Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IG
Hochgeladen von
Ke Syukuran KuOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IG
Hochgeladen von
Ke Syukuran KuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
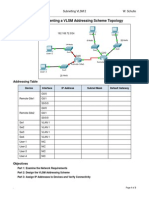
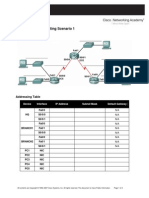
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing
Scheme Topology
You will receive one of three possible topologies.
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
[[R1G0Add]]
[[R1G0Sub]]
N/A
G0/1
[[R1G1Add]]
[[R1G1Sub]]
N/A
S0/0/0
[[R1S0Add]]
[[R1S0Sub]]
N/A
G0/0
[[R2G0Add]]
[[R2G0Sub]]
N/A
G0/1
[[R2G1Add]]
[[R2G1Sub]]
N/A
S0/0/0
[[R2S0Add]]
[[R2S0Sub]]
N/A
[[S1Name]]
VLAN 1
[[S1Add]]
[[S1Sub]]
[[R1G0Add]]
[[S2Name]]
VLAN 1
[[S2Add]]
[[S2Sub]]
[[R1G1Add]]
[[S3Name]]
VLAN 1
[[S3Add]]
[[S3Sub]]
[[R2G0Add]]
[[S4Name]]
VLAN 1
[[S4Add]]
[[S4Sub]]
[[R2G1Add]]
[[PC1Name]]
NIC
[[PC1Add]]
[[PC1Sub]]
[[R1G0Add]]
[[PC2Name]]
NIC
[[PC2Add]]
[[PC2Sub]]
[[R1G1Add]]
[[PC3Name]]
NIC
[[PC3Add]]
[[PC3Sub]]
[[R2G0Add]]
[[PC4Name]]
NIC
[[PC4Add]]
[[PC4Sub]]
[[R2G1Add]]
[[R1Name]]
[[R2Name]]
Objectives
Part 1: Examine the Network Requirements
Part 2: Design the VLSM Addressing Scheme
Part 3: Assign IP Addresses to Devices and Verify Connectivity
Background
In this activity, you are given a /24 network address to use to design a VLSM addressing scheme. Based on a
set of requirements, you will assign subnets and addressing, configure devices and verify connectivity.
Part 1: Examine the Network Requirements
Step 1: Determine the number of subnets needed.
You will subnet the network address [[DisplayNet]]. The network has the following requirements:
[[S1Name]] LAN will require [[HostReg1]] host IP addresses
[[S2Name]] LAN will require [[HostReg2]] host IP addresses
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
[[S3Name]] LAN will require [[HostReg3]] host IP addresses
[[S4Name]] LAN will require [[HostReg4]] host IP addresses
How many subnets are needed in the network topology? 5
Step 2: Determine the subnet mask information for each subnet.
a. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for [[S1Name]]?
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
b. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for [[S2Name]]?
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
c.
Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for [[S3Name]]?
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
d. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for [[S4Name]]?
How many usable host addresses will this subnet support?
e. Which subnet mask will accommodate the number of IP addresses required for the connection between
[[R1Name]] and [[R2Name]]?
Design the VLSM Addressing Scheme
Step 1: Divide the [[DisplayNet]] network based on the number of hosts per subnet.
a. Use the first subnet to accommodate the largest LAN.
b. Use the second subnet to accommodate the second largest LAN.
c.
Use the third subnet to accommodate the third largest LAN.
d. Use the fourth subnet to accommodate the fourth largest LAN.
e. Use the fifth subnet to accommodate the connection between [[R1Name]] and [[R2Name]].
Step 2: Document the VLSM subnets.
Complete the Subnet Table, listing the subnet descriptions (e.g. [[S1Name]] LAN), number of hosts needed,
then network address for the subnet, the first usable host address, and the broadcast address. Repeat until all
addresses are listed.
Subnet Table
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
Subnet
Description
Number of
Hosts
Needed
Network
Address/CIDR
First Usable
Host Address
Broadcast
Address
Step 1: Document the addressing scheme.
a. Assign the first usable IP addresses to [[R1Name]] for the two LAN links and the WAN link.
b. Assign the first usable IP addresses to [[R2Name]] for the two LANs links. Assign the last usable IP
address for the WAN link.
c.
Assign the second usable IP addresses to the switches.
d. Assign the last usable IP addresses to the hosts.
Assign IP Addresses to Devices and Verify Connectivity
Most of the IP addressing is already configured on this network. Implement the following steps to complete
the addressing configuration.
Step 2: Configure IP addressing on [[R1Name]] LAN interfaces.
