancis PhimphivongNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOC 315 - Lecture - 1Dokument28 SeitenBIOC 315 - Lecture - 1Kevin KipropNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOWEEK5RANESDokument29 SeitenBIOWEEK5RANESvrbatitangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 (2.1)Dokument13 SeitenChapter 2 (2.1)mrtheunknownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Worlds: MDSC 1001 PBL Problem 1 Tutor: DR S. ChaseDokument27 SeitenCellular Worlds: MDSC 1001 PBL Problem 1 Tutor: DR S. Chasebrennan12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDokument10 SeitenClass 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesHARKIRIT KAUR100% (1)
- Cell StrucutreDokument40 SeitenCell StrucutreJeevitha VanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure & MembraneDokument24 SeitenCell Structure & MembraneAbhishek Singh ChandelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceDokument34 SeitenChapter - 5 Cell - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Class Ix Cbse - ScienceMadhav DayareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Dokument10 SeitenSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Ali InamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Notes in Histology LecDokument8 SeitenAdditional Notes in Histology LecJISOO KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiDokument10 SeitenBiological Membranes: by Hajar SaihiMariam El KhatibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of CellDokument42 SeitenStructure of CellJeevitha VanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - kh201295 kh201295Dokument11 Seiten2 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 4 Plasma MembraneDokument22 Seiten2 4 Plasma Membraneıamnıkolaı 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDokument2 SeitenCell and Molecular BiologyAttaullah36Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology 2Dokument25 SeitenMicrobiology 2Ba SitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure & OrganellesDokument14 SeitenEukaryotic Cell Structure & OrganellesCamyChaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport MechanismDokument2 SeitenTransport MechanismStephanie Cyrelle Jane BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rs Animal Ethics 2nd ClassDokument3 Seiten3rs Animal Ethics 2nd Classapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3rs Animal Ethics 1st ClassDokument3 Seiten3rs Animal Ethics 1st Classapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity Liz RaynerDokument21 SeitenBiodiversity Liz Raynerapi-292439032100% (1)
- 5 Kingdoms - ClassificationDokument1 Seite5 Kingdoms - Classificationapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- ClassificationDokument26 SeitenClassificationapi-292439032100% (2)
- Conservation StrategiesDokument13 SeitenConservation Strategiesapi-292439032100% (1)
- 3 Unit 2a NutrientsDokument29 Seiten3 Unit 2a Nutrientsapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Revision Unit 1 ExamDokument4 SeitenBiology Revision Unit 1 Examapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Energy and Matter in EcosystemsDokument30 SeitenEnergy and Matter in Ecosystemsapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classifying EcosystemsDokument18 SeitenClassifying Ecosystemsapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity Classification RevisionDokument3 SeitenBiodiversity Classification Revisionapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is It A Theory Hypothesis PredictionDokument2 SeitenIs It A Theory Hypothesis Predictionapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument12 SeitenCellsapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific MethodDokument20 SeitenScientific Methodapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- MicropartsDokument2 SeitenMicropartsapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis ExamplesDokument1 SeiteHypothesis Examplesapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- MicroscopecalculationsDokument4 SeitenMicroscopecalculationsapi-292439032100% (1)
- Surface Area To Volume RatioDokument1 SeiteSurface Area To Volume Ratioapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example Scientific Report 1Dokument12 SeitenExample Scientific Report 1api-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multicellular OrganismsDokument19 SeitenMulticellular Organismsapi-292439032100% (1)
- Biological MoleculesDokument9 SeitenBiological Moleculesapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Scientific MethodDokument6 SeitenThe Scientific Methodapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry NutrientsDokument12 SeitenBiochemistry Nutrientsapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 MetabolismDokument19 SeitenUnit 2 Metabolismapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example Scientific ReportDokument13 SeitenExample Scientific Reportapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Movements Across The Plasma MembraneDokument3 SeitenMovements Across The Plasma Membraneapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDokument14 SeitenTransport Across The Cell Membraneapi-292439032Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adelino Horizontal Multistage PumpDokument13 SeitenAdelino Horizontal Multistage PumpJaved HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Cooler LeafletDokument2 SeitenAir Cooler LeafletSaad zubayr MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines DC MotorDokument5 SeitenElectrical Machines DC MotorKitkay NivramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Potential EnergyDokument3 SeitenFactors Affecting Potential EnergyArgyll PaguibitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsional Vibration in CrankshaftsDokument10 SeitenTorsional Vibration in Crankshaftscharans100% (4)
- Production Range: EUROPIPE. The World Trusts UsDokument8 SeitenProduction Range: EUROPIPE. The World Trusts UsIslam-Lotfi Hadj-ArabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engines for Unrestricted Continuous OperationDokument2 SeitenDiesel Engines for Unrestricted Continuous OperationJorge Bellido100% (1)
- Installation Manual E-Brick en LoresDokument80 SeitenInstallation Manual E-Brick en LoresvideoramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Material ApplicationDokument16 SeitenValve Material Applicationehab8320014413100% (1)
- United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,106,570 B2Dokument20 SeitenUnited States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,106,570 B2zahra sdeghiniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two-Phase Flow (Gas-Flow) Line SizingDokument24 SeitenTwo-Phase Flow (Gas-Flow) Line SizingvictorvikramNoch keine Bewertungen
- DistanceDokument16 SeitenDistanceMostafa Mohmmed100% (1)
- Dose Complete CatalogueDokument272 SeitenDose Complete CatalogueBerkan OranusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine Chock InstallationDokument48 SeitenMarine Chock InstallationSumeet SawantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 320, 320L Medicion de Presiones Bomba Hidraulica PDFDokument181 Seiten320, 320L Medicion de Presiones Bomba Hidraulica PDFrprim100% (2)
- Waste Water-Sewage PumpDokument111 SeitenWaste Water-Sewage Pumpcharadeg100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aviation Tinning and SolderingDokument16 SeitenAviation Tinning and SolderingRebecca RiversNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Efficiency Battery Charger Using DC-DC ConverterDokument4 SeitenHigh Efficiency Battery Charger Using DC-DC ConvertersanilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Distillation and Flash DistillationDokument19 SeitenIntroduction to Distillation and Flash DistillationSalman HaniffaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVC6200Dokument4 SeitenDVC6200Jesus BolivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Slotting MachineDokument3 SeitenPneumatic Slotting MachineSwami NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ 140Dokument14 SeitenMCQ 140Aawez AkhterNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Electric Cars Work: A Guide to EV TechnologyDokument4 SeitenHow Electric Cars Work: A Guide to EV TechnologyCarla LoiaconoNoch keine Bewertungen
- R6.3 TR-XXL Parameter Settings ReleaseDokument493 SeitenR6.3 TR-XXL Parameter Settings Releasemishu35Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLF-76T Service ManualDokument40 SeitenPLF-76T Service Manualapi-3711045100% (1)
- Wind Turbine Installation-ManualDokument23 SeitenWind Turbine Installation-Manualויליאם סן מרמיגיוסNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Network of The Automotive Multi-Sectional Thermoelectric Generator With MPPT Based Device UsageDokument10 SeitenElectrical Network of The Automotive Multi-Sectional Thermoelectric Generator With MPPT Based Device UsageMouna MorchidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Energy - University QuesDokument2 SeitenWind Energy - University QuesKsn Hari100% (2)
- Boundary Layer ThicknessDokument23 SeitenBoundary Layer ThicknessPridhar ThiagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen