Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
PR2016 Mat 131 1477 Mapa Curricular Global
Hochgeladen von
Leonardo Torres PaganOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PR2016 Mat 131 1477 Mapa Curricular Global
Hochgeladen von
Leonardo Torres PaganCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
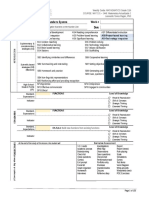
MARTES
TEMA: Los reales y
operaciones
JUEVES
1
2
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
TEMA: Propiedades.
Clausura
VIERNES
14
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
TEMA: Ecuaciones y
desigualdades
15
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
Determine if a number is a solution of an equation
Use the Addition Property of Equality to solve linear equations
Use the Multiplication Property of Equality to solve linear equations
Apply the Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality to solve linear
equations
Combine like terms and apply the Distributive Property to solve linear
equations
Solve linear equation with the variable on both sides of the equation
Use linear equations to solve problems
Use the least common denominator to solve linear equation containing
fractions
Solve linear equations containing decimals
Classify linear equations as identity, conditional, or contradiction
Use linear equations to solve problems
Evaluate a formula
Solve a formula for a variable
Translate English phrases to algebraic expressions
Translate English sentences to equations
Build odels for solving direct translation problems
Solve direct translation problems involving percent
Model and solve direct translation problems from business involving percent
Set up and solve complementary and supplementary angle problems
Set up and solve angles of a triangle problems
Use geometry formulas to solve problems
Set up and solve uniform motion problems
OBJETIVOS
Math 6. Module 3 Signed numbers
Represent inequalities using set builder notation, the real number line and
interval notation
Solve linear inequalities
Solve problems involving linear inequalities
Determine the intersection or union of two sets
Solve compound inequalities involving and
Solve compound inequalities involving or
Solve problem using compound inequalities
Solve absolute value equations
Solve absolute inequalities involving <,
Solve compound inequalities involving >,
Solve applied problems involving absolute value inequalities
MATH 6. MODULE 4G
MATH 8. MODULE 4: Linear equations
TEMA: Relaciones y
TEMA: Prop. y
21
TEMA:
grficas. Dominio
transformaciones
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Identify the graph of a function
Obtain information from or about the graph of a function
Determine even and odd functions from a graph
Identify even and odd functions from the equation
Use a graph to determine where a function is increasing, drcreasing, or
constant
Use a graph to locate maxima and local minima
Use a graph to locate the absolute maximum and the absolute minimum
Use a graphing utility to approximate local maxima or minima and to
determine where a function is increasing or decreasing
Find the average rate of change of a function
Plot points in the rectangular coordinate system
Determine if an ordered pair satisfies an equation
Create tables of values that satisfies an equation
Apply the distance formula
Apply the midpoint formula
Graph an equation using the point plotting method
Identify the intercepts from the graph of the equation
Test an equation for symmetry with respect to the x-axis, the y-axis, and the
origin
Interpret graphs
Find the domain and range of a relation
Graph a relation defines by an equation
Determine whether a relation expressed as a map or ordered pairs
represents a function
Determine whether a relation expressed as an equation represents a
function
Determine whether a relation expressed as a graph represents a function
Graph a function
Find the value of a function
Work with applications of functions
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
Graph and identify the functions listed in the library of functions
Graph piecewise defined functions
Graph functions using vertical and horizontal shifts
Graphs functions using compressions and stretches
Graph functions using reflections about the x-axis or y-axis
Build and analyze functions
Find the domain of a function defines by an equation
Obtain information from the graph of a function
Interpret graphs of a function
TEMA: Arit funciones.
Composicin
2
6
TEMA El crculo
28
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Form the sum, difference, product, and quotient of two
functions.
Composite functions
Write the standards form of the equation of a circle
Graph a circle
Find the center and radius of a circle from an equation in general form
TEMAPendiente y
ecuaciones
TEMA: Sist. ecuaciones e
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
Graph ellipses in which the center is in the origin
Find the equation of an ellipse in which the center is in t eorigin
Graph ellipses in which the center is not the origin
Solve applied problems involving ellipses
TEMA
inecuaciones
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Determine if an ordered pair is a solution of a system of linear equations
Solve a system of linear equations by graphing
Classify systems of linear equations as consistent or inconsistent
Solve applied problems involving systems of linear equations
Solve a system of linear equations using the substitution method
Graph a line by plotting points
Distinguish between linear and nonlinear relations
Graph a line using intercepts
Graph vertical and horizontal lines
TEMA: EXAMEN
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
29
Find the slope of a line given two points
Find the slope of vertical and horizontal lines
Graph a line using its slope and a point on the line
Solve problems involving the slope
Use the slope intercept form to identify the slope and the y-intercept of a
line
Graph a line whose equation is in slope-intercept form
Graph a line whose equation of a line is in the form Ax+By+C=0
Find the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept
Identify the slope and the y-intercept of a line from its equation
Graph lines written in general form using intercepts
Analyze linear models in slope intercept form
Find the equation of a line given a point and a slope
Find the equation of a line given two points
Build linear models using the point slope form of a line
Determine whether two lines are parallel
Find the equation of a line parallel to a given line
Determine whether two lines are perpendicular
Find the equation of a line perpendicular to a given line
Construct a model and solve direct variation problems
Construct a model and solve inverse variation problems
Solve applied problems involving systems of linear equations
Solve a system of linear equations using the elimination method
Solve applies problems involving systems of linear equations
Solve systems of Three Linear Equations containing three variables
Identify inconsistent systems
Express the solution of a system of dependent equations
Model and solve problems involving three linear equations containing three
unknowns
Graph an inequality
Graph a system of inequalities
Solve a system of nonlinear equations using substitution
Solve a system of non-linear equations using elimination
Graph linear functions
Use average rate of change to identify linear functions
Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing or constant
Build linear models from verbal descriptions
Build linear models from data
Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of a linear inequality
Graph linear inequalities
Solve problems involving linear inequalities
TEMA: MODELOS
CUADRATICOS
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Solve quadratic equations using the square root property
Complete the square in one variable
Solve quadratic equations by completing the square
Solve problems using the Pythagorean Theorem
Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula
Use the discriminant to determine the nature of solutions in a a quadratic
equation
Model and solve problems involving quadratic equations
Graph quadratic functions using transformations
2
Graph quadratic functions of the form
f ( x )=x +k
Graph quadratic functions of the form
f ( x )=( xh )2
Graph quadratic functions of the form
f ( x )=a x 2
Graph quadratic functions of the form
f ( x )=a x 2
Find the quadratic function from its graph
TEMA: PEAU
TEMA: PRAEP 2
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
12
Graph quadratic functions of the form
f ( x )=a x 2 +bx +c
Find the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function
Identify the axis of symmetry of a quadratic function
Graph a quadratic function using its vertex, axis, and intercepts
Find a quadratic function given its vertex and one other point
Model and solve optimization problems involving quadratic functions
Solve quadratic inequalities
ALGEBRA I. MODULO 4.A
TEMA: COMPLEJOS
1
6
TEMA: POLINMICAS
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Identify polynomial functions and their degree
Graph polynomial functions using transformations
Identify the real zeros of a polynomial function and their multiplicity
Analyze the graph of a polynomial function
Build cubic models from data
Evaluate the square root of negative real numbers
Add or subtract complex numbers
Multiply complex numbers
Divide complex numbers
Evaluate the power of i.