Step 3: Configure IP addressing on [[S3Name]], including the default gateway.
Step 4: Configure IP addressing on [[PC4Name]], including the default gateway.
Step 5: Verify connectivity.
You can only verify connectivity from [[R1Name]], [[S3Name]], and [[PC4Name]]. However, you should be
able to ping every IP address listed in the Addressing Table.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
Activity Section
Part 1: Examine the
Network Requirements
Question
Location
Possible
Points
Step 1
Step 2
Part 1 Total
Earned
Points
Part 2: Design the VLSM Addressing Scheme
Complete Subnet Table
25
Document Addressing
40
Part 2 Total
65
Packet Tracer Score
30
Total Score
100
ID:[[indexAdds]][[indexNames]][[indexTopos]]
Scenario 1 - Network Address: 10.11.48.0/24
Subnet Table
Number of
Hosts
Needed
Subnet
Description
Network
Address/CIDR
First Usable
Host Address
Last Usable
Host Address
Broadcast
Address
Host-D LAN
60
10.11.48.0/26
10.11.48.1
10.11.48.62
10.11.48.63
Host-B LAN
30
10.11.48.64/27
10.11.48.65
10.11.48.94
10.11.48.95
Host-A LAN
14
10.11.48.96/28
10.11.48.97
10.11.48.110
10.11.48.111
Host-C LAN
10.11.48.112/29
10.11.48.113
10.11.48.118
10.11.48.119
WAN Link
10.11.48.120/30
10.11.48.121
10.11.48.122
10.11.48.123
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
Device
Interface
Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
10.11.48.97
255.255.255.240
N/A
G0/1
10.11.48.65
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
10.11.48.121
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
10.11.48.113
255.255.255.248
N/A
G0/1
10.11.48.1
255.255.255.192
N/A
Building2
S0/0/0
10.11.48.122
255.255.255.252
N/A
ASW1
VLAN 1
10.11.48.98
255.255.255.240
10.11.48.97
ASW2
VLAN 1
10.11.48.66
255.255.255.224
10.11.48.65
ASW3
VLAN 1
10.11.48.114
255.255.255.248
10.11.48.113
ASW4
VLAN 1
10.11.48.2
255.255.255.192
10.11.48.1
Host-A
NIC
10.11.48.110
255.255.255.240
10.11.48.97
Host-B
NIC
10.11.48.94
255.255.255.224
10.11.48.65
Host-C
NIC
10.11.48.118
255.255.255.248
10.11.48.113
Host-D
NIC
10.11.48.62
255.255.255.192
10.11.48.1
Building1
Building 1
en
conf t
int g0/0
ip add 10.11.48.97 255.255.255.240
no shut
int g0/1
ip add 10.11.48.65 255.255.255.224
no shut
ASW3
en
conf t
int vlan 1
ip add 10.11.48.114 255.255.255.248
no shut
ip def 10.11.48.113
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 5 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
Scenario 2 - Network Address: 172.31.103.0/24
Subnet Table
Number of
Hosts
Needed
Subnet
Description
Network
Address/CIDR
First Usable
Host Address
Last Usable
Host Address
Broadcast
Address
PC-A LAN
27
172.31.103.0/27
172.31.103.1
172.31.103.30
172.31.103.31
PC-B LAN
25
172.31.103.32/27
172.31.103.33
172.31.103.62
172.31.103.63
PC-C LAN
14
172.31.103.64/28
172.31.103.65
172.31.103.78
172.31.103.79
PC-D LAN
172.31.103.80/28
172.31.103.81
172.31.103.94
172.31.103.95
WAN Link
172.31.103.96/30
172.31.103.97
172.31.103.98
172.31.103.99
Device
Interface
Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
172.31.103.1
255.255.255.224
N/A
G0/1
172.31.103.33
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
172.31.103.97
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
172.31.103.65
255.255.255.240
N/A
G0/1
172.31.103.81
255.255.255.240
N/A
Branch2
S0/0/0
172.31.103.98
255.255.255.252
N/A
Room-114
VLAN 1
172.31.103.2
255.255.255.224
172.31.103.1
Room-279
VLAN 1
172.31.103.34
255.255.255.224
172.31.103.33
Room-312
VLAN 1
172.31.103.66
255.255.255.240
172.31.103.65
Room-407
VLAN 1
172.31.103.82
255.255.255.240
172.31.103.81
PC-A
NIC
172.31.103.30
255.255.255.224
172.31.103.1
PC-B
NIC
172.31.103.62
255.255.255.224
172.31.103.33
PC-C
NIC
172.31.103.78
255.255.255.240
172.31.103.65
PC-D
NIC
172.31.103.94
255.255.255.240
172.31.103.81
Branch1
Branch 1
en
conf t
int g0/0
ip add 172.31.103.1 255.255.255.224
no shut
int g0/1
ip add 172.31.103.33 255.255.255.224
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 6 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
no shut
Room-312
en
conf t
int vlan 1
ip add 172.31.103.66 255.255.255.240
no shut
ip def 172.31.103.65
Scenario 3 - Network Address: 192.168.72.0/24
Subnet Table
Number of
Hosts
Needed
Subnet
Description
Network
Address/CIDR
First Usable
Host Address
Last Usable
Host Address
Broadcast
Address
User-4 LAN
58
192.168.72.0/26
192.168.72.1
192.168.72.62
192.168.72.63
User-3 LAN
29
192.168.72.64/27
192.168.72.65
192.168.72.94
192.168.72.95
User-2 LAN
15
192.168.72.96/27
192.168.72.97
192.168.72.126
192.168.72.127
User-1 LAN
192.168.72.128/28
192.168.72.129
192.168.72.142
192.168.72.143
WAN Link
192.168.72.144/30
192.168.72.145
192.168.72.146
192.168.72.147
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 7 of 8
Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme
Device
Interface
Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
192.168.72.129
255.255.255.240
N/A
G0/1
192.168.72.97
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.72.145
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
192.168.72.65
255.255.255.224
N/A
G0/1
192.168.72.1
255.255.255.192
N/A
Remote-Site2
S0/0/0
192.168.72.146
255.255.255.252
N/A
Sw1
VLAN 1
192.168.72.130
255.255.255.240
192.168.72.129
Sw2
VLAN 1
192.168.72.98
255.255.255.224
192.168.72.97
Sw3
VLAN 1
192.168.72.66
255.255.255.224
192.168.72.65
Sw4
VLAN 1
192.168.72.2
255.255.255.192
192.168.72.1
User-1
NIC
192.168.72.142
255.255.255.240
192.168.72.129
User-2
NIC
192.168.72.126
255.255.255.224
192.168.72.97
User-3
NIC
192.168.72.94
255.255.255.224
192.168.72.65
User-4
NIC
192.168.72.62
255.255.255.192
192.168.72.1
Remote-Site1
Remote-Site1
en
conf t
int g0/0
ip add 192.168.72.129 255.255.255.240
no shut
int g0/1
ip add 192.168.72.97 255.255.255.224
no shut
Sw-3
en
conf t
int vlan 1
ip add 192.168.72.66 255.255.255.224
no shut
ip def 192.168.72.65
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 8 of 8
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDokument4 Seiten9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- WAN Subnetting VLSMDokument3 SeitenWAN Subnetting VLSMMuz QazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing Table: ObjectivesDokument5 SeitenAddressing Table: ObjectivesStasicc SNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesVon EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDokument4 SeitenLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Final Project TastDokument3 SeitenCCNA Final Project Tastsathish77s100% (1)
- 2.4.3.4 Packet TracerDokument11 Seiten2.4.3.4 Packet TracercoleparksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMDokument8 Seiten19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMjohannachicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationDokument17 Seiten3.3.2.8 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationLarry Abisaí0% (2)
- Lab 8.3.3.6Dokument10 SeitenLab 8.3.3.6Justine DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route PropagationDokument4 SeitenLab 5.2.3 Configuring Ripv2 With VLSM, and Default Route Propagationmohammad_shahzad_iiuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsDokument3 Seiten9.3.1.4 Packet Tracer - Implementing A Subnetted IPv6 Addressing Scheme InstructionsAhmadHijazi100% (2)
- E2 Lab 3 5 4Dokument3 SeitenE2 Lab 3 5 4Ninja NuggetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Router Igrp Configuration LabDokument5 Seiten3 Router Igrp Configuration LabSiddhant SingalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess NetworkDokument6 Seiten5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 On A Multiaccess Networkرافد البركيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco IOS Modes TutorialDokument11 SeitenCisco IOS Modes Tutorialheruye mulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Few Things To Keep in Mind While Completing This ActivityDokument5 SeitenA Few Things To Keep in Mind While Completing This ActivityDiego BenitesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Dokument5 Seiten8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Alex VolkovNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFDokument8 Seiten9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFEl Amrani MoutiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Length Subnetting: Jim Blanco Aparicio-Levy Technical CenterDokument14 SeitenVariable Length Subnetting: Jim Blanco Aparicio-Levy Technical Centerhussien amareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Router Configuration Commands GuideDokument17 SeitenCisco Router Configuration Commands GuideBazir AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsDokument3 Seiten4.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsDaniel OsorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 3 Ex - OspfDokument25 SeitenCcna 3 Ex - OspfJosueChalenSarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.4.1.1 Lab - Configure An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) PDFDokument21 Seiten5.4.1.1 Lab - Configure An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) PDFIvan ZuritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing DesignDokument6 SeitenBasic VLSM Calculation and Addressing DesignnujugtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDokument7 SeitenLab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramPaintMeAnEpicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Training - 03 OSPFDokument23 SeitenCisco Training - 03 OSPFIrfan Irawan CbnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5.2.6a Password Recovery Procedures: Background/PreparationDokument5 SeitenLab 5.2.6a Password Recovery Procedures: Background/Preparationoghab_e_shomaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Training Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP TutorialDokument4 SeitenCCNA Training Hot Standby Router Protocol HSRP Tutorialokotete evidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDokument5 Seiten6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtcre PDFDokument16 SeitenMtcre PDFGuilherme Leardini0% (1)
- OSPF Practice Skills Assessment - Packet TracerDokument13 SeitenOSPF Practice Skills Assessment - Packet Tracerjohn doeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 2 RSE Practice Skills Assessment v5.2– PT 2015Dokument11 SeitenCCNA 2 RSE Practice Skills Assessment v5.2– PT 2015Hermo MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Routing and Switching S3Dokument16 SeitenCCNA Routing and Switching S3FiskoaujNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.1.2.7 Packet Tracer - Investigating A VLAN Implementation InstructionsDokument4 Seiten6.1.2.7 Packet Tracer - Investigating A VLAN Implementation InstructionsOswaldo VélizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 07 RIP ConfigurationDokument12 SeitenLab 07 RIP Configurationmuhammad.mursleen025Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 3 (v5.0) OSPF Practice Skills Assessment Exam Answer: Network DiagramDokument22 SeitenCCNA 3 (v5.0) OSPF Practice Skills Assessment Exam Answer: Network DiagramMark BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - SolutionDokument16 Seiten2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - SolutionVarinava Bola100% (3)
- 20-Troubleshooting Basic Network Services IIDokument19 Seiten20-Troubleshooting Basic Network Services IImansoorali_afNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cisco Router Configuration StepsDokument2 SeitenBasic Cisco Router Configuration StepsTeny VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtcna Training Materials (2013-01)Dokument432 SeitenMtcna Training Materials (2013-01)Tekno VlogNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDokument7 Seiten4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPjb100% (1)
- Lab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Dokument4 SeitenLab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Rico Agung FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF On 3 RoutersDokument8 SeitenOSPF On 3 RoutersepocableoilsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring Multi-Area OSPFv3Dokument16 SeitenConfiguring Multi-Area OSPFv3etitahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA 2 Final Exam QuestionsDokument67 SeitenCCNA 2 Final Exam Questionsradek1911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDokument4 SeitenLab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramMunkieBoneZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsVon EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GVon EverandFundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionVon EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandCisco Certified Security Professional A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.2.1.4 PT - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing SchemeDokument8 Seiten8.2.1.4 PT - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Schemeyazmin caballero0% (1)
- 10.2.2.8 Packet Tracer - DHCP and DNS ServersDokument4 Seiten10.2.2.8 Packet Tracer - DHCP and DNS ServersKe Syukuran Ku100% (1)
- 10.2.1.8 Packet Tracer - Web and Email InstructionsDokument3 Seiten10.2.1.8 Packet Tracer - Web and Email InstructionsnskpotulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesDokument7 Seiten5.1.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesBenjamin Gm100% (4)
- 11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesDokument2 Seiten11.2.5.7 Packet Tracer - Backing Up Configuration FilesParthPatel33% (3)
- Week7Lab: Oophp + MVCDokument8 SeitenWeek7Lab: Oophp + MVCKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Dokument4 SeitenAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Dokument4 SeitenAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning System Design GuideDokument19 SeitenMachine Learning System Design GuideKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2Dokument4 SeitenAppendix Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 2ParthPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regular ExpressionDokument4 SeitenRegular ExpressionKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsDokument4 Seiten6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsDokument4 Seiten6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN InstructionsDokument5 Seiten6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN InstructionsKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.2.1.8 Packet Tracer Web and Email InstructionsDokument3 Seiten10.2.1.8 Packet Tracer Web and Email InstructionsThalia SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet11 Wireshark Capture Ethernet FrameDokument8 SeitenWorksheet11 Wireshark Capture Ethernet FrameKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Regression Final KeyDokument7 SeitenPractice Regression Final KeyKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsDokument4 Seiten6.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Initial Router Settings InstructionsKe Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Final Exam S13Dokument15 SeitenPractice Final Exam S13Ke Syukuran KuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesDokument7 Seiten5.1.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesBenjamin Gm100% (4)