18
TEMA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
Use the remainder and Factor Theorem
Use the rational Zeros Theorem tolist the potential rational zeros of a
polynomial function
Find the real zeros of a polynomial function
Solve polynomial equations
Use the Theorem for Bounds on Zeros
Use the Intermediate Value Theorem
Use the Conjugate Pairs Theorem
Find a polynomial function with specified zeros
Find the complex zeros of a polynomial
PRECALCULUS MODULE 1
Use the Conjugate Pairs Theorem
Find a polynomial function with specified zeros
Find the complex zeros of a polynomial
ALGEBRA II, MODULE 1
PRECALCULUS MODULE 3
TEMA: ART POLINOMIOS
2
3
TEMA: FUNC RACIONALES
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Find the domain of a rational function
Find the vertical asymptotes of a rational function
Find the horizontal or oblique asymptote of a rational function
Analyze the graph of a rational function
Solve applied problems involving rational functions
Define monomial and determine the degree of a monomial
Define polynomial and determine the degree of a polynomial
Simplify polynomials by combining like terms
Evaluate polynomials
Multiply a polynomial by a monomial
Multiply two binomials using the distributive property
Multiply two binomials using the FOIL method
Multiply the sum and difference of two terms
Square a binomial
ALGEBRA II, MODULE 1
25
TEMA: EXAMEN
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
26
Multiply a polynomial by a polynomial
Divide a polynomial by a monomial
Divide a polynomial by a binomial
Divide polynomials using synthetic division
ALGEBRA II, MODULE 1
TEMA: ANGULOS
TEMA: CIRCULO UNITARIO
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Find the values of trigonometric functions of acute angles
Use the fundamental identities
Find the values of the remaining trigonometric functions, given the values of
one of them
Convert between decimals and degrees, minutes, seconds measures for
angles
Find the length of an arc of a circle
Convert from degrees to radians and from radians to degrees
Find the area of a sector of a circle
Find the linear speed of an object traveling in circular motion
TEMA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ALGRBRA II, MODULE 2.
PRECALCULUS MODULE 4
ALGRBRA II, MODULE 2.
TEMA: PROPIEDADES
TRIGON
TEMA: MODELOS
PERIODICOS
10
TEMA: TRIANGULOS
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Graph sinusoidal functions using transformations
Determine the amplitude and period of sinusoidal functions
Graph sinusoidal functions using key points
Find the equation for a sinusoidal graph
Find the value of trigonometric functions of acute angles using right
triangles
Use complementary angle theorem
Solve right triangles
Solve applied problems
Determine the domain and the range of the trigonometric functions
Determine the period of trigonometric functions
Determine the signs of the trigonometric functions in a given quadrant
Find the values of the trigonometric functions using fundamental identities
Find the exact values of the trigonometric function of an angle given one of
the functions and the quadrant of the angle
Use even-odd properties to find the exact values of the trigonometric
functions
Use the complementary angle theorem
Use algebra to simplify trigonometric expressions
Establish identities
Graph sinusoidal functions of the form
y= Asin ( Bxc )+ D
Build periodic models from data
ALGEBRA II. MODULE 2
PRECALCULUS MODULE 4
TEMA: TRIANGULO RECTO
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Find the value of trigonometric functions of acute angles using right
triangles
Use complementary angle theorem
Solve right triangles
1
5
TEMA: EXAMEN
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
17
TEMA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
11
Solve applied problems
TEMA: PRUEBAS Y
TEOREMAS
2
9
TEMA: GEOM ANALITICA
31
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Write and graph linear equations
Relate statistics and equations of lines to geometric
concepts
Prove theorems using coordinate proofs
Draw, locate or describe a locus in a plane or in space
Determine line symmetry and point symmetry
Draw reflections, translations, rotations, and dilations on
the coordinate plane
TEMA: ESTADISTICA
DESCRIPTIVA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
1. Construct frequency distributions both manually and with your
computer.
2. Construct and interpret a frequency histogram.
3. Develop and interpret joint frequency distributions.
4. Construct and interpret various types of bar charts.
5. Build a stem and leaf diagram.
6. Create a line chart and interpret the trend in the data.
7. Construct a scatter diagram and interpret it.
8. Compute the mean, median, mode, and weighted mean for a set
of data and understand what these values represent.
9. Construct a box and whisker graph and interpret it.
10. Compute the range, interquartile range, variance, and standard
TEMA: EXAMEN
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
TEMA: CONGRUENCIA Y
SEMEJANZA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
Similarity
Recognize and use rations and proportions
Identify similar figures and use the properties of similar
figures to solve problems
Use proportional parts of triangles to solve problems
MATH 7. MODULE 1, Rations and proportions
MATH 8. MODULE 2, Congruence
MATH 8. MODULE 3, Similarity
TEMA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
deviation and know what these values mean.
11. Compute a z score and the coefficient of variation and
understand how they are applied in decision-making situations.
12. Understand the Emperical Rule and Tchebysheffs Theorem.
MATH 6. MODULE 6
ALGEBRA I. MODULO 2
TEMA: CORRELACION Y
REGRESION
1
2
TEMA: PROBABILIDAD
14
TEMA: CURVA NORMAL
15
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
Find all the subsets of a set
Count the number of elements in a set
Solve counting problems using the multiplication principle
Solve counting problems using permutations involving n distinct object
Solve counting problems using combinations
Solve counting problems using permutations involving n-non distinct objects
Recognize when the normal distribution might apply in a decisionmaking process.
Be able to calculate probabilities using the normal distribution table
and be able to apply the normal distribution in appropriate business
situations.
Calculate and interpret the simple correlation between two
variables.
Determine whether the correlation is significant.
Calculate the simple linear regression equation for a set of data
and know the basic assumptions behind regression analysis.
Construct probability models
Compute probabilities of equally likely outcomes
Find probabilities of the union of two events
Use the complement rule to find probabilities
To compute probabilities from the normal distribution
To use the normal probability plot to determine whether a set of
data is approximately normally distributed
Determine whether a regression model is significant.
1. Understand the three approaches to assessing probabilities.
Calculate and interpret confidence intervals for the regression
coefficients.
2. Be able to apply the Addition Rule.
To compute probabilities from the uniform distribution
3. Know how to use the Multiplication Rule.
To compute probabilities from the exponential distribution
4. Know how to use Bayes Theorem for applications involving
conditional probabilities.
To approximate binomial probabilities using the normal
distribution
Recognize regression analysis applications for purposes of
prediction and description.
Recognize some potential problems if regression analysis is used
incorrectly.
Recognize several nonlinear relationships between two variables
and be able to introduce the appropriate transformation to apply
linear regression analysis.
To use regression analysis to predict the value of a dependent
variable based on an independent variable
The meaning of the regression coefficients b0 and b1
To evaluate the assumptions of regression analysis and know
what to do if the assumptions are violated
To make inferences about the slope and correlation coefficient
To estimate mean values and predict individual values
TEMA: REPASO
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
OBJETIVOS
1
9
TEMA: MEGA
SMACKDOWN
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
21
TEMA
ESTANDAR/INDICADOR
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewDokument93 SeitenFTC MATH 1010 Week 1 OverviewLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus in ContextDokument20 SeitenCalculus in ContextLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Expressions & Equations: Prerequisite Skills NeededDokument21 SeitenIntro To Expressions & Equations: Prerequisite Skills NeededLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR2016 Concepcion English RubricDokument2 SeitenPR2016 Concepcion English RubricLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument11 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument13 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BDokument136 SeitenPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nature of Mathematics Karl Smith LogicDokument41 SeitenThe Nature of Mathematics Karl Smith LogicLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument12 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument17 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument11 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument10 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument9 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BDokument136 SeitenPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 1BLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument8 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument10 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument10 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument10 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 - 6.3.13Dokument10 SeitenPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 - 6.3.13Leonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument11 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument10 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument9 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument10 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument9 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: Week PlanDokument1 SeiteMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: Week PlanLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Guide: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokument3 SeitenUnit Guide: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 3Dokument16 SeitenPR2016 Mat 131 - 1468 UNIT 3Leonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationDokument9 SeitenUnit The Real Numbers System Week # Lesson Date: AS8 Project-Based Learning AS9 Technology IntegrationLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR2016 MAT 131 1477 Weekly Plan GenericDokument91 SeitenPR2016 MAT 131 1477 Weekly Plan GenericLeonardo Torres PaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Calculus Single Variable Canadian 9th Edition Adams Test BankDokument26 SeitenCalculus Single Variable Canadian 9th Edition Adams Test BankRebeccaPottsyxdj100% (58)