- 2.1.4.8 Packet Tracer - Navigating The IOS InstrucDokument5 Seiten2.1.4.8 Packet Tracer - Navigating The IOS InstrucVanessa MorochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworkDokument14 Seiten2.3.3.4 Lab - Building A Simple NetworknikolapekovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC upholds conviction of accused who pleaded guilty to kidnapping and murderDokument3 SeitenSC upholds conviction of accused who pleaded guilty to kidnapping and murderTelle MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, Volume 52 PDFDokument349 SeitenAdvances in Experimental Social Psychology, Volume 52 PDFJose LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Request for Learner Data CorrectionDokument4 SeitenRequest for Learner Data CorrectionChaii Madlangsakay TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RecitationDokument3 SeitenRecitationViola NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdvocacyDokument3 SeitenAdvocacyGc Borres100% (2)
- Salesforce CRMDokument22 SeitenSalesforce CRMkrishna_mf01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. Devilal State Institute of Engineering and Technology, Panniwala Mota (Sirsa)Dokument15 SeitenCh. Devilal State Institute of Engineering and Technology, Panniwala Mota (Sirsa)NKNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Start A Startup Book PreviewDokument23 SeitenHow To Start A Startup Book PreviewNikki SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Young Pianist CompetitionDokument2 SeitenYoung Pianist CompetitionAleksa SarcevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSC&O Lab4Dokument3 SeitenPSC&O Lab4Hafeez AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satr W 2012Dokument1 SeiteSatr W 2012Mohammed Hamed BaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incoming Inspection Procedure: Document Part No. Rev 100-0044 007 1 of 11Dokument11 SeitenIncoming Inspection Procedure: Document Part No. Rev 100-0044 007 1 of 11Sandip Jawalkar100% (1)
- 42 M Bow String Girder-10408-6-R PDFDokument1 Seite42 M Bow String Girder-10408-6-R PDFPhanindra MajetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Yogurt Drink MarketDokument13 SeitenGlobal Yogurt Drink MarketjennifermeichangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Philippine Tourism Master Plan 1991-2010Dokument7 SeitenThe Philippine Tourism Master Plan 1991-2010Zcephra MalsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics I A (EM) BLM 2021-22Dokument130 SeitenMathematics I A (EM) BLM 2021-22Pranav AdithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Follower Robot ProjectDokument8 SeitenLine Follower Robot ProjectPuneeth ShettigarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP SanitaryDokument2 SeitenCP SanitaryMuthu ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OHSAS 18001-2007 Lead Auditor CourseDokument3 SeitenOHSAS 18001-2007 Lead Auditor Coursesharaby81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Context CluesDokument4 SeitenContext CluesSherelyn BaidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gearbox Reliability Collaborative Phase 3 Gearbox 2 Test 1Dokument46 SeitenGearbox Reliability Collaborative Phase 3 Gearbox 2 Test 1sebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP For Calibration of Instruments in Production and Quality Control - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDokument2 SeitenSOP For Calibration of Instruments in Production and Quality Control - Pharmaceutical Guidelinest836549Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2: Ebook HomeworkDokument2 SeitenCHAPTER 2: Ebook HomeworkCHRISTINA HANAVI MILLANNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Origins of Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms PDFDokument361 SeitenThe Origins of Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms PDFEric DubourgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding culture through sociological perspectivesDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding culture through sociological perspectivesAnjaneth Cabutin0% (1)
- Subject Centered - Correlational DesignDokument13 SeitenSubject Centered - Correlational DesignWarrenBualoySayagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Plans and Strength RequirementsDokument8 SeitenConstruction Plans and Strength Requirementsstormriderbh100% (1)
- Indonesian Recipes Discover The Taste of Indonesia (Stephanie Sharp) (Z-Library)Dokument74 SeitenIndonesian Recipes Discover The Taste of Indonesia (Stephanie Sharp) (Z-Library)Daniel Proulx100% (1)
- Scepticism and Animal Rationality: The Fortune of Chrysippus' Dog in The History of Western ThoughtDokument31 SeitenScepticism and Animal Rationality: The Fortune of Chrysippus' Dog in The History of Western ThoughtNicolás Antonio Rojas CortésNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Financial LiteracyDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan Financial Literacyapi-438803241Noch keine Bewertungen