- Mps in Elementary Mathematics: First QuarterDokument4 SeitenMps in Elementary Mathematics: First QuarterNoel TorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding EscherDokument17 SeitenUnderstanding EscherDoug WhittierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Algebra 12th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual DownloadDokument83 SeitenIntroductory Algebra 12th Edition Bittinger Solutions Manual DownloadJames Yarborough100% (23)
- Prime Factorization GCF LCM Word Problems Packet 2015Dokument20 SeitenPrime Factorization GCF LCM Word Problems Packet 2015Kelvin RequenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Review Center Solutions To Take Home Exam - Analytic Geometry 1Dokument5 SeitenExcel Review Center Solutions To Take Home Exam - Analytic Geometry 1Red David BallesterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breaking Classical Rules - One Third Angle in Trigonometry (New Method For Cubic Equation)Dokument19 SeitenBreaking Classical Rules - One Third Angle in Trigonometry (New Method For Cubic Equation)Bhava Nath Dahal100% (1)
- Pinpin 2Dokument4 SeitenPinpin 2api-296541337Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric ProofsDokument20 SeitenGeometric Proofsshanna_heena100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing OBJECTIVE BITS With Answers - M V ReddyDokument6 SeitenEngineering Drawing OBJECTIVE BITS With Answers - M V ReddyVenkateswar Reddy Mallepally86% (7)
- 12 GRE Quant Practice QuestionsDokument14 Seiten12 GRE Quant Practice QuestionsSOMYA BANSALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2.1 - Area and Volumes of Geometric FiguresDokument62 SeitenUnit 2.1 - Area and Volumes of Geometric FiguresAdrian Monteclaro100% (1)
- Trigonometry - How To Find Minimum-Maximum Values QuicklyDokument25 SeitenTrigonometry - How To Find Minimum-Maximum Values Quicklyamitaich1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic GeometryDokument14 SeitenAnalytic GeometrySherwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pbis Cool Tool Respectfully Following DirectionsDokument3 SeitenPbis Cool Tool Respectfully Following Directionsapi-235822598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrations of Hyperbolic FunctionsDokument11 SeitenIntegrations of Hyperbolic Functionsricaosio91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Application Form For Studying in Huazhong Agricultural UniversityDokument3 SeitenApplication Form For Studying in Huazhong Agricultural UniversityuaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITL Public School Summative Assessment 1 MathsDokument4 SeitenITL Public School Summative Assessment 1 MathsAmrita SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chords Arcs Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesDokument11 SeitenChords Arcs Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesMaylieh MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 430-C-1 - Maths (Basic)Dokument19 Seiten430-C-1 - Maths (Basic)pranjal kunwar0% (1)
- 1 - Q3 MathematicsDokument23 Seiten1 - Q3 Mathematicsmaximo meridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Building Classroom Puzzle Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenCommunity Building Classroom Puzzle Lesson Planapi-340141530100% (1)
- Art of Coordinate BashingDokument4 SeitenArt of Coordinate BashingShark GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Servey Report - The Missing Piece (2012) PDFDokument60 SeitenServey Report - The Missing Piece (2012) PDFDaniela DumulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- (L5) - Quadrilateral - Class 9Dokument34 Seiten(L5) - Quadrilateral - Class 9heueuueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of WingwallDokument29 SeitenDesign of WingwallMar MartillanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - VIII Ut 2 Maths Set - A - QPDokument3 SeitenClass - VIII Ut 2 Maths Set - A - QPRudraksh ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Classroom Readiness ChecklistDokument3 SeitenDepartment of Education: Classroom Readiness ChecklistL.V. BendañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawatan Pelajar Jepun 2012 Dari University of Bukyo Gakuin Ke SMK Puteri AMpang, KLDokument182 SeitenLawatan Pelajar Jepun 2012 Dari University of Bukyo Gakuin Ke SMK Puteri AMpang, KLAidil AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